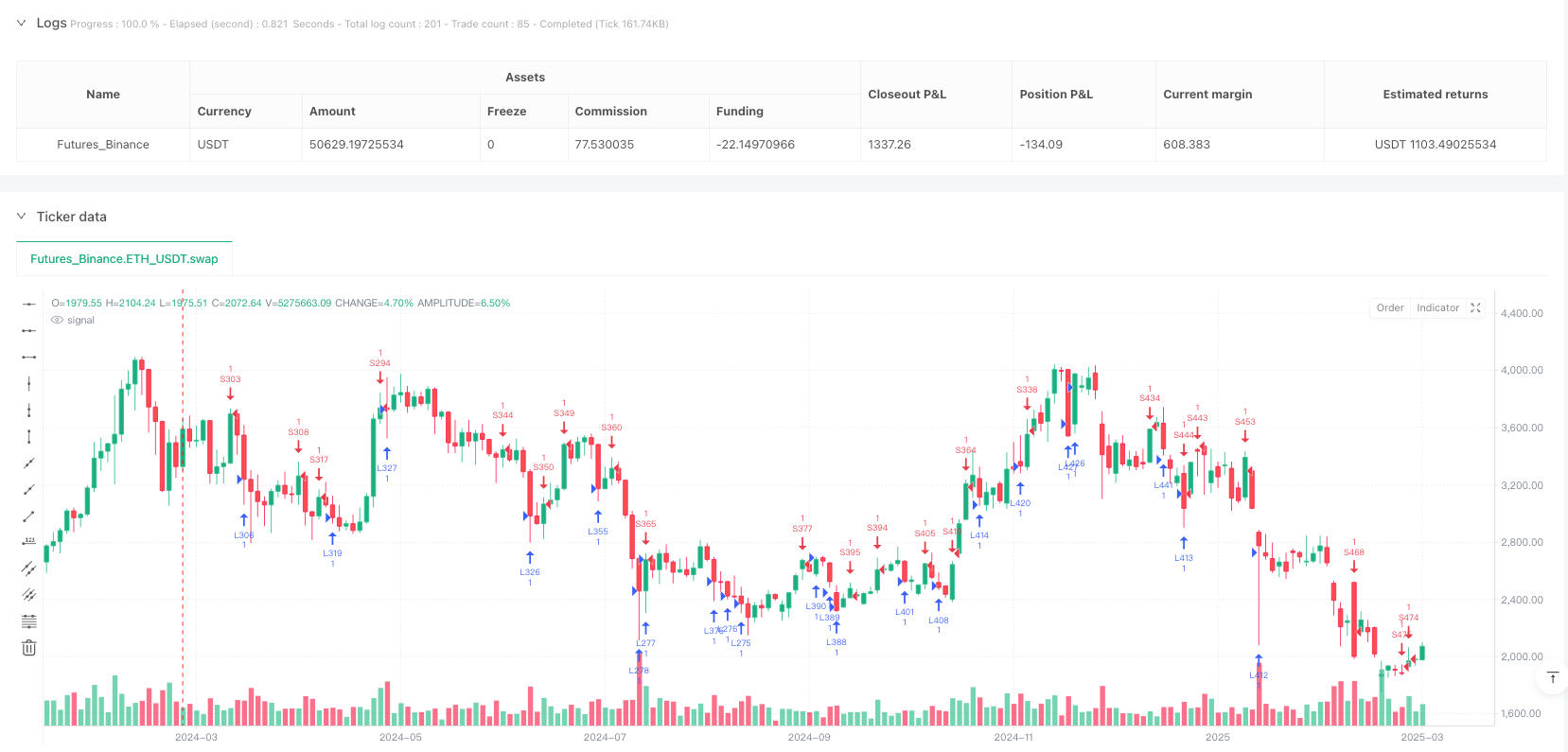
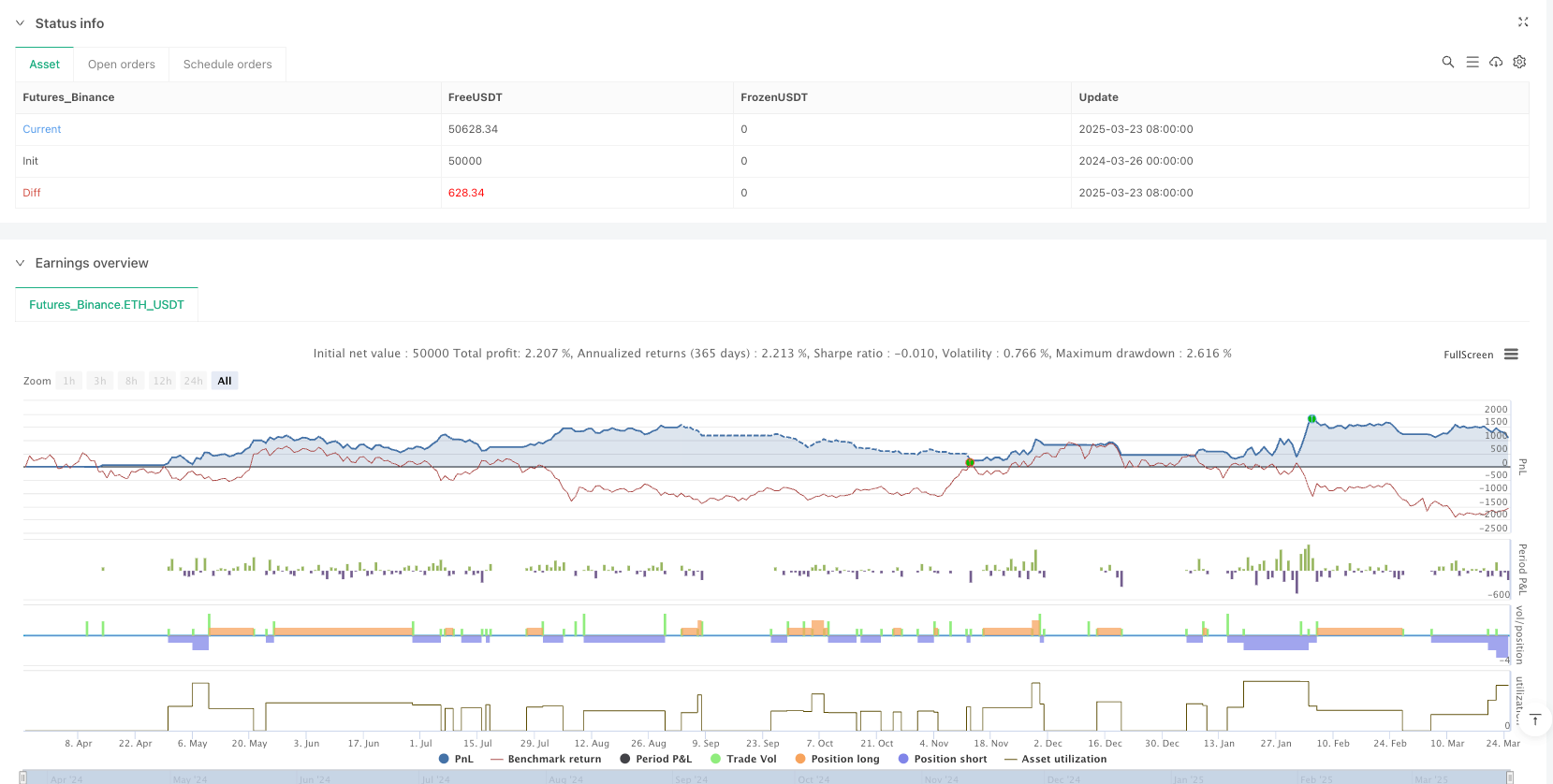
Overview
The Dynamic Fair Value Gap Intraday Trading Strategy is a quantitative trading system based on market structure theory, focusing on identifying and trading Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) in price action. The strategy employs a three-candle pattern to detect supply-demand imbalances in price behavior and enters trades when price retests these areas. It implements risk management with a fixed risk-reward ratio and includes a forced exit mechanism at a specific time each day to avoid overnight risk. This approach is derived from Smart Money Concept (SMC) theory, which focuses on institutional money behavior and changes in market microstructure. By systematically identifying and trading these high-probability-reward zones, the strategy aims to capture intraday price movements while maintaining strict risk control measures.
Strategy Principles
The core principle of the Fair Value Gap trading strategy is based on “unfilled areas” or “gaps” left when price moves rapidly. These areas represent significant supply-demand imbalances that will typically be “filled” or “retested” in the future. Specifically, the strategy works as follows:
Gap Detection Mechanism: The strategy uses a three-candle pattern to identify two types of FVGs:
- Bullish FVG: Current candle’s low is higher than the high of the candle two periods ago, AND the previous candle’s close is higher than the high of the candle two periods ago.
- Bearish FVG: Current candle’s high is lower than the low of the candle two periods ago, AND the previous candle’s close is lower than the low of the candle two periods ago.
Retest Entry Logic: The strategy doesn’t enter immediately when an FVG forms but waits for price to retest these areas:
- Bullish FVG: Long entry is triggered when price drops back to the upper boundary (high) of the FVG area.
- Bearish FVG: Short entry is triggered when price bounces up to the lower boundary (low) of the FVG area.
Risk Management:
- Stop loss is placed at the boundary of the respective FVG (low of bullish FVG or high of bearish FVG).
- Profit target uses a 1:2 risk-reward ratio, calculated as: entry price ± (entry price - stop loss) × 2.
