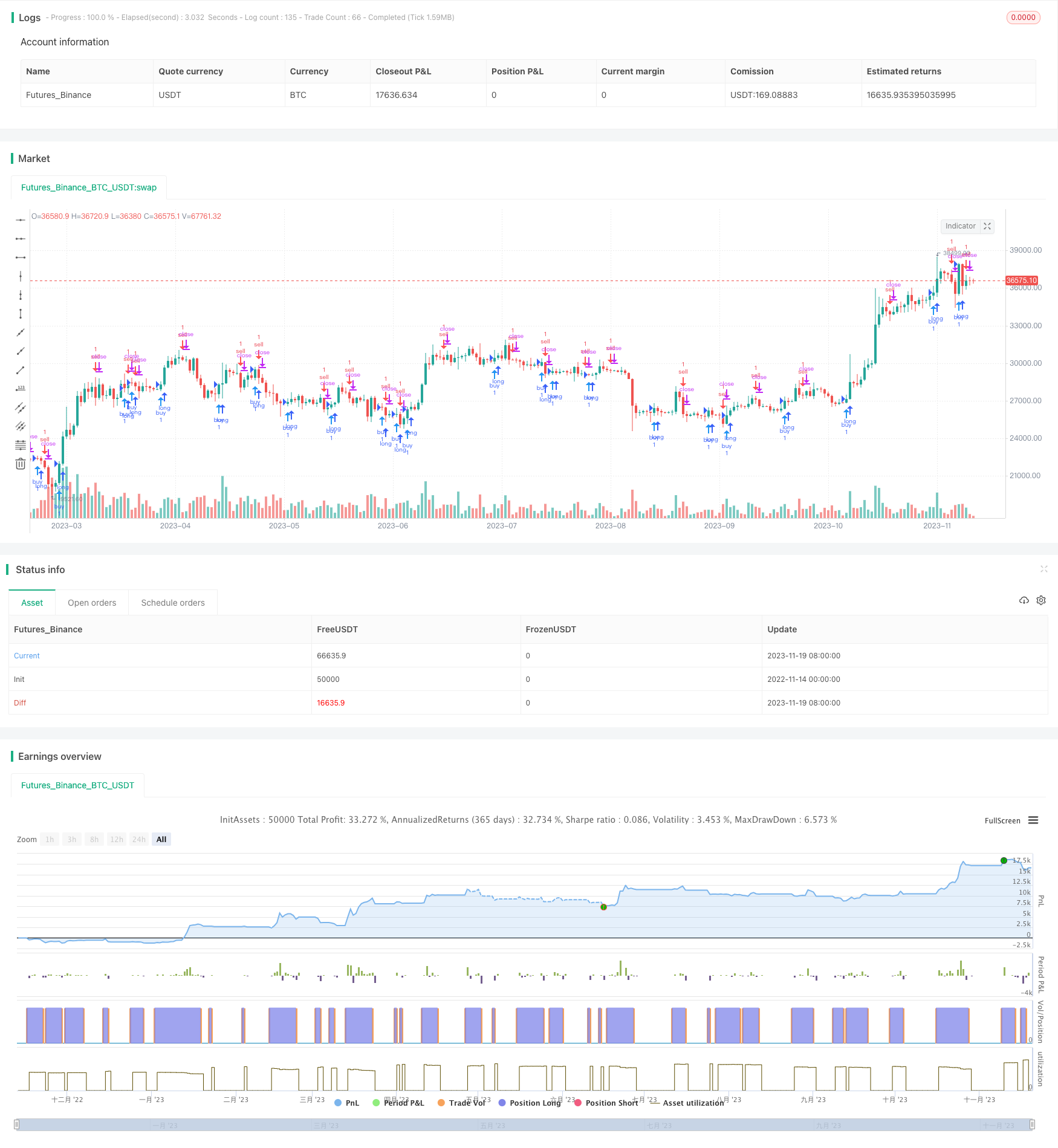
概述
该策略通过计算MACD指标的双均线交叉来判断买入和卖出时机。它会在图表上绘制箭头形状来提示交易信号。
原理
该策略首先计算快线(EMA 12期)、慢线(EMA 26期)和MACD差值。然后根据快线和慢线的金叉死叉以及MACD差值的正负来判断买入和卖出时机:
- 当快线上穿慢线(金叉)且MACD差值上穿0时为买入信号
- 当快线下穿慢线(死叉)且MACD差值下穿0时为卖出信号
为了过滤假信号,代码中还判断了前一个K线的信号情况。只有当前一个K线是反向信号时(买入转为卖出或卖出转为买入),当前信号才会被触发。
此外,代码中还绘制了箭头图形在K线上提示买入和卖出时机。
优势
该策略具有以下优势:
- 使用双均线交叉判断,可以有效过滤市场噪音,识别趋势
- 结合MACD差值判断,可以避免漏单和误判
- 使用箭头提示买卖时机,操作更明确
- 规则简单清晰,容易理解与复制
风险与解决方案
该策略也存在一些风险:
- 双均线交叉容易产生假信号,可能导致过度交易。可以适当调整均线参数或增加其他过滤条件来减少假信号
- 无法判断趋势中的震荡,可能出现亏损。可以结合趋势指标如ADX来避免这种情况
- 固定的买卖条件使策略 mechanize,无法适应市场变化。可以尝试机器学习等自适应方式来优化
优化方向
该策略可以从以下几个方向进行优化:
- 测试不同的参数组合,找到最佳的快线、慢线和MACD参数
- 增加入场条件,如交易量突破来过滤信号
- 增加止损机制来控制单笔亏损
- 结合VIX等波动率指标来判断风险偏好
- 尝试机器学习模型来代替固定规则,实现策略的自适应优化
总结
该双均线交叉箭头策略整体来说较为简单实用,通过双均线交叉判断和MACD差值过滤,可以识别中长线趋势中的买入卖出点,避免错过价格转折。箭头提示也使操作更清晰明确。后期通过参数优化、增加过滤条件等方式还可以进一步增强策略稳定性和收益率。
策略源码
/*backtest
start: 2022-11-14 00:00:00
end: 2023-11-20 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=3
//Daniels stolen code
strategy(shorttitle="Daniels Stolen Code", title="Daniels Stolen Code", overlay=true, calc_on_order_fills=true, pyramiding=0)
//Define MACD Variables
fast = 12, slow = 26
fastMACD = ema(hlc3, fast)
slowMACD = ema(hlc3, slow)
macd = fastMACD - slowMACD
signal = sma(macd, 9)
hist = macd - signal
currMacd = hist[0]
prevMacd = hist[1]
currPrice = hl2[0]
prevPrice = hl2[1]
buy = currPrice > prevPrice and currMacd > prevMacd
sell = currPrice < prevPrice and currMacd < prevMacd
neutral = (currPrice < prevPrice and currMacd > prevMacd) or (currPrice > prevPrice and currMacd < prevMacd)
//Plot Arrows
