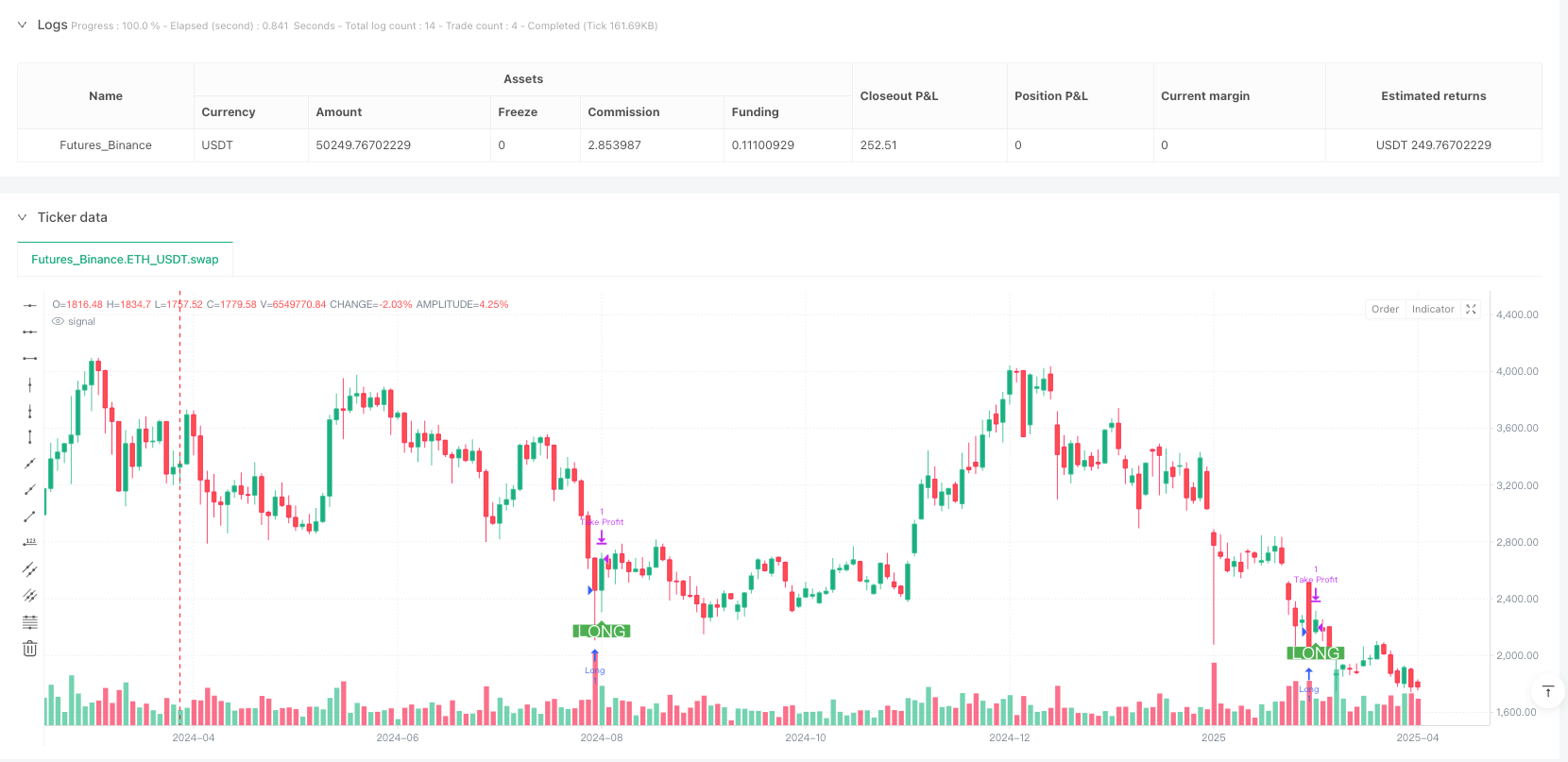
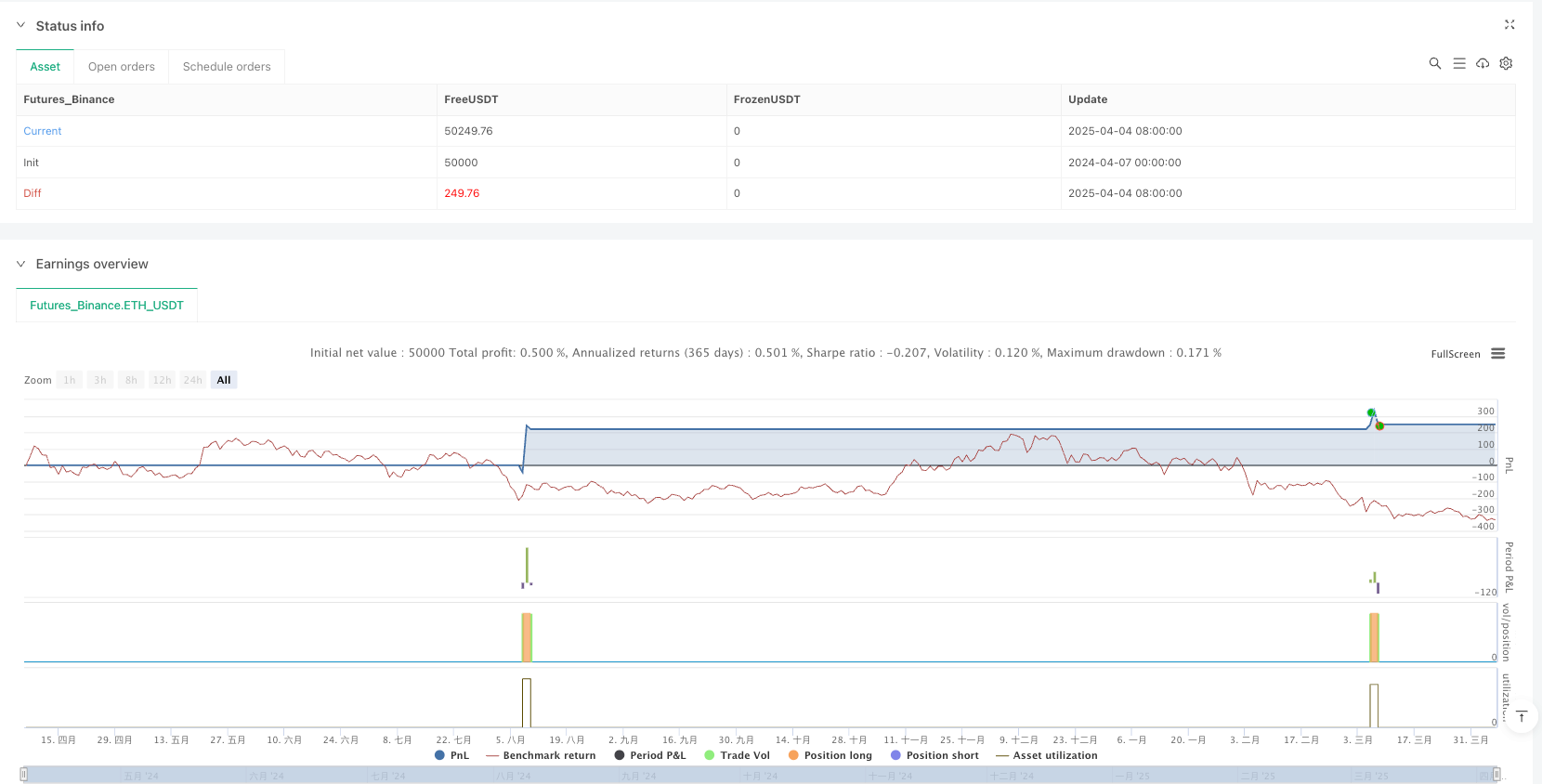
Overview
The Dynamic ATR Grid Pullback Capture Quantitative Trading Strategy is a high-frequency trading system designed for short-term traders aiming to capitalize on market pullbacks. This strategy utilizes a dynamic grid system based on the Average True Range (ATR) to define optimal entry points, ensuring precise trade execution. It integrates volatility filtering and a Relative Strength Index (RSI) confirmation mechanism to enhance signal accuracy and reduce false entries. The strategy is specifically optimized for scalping by dynamically adjusting trading levels based on current market conditions. The grid-based system helps capture retracement opportunities while maintaining strict trade management through predefined profit targets and trailing stop-loss mechanisms.