End-of-Day Exit: The strategy automatically closes all positions at 3:15 PM IST each day and clears all FVG arrays, preparing for the next trading day.
Pyramiding: The strategy allows up to 5 pyramiding trades, meaning multiple positions can be held in the same direction, amplifying gains in strong trending markets.
This approach leverages discontinuities in market structure and price action theory to capture predictable behavior as price fills these imbalance areas.
Strategy Advantages
Upon deep analysis of the code, the strategy demonstrates several advantages:
Objective Trading Criteria: The strategy uses clearly defined mathematical conditions to identify FVGs and entry points, eliminating subjective judgment and improving trading discipline and consistency.
Market Structure-Based Trading: By trading Fair Value Gaps, the strategy focuses on genuine supply-demand imbalance areas in the market rather than relying on signals from traditional indicators, which often lag price action.
Risk Control Mechanisms:
- Predefined stop losses clearly define the maximum risk for each trade.
- Fixed risk-reward ratio ensures a reasonable win rate needed for long-term profitability.
- End-of-day forced exit eliminates overnight risk.
Compound Profit Potential: By allowing pyramiding (up to 5 positions), the strategy can significantly increase returns in strongly trending markets while controlling risk on each position through stop losses.
Adaptability: The strategy doesn’t depend on fixed price levels but dynamically identifies key areas in current market conditions, making it adaptable across different market environments and instruments.
Programming Efficiency: The code uses arrays to store FVG information and efficiently manages multiple potential trade opportunities, ensuring the system can track and respond to multiple price levels.
Visual Assistance: The strategy visually displays FVG areas on the chart (green for bullish FVGs, red for bearish FVGs), helping traders understand the system’s decision-making process.
Risk Analysis
Despite its solid theoretical foundation and numerous advantages, the strategy also presents several risk factors that need attention:
False Breakout Risk: In ranging markets, price may touch FVG boundaries multiple times without forming sustained trends, leading to multiple stop-outs. Solutions might include adding additional market environment filters or trend confirmation indicators.
Pyramiding Risk: Allowing up to 5 positions in the same direction could lead to excessive exposure in the wrong direction, especially during sudden trend reversals. Consider implementing overall risk limits, such as maximum risk across all positions not exceeding a specific percentage of the account.
Fixed Risk-Reward Ratio Limitations: Using a fixed 1:2 risk-reward ratio may not be optimal for all market conditions. In less volatile markets, such targets might be difficult to achieve; in highly volatile markets, it might exit profitable trades too early. Consider adjusting profit targets based on market volatility.
Lack of Market Environment Filtering: The strategy generates signals in all market conditions regardless of the overall trend or volatility state. Trading counter-trend FVGs in strong trending environments can lead to consecutive losses. Adding trend filters could significantly improve performance.
Absence of Volume Confirmation: The strategy relies solely on price action without considering volume confirmation, which might lead to false signals in low-volume areas. Integrating volume analysis could improve signal quality.
Fixed-Time Exit Potential Issues: Exiting at a specific time daily might lead to premature exits from favorable positions or missed better exit opportunities in unfavorable ones. Consider combining price action-based exit conditions.
Reliance on Historical Backtesting Assumptions: The strategy assumes future FVG behavior will be similar to patterns observed in the past. Market dynamics may change, weakening the effectiveness of these patterns. Regular parameter re-optimization and hypothesis validation is important.
Strategy Optimization Directions
Based on deep analysis of the code, here are several potential optimization directions:
Market Structure Filtering:
- Implement higher-level trend identification systems to trade FVGs only in the trend direction.
- Simple moving average direction filters or more complex market structure analysis could be added.
- Such filtering could significantly reduce losses from counter-trend trades.
Volatility Adjustment:
- Implement dynamic stop losses and profit targets based on current market volatility instead of using fixed risk-reward ratios.
- Widen targets in high-volatility environments and tighten them in low-volatility ones.
- ATR (Average True Range) or similar indicators could be used to quantify volatility.
Volume Confirmation:
- Add volume conditions to ensure sufficient volume supports FVG formation and retests.
- This can reduce false signals in low-liquidity environments.
Adaptive Position Sizing:
- Implement dynamic position sizing based on historical win rates, current volatility, and specific FVG characteristics.
- Increase position size for “cleaner” FVGs (more distinct three-candle pattern) or those forming within strong trends.
Multiple Timeframe Analysis:
- Integrate FVG analysis from higher timeframes, prioritizing signals that align with higher timeframe FVGs.
- This approach can improve signal quality and overall success rate.
Smart Pyramiding:
- Modify the pyramiding logic to base it on trend strength and previous trade success.
- Increase the likelihood of pyramiding after profitable trades and reduce it after losing ones.
Machine Learning Enhancement:
- Implement machine learning algorithms to identify FVG characteristics most likely to succeed.
- This could include analyzing FVG size, formation speed, market environment, etc.
