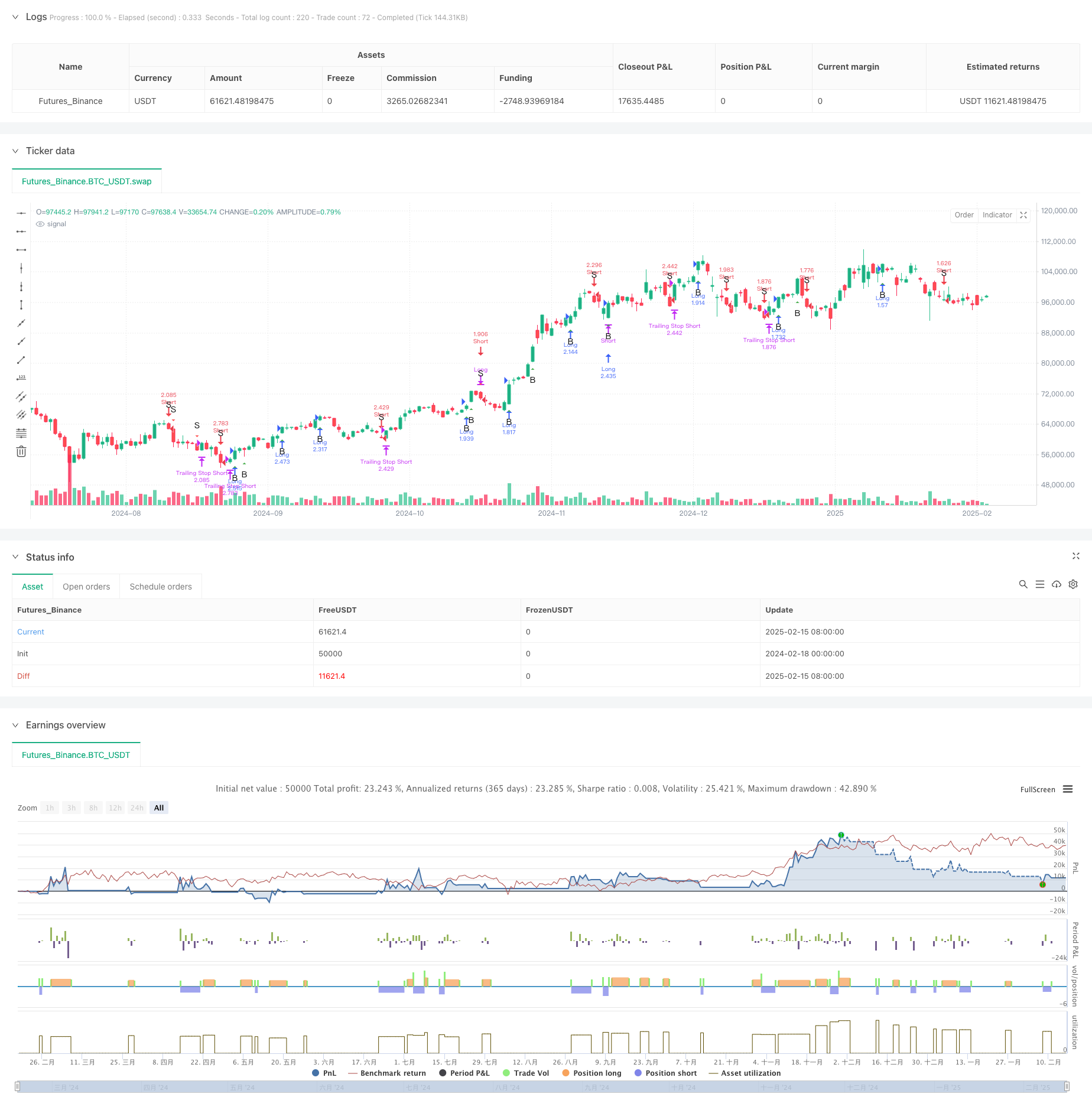
Overview
This is a quantitative trading strategy that combines Bill Williams’ bar-thirds analysis method with dynamic trailing stop functionality. The strategy generates clear long and short signals by analyzing the structural characteristics of current and previous bars, while utilizing a configurable trailing stop mechanism to protect positions, achieving precise entry/exit and risk management.
Strategy Principle
The core logic of the strategy is based on the following key components: 1. Bar-thirds Calculation: Divides each bar’s range (high-low) into three equal parts, obtaining boundary values for upper and lower regions. 2. Bar Pattern Classification: Categorizes bars into different types based on the position of opening and closing prices within the three regions. For example, when the opening price is in the lower region and the closing price is in the upper region, it’s considered a strong bullish pattern. 3. Signal Generation Rules: Determines valid trading signals by combining analysis of current and previous bar patterns. For instance, a buy signal is triggered when two consecutive bars show strong characteristics. 4. Dynamic Trailing Stop: Uses the lowest price (for longs) or highest price (for shorts) of the previous N bars in the specified timeframe as a moving stop loss level.
Strategy Advantages
- Clear Logic: The strategy uses intuitive bar structure analysis methods with explicit and easy-to-understand trading rules.
- Comprehensive Risk Management: Effectively controls drawdown risk while maintaining sufficient profit potential through dynamic trailing stop mechanism.
