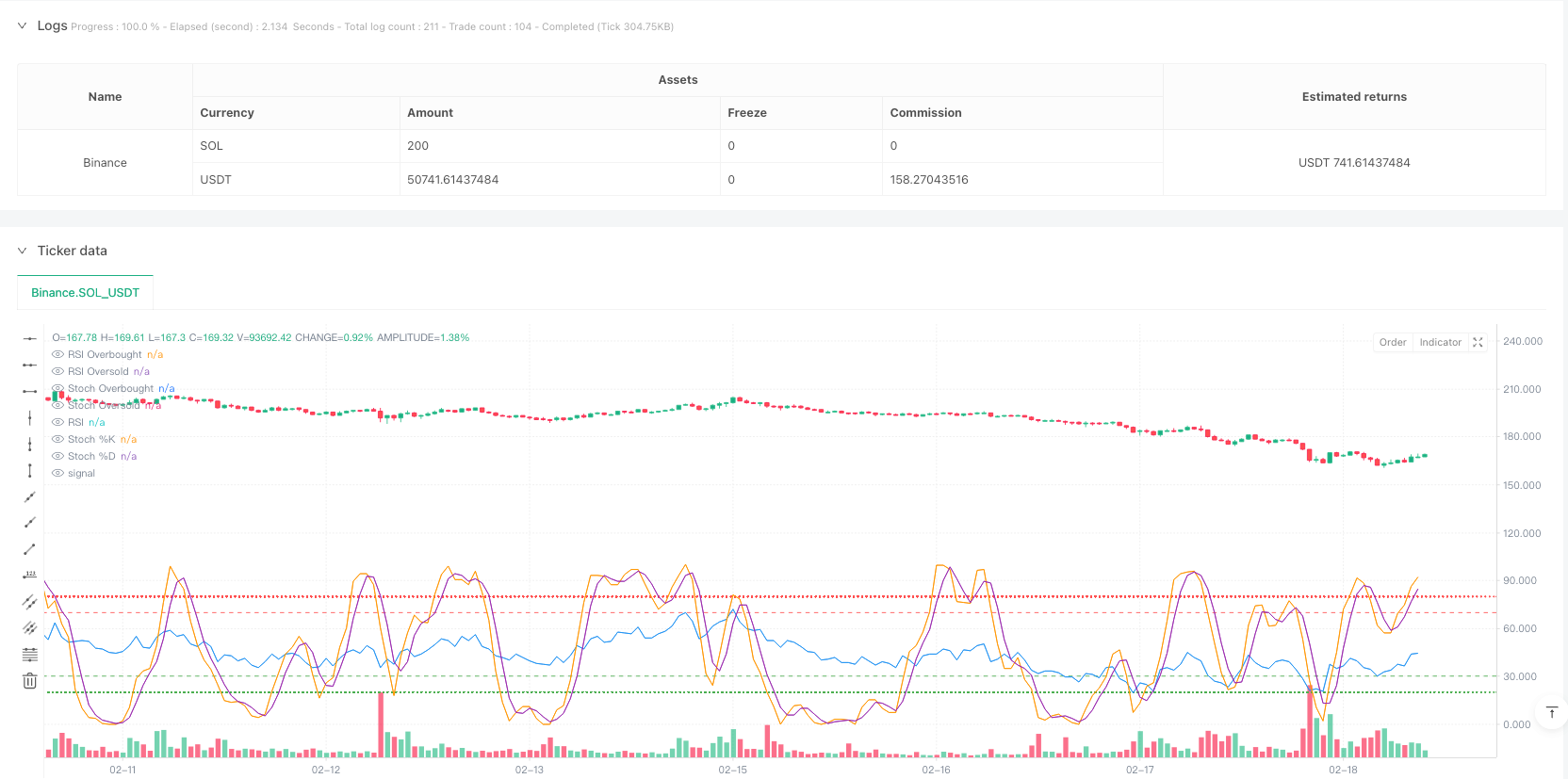
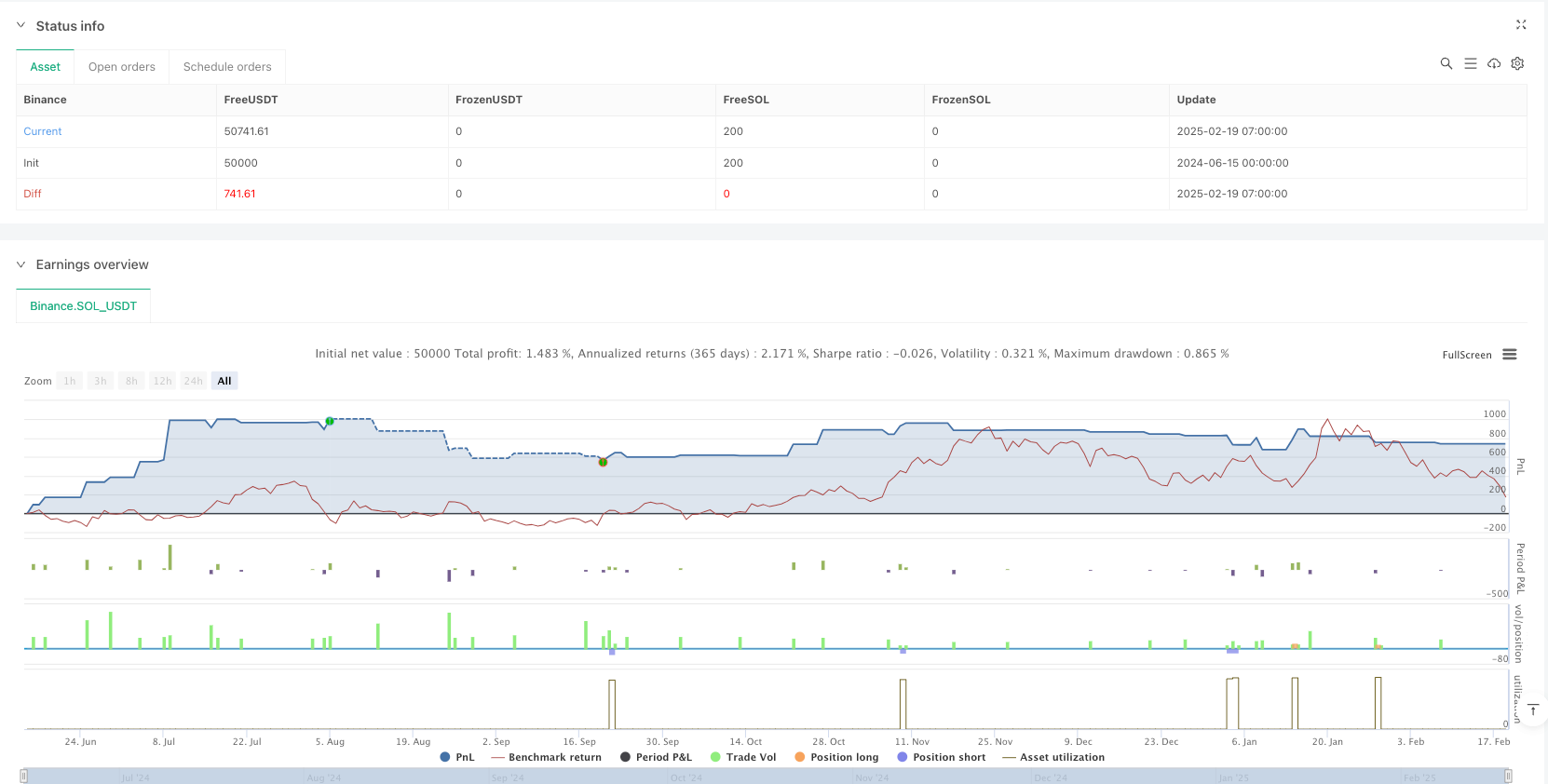
概述
这是一个结合相对强弱指标(RSI)和随机相对强弱指标(Stochastic RSI)的趋势反转交易策略。该策略通过识别市场的超买超卖状态以及动量变化来捕捉潜在的反转点,从而进行交易。策略的核心是将RSI指标作为基础动量指标,再在此基础上计算Stochastic RSI来进一步确认价格动量的变化方向。
策略原理
策略的主要逻辑包含以下几个关键步骤: 1. 首先计算收盘价的RSI值,用于判断整体的超买超卖状态 2. 以RSI值为基础计算Stochastic RSI的%K线和%D线 3. 在RSI处于超卖区域(默认低于30)且Stochastic RSI的%K线自下而上穿越%D线时,触发做多信号 4. 在RSI处于超买区域(默认高于70)且Stochastic RSI的%K线自上而下穿越%D线时,触发做空信号 5. 当出现相反的RSI条件或Stochastic RSI发生反向交叉时,平仓退出
策略优势
- 双重确认机制 - 通过RSI和Stochastic RSI的配合使用,可以有效降低假突破带来的风险
- 可自定义参数 - 策略的关键参数如RSI周期、超买超卖阈值等都可以根据不同市场情况进行调整
- 动态可视化 - 策略提供了RSI和Stochastic RSI的实时图表展示,便于交易者进行监控
- 风险管理集成 - 包含了完整的止损和获利了结机制
- 适应性强 - 可以应用于不同的时间周期和市场环境
策略风险
- 震荡市场风险 - 在横盘震荡市场中可能产生频繁的假信号
- 滞后性风险 - 由于使用了多重均线平滑,信号可能出现一定程度的滞后
- 参数敏感性 - 不同的参数设置可能导致显著不同的交易结果
- 市场环境依赖 - 在强趋势市场中可能会错过部分行情
- 资金管理风险 - 需要合理设置持仓比例以控制风险
策略优化方向
- 增加趋势过滤器 - 可以添加长期移动平均线作为趋势过滤器,只在趋势方向上开仓
- 优化止损机制 - 可以引入动态止损,如跟踪止损或ATR止损
- 引入成交量指标 - 结合成交量分析可以提高信号的可靠性
- 添加时间过滤 - 可以避开重要新闻发布时间或者低流动性时段
- 开发自适应参数 - 根据市场波动率自动调整策略参数
总结
这是一个结合了动量和趋势反转的综合策略,通过RSI和Stochastic RSI的协同作用来识别潜在的交易机会。策略设计合理,具有较好的可调整性和适应性。但在实际应用中需要注意市场环境的选择和风险控制,建议在实盘交易前进行充分的回测和参数优化。
策略源码
/*backtest
start: 2024-06-15 00:00:00