Strategy Principles
The core principle of this strategy is the combination of a dynamic grid system calculated using ATR with an RSI filter. The strategy first calculates the 10-period ATR value, then creates 15 grid levels using a grid factor (default 0.2). These grid levels form the foundational framework for trading decisions.
The trading logic is divided into four key components: 1. Grid Calculation: Uses the current closing price plus the product of ATR value and grid factor to dynamically generate 15 grid levels, which adjust with market volatility. 2. Volatility Filtering: Ensures trades are only executed when market volatility is sufficiently high by calculating the ratio of price amplitude to price, avoiding trading in low volatility zones. 3. RSI Confirmation: Uses 14-period RSI as an additional trade confirmation condition. Long trades require RSI below 30 (oversold), short trades require RSI above 70 (overbought). 4. Entry Logic: Long entry conditions are price below the first grid level, market volatility above the “no trade zone” setting, and RSI below 30. Short entry conditions are price above the last grid level, volatility meeting conditions, and RSI above 70.
Once a trade is triggered, the strategy sets a profit target and an ATR-based trailing stop. The profit target is defaulted to 0.2%, while the trailing stop uses the ATR value as an offset to adapt to market volatility and protect accrued profits.
Strategy Advantages
Through in-depth analysis of the strategy’s code, the following significant advantages can be summarized:
Dynamic Adaptability: The strategy uses ATR to calculate grid levels, allowing it to dynamically adjust to current market volatility. This means grid spacing widens during high volatility periods and narrows during low volatility periods, enabling the strategy to adapt to different market environments.
Multiple Filtering Mechanisms: The strategy combines price grids, volatility filtering, and RSI indicators as entry conditions. This multi-layered filtering mechanism significantly reduces false signals and improves trade quality.
Precise Entry Points: The grid system predefines entry levels, avoiding situations where trades are chased at unfavorable price levels, enhancing execution discipline.
Integrated Risk Management: The strategy has built-in profit targets and trailing stop mechanisms, ensuring each trade has clear risk management rules, which is particularly important for high-frequency trading.
Overbought/Oversold Capture: By incorporating the RSI indicator, the strategy can trade in price overbought or oversold areas, increasing the success rate of counter-trend trading.
Visual Assistance: The code includes visualization of grid levels and trade entry markers, allowing traders to intuitively observe the strategy’s operation, facilitating backtest analysis and strategy adjustment.
Strategy Risks
Despite its sophisticated design, there are several risk factors that need attention:
Frequent Trading Risk: As a high-frequency strategy, it may generate numerous trades, leading to high transaction costs, especially in markets with high fees. The solution is to adjust the grid factor and profit target to reduce trading frequency or increase per-trade profit.
Counter-trend Risk in Trending Markets: This strategy is essentially a pullback capture strategy and may frequently trigger counter-trend trades in strong trending markets, resulting in consecutive losses. The solution is to add a trend filter to pause counter-trend trading when strong trends are identified.
Parameter Sensitivity: Strategy effectiveness is highly dependent on parameters such as ATR length, grid factor, and profit target. Different markets and timeframes may require different parameter combinations. Comprehensive parameter optimization and backtesting are recommended.
No Trade Zone Setting Sensitivity: An excessively high no-trade zone value may cause missed opportunities, while a value too low may lead to undesirable trades in low volatility environments. This parameter should be adjusted based on the typical volatility characteristics of the specific market.
Imperfect Stop-Loss Mechanism: Although the strategy includes trailing stops, it lacks hard stop-loss settings and may sustain significant losses under extreme market conditions. Adding hard stop-loss limits based on fixed points or percentages is recommended.
Strategy Optimization Directions
Based on code analysis, the strategy can be optimized in the following directions:
Add Trend Filter: Integrate medium to long-term trend indicators (such as moving average crossovers or MACD) to avoid counter-trend trading in strong trending markets. This can significantly reduce losing trades, as pullback strategies typically perform better when aligned with the main trend.
Dynamic Profit Targets: The current profit target is fixed at 0.2% and could be changed to a dynamic value based on ATR, allowing it to set higher targets during high volatility periods and more conservative targets during low volatility periods. This will improve strategy adaptability under different market conditions.
Time Filter: Add trading time window filtering to avoid trading during abnormal volatility market opening/closing sessions or important economic data release periods. This can reduce false signals caused by short-term abnormal volatility.
