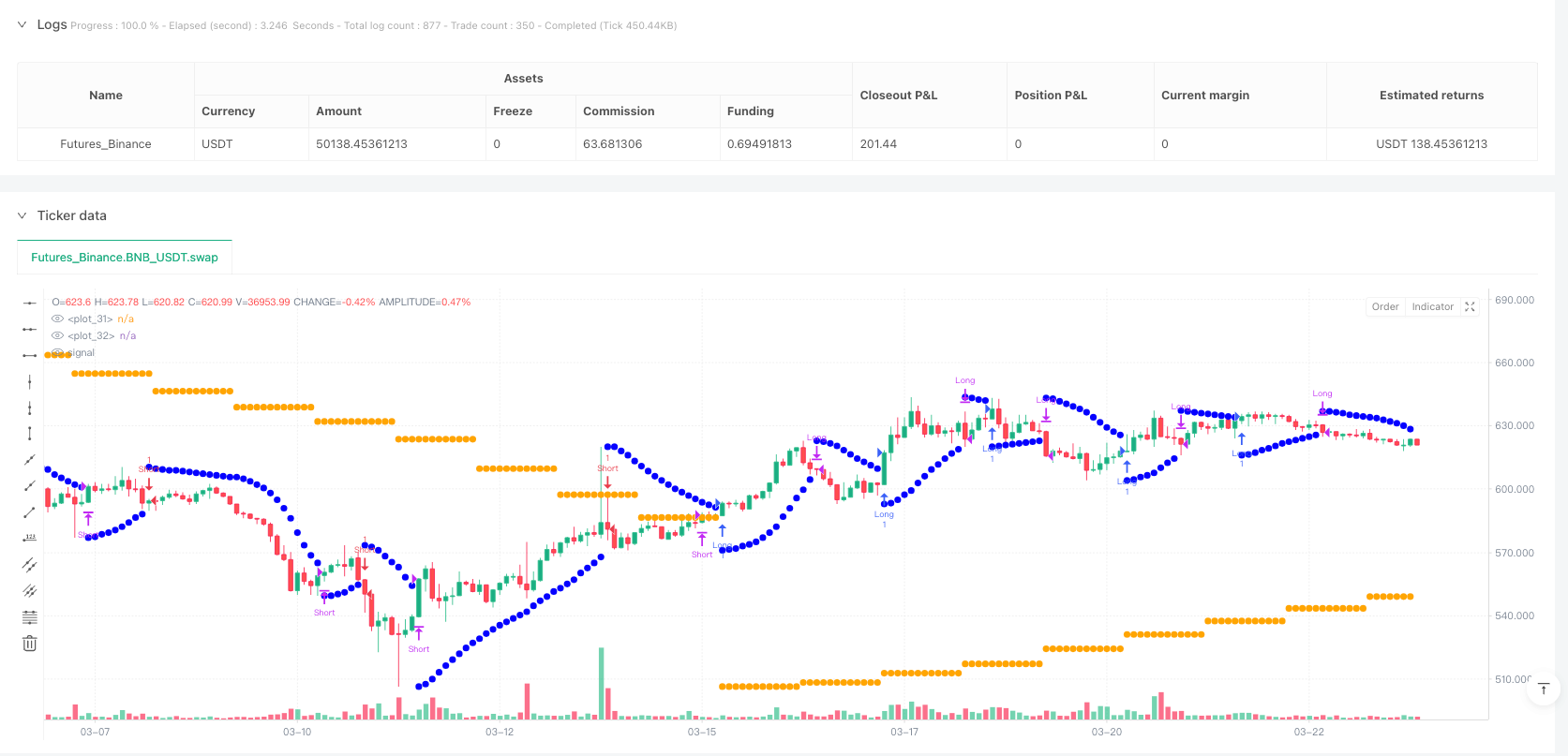
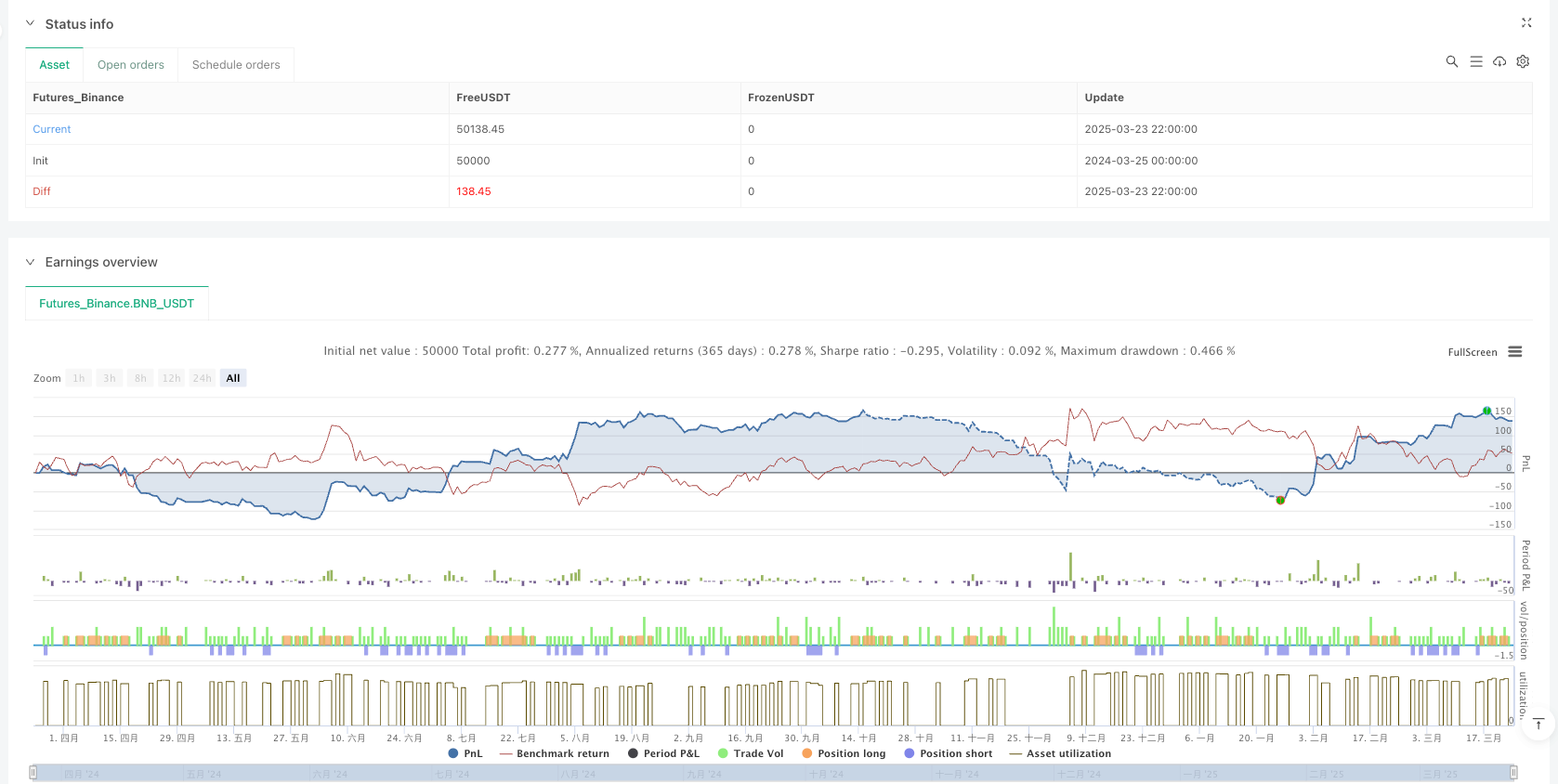
Overview
The Multi-Timeframe Parabolic SAR Dynamic Trend Following Quantitative Strategy is an advanced quantitative trading system that combines the Parabolic SAR indicator across multiple timeframes. This strategy innovatively integrates the PSAR indicator from both the current chart timeframe and a user-defined higher timeframe to achieve more precise trend identification, entry/exit signals, and dynamic stop-loss management. Through multi-timeframe analysis, this strategy effectively filters market noise, improves trading accuracy, and captures more significant market movements.
Strategy Principles
The core principle of this strategy is based on the application and synergistic effect of the Parabolic SAR (Stop and Reverse) indicator across multiple timeframes. The strategy calculation logic includes:
Dual Timeframe Analysis: Simultaneously calculates the Parabolic SAR on both the current chart timeframe and a higher timeframe (such as Daily PSAR on a 1-hour chart), ensuring that trade direction aligns with the dominant trend.
Trend Direction Determination: Determines trend direction based on the position of PSAR dots - uptrend when price is above PSAR dots (PSAR dots below price), and downtrend when price is below PSAR dots (PSAR dots above price).
