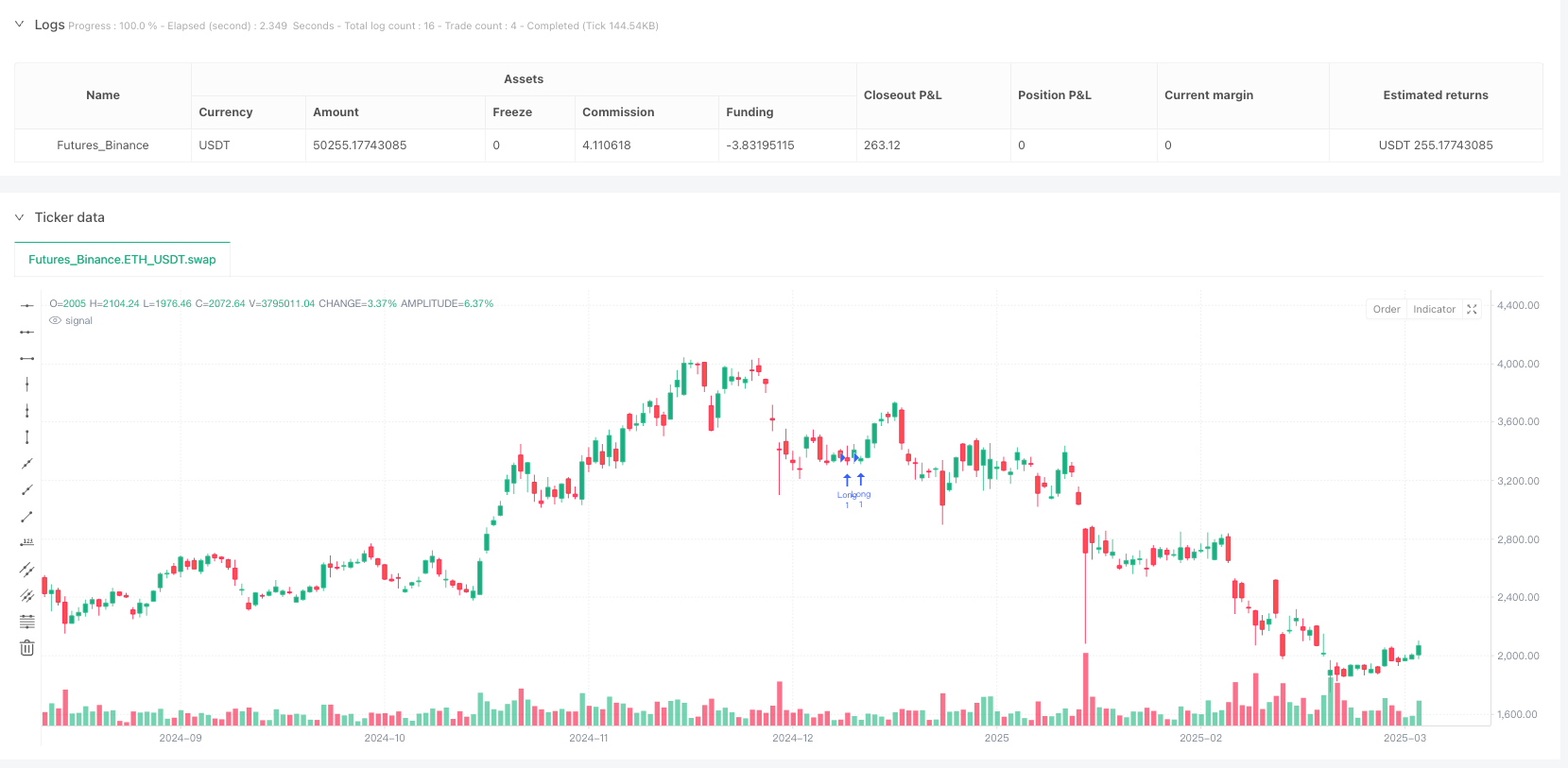
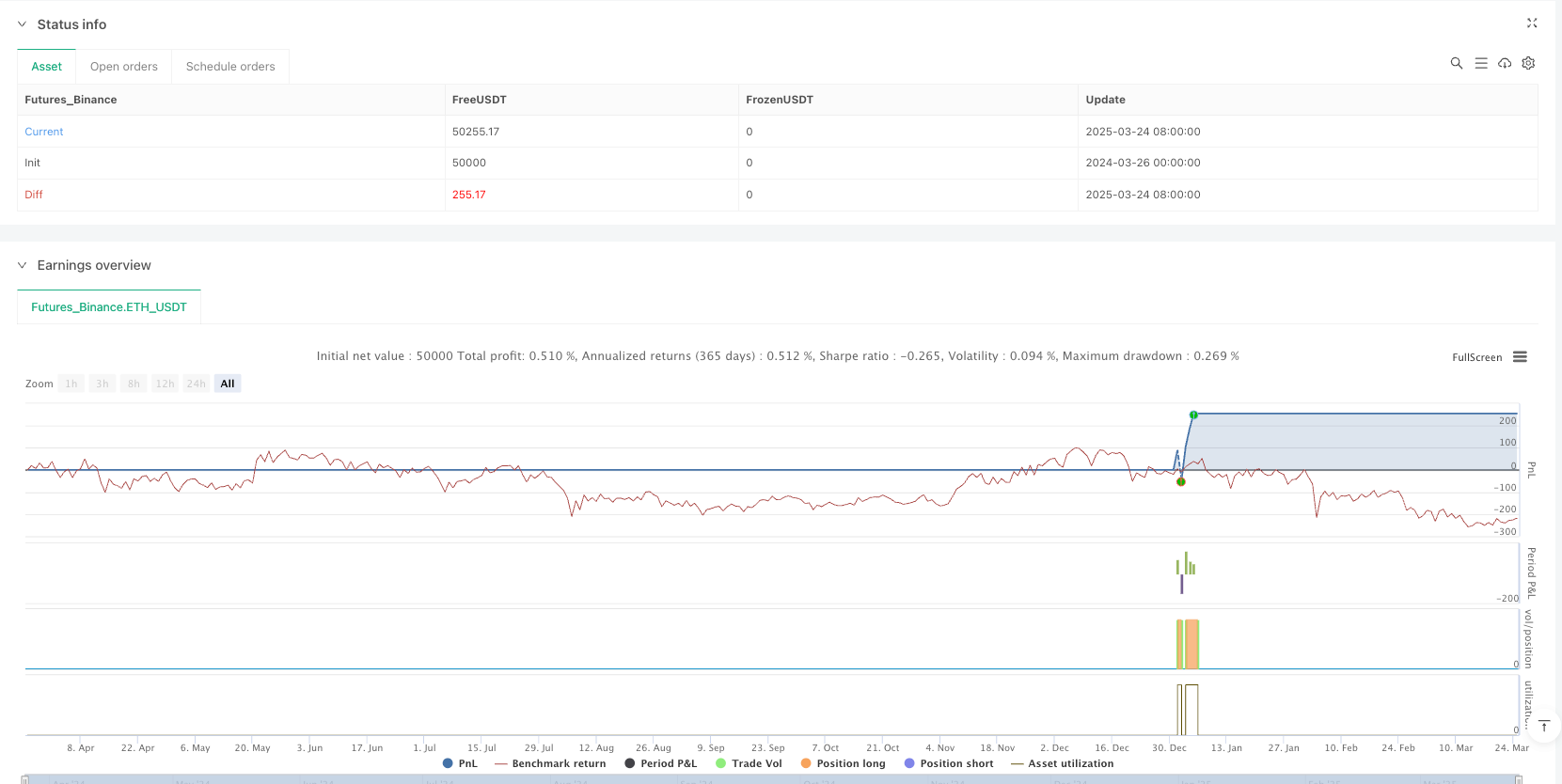
Overview
The Similar Rectangle Height Pattern Quantitative Strategy is a trading system based on price movement characteristics that captures potential trading opportunities by identifying rectangular patterns with similar heights in the market. The core of the strategy lies in finding patterns with similar price movement amplitudes, combined with RSI indicators, volume confirmation, and dynamically adjusted stop-loss and take-profit positions to manage risk and optimize trading results. This strategy is applicable to various trading instruments and provides traders with a systematic method to identify potential trend reversal or continuation signals through precise calculation of price height ratio relationships.
Strategy Principle
The core principle of this strategy is based on the geometric property analysis of price patterns, focusing on the following key points:
Height Pattern Recognition: The strategy mainly focuses on two types of height patterns - the primary height (a user-defined percentage of price) and the correction height (similarly defined smaller percentage). The system dynamically calculates these height values to adapt to different market conditions.