timetobuy = buy==1 and (sell[1]==1 or (neutral[1]==1 and sell[2]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and sell[3]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and sell[4]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and neutral[4]==1 and sell[5]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and neutral[4]==1 and neutral[5]==1 and sell[6]==1))
timetosell = sell==1 and (buy[1]==1 or (neutral[1]==1 and buy[2]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and buy[3]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and buy[4]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and neutral[4]==1 and buy[5]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and neutral[4]==1 and neutral[5]==1 and buy[6]==1))
plotshape(timetobuy, color=blue, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.arrowup)
plotshape(timetosell, color=red, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.arrowdown)
//plotshape(neutral, color=black, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.circle)
//Test Strategy
// strategy.entry("long", true, 1, when = timetobuy and time > timestamp(2017, 01, 01, 01, 01)) // buy by market if current open great then previous high
// strategy.close("long", when = timetosell and time > timestamp(2017, 01, 01, 01, 01))
strategy.order("buy", true, 1, when=timetobuy==1 and time > timestamp(2019, 01, 01, 01, 01))
strategy.order("sell", false, 1, when=timetosell==1 and time > timestamp(2019, 01, 01, 01, 01))
// strategy.entry(id = "Short", long = false, when = enterShort())
// strategy.close(id = "Short", when = exitShort())
//strategy.entry("long", true, 1, when = open > high[1]) // enter long by market if current open great then previous high
// strategy.exit("exit", "long", profit = 10, loss = 5) // ge