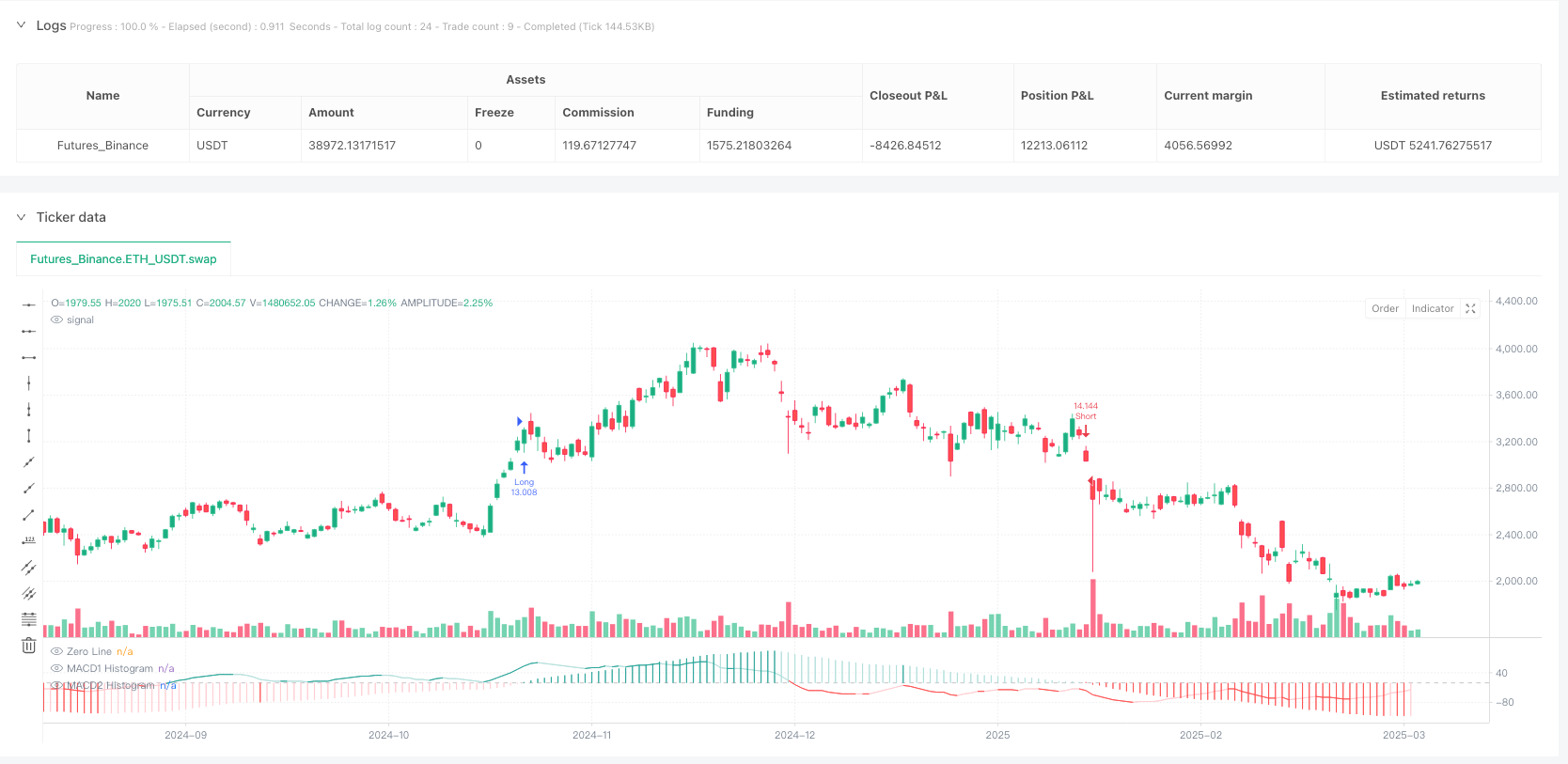

Overview
The Dual MACD Trend Signal Capture and Filtering Quantitative Strategy is a quantitative trading strategy based on two Moving Average Convergence-Divergence (MACD) indicators with different timeframes. This strategy captures market trading opportunities by combining short-term and long-term trend signals, effectively filtering market noise and improving the accuracy of trading signals. Implemented on the TradingView platform, this strategy operates independently of the price chart overlay and is suitable for various financial markets, including stocks, futures, and forex.