Multiple Pattern Detection:
- Bullish Pattern: Identifies formations where a specific height increase occurs after a bottom forms
- Bearish Pattern: Identifies formations where a specific height decrease occurs after a top forms
- Bullish Correction: Identifies specific magnitude pullbacks in an uptrend
- Bearish Correction: Identifies specific magnitude rebounds in a downtrend
Parameter Optimization:
- Lookback Period: Determines the range of historical data for analysis
- Pattern Width Constraints: Controls the timespan of formations through minimum and maximum width parameters
- Height Matching Tolerance: Allows 20% deviation between actual height and ideal height, increasing pattern recognition flexibility
Technical Indicator Filtering:
- RSI Indicator: Optionally uses RSI overbought/oversold levels to filter trading signals
- Volume Confirmation: Optionally requires trading signals to be valid only when volume is above average level
Entry and Exit Strategy:
- Entry Signals: Long when bullish patterns or bullish corrections are detected; short when bearish patterns or bearish corrections are detected
- Exit Strategy: Uses correction height for stop-loss and primary height for take-profit, forming a trading system with clear risk-reward ratios
Strategy Advantages
Through in-depth analysis of the code implementation, this strategy demonstrates the following significant advantages:
Objective Signal Generation Mechanism: Based on mathematical calculations and clearly defined geometric relationships, reducing the impact of subjective judgment and making trading decisions more systematic and consistent.
Adaptive Market Conditions: By calculating height parameters as percentages of average price, the strategy can automatically adapt to market environments with different price ranges and volatility.
Multi-dimensional Confirmation Mechanism: Combining pattern recognition, RSI indicators, and volume analysis provides multi-layered signal confirmation, helping to filter out low-quality trading signals.
Clear Risk Management Framework: Each trade has predefined stop-loss and take-profit positions, helping traders control risk and maintain consistent risk-reward ratios.
Visual Assistance: Intuitively displays identified trading patterns by drawing rectangles and labels on charts, facilitating understanding and verification of signals by traders.
Parameterized Design: The strategy provides multiple adjustable parameters, allowing traders to optimize according to specific market conditions and personal risk preferences.
Multiple Pattern Recognition: Not only identifies the formation of main trends but also captures correction opportunities within trends, providing more trading entry points.
Strategy Risks
Despite its many advantages, the strategy still has the following potential risks:
Parameter Sensitivity: Strategy performance highly depends on parameter settings; inappropriate parameters may lead to overtrading or missing important signals. The solution is to find optimal parameter combinations through historical backtesting and periodically reassess parameter effectiveness.
False Breakout Risk: The market may form patterns similar to expected ones but subsequently reverse, leading to false signals. It is recommended to add confirmation mechanisms, such as waiting for closing price confirmation or cross-validation with other indicators.
Fixed Percentage Limitations: Using fixed percentages to calculate heights may not be suitable for markets with rapidly changing volatility. Consider introducing dynamic height calculation methods based on ATR or historical volatility.
Computation-Intensive Processing: The strategy involves multiple loops and conditional judgments, which may lead to performance issues when processing large amounts of data. Optimizing code structure or simplifying certain calculation steps can improve execution efficiency.
Simplified Trend Judgment: Current trend judgment is based on simple comparisons of moving averages, which may not accurately capture complex market structures. Consider integrating more sophisticated trend identification algorithms to improve accuracy.
Static Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Settings: Fixed use of correction height and primary height as stop-loss and take-profit may not be flexible enough. Consider introducing dynamic stop-loss and take-profit mechanisms based on market volatility or support/resistance levels.
Strategy Optimization Directions
Based on code analysis, here are possible optimization directions for this strategy:
Dynamic Parameter Adjustment: Introduce adaptive parameter mechanisms to automatically adjust height percentages and pattern width parameters according to market volatility and trading cycles. This allows better adaptation to characteristics of different market phases.
Enhanced Trend Confirmation: Integrate more complex trend identification methods, such as multi-period trend analysis, Bollinger Band width changes, or Directional Movement Index (DMI), to improve trend judgment accuracy.
Optimized Signal Filtering: Introduce additional filtering conditions, such as price relationship with moving averages, multi-period RSI consistency analysis, or volume distribution characteristics, to reduce false signals.
Improved Backtesting Evaluation: Add more comprehensive strategy evaluation metrics, such as maximum drawdown, Sharpe ratio, profit factor, etc., to comprehensively evaluate strategy performance and guide parameter optimization.
