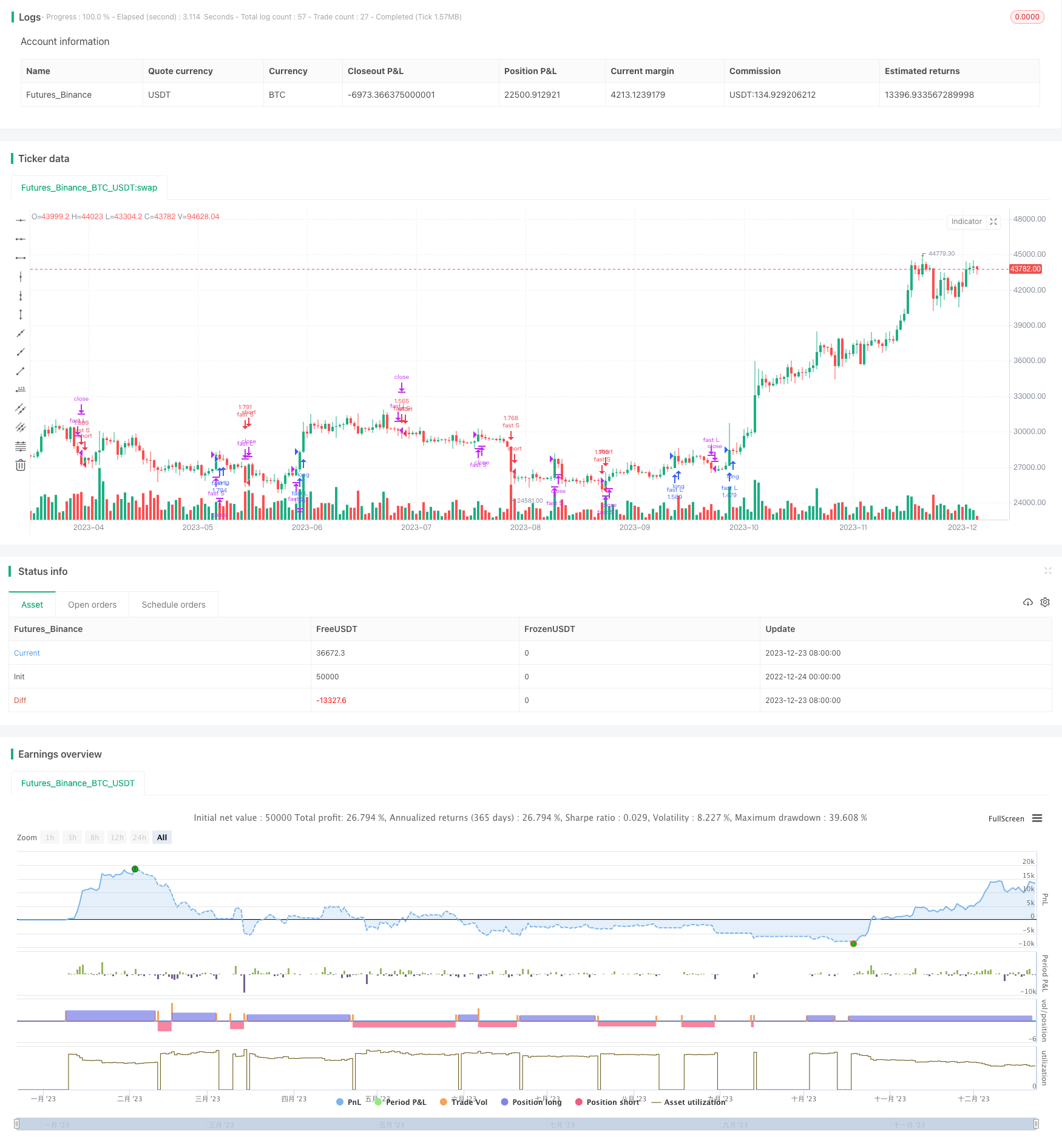
概述
海龟交易策略(Turtle Trading Strategy)是一种追踪突破动量的趋势跟踪策略。它由著名交易员理查德·丹尼斯(Richard Dennis)在20世纪80年代开发,用来验证交易员是否可以通过规则来培养,而不是天生的。该策略的核心理念是追踪价格突破并跟踪趋势,同时严格遵守资金管理原则以限制下行风险。
策略原理
海龟交易策略使用两个参数N和N/2构建通道。具体来说,分别计算最近N天和N/2天内的最高价、最低价。当价格超过N天通道时建立多头仓位,当价格跌破N/2天通道时平仓;当价格跌破N天通道时建立空头仓位,当价格超过N/2天通道时平仓。这样做的目的是追踪价格趋势同时控制风险。
代码中,N对应enter_slow,N/2对应enter_fast。分别计算最近55天和20天的最高价ighest(slowL和fastL)、最低价lowest(slowS和fastS)。当价格超过55天通道时做多(enterL2),当价格跌破20天通道时平多仓(exitL1);当价格跌破55天通道时做空(enterS2),当价格超过20天通道时平空仓(exitS1`)。
优势分析
海龟交易策略最大的优势在于风险控制。通过在价格突破时建立仓位,在价格回撤时快速止损,可以有效控制单笔损失。同时采用固定份额资金管理原则,进一步降低了风险。
另一个优势是参数选择简单。整个策略只有4个参数,容易理解和调整。参数本身也比较稳定,不需要频繁优化。
风险分析
海龟交易策略最大的风险在于无法跟踪长期趋势。当趋势开始形成时,该策略可能错过入场机会。另外,价格震荡趋势中,该策略会频繁开仓平仓,增加交易成本和滑点风险。
此外,固定的参数设置也可能在不同品种和市场环境下效果差异很大。这需要人工经验进行调整。
优化方向
海龟交易策略可以从以下几个方面进行优化:
增加参数自适应功能。允许N、N/2的参数根据市场波动性和信号频繁度自动调整,适应更多场景。
增加趋势判断规则。在入场之前判断趋势方向,避免价格震荡行情的错误入场。
结合多个时间周期unity策略。在更高时间周期确定趋势方向,在更低时间周期入场。
优化止损策略。trailing 止损或时间止损,降低回撤。
总结
海龟交易策略通过简单的突破系统实现了有效的趋势跟踪。风险控制是该策略最大的优势,这得益于快速止损和固定资金管理。与此同时,我们也看到该策略可以从多个维度进行扩展与优化,适应更多品种和市场环境。总的来说,海龟交易策略提供了一个风险可控的方法来捕捉价格趋势,是量化交易的一个重要参考。
/*backtest
start: 2022-12-24 00:00:00
end: 2023-12-24 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=2
//oringinally coded by tmr0, modified by timchep
//original idea from «Way of the Turtle: The Secret Methods that Turned Ordinary People into Legendary Traders» (2007) CURTIS FAITH
strategy("Turtles", shorttitle = "Turtles", overlay=true, pyramiding=1, default_qty_type= strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value = 100)
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Component Code Start
testStartYear = input(2011, "Backtest Start Year")
testStartMonth = input(12, "Backtest Start Month")
testStartDay = input(1, "Backtest Start Day")
