Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy:
This strategy illustrates the use of the recently published Delta-RSI Oscillator as a stand-alone indicator.
Delta-RSI represents a smoothed time derivative of the RSI , plotted as a histogram and serving as a momentum indicator .
There are three optional conditions to generate trading signals (set separately for Buy, Sell and Exit signals): Zero-crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses zero from negative to positive values ( bearish otherwise) Signal Line Crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses from below to above the signal line ( bearish otherwise) Direction Change: bullish when D-RSI was negative and starts ascending ( bearish otherwise) Since D-RSI oscillator is based on polynomial fitting of the RSI curve, there is also an option to filter trade signal by means of the root mean-square error of the fit (normalized by the sample average).
backtest
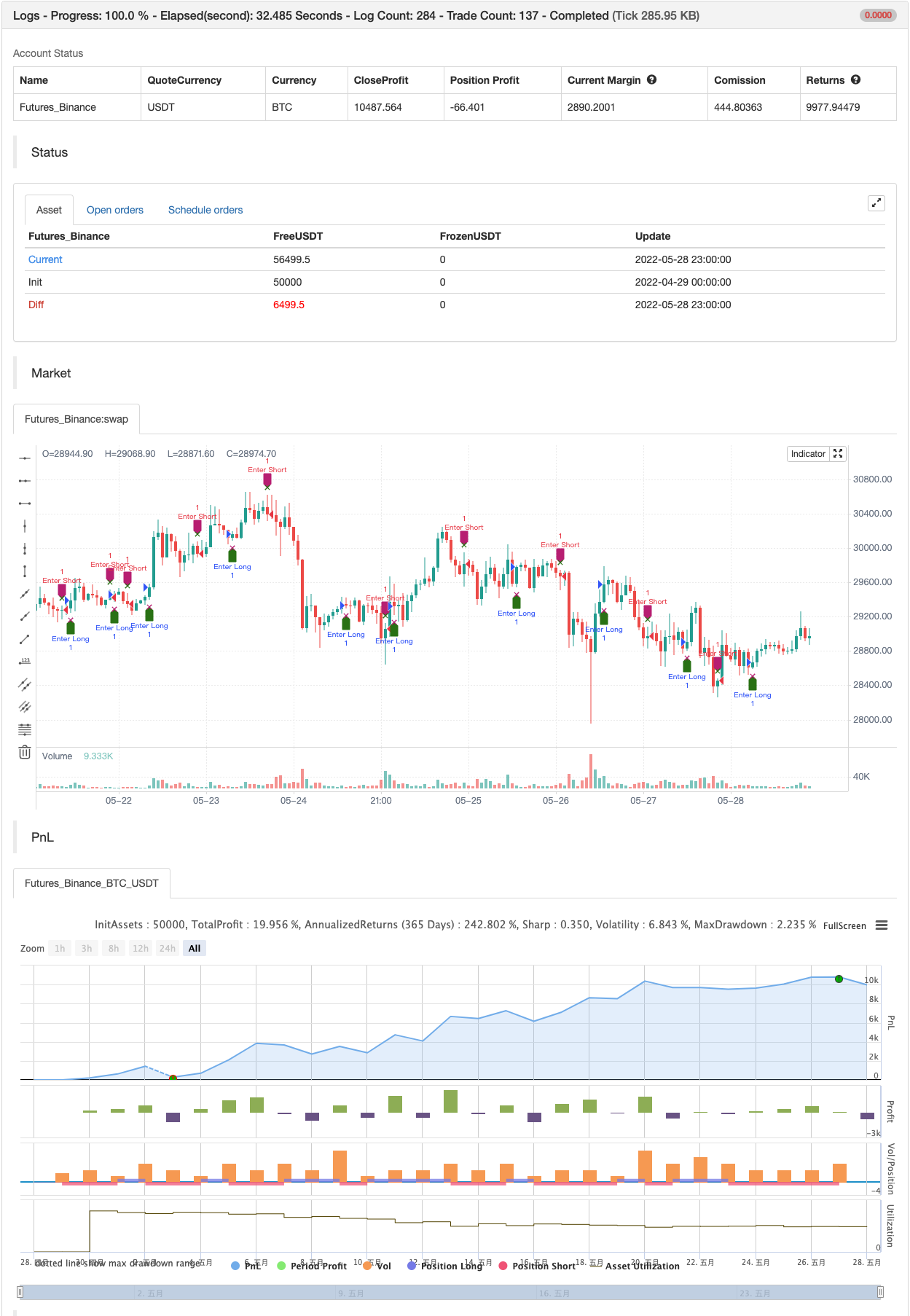
/*backtest
start: 2022-04-29 00:00:00
end: 2022-05-28 23:59:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © tbiktag
//
// Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy
//
// A strategy that uses Delta-RSI Oscillator (© tbiktag) as a stand-alone indicator:
// https://www.tradingview.com/script/OXQVFTQD-Delta-RSI-Oscillator/
//
// Delta-RSI is a smoothed time derivative of the RSI, plotted as a histogram
// and serving as a momentum indicator.