Adaptive Stop-Loss Mechanism: Dynamically adjust stop-loss levels based on ATR or recent volatility, rather than simply using fixed correction heights, to improve risk management effectiveness.
Integrated Market Environment Analysis: Add market environment classification functionality to adopt different parameter settings or trading logic under different market states (such as high volatility, low volatility, strong trend, or range-bound).
Optimized Execution Efficiency: Refactor pattern recognition algorithms, reduce nested loops and repetitive calculations to improve strategy execution speed in real-time environments.
Add Time Filtering: Add time-based filtering conditions to avoid volatile periods such as market opening, closing, or important news releases, improving signal quality.
Summary
The Similar Rectangle Height Pattern Quantitative Strategy is a unique technical analysis method that captures trading opportunities by precisely defining and identifying geometric characteristics of price movements. Its core innovation is converting abstract chart patterns into quantifiable mathematical relationships and using technical indicators for multiple confirmations. The strategy provides a complete trading framework, including entry signal generation, risk management, and graphical display, suitable for traders pursuing systematic trading methods.
While this strategy offers a novel angle for market analysis, its effectiveness largely depends on parameter optimization and market adaptability. Through continuous improvement of signal filtering mechanisms, enhanced trend judgment accuracy, and optimized risk management methods, this strategy has the potential to become an effective tool in a trader’s toolbox. Most importantly, traders should conduct thorough historical backtesting and simulated trading before real-world application to ensure the strategy matches their personal trading style and risk tolerance.
Although this strategy provides a novel perspective for analyzing markets, its effectiveness largely depends on parameter optimization and market adaptability. By continuously improving signal filtering mechanisms, enhancing trend judgment accuracy, and optimizing risk management methods, this strategy has the potential to become an effective tool in a trader’s arsenal. Most importantly, traders should conduct thorough historical backtesting and paper trading before live implementation to ensure the strategy aligns with their personal trading style and risk tolerance capacity.
/*backtest
start: 2024-03-26 00:00:00
end: 2025-03-25 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"ETH_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("Similar Rectangle Heights - Strategy", overlay=true)
// Strategy parameters
lookbackPeriod = input.int(45, "Analysis period", minval=10)
primaryHeightPercent = input.float(5.0, "Primary height (% of price)", minval=0.5, maxval=20.0, step=0.5)
correctionHeightPercent = input.float(2.2, "Correction height (% of price)", minval=0.5, maxval=10.0, step=0.5)
minPatternBars = input.int(5, "Minimum pattern width (candles)", minval=3)
maxPatternBars = input.int(14, "Maximum pattern width (candles)", minval=5)
useVolume = input.bool(false, "Include volume")
useRSI = input.bool(true, "Include RSI")
rsiPeriod = input.int(23, "RSI period", minval=5)
rsiOverbought = input.int(55, "RSI overbought level", minval=50, maxval=90)
rsiOversold = input.int(50, "RSI oversold level", minval=10, maxval=50)
// Calculate primary height and correction height in price points
avgPrice = ta.sma(close, lookbackPeriod)
primaryHeight = avgPrice * primaryHeightPercent / 100
correctionHeight = avgPrice * correctionHeightPercent / 100
// Calculate RSI
rsi = ta.rsi(close, rsiPeriod)
// Function to detect a bullish pattern
bullishPattern(idx) =>
// Check if there is a low followed by a rise of a specified height
lowestLow = ta.lowest(low, minPatternBars)[idx]
highAfterLow = ta.highest(high, minPatternBars)[idx]
patternHeight = highAfterLow - lowestLow
// Check if pattern height matches the primary height
heightMatch = math.abs(patternHeight - primaryHeight) <= primaryHeight * 0.2
// Check if pattern width is within range
patternWidth = 0
for i = 0 to maxPatternBars - 1
if idx + i < lookbackPeriod and low[idx + i] == lowestLow
for j = i to maxPatternBars - 1
if idx + j < lookbackPeriod and high[idx + j] == highAfterLow