Statistical Backtesting Framework:
- Develop a more comprehensive backtesting framework to assess strategy performance across different market conditions.
- Use Monte Carlo simulations to evaluate expected outcomes under different parameter combinations and market conditions.
Conclusion
The Dynamic Fair Value Gap Intraday Trading Strategy offers a systematic approach to identifying and trading supply-demand imbalance areas in the market. Through the use of the three-candle FVG pattern and clear retest entry rules, the strategy provides both theoretical soundness and practical operability. Its robust risk management framework, including predefined stop losses, fixed risk-reward ratios, and end-of-day exit mechanisms, provides a solid foundation for trading discipline.
The strategy’s main strengths lie in its objectivity and market structure-based approach, allowing it to remain relevant across different market environments. However, its effectiveness could be significantly enhanced through the implementation of suggested optimization directions, particularly market environment filtering, volatility-based adjustments, and volume confirmation.
It’s worth noting that no trading strategy, no matter how sophisticated, can guarantee success. Successful trading requires not only a sound strategy but also strict execution discipline, proper money management, and a deep understanding of the markets. The Dynamic Fair Value Gap strategy provides a good starting point that traders can further customize and optimize according to their risk tolerance and market views.
/*backtest
start: 2024-03-26 00:00:00
end: 2025-03-25 00:00:00
period: 2d
basePeriod: 2d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"ETH_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=6
strategy("Intraday FVG", overlay=true, pyramiding=5, max_bars_back=500, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, commission_type=strategy.commission.percent)
// 2. FVG Detection (Three-Candle Pattern)
var bullFVGHigh = array.new_float()
var bullFVGLow = array.new_float()
var bullFVGIndex = array.new_int()
var bearFVGHigh = array.new_float()
var bearFVGLow = array.new_float()
var bearFVGIndex = array.new_int()
detectFVG() =>
// Bullish FVG: Current low > prior high AND next high < current low
bullCondition = low > high[2] and close[1] > high[2]
// Bearish FVG: Current high < prior low AND next low > current high
bearCondition = high < low[2] and close[1] < low[2]
if bullCondition
// log.info("bull condition met: {0} {0} {0}", high[2], close[1], low)
array.push(bullFVGHigh, low)
array.push(bullFVGLow, low[2])
array.push(bullFVGIndex, bar_index)
if bearCondition
// log.info("bear condition met: {0} {0} {0}", low[2], close[1], high)
array.push(bearFVGHigh, high[2])
array.push(bearFVGLow, high)
array.push(bearFVGIndex, bar_index)
detectFVG()
// 3. Retest Execution Logic
checkRetests(arrayHigh, arrayLow, barIndex, direction) =>
// log.info("{0} : {1}", bar_index, time)
i = array.size(arrayHigh) - 1
while i >= 0
// log.info("barIndex : {0}" , array.get(barIndex, i))
// log.info("bar_index : {0}" , bar_index)
if array.get(barIndex, i) < bar_index
fvgHigh = array.get(arrayHigh, i)
fvgLow = array.get(arrayLow, i)
// log.info("visting : {0} : {1} : {2} : {3} ", array.get(barIndex, i), bar_index, fvgHigh, fvgLow)
if direction == "long" and low <= fvgHigh
// log.info("entering long")
sl = array.get(arrayLow, i) // Previous candle's low
entry = close
tp = entry + (entry - sl)*2
strategy.entry("L"+str.tostring(array.get(barIndex, i)), strategy.long)
strategy.exit("XL"+str.tostring(array.get(barIndex, i)), "L"+str.tostring(array.get(barIndex, i)), stop=sl, limit=tp)
array.remove(arrayHigh, i)
array.remove(arrayLow, i)
array.remove(barIndex, i)
if direction == "short" and high >= fvgLow
// log.info("entering short")
sl = array.get(arrayHigh, i) // Previous candle's low
entry = close
tp = entry - (sl - entry)*2
strategy.entry("S"+str.tostring(array.get(barIndex, i)), strategy.short)
strategy.exit("XS"+str.tostring(array.get(barIndex, i)), "S"+str.tostring(array.get(barIndex, i)), stop=sl, limit=tp)
array.remove(arrayHigh, i)
array.remove(arrayLow, i)
array.remove(barIndex, i)
i := i - 1
checkRetests(bullFVGHigh, bullFVGLow, bullFVGIndex, "long")
checkRetests(bearFVGHigh, bearFVGLow, bearFVGIndex,"short")
// 5. Daily Exit at 3:15 PM IST
exitTime = hour == 15 and minute >= 15
if exitTime
strategy.close_all()
array.clear(bullFVGHigh)
array.clear(bullFVGLow)
array.clear(bearFVGHigh)
array.clear(bearFVGLow)
array.clear(bullFVGIndex)
array.clear(bearFVGIndex)