//
// Input parameters:
// RSI Length: The timeframe of the RSI that serves as an input to D-RSI.
// Length: The length of the lookback frame used for local regression.
// Polynomial Order: The order of the local polynomial function used to interpolate the RSI.
// Signal Length: The length of a EMA of the D-RSI series that is used as a signal line.
// Trade signals are generated based on three optional conditions:
// - Zero-crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses zero from negative to positive values (bearish otherwise)
// - Signal Line Crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses from below to above the signal line (bearish otherwise)
// - Direction Change: bullish when D-RSI was negative and starts ascending (bearish otherwise)
//
// Since D-RSI oscillator is based on polynomial fitting of the RSI curve, there is also an option
// to filter trade signal by means of the root mean-square error of the fit (normalized by the sample average).
//
//@version=4
study(title="Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy", shorttitle = "D-RSI", overlay = true)
// ---Subroutines---
matrix_get(_A,_i,_j,_nrows) =>
// Get the value of the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.get(_A,_i+_nrows*_j)
matrix_set(_A,_value,_i,_j,_nrows) =>
// Set a value to the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array, changed on output: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _value :: float: the new value to be set
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.set(_A,_i+_nrows*_j,_value)
transpose(_A,_nrows,_ncolumns) =>
// Transpose an implied 2d matrix
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _AT :: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions: _ncolums x _nrows
var _AT = array.new_float(_nrows*_ncolumns,0)
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
for j = 0 to _ncolumns-1
matrix_set(_AT, matrix_get(_A,i,j,_nrows),j,i,_ncolumns)
_AT
multiply(_A,_B,_nrowsA,_ncolumnsA,_ncolumnsB) =>
// Calculate scalar product of two matrices
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _B :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _nrowsA :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumnsA :: integer: number of columns in _A
// _ncolumnsB :: integer: number of columns in _B
// output:
// _C:: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions _nrowsA x _ncolumnsB
var _C = array.new_float(_nrowsA*_ncolumnsB,0)
int _nrowsB = _ncolumnsA
float elementC= 0.0
for i = 0 to _nrowsA-1
for j = 0 to _ncolumnsB-1
elementC := 0
for k = 0 to _ncolumnsA-1
elementC := elementC + matrix_get(_A,i,k,_nrowsA)*matrix_get(_B,k,j,_nrowsB)
matrix_set(_C,elementC,i,j,_nrowsA)
_C
vnorm(_X,_n) =>
//Square norm of vector _X with size _n
float _norm = 0.0
for i = 0 to _n-1
_norm := _norm + pow(array.get(_X,i),2)
sqrt(_norm)
qr_diag(_A,_nrows,_ncolumns) =>
//QR Decomposition with Modified Gram-Schmidt Algorithm (Column-Oriented)
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _Q: unitary matrix, implied dimenstions _nrows x _ncolumns
// _R: upper triangular matrix, implied dimansions _ncolumns x _ncolumns
var _Q = array.new_float(_nrows*_ncolumns,0)
var _R = array.new_float(_ncolumns*_ncolumns,0)
var _a = array.new_float(_nrows,0)
var _q = array.new_float(_nrows,0)
float _r = 0.0
float _aux = 0.0
//get first column of _A and its norm:
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
array.set(_a,i,matrix_get(_A,i,0,_nrows))
_r := vnorm(_a,_nrows)
//assign first diagonal element of R and first column of Q
matrix_set(_R,_r,0,0,_ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
matrix_set(_Q,array.get(_a,i)/_r,i,0,_nrows)
if _ncolumns != 1
//repeat for the rest of the columns
for k = 1 to _ncolumns-1
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
array.set(_a,i,matrix_get(_A,i,k,_nrows))
for j = 0 to k-1
//get R_jk as scalar product of Q_j column and A_k column:
_r := 0
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
_r := _r + matrix_get(_Q,i,j,_nrows)*array.get(_a,i)
matrix_set(_R,_r,j,k,_ncolumns)
//update vector _a
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
_aux := array.get(_a,i) - _r*matrix_get(_Q,i,j,_nrows)
array.set(_a,i,_aux)
//get diagonal R_kk and Q_k column
_r := vnorm(_a,_nrows)
matrix_set(_R,_r,k,k,_ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
matrix_set(_Q,array.get(_a,i)/_r,i,k,_nrows)
[_Q,_R]
pinv(_A,_nrows,_ncolumns) =>
//Pseudoinverse of matrix _A calculated using QR decomposition
// Input:
// _A:: array: implied as a (_nrows x _ncolumns) matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(_ncolumns-1)]]
// Output:
// _Ainv:: array implied as a (_ncolumns x _nrows) matrix _A = [[row_0],[row_1],...,[row_(_nrows-1)]]
// ----
// First find the QR factorization of A: A = QR,
// where R is upper triangular matrix.