The core of the strategy lies in utilizing two MACD indicators: MACD1 (short-term) and MACD2 (long-term). MACD1 has default fast length of 34, slow length of 144, and signal smoothing of 9, used to detect short-term trend changes; MACD2 has default fast length of 100, slow length of 200, and signal smoothing of 50, used to assess long-term trend direction. Users can customize the fast, slow, and signal lengths and choose between SMA (Simple Moving Average) or EMA (Exponential Moving Average) for calculations.
Strategy Principles
The core principle of the Dual MACD strategy is to identify market trends and generate trading signals using two MACD indicators with different timeframes. The strategy code first calculates two MACD indicators and their related parameters:
MACD1 (short-term indicator):
- Fast length default is 34
- Slow length default is 144
- Signal smoothing default is 9
MACD2 (long-term indicator):
- Fast length default is 100
- Slow length default is 200
- Signal smoothing default is 50
The trading logic is clear and strict:
Long Condition:
- MACD1 histogram crosses above the zero line (short-term bullish)
- MACD2 histogram is positive (long-term bullish)
- MACD2 histogram has just crossed above zero with a deepening green (trend confirmation)
Short Condition:
- MACD1 histogram crosses below the zero line (short-term bearish)
- MACD2 histogram is negative (long-term bearish)
- MACD2 histogram has just crossed below zero with a deepening red (trend confirmation)
The strategy also includes risk management measures with adjustable stop-loss and take-profit parameters, default stop-loss at 1% (minimum 0.1%), take-profit at 1.5% (minimum 0.1%), dynamically calculated based on entry price. Trades are processed at candle close to ensure signal stability.
Strategy Advantages
Through in-depth code analysis, this Dual MACD strategy demonstrates multiple advantages:
Dual Trend Confirmation Mechanism: By combining short-term MACD and long-term MACD, the strategy effectively filters market noise, reduces false signals, and improves trading accuracy. Trading signals are only generated when both short-term and long-term signals align.
Flexible Parameter Settings: The strategy allows users to customize MACD parameters (fast length, slow length, and signal smoothing) and calculation methods (SMA or EMA), enabling the strategy to adapt to different market environments and user preferences.
Intuitive Visual Feedback: The strategy provides intuitive visualization of trend strength through dynamic color changes (deepening green for rising trends, deepening red for declining trends), helping traders better understand market conditions.
Comprehensive Risk Management: Built-in adjustable stop-loss and take-profit parameters protect capital safety and lock in profits. These parameters can be adjusted according to market volatility and individual risk tolerance.
Real-time Alert Functionality: The strategy provides long and short entry signal alerts for real-time monitoring and automated trading, allowing traders to seize market opportunities promptly.
Wide Applicability: The strategy is applicable to various financial markets, including stocks, futures, and forex, making it a practical tool for multiple trading scenarios.
Strategy Risks
Despite the well-designed Dual MACD strategy, there are several potential risks:
Trend Reversal Risk: In volatile markets, trends may reverse rapidly, causing the strategy to incur losses. Even with stop-loss settings, actual stop-loss prices may experience significant slippage under extreme market conditions.
Parameter Sensitivity: Strategy performance is highly dependent on MACD parameter settings. Inappropriate parameters may lead to excessive false signals or missed important trading opportunities. Users need to carefully optimize parameters according to specific markets and timeframes.
Lag Issues: MACD is inherently a lagging indicator, calculated based on historical price data. In rapidly changing markets, signals may come too late, missing optimal entry points or causing unnecessary losses.
Poor Performance in Ranging Markets: This strategy performs best in strong trending markets but may generate frequent false signals in ranging or directionless markets, leading to consecutive small losses.