- High Adaptability: Strategy parameters can be adjusted according to different market environments, demonstrating good adaptability.
- High Automation: Achieves full automation from signal generation to position management, reducing human intervention.
Strategy Risks
- Choppy Market Risk: May generate frequent false breakout signals in sideways markets, leading to overtrading.
- Gap Risk: Trailing stops may not trigger timely during significant price gaps, causing unexpected losses.
- Parameter Sensitivity: The choice of trailing stop parameters significantly impacts strategy performance; inappropriate settings may lead to premature exits or insufficient protection.
Strategy Optimization Directions
- Add Market Environment Filtering: Introduce trend or volatility indicators to dynamically adjust strategy parameters in different market conditions.
- Optimize Stop Loss Mechanism: Consider incorporating ATR indicator for more flexible stop loss distances, improving stop loss adaptability.
- Introduce Position Sizing: Dynamically adjust position size based on signal strength and market volatility for more refined risk control.
- Enhance Exit Optimization: Add profit targets or technical indicators to assist in determining optimal exit timing.
Summary
This is a well-structured quantitative trading strategy with clear logic, combining classical technical analysis methods with modern risk management techniques, demonstrating good practicality. The strategy design fully considers real trading needs, including signal generation, position management, and risk control. Through further optimization and improvement, this strategy has the potential to achieve better performance in actual trading.
/*backtest
start: 2024-02-18 00:00:00
end: 2025-02-16 08:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("TrinityBar with Trailing Stop", overlay=true, initial_capital=100000,
default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value=250)
//─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
// 1. BAR THIRDS CALCULATIONS
//─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
cur_range = high - low
cur_lowerThird = low + cur_range / 3
cur_upperThird = high - cur_range / 3
prev_range = high[1] - low[1]
prev_lowerThird = low[1] + prev_range / 3
prev_upperThird = high[1] - prev_range / 3
//─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
// 2. DEFINE BULLISH & BEARISH BAR TYPES (CURRENT & PREVIOUS)
//─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
// Current bar types
is_1_3 = (open <= cur_lowerThird) and (close >= cur_upperThird)
is_3_3 = (open >= cur_upperThird) and (close >= cur_upperThird)
is_2_3 = (open > cur_lowerThird) and (open < cur_upperThird) and (close >= cur_upperThird)
is_3_1 = (open >= cur_upperThird) and (close <= cur_lowerThird)
is_1_1 = (open <= cur_lowerThird) and (close <= cur_lowerThird)
is_2_1 = (open > cur_lowerThird) and (open < cur_upperThird) and (close <= cur_lowerThird)
// Previous bar types
prev_is_1_3 = (open[1] <= prev_lowerThird) and (close[1] >= prev_upperThird)
prev_is_3_3 = (open[1] >= prev_upperThird) and (close[1] >= prev_upperThird)
prev_is_2_3 = (open[1] > prev_lowerThird) and (open[1] < prev_upperThird) and (close[1] >= prev_upperThird)
prev_is_3_1 = (open[1] >= prev_upperThird) and (close[1] <= prev_lowerThird)
prev_is_1_1 = (open[1] <= prev_lowerThird) and (close[1] <= prev_lowerThird)
prev_is_2_1 = (open[1] > prev_lowerThird) and (open[1] < prev_upperThird) and (close[1] <= prev_lowerThird)
//─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
// 3. VALID SIGNAL CONDITIONS
//─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
validBuy = (prev_is_2_3 or prev_is_3_3 or prev_is_1_3) and (is_1_3 or is_3_3)
validSell = (prev_is_2_1 or prev_is_1_1 or prev_is_3_1) and (is_1_1 or is_3_1)
//─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
// 4. PLOT SIGNAL TRIANGLES
//─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
plotshape(validBuy, title="Valid Buy", style=shape.triangleup, location=location.belowbar,
color=color.green, size=size.small, text="B")
plotshape(validSell, title="Valid Sell", style=shape.triangledown, location=location.abovebar,
color=color.red, size=size.small, text="S")
//─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
// 5. MARKET ORDER EXECUTION BASED ON SIGNALS
//─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
if validBuy
// Close any short positions.
strategy.close("Short", comment="")
// If not already long, enter a market long.
if strategy.position_size <= 0
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long, comment="")
if validSell
// Close any long positions.
strategy.close("Long", comment="")
// If not already short, enter a market short.
if strategy.position_size >= 0
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short, comment="")
//─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
// 6. TRAILING STOP LOSS FUNCTION
//─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
// Inputs for trailing stop settings:
trailBars = input.int(title="Trailing Stop Bars Back", defval=1, minval=1)
trailTF = input.timeframe(title="Trailing Stop Timeframe", defval="") // "" = current timeframe
// For long positions, use the low from 'trailBars' bars back on the specified timeframe.
// For short positions, use the high from 'trailBars' bars back.
trailStopLong = request.security(syminfo.tickerid, trailTF, low[trailBars])
trailStopShort = request.security(syminfo.tickerid, trailTF, high[trailBars])
// Apply trailing stops if a position is open.
if strategy.position_size > 0
strategy.exit("Trailing Stop Long", from_entry="Long", stop=trailStopLong)
if strategy.position_size < 0
strategy.exit("Trailing Stop Short", from_entry="Short", stop=trailStopShort)