end: 2025-02-19 08:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Binance","currency":"SOL_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("RSI + Stochastic RSI Strategy", overlay=true, initial_capital=100000, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value=10)
// INPUTS
// RSI settings
rsiLength = input.int(14, "RSI Length", minval=1)
rsiOverbought = input.int(70, "RSI Overbought Level")
rsiOversold = input.int(30, "RSI Oversold Level")
// Stochastic RSI settings
stochLength = input.int(14, "Stoch RSI Length", minval=1)
smoothK = input.int(3, "Stoch %K Smoothing", minval=1)
smoothD = input.int(3, "Stoch %D Smoothing", minval=1)
stochOverbought = input.int(80, "Stoch Overbought Level")
stochOversold = input.int(20, "Stoch Oversold Level")
// CALCULATIONS
// Compute RSI value on the closing price
rsiValue = ta.rsi(close, rsiLength)
// Calculate Stochastic RSI using the RSI value as source
rsiStoch = ta.stoch(rsiValue, rsiValue, rsiValue, stochLength)
kValue = ta.sma(rsiStoch, smoothK)
dValue = ta.sma(kValue, smoothD)
// PLOTTING
// Plot RSI and reference lines
plot(rsiValue, title="RSI", color=color.blue)
hline(rsiOverbought, "RSI Overbought", color=color.red)
hline(rsiOversold, "RSI Oversold", color=color.green)
// Plot Stochastic RSI %K and %D along with overbought/oversold levels