Capital Management Risk: The default setting uses 100% of account equity for trading, which may lead to excessive leverage and improper capital management. Traders should consider reducing the percentage of funds for each trade to better manage risk.
To mitigate these risks, traders should consider: combining other technical indicators for cross-validation; regularly backtesting and optimizing strategy parameters; adjusting capital allocation based on market conditions; manually intervening during extreme market conditions; and setting reasonable risk/reward ratios.
Strategy Optimization Directions
Through in-depth code analysis, here are possible optimization directions:
Add Filtering Conditions: Additional technical indicators (such as Relative Strength Index RSI or Bollinger Bands) can be added as filters to reduce false signals. For example, only trade when RSI indicates the market is not in overbought/oversold conditions.
Adaptive Parameters: Implement adaptive adjustment of MACD parameters based on market volatility. In high-volatility markets, increase fast and slow lengths to reduce noise; in low-volatility markets, decrease parameters to improve sensitivity.
Improve Stop-Loss Strategy: Implement volatility-based dynamic stop-loss, such as ATR (Average True Range) based stop-loss settings, rather than fixed percentages. This will make stop-losses more adaptable to current market conditions.
Add Partial Position Closing Mechanism: Allow partial position closing when specific profit targets are reached, locking in partial profits while allowing remaining positions to continue profiting.
Trading Time Filters: Add trading time filters to avoid trading during high-volatility periods like market open/close or during low-liquidity periods.
Capital Management Optimization: Implement capital management based on the Kelly Criterion or fixed proportion risk model, dynamically adjusting position sizes based on win rate and risk/reward ratio.
Combine Multiple Timeframes: In addition to the current two MACDs, consider adding a third, longer-term MACD to provide a more comprehensive market perspective.
Market State Classification: Add market state classification logic (such as trending market vs. ranging market) and adjust trading strategies and parameters based on different market states.
These optimizations can enhance the strategy’s robustness and adaptability, allowing it to maintain good performance under various market conditions.
Summary
The Dual MACD Trend Signal Capture and Filtering Quantitative Strategy creates a powerful trend-following system by cleverly combining short-term and long-term MACD indicators. The core advantage of this strategy lies in its strict dual confirmation mechanism, which effectively reduces false signals and improves trading accuracy. Meanwhile, flexible parameter settings and intuitive visual feedback make it a practical tool for various market participants.
Although there are risks such as trend reversals, parameter sensitivity, and poor performance in ranging markets, these risks can be effectively controlled through appropriate risk management measures and strategy optimizations. Future optimization directions may include adding additional filtering conditions, implementing adaptive parameters, improving stop-loss strategies, and optimizing capital management.
Overall, the Dual MACD strategy provides quantitative traders with a solid framework, particularly suitable for medium to short-term trend traders. By combining classic technical analysis tools with flexible trading rules, this strategy offers a robust trading system for traders seeking consistent returns. For traders willing to invest time in optimizing parameters and understanding potential risks, this is an extremely valuable strategy.