// Then _Ainv = R^-1*Q^T.
// ----
[_Q,_R] = qr_diag(_A,_nrows,_ncolumns)
_QT = transpose(_Q,_nrows,_ncolumns)
// Calculate Rinv:
var _Rinv = array.new_float(_ncolumns*_ncolumns,0)
float _r = 0.0
matrix_set(_Rinv,1/matrix_get(_R,0,0,_ncolumns),0,0,_ncolumns)
if _ncolumns != 1
for j = 1 to _ncolumns-1
for i = 0 to j-1
_r := 0.0
for k = i to j-1
_r := _r + matrix_get(_Rinv,i,k,_ncolumns)*matrix_get(_R,k,j,_ncolumns)
matrix_set(_Rinv,_r,i,j,_ncolumns)
for k = 0 to j-1
matrix_set(_Rinv,-matrix_get(_Rinv,k,j,_ncolumns)/matrix_get(_R,j,j,_ncolumns),k,j,_ncolumns)
matrix_set(_Rinv,1/matrix_get(_R,j,j,_ncolumns),j,j,_ncolumns)
//
_Ainv = multiply(_Rinv,_QT,_ncolumns,_ncolumns,_nrows)
_Ainv
norm_rmse(_x, _xhat) =>
// Root Mean Square Error normalized to the sample mean
// _x. :: array float, original data
// _xhat :: array float, model estimate
// output
// _nrmse:: float
float _nrmse = 0.0
if array.size(_x) != array.size(_xhat)
_nrmse := na
else
int _N = array.size(_x)
float _mse = 0.0
for i = 0 to _N-1
_mse := _mse + pow(array.get(_x,i) - array.get(_xhat,i),2)/_N
_xmean = array.sum(_x)/_N
_nrmse := sqrt(_mse) /_xmean
_nrmse
diff(_src,_window,_degree) =>
// Polynomial differentiator
// input:
// _src:: input series
// _window:: integer: wigth of the moving lookback window
// _degree:: integer: degree of fitting polynomial
// output:
// _diff :: series: time derivative
// _nrmse:: float: normalized root mean square error
//
// Vandermonde matrix with implied dimensions (window x degree+1)
// Linear form: J = [ [z]^0, [z]^1, ... [z]^degree], with z = [ (1-window)/2 to (window-1)/2 ]
var _J = array.new_float(_window*(_degree+1),0)
for i = 0 to _window-1
for j = 0 to _degree
matrix_set(_J,pow(i,j),i,j,_window)
// Vector of raw datapoints:
var _Y_raw = array.new_float(_window,na)
for j = 0 to _window-1
array.set(_Y_raw,j,_src[_window-1-j])
// Calculate polynomial coefficients which minimize the loss function
_C = pinv(_J,_window,_degree+1)
_a_coef = multiply(_C,_Y_raw,_degree+1,_window,1)
// For first derivative, approximate the last point (i.e. z=window-1) by
float _diff = 0.0
for i = 1 to _degree
_diff := _diff + i*array.get(_a_coef,i)*pow(_window-1,i-1)
// Calculates data estimate (needed for rmse)
_Y_hat = multiply(_J,_a_coef,_window,_degree+1,1)
float _nrmse = norm_rmse(_Y_raw,_Y_hat)
[_diff,_nrmse]
/// --- main ---
degree = input(title="Polynomial Order", group = "Model Parameters:",
inline = "linepar1", type = input.integer, defval=2, minval = 1)
rsi_l = input(title = "RSI Length", group = "Model Parameters:",
inline = "linepar1", type = input.integer, defval = 21, minval = 1,
tooltip="The period length of RSI that is used as input.")