patternWidth := j - i + 1
break
break
widthMatch = patternWidth >= minPatternBars and patternWidth <= maxPatternBars
// Check volume and RSI conditions
volumeCondition = not useVolume or volume > ta.sma(volume, lookbackPeriod)
rsiCondition = not useRSI or rsi[idx] < rsiOversold
// Return true if all conditions are met
heightMatch and widthMatch and volumeCondition and rsiCondition
// Function to detect a bearish pattern
bearishPattern(idx) =>
// Check if there is a high followed by a drop of a specified height
highestHigh = ta.highest(high, minPatternBars)[idx]
lowAfterHigh = ta.lowest(low, minPatternBars)[idx]
patternHeight = highestHigh - lowAfterHigh
// Check if pattern height matches the primary height
heightMatch = math.abs(patternHeight - primaryHeight) <= primaryHeight * 0.2
// Check if pattern width is within range
patternWidth = 0
for i = 0 to maxPatternBars - 1
if idx + i < lookbackPeriod and high[idx + i] == highestHigh
for j = i to maxPatternBars - 1
if idx + j < lookbackPeriod and low[idx + j] == lowAfterHigh
patternWidth := j - i + 1
break
break
widthMatch = patternWidth >= minPatternBars and patternWidth <= maxPatternBars
// Check volume and RSI conditions
volumeCondition = not useVolume or volume > ta.sma(volume, lookbackPeriod)
rsiCondition = not useRSI or rsi[idx] > rsiOverbought
// Return true if all conditions are met
heightMatch and widthMatch and volumeCondition and rsiCondition
// Function to detect a bullish correction in an uptrend
bullishCorrection(idx) =>
// Check if there is a pullback of correction height after a rise
highBeforeCorrection = ta.highest(high, minPatternBars)[idx]
lowDuringCorrection = ta.lowest(low, minPatternBars)[idx]
correctionSize = highBeforeCorrection - lowDuringCorrection
// Check if correction height matches expected height
heightMatch = math.abs(correctionSize - correctionHeight) <= correctionHeight * 0.2
// Check if correction width is within range
correctionWidth = 0
for i = 0 to maxPatternBars - 1
if idx + i < lookbackPeriod and high[idx + i] == highBeforeCorrection
for j = i to maxPatternBars - 1
if idx + j < lookbackPeriod and low[idx + j] == lowDuringCorrection
correctionWidth := j - i + 1
break
break
widthMatch = correctionWidth >= minPatternBars / 2 and correctionWidth <= maxPatternBars / 2
// Check if we are in an uptrend
uptrend = ta.sma(close, lookbackPeriod)[idx] > ta.sma(close, lookbackPeriod)[idx + minPatternBars]
// Return true if all conditions are met
heightMatch and widthMatch and uptrend
// Function to detect a bearish correction in a downtrend
bearishCorrection(idx) =>
// Check if there is a pullback of correction height after a drop
lowBeforeCorrection = ta.lowest(low, minPatternBars)[idx]
highDuringCorrection = ta.highest(high, minPatternBars)[idx]
correctionSize = highDuringCorrection - lowBeforeCorrection
// Check if correction height matches expected height
heightMatch = math.abs(correctionSize - correctionHeight) <= correctionHeight * 0.2
// Check if correction width is within range
correctionWidth = 0
for i = 0 to maxPatternBars - 1
if idx + i < lookbackPeriod and low[idx + i] == lowBeforeCorrection
for j = i to maxPatternBars - 1
if idx + j < lookbackPeriod and high[idx + j] == highDuringCorrection
correctionWidth := j - i + 1
break
break
widthMatch = correctionWidth >= minPatternBars / 2 and correctionWidth <= maxPatternBars / 2
// Check if we are in a downtrend
downtrend = ta.sma(close, lookbackPeriod)[idx] < ta.sma(close, lookbackPeriod)[idx + minPatternBars]
// Return true if all conditions are met
heightMatch and widthMatch and downtrend
// Detecting signals
var float entryPrice = na
var float stopLoss = na
var float takeProfit = na
// Buy signal
buySignal = false
for i = 0 to 3
if bullishPattern(i) or (i > 0 and bullishCorrection(i))
buySignal := true
break
// Sell signal
sellSignal = false
for i = 0 to 3
if bearishPattern(i) or (i > 0 and bearishCorrection(i))
sellSignal := true
break
// Execute strategy
if buySignal
entryPrice := close
stopLoss := close - correctionHeight
takeProfit := close + primaryHeight
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
strategy.exit("Exit Long", "Long", stop=stopLoss, limit=takeProfit)
if sellSignal
entryPrice := close
stopLoss := close + correctionHeight
takeProfit := close - primaryHeight
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
strategy.exit("Exit Short", "Short", stop=stopLoss, limit=takeProfit)