Flexible Entry Conditions: The strategy offers three entry strategy options:
- Confirmation Mode: Requires agreement between current timeframe and higher timeframe PSAR signals, and the current timeframe PSAR must have just flipped direction
- Current Timeframe Only Mode: Trades based solely on current timeframe PSAR signals
- Higher Timeframe Only Mode: Trades based solely on higher timeframe PSAR signals
Dynamic Trailing Stop: Uses the current timeframe’s PSAR as a dynamic trailing stop, automatically adjusting the stop-loss position as price moves, protecting profits and limiting losses.
No Repainting Design: The strategy uses the
lookahead=barmerge.lookahead_offparameter to ensure that higher timeframe data access does not experience data leakage, preventing repainting issues.
Key implementations in the code include PSAR calculation (ta.sar), multi-timeframe data requests (request.security), trend direction determination (based on price and PSAR relationship), and the logical combination of entry and exit conditions, forming a complete strategy trading system.
Strategy Advantages
Analyzing the code implementation of this strategy reveals the following significant advantages:
Enhanced Trend Identification: Through multi-timeframe analysis, the accuracy of trend identification is improved. When short-term and long-term PSAR indicators agree, the reliability of trading signals significantly increases.
Reduced False Signals: The higher timeframe PSAR acts as a filter, effectively reducing false signals from lower timeframes and frequent trading in oscillating markets.
High Customizability: The strategy allows users to adjust PSAR parameters (start value, increment, maximum), select higher timeframes, configure display options and colors, enabling fine-tuned customization.
Dynamic Risk Management: Employs PSAR-based dynamic trailing stops that automatically adjust stop-loss positions with market fluctuations, both protecting profits and controlling maximum risk.
Visual Clarity: Different colors distinguish between current and higher timeframe PSAR dots, providing intuitive visual signals for quick decision-making.
Strong Adaptability: Suitable for various trading styles (swing trading, day trading, trend following) and various markets (stocks, forex, cryptocurrencies, etc.).
Logical Simplicity: The strategy logic is clear, implementation is concise and effective, without complex calculations, resulting in high operational efficiency.
Strategy Risks
Despite its multiple advantages, this strategy also has the following potential risks and limitations:
Lag Issues: PSAR is inherently a lagging indicator and may miss optimal entry or exit opportunities near trend turning points. Solution: Combine with other forward-looking indicators for supplementary judgment.
Poor Performance in Oscillating Markets: In sideways consolidation or highly volatile range-bound markets, PSAR can generate frequent false signals, leading to overtrading and consecutive losses. Solution: Add market type identification to pause trading during oscillating markets.
Parameter Sensitivity: Strategy performance is highly sensitive to PSAR parameters (start value, increment, maximum), and different markets and timeframes may require different parameter configurations. Solution: Conduct thorough historical backtesting and parameter optimization.
Gap Risk for Stop-Loss: In highly volatile markets, prices may gap through the PSAR stop-loss level, resulting in actual stop-loss prices far lower than expected. Solution: Consider adding hard stop-loss limits.
Slow Reaction to Trend Changes: When trends suddenly reverse, dynamic stops may not trigger in time, leading to larger drawdowns. Solution: Consider adding additional market sentiment or volatility indicators for supplementary judgment.
Multi-Timeframe Consistency Challenges: At market turning points, different timeframes may show inconsistent signals, increasing decision-making complexity. Solution: Establish clear priority rules or weighting mechanisms.
Strategy Optimization Directions
Based on code analysis, the strategy has the following optimization potential:
Market Type Adaptation: Add market type identification functionality (trend vs. oscillation) to automatically adjust PSAR parameters or trading logic in different market environments. This can significantly improve performance in sideways markets.
Volatility Adjustment Mechanism: Integrate the ATR (Average True Range) indicator to dynamically adjust PSAR parameters based on market volatility. Increase parameters during high volatility periods to reduce false signals and decrease parameters during low volatility periods to improve sensitivity.
Volume Confirmation: Add volume analysis dimension, requiring signals to be accompanied by increased trading volume to further filter low-quality signals.
Multi-Indicator Comprehensive Decision-Making: Introduce additional trend confirmation indicators (such as moving average systems or ADX) to establish a multi-indicator scoring system, improving the reliability of entry signals.
Partial Position Management: Implement partial position management based on signal strength, rather than simple all-in/all-out. For example, use larger positions when multiple timeframe signals agree and smaller positions when they don’t.
Time Filter: Add trading session filtering to avoid low liquidity or high volatility sessions, improving overall win rate.
Profit-Taking Mechanism Improvement: The current strategy relies only on PSAR reversal as exit conditions. Consider adding price structure-based profit-taking mechanisms to lock in partial profits in cases of significant gains.