Quantify RSI Conditions: Currently, RSI uses fixed 30⁄70 thresholds. Consider using dynamic thresholds, such as calculating RSI’s average and standard deviation, triggering signals when RSI deviates from the average by specific standard deviations. This approach can better adapt to different market RSI characteristics.
Add Volume Confirmation: Include volume confirmation in entry conditions to ensure trades are only executed when significant volume is present. This can improve signal quality and reduce erroneous trades caused by market noise.
Optimize Grid Density: The current strategy uses 15 fixed grid points. Consider dynamically adjusting the number and density of grids based on market volatility. Increase grid density in high volatility markets and reduce grid points in low volatility markets to enhance strategy flexibility.
Conclusion
The Dynamic ATR Grid Pullback Capture Quantitative Trading Strategy is a high-frequency trading system combining ATR dynamic grids and RSI filtering, specifically designed for capturing short-term market pullbacks. It ensures trading at technically reasonable price levels through a dynamic grid system based on market volatility, while improving signal quality through RSI filtering and volatility detection.
The strategy’s main advantage lies in its ability to dynamically adapt to different market environments and its strict trading rules, though it may face challenges in strongly trending markets. By adding trend filters, optimizing grid density, and implementing dynamic profit targets, the strategy’s robustness and performance can be further enhanced.
For experienced short-term traders, this strategy provides a systematic method to capture price pullbacks, particularly suitable for markets with significant volatility. However, as with all trading strategies, thorough backtesting and parameter optimization should be conducted before practical application, and it should be used in conjunction with appropriate money management rules.
/*backtest
start: 2024-04-07 00:00:00
end: 2025-04-06 00:00:00
period: 2d
basePeriod: 2d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"ETH_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=6
strategy("Smart Grid Scalping (Pullback) Strategy[BullByte]", overlay=true, shorttitle="SGS Scalping")
// ===== Input Parameters =====
atrLength = input(10, title="ATR Length") // ATR period for volatility measurement
gridFactor = input(0.2, title="Grid Factor") // Multiplier to determine grid spacing based on ATR
profitTarget = input(0.002, title="Profit Target (0.1% = 0.001)")
noTradeZone = input(0.005, title="No Trade Zone (%)") // Defines a price range where trades are avoided
// ===== ATR Calculation =====
atrValue = ta.atr(atrLength)
// ===== Grid Level Calculation =====
gridLevels = array.new_float(15) // Create an array to hold 15 grid levels
for i = 0 to 14
array.set(gridLevels, i, close + (i + 1) * atrValue * gridFactor)
// ===== Trading Logic =====
// Additional RSI filter for extra confirmation
rsiValue = ta.rsi(close, 14)
// Conditions for entry:
// - Long: Price is below the first grid level, volatility is above the no trade zone, and RSI indicates oversold (<30).
// - Short: Price is above the last grid level, volatility is above the no trade zone, and RSI indicates overbought (>70).
longCondition = close < array.get(gridLevels, 0) and (high - low) / low > noTradeZone and rsiValue < 30
shortCondition = close > array.get(gridLevels, 14) and (high - low) / high > noTradeZone and rsiValue > 70
if (longCondition)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
if (shortCondition)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
// ===== Take Profit with Trailing Stop Logic =====
if (strategy.position_size > 0)
strategy.exit("Take Profit", "Long",
limit=close * (1 + profitTarget),
trail_price=close * (1 + profitTarget * 0.5),
trail_offset=atrValue)
if (strategy.position_size < 0)
strategy.exit("Take Profit", "Short",
limit=close * (1 - profitTarget),
trail_price=close * (1 - profitTarget * 0.5),
trail_offset=atrValue)
// ===== Plot Trade Entry Labels =====
// Plot labels only on the bar where the position is initiated
longEntry = strategy.position_size > 0 and (strategy.position_size[1] <= 0)
shortEntry = strategy.position_size < 0 and (strategy.position_size[1] >= 0)
plotshape(longEntry, location=location.belowbar,
color=color.new(color.green, 0), style=shape.labelup, text="LONG", textcolor=color.white, size=size.normal)
plotshape(shortEntry, location=location.abovebar,
color=color.new(color.red, 0), style=shape.labeldown, text="SHORT", textcolor=color.white, size=size.normal)