window = input(title="Length ( > Order)", group = "Model Parameters:",
inline = "linepar2", type = input.integer, defval=21, minval = 2)
signalLength = input(title="Signal Length", group = "Model Parameters:",
inline = "linepar2", type=input.integer, defval=9,
tooltip="The signal line is a EMA of the D-RSI time series.")
islong = input(title = "Buy", group = "Show Signals:",
inline = "lineent",type = input.bool, defval = true)
isshort = input(title = "Sell", group = "Show Signals:",
inline = "lineent", type = input.bool, defval= true)
showendlabels = input(title = "Exit", group = "Show Signals:",
inline = "lineent", type = input.bool, defval= true)
buycond = input(title="Buy", group = "Entry and Exit Conditions:",
inline = "linecond",type = input.string, defval="Zero-Crossing",
options=["Zero-Crossing", "Signal Line Crossing","Direction Change"])
sellcond = input(title="Sell", group = "Entry and Exit Conditions:",
inline = "linecond",type = input.string, defval="Zero-Crossing",
options=["Zero-Crossing", "Signal Line Crossing","Direction Change"])
endcond = input(title="Exit", group = "Entry and Exit Conditions:",
inline = "linecond",type = input.string, defval="Zero-Crossing",
options=["Zero-Crossing", "Signal Line Crossing","Direction Change"])
usenrmse = input(title = "", group = "Filter by Means of Root-Mean-Square Error of RSI Fitting:",
inline = "linermse",type = input.bool, defval = false)
rmse_thrs = input(title = "RSI fitting Error Threshold, %", type = input.float,
group = "Filter by Means of Root-Mean-Square Error of RSI Fitting:",
inline = "linermse", defval = 10, minval = 0.0) /100
src = rsi(close,rsi_l)
[drsi,nrmse] = diff(src,window,degree)
signalline = ema(drsi, signalLength)
// Conditions and filters
filter_rmse = usenrmse?nrmse<rmse_thrs:true
dirchangeup = (drsi>drsi[1]) and (drsi[1]<drsi[2]) and drsi[1]<0.0
dirchangedw = (drsi<drsi[1]) and (drsi[1]>drsi[2]) and drsi[1]>0.0
crossup = crossover(drsi,0.0)
crossdw = crossunder(drsi,0.0)
crosssignalup = crossover(drsi,signalline)
crosssignaldw = crossunder(drsi,signalline)
//Signals
golong = (buycond=="Direction Change"?dirchangeup:(buycond=="Zero-Crossing"?crossup:crosssignalup)) and filter_rmse
goshort= (sellcond=="Direction Change"?dirchangedw:(sellcond=="Zero-Crossing"?crossdw:crosssignaldw)) and filter_rmse
endlong = (endcond=="Direction Change"?dirchangedw:(endcond=="Zero-Crossing"?crossdw:crosssignaldw)) and filter_rmse
endshort= (endcond=="Direction Change"?dirchangeup:(endcond=="Zero-Crossing"?crossup:crosssignalup)) and filter_rmse
plotshape((golong and islong) ? low : na, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.labelup, color=#2E7C13, size=size.small, title='Buy')
plotshape((goshort and isshort) ? high: na, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.labeldown, color=#BF217C, size=size.small, title='Sell')
plotshape((showendlabels and endlong and islong) ? high: na, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.xcross, color=#2E7C13, size=size.tiny, title='Exit Long')
plotshape((showendlabels and endshort and isshort) ? low : na, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.xcross, color=#BF217C, size=size.tiny, title='Exit Short')
alertcondition(golong, title='Long Signal', message='D-RSI: Long Signal')
alertcondition(goshort, title='Short Signal', message='D-RSI: Short Signal')
alertcondition(endlong, title='Exit Long Signal', message='D-RSI: Exit Long')
alertcondition(endshort, title='Exit Short Signal', message='D-RSI: Exit Short')
if golong
strategy.entry("Enter Long", strategy.long)
else if goshort
strategy.entry("Enter Short", strategy.short)