Capital Management Optimization: Integrate more complex money management algorithms, such as the Kelly criterion or fixed proportion risk model, to dynamically adjust position size based on historical performance.
Summary
The Multi-Timeframe Parabolic SAR Dynamic Trend Following Quantitative Strategy is an advanced quantitative trading system that combines the advantages of PSAR indicator analysis across multiple timeframes. By simultaneously monitoring PSAR signals from current and higher timeframes, this strategy effectively enhances trend identification capabilities, reduces false signals, and implements dynamic risk management.
The core advantages of the strategy lie in its flexible entry mode selection, intuitive visual signals, and high customizability, making it adaptable to various trading styles and market environments. However, as a PSAR-based system, it also inherits the inherent limitations of the PSAR indicator, such as lag issues and poor performance in oscillating markets.
Through the introduction of market type identification, volatility adjustment, volume confirmation, and other optimization measures, this strategy has significant room for improvement. Ultimately, this strategy provides trend-following traders with a solid quantitative trading framework, particularly suitable for medium to long-term trend capture and risk control.
/*backtest
start: 2024-03-25 00:00:00
end: 2025-03-24 00:00:00
period: 2h
basePeriod: 2h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BNB_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("Multi-Timeframe Parabolic SAR Strategy ver 1.0", overlay=true, shorttitle="MTF PSAR Strategy ver 1.0")
// --- Input Settings ---
// PSAR Settings
start = input.float(0.02, title="Start", minval=0.001)
increment = input.float(0.02, title="Increment", minval=0.001)
maximum = input.float(0.2, title="Maximum", maxval=1)
// Multi-Timeframe Settings
higherTimeframe = input.timeframe("D", title="Higher Timeframe PSAR")
showCurrentTF = input.bool(true, title="Show Current Timeframe PSAR")
showHigherTF = input.bool(true, title="Show Higher Timeframe PSAR")
// Color Settings
currentTFColor = input.color(color.blue, title="Current TF PSAR Color")
higherTFColor = input.color(color.orange, title="Higher TF PSAR Color")
// --- PSAR Calculations ---
// Current Timeframe PSAR
currentPSAR = ta.sar(start, increment, maximum)
// Higher Timeframe PSAR
higherPSAR = request.security(syminfo.tickerid, higherTimeframe, ta.sar(start, increment, maximum), lookahead=barmerge.lookahead_off)
// --- Plotting ---
plot(showCurrentTF ? currentPSAR : na, style=plot.style_circles, color=currentTFColor, linewidth=2)
plot(showHigherTF ? higherPSAR : na, style=plot.style_circles, color=higherTFColor, linewidth=2)
// --- Strategy Logic ---
// Determine Trend Direction based on PSAR
currentTrend = close > currentPSAR ? 1 : -1
higherTrend = close > higherPSAR ? 1 : -1 //compare to close of current timeframe
// Entry Conditions
longCondition = showCurrentTF and showHigherTF and currentTrend == 1 and higherTrend == 1 and currentTrend[1] == -1 //Both bullish and Current flipped
shortCondition = showCurrentTF and showHigherTF and currentTrend == -1 and higherTrend == -1 and currentTrend[1] == 1 //Both bearish and Current flipped
longConditionSingleTF = showCurrentTF and not showHigherTF and currentTrend == 1 and currentTrend[1] == -1 // Current TF bullish, HTF disabled
shortConditionSingleTF = showCurrentTF and not showHigherTF and currentTrend == -1 and currentTrend[1] == 1 // Current TF bearish, HTF disabled
longConditionHTFOnly = not showCurrentTF and showHigherTF and higherTrend == 1 and higherTrend[1] == -1
shortConditionHTFOnly = not showCurrentTF and showHigherTF and higherTrend == -1 and higherTrend[1] == 1
// Exit Conditions (Trailing Stop using Current Timeframe PSAR)
longExitCondition = showCurrentTF ? currentTrend == -1 : false
shortExitCondition = showCurrentTF ? currentTrend == 1 : false
longExitConditionHTF = showHigherTF ? higherTrend == -1 : false
shortExitConditionHTF = showHigherTF ? higherTrend == 1: false
// --- Strategy Orders ---
if (longCondition or longConditionSingleTF or longConditionHTFOnly)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
if (shortCondition or shortConditionSingleTF or shortConditionHTFOnly)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
if (longExitCondition or longExitConditionHTF)
strategy.close("Long", comment="PSAR Exit") // Close long position when PSAR flips
if (shortExitCondition or shortExitConditionHTF)
strategy.close("Short", comment="PSAR Exit") // Close short position when PSAR flips