plot(kValue, title="Stoch %K", color=color.orange)
plot(dValue, title="Stoch %D", color=color.purple)
hline(stochOverbought, "Stoch Overbought", color=color.red, linestyle=hline.style_dotted)
hline(stochOversold, "Stoch Oversold", color=color.green, linestyle=hline.style_dotted)
// STRATEGY CONDITIONS
// Long Condition: RSI below oversold and Stoch RSI crosses upward while in oversold territory
longCondition = (rsiValue < rsiOversold) and (kValue < stochOversold) and ta.crossover(kValue, dValue)
// Long Exit: When RSI goes above overbought or a downward cross occurs on the Stoch RSI
longExit = (rsiValue > rsiOverbought) or ta.crossunder(kValue, dValue)
// Short Condition: RSI above overbought and Stoch RSI crosses downward while in overbought territory
shortCondition = (rsiValue > rsiOverbought) and (kValue > stochOverbought) and ta.crossunder(kValue, dValue)
// Short Exit: When RSI goes below oversold or an upward cross occurs on the Stoch RSI
shortExit = (rsiValue < rsiOversold) or ta.crossover(kValue, dValue)
// EXECUTE TRADES
if (longCondition)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
if (longExit)
strategy.close("Long")
if (shortCondition)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
if (shortExit)
strategy.close("Short")
相关推荐