testPeriodStart = timestamp(testStartYear,testStartMonth,testStartDay,0,0)
testStopYear = input(2030, "Backtest Stop Year")
testStopMonth = input(12, "Backtest Stop Month")
testStopDay = input(30, "Backtest Stop Day")
testPeriodStop = timestamp(testStopYear,testStopMonth,testStopDay,0,0)
// A switch to control background coloring of the test period
testPeriodBackground = input(title="Color Background?", type=bool, defval=false)
testPeriodBackgroundColor = testPeriodBackground and (time >= testPeriodStart) and (time <= testPeriodStop) ? #00FF00 : na
bgcolor(testPeriodBackgroundColor, transp=97)
testPeriod() => true
// Component Code Stop
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
shortingEnabled = input(title="Enable Shorting?", type=bool, defval=true)
enter_fast = input(20, minval=1)
exit_fast = input(10, minval=1)
enter_slow = input(55, minval=1)
exit_slow = input(20, minval=1)
fastL = highest(enter_fast)
fastLC = lowest(exit_fast)
fastS = lowest(enter_fast)
fastSC = highest(exit_fast)
slowL = highest(enter_slow)
slowLC = lowest(exit_slow)
slowS = lowest(enter_slow)
slowSC = highest(exit_slow)
enterL1 = high > fastL[1]
exitL1 = low <= fastLC[1]
enterS1 = low < fastS[1]
exitS1 = high >= fastSC[1]
enterL2 = high > slowL[1]
exitL2 = low <= slowLC[1]
enterS2 = low < slowS[1]
exitS2 = high >= slowSC[1]
if testPeriod()
strategy.entry("fast L", strategy.long, when = enterL1)
if not enterL1
strategy.entry("slow L", strategy.long, when = enterL2)
strategy.close("fast L", when = exitL1)
strategy.close("slow L", when = exitL2)
if shortingEnabled and testPeriod()
strategy.entry("fast S", strategy.short, when = enterS1)
if not enterS2
strategy.entry("slow S", strategy.short, when = enterS2)
strategy.close("fast S", when = exitS1)
strategy.close("slow S", when = exitS2)