/*backtest
start: 2024-03-25 00:00:00
end: 2025-03-24 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"ETH_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=6
strategy(title="Dual MACD Strategy [Jason Kasei]", shorttitle="DualMACD", overlay=false, margin_long=0, margin_short=0, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity,
default_qty_value=100, process_orders_on_close=true, initial_capital=10000)
// --- 输入参数 ---
// MACD1 参数
macd1_fast_length = input.int(title="MACD1 Fast Length", defval=34)
macd1_slow_length = input.int(title="MACD1 Slow Length", defval=144)
macd1_signal_length = input.int(title="MACD1 Signal Smoothing", minval=1, maxval=50, defval=9)
macd1_sma_source = input.string(title="MACD1 Oscillator MA Type", defval="EMA", options=["SMA", "EMA"])
macd1_sma_signal = input.string(title="MACD1 Signal Line MA Type", defval="EMA", options=["SMA", "EMA"])
// MACD2 参数
macd2_fast_length = input.int(title="MACD2 Fast Length", defval=100)
macd2_slow_length = input.int(title="MACD2 Slow Length", defval=200)
macd2_signal_length = input.int(title="MACD2 Signal Smoothing", minval=1, maxval=50, defval=50)
macd2_sma_source = input.string(title="MACD2 Oscillator MA Type", defval="EMA", options=["SMA", "EMA"])
macd2_sma_signal = input.string(title="MACD2 Signal Line MA Type", defval="EMA", options=["SMA", "EMA"])
// 止损止盈参数
stop_loss_pct = input.float(title="Stop Loss %", defval=1.0, minval=0.1, step=0.1)
take_profit_pct = input.float(title="Take Profit %", defval=1.5, minval=0.1, step=0.1)
// --- 计算 MACD1 ---
src = close
macd1_fast_ma = macd1_sma_source == "SMA" ? ta.sma(src, macd1_fast_length) : ta.ema(src, macd1_fast_length)
macd1_slow_ma = macd1_sma_source == "SMA" ? ta.sma(src, macd1_slow_length) : ta.ema(src, macd1_slow_length)
macd1 = macd1_fast_ma - macd1_slow_ma
macd1_signal = macd1_sma_signal == "SMA" ? ta.sma(macd1, macd1_signal_length) : ta.ema(macd1, macd1_signal_length)
macd1_hist = macd1 - macd1_signal
// --- 计算 MACD2 ---
macd2_fast_ma = macd2_sma_source == "SMA" ? ta.sma(src, macd2_fast_length) : ta.ema(src, macd2_fast_length)
macd2_slow_ma = macd2_sma_source == "SMA" ? ta.sma(src, macd2_slow_length) : ta.ema(src, macd2_slow_length)
macd2 = macd2_fast_ma - macd2_slow_ma
macd2_signal = macd2_sma_signal == "SMA" ? ta.sma(macd2, macd2_signal_length) : ta.ema(macd2, macd2_signal_length)
macd2_hist = macd2 - macd2_signal
// --- 绘制 MACD1 和 MACD2
hline(0, "Zero Line", color=color.new(#787B86, 50))
plot(macd1_hist, title="MACD1 Histogram", style=plot.style_line, color=(macd1_hist >= 0 ? (macd1_hist[1] < macd1_hist ? #26A69A : #B2DFDB) : (macd1_hist[1] < macd1_hist ? #FFCDD2 : #FF5252)))
plot(macd2_hist, title="MACD2 Histogram", style=plot.style_histogram, color=(macd2_hist >= 0 ? (macd2_hist[1] < macd2_hist ? #26A69A : #B2DFDB) : (macd2_hist[1] < macd2_hist ? #FFCDD2 : #FF5252)))
// --- 交易条件 ---
is_deep_green_macd2 = ta.cross(macd2_hist, 0) and macd2_hist > 0 and macd2_hist[1] < macd2_hist
is_deep_red_macd2 = ta.cross(macd2_hist, 0) and macd2_hist < 0 and macd2_hist[1] > macd2_hist
// 检测 MACD1 hist 穿越零轴
macd1_cross_up = macd1_hist > 0
macd1_cross_down = macd1_hist < 0
// 做多条件
long_condition = macd1_cross_up and macd2_hist > 0 and is_deep_green_macd2
// 做空条件
short_condition = macd1_cross_down and macd2_hist < 0 and is_deep_red_macd2
// --- 交易逻辑 ---
if long_condition
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
stop_loss_long = strategy.position_avg_price * (1 - stop_loss_pct / 100)
take_profit_long = strategy.position_avg_price * (1 + take_profit_pct / 100)
strategy.exit("Long Exit", "Long", stop=stop_loss_long, limit=take_profit_long)
if short_condition
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
stop_loss_short = strategy.position_avg_price * (1 + stop_loss_pct / 100)
take_profit_short = strategy.position_avg_price * (1 - take_profit_pct / 100)
strategy.exit("Short Exit", "Short", stop=stop_loss_short, limit=take_profit_short)
// --- 警报条件 ---
alertcondition(long_condition, title="Long Entry", message="Dual MACD Strategy: Long Entry Signal")
alertcondition(short_condition, title="Short Entry", message="Dual MACD Strategy: Short Entry Signal")