Bollinger Bands and EMA Multi-Standard Deviation Mean Reversion Trading Strategy
BB EMA SMA stdev 均值回归 波动率交易 多重标准差 止损止盈 MEAN REVERSION Volatility Trading Multiple Standard Deviation STOP LOSS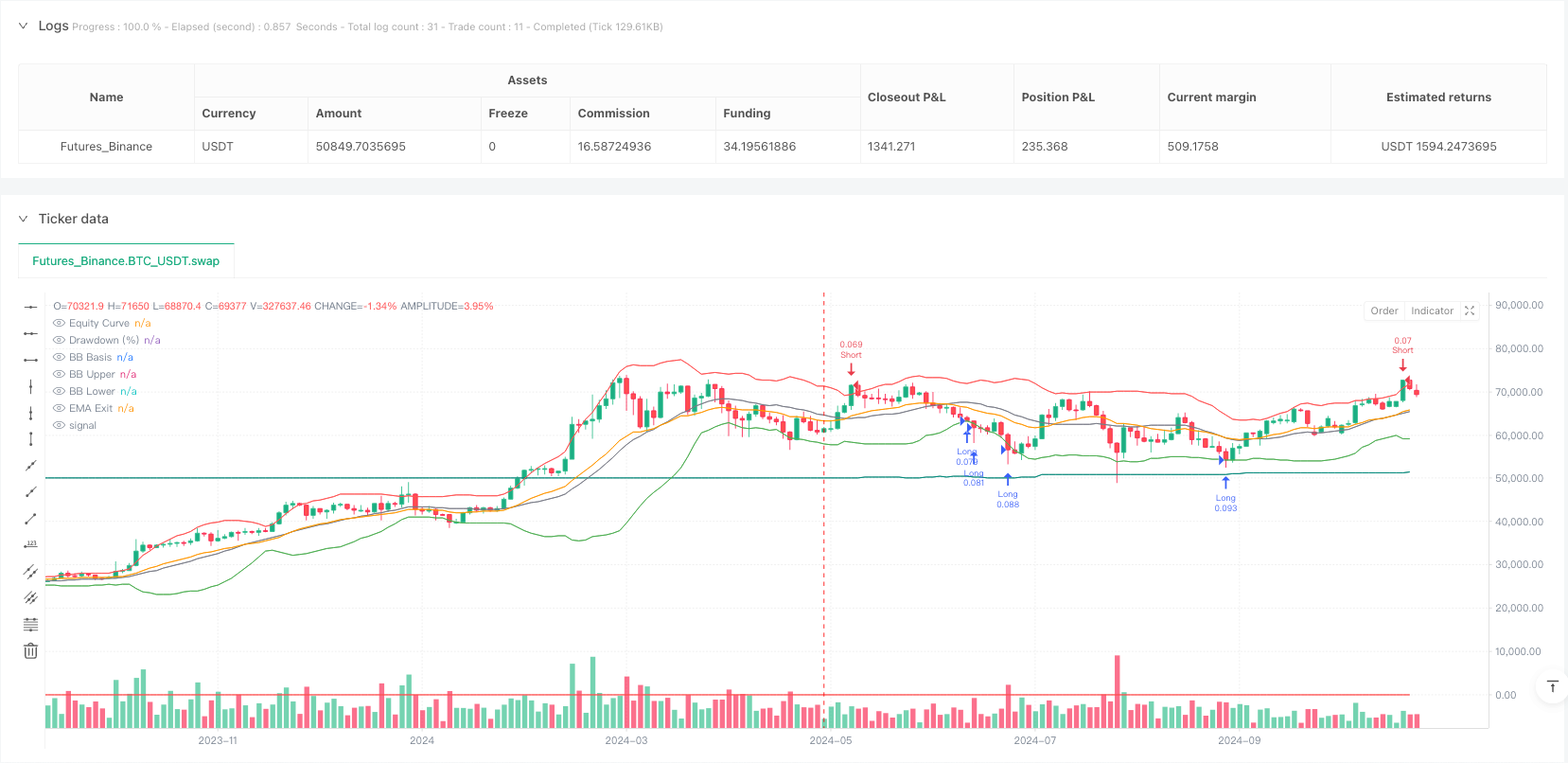
Overview
The Bollinger Bands and EMA Multi-Standard Deviation Mean Reversion Trading Strategy is a quantitative trading system based on the principle of mean reversion, cleverly combining the volatility breakout signals of Bollinger Bands with the trend-following characteristics of the Exponential Moving Average. This strategy identifies extreme price deviations using customizable standard deviation multipliers, establishing long positions when prices fall significantly below the Bollinger Band by a specific standard deviation multiplier and short positions when prices rise above it. Meanwhile, the strategy employs wider Bollinger Band standard deviation ranges as stop-loss points and uses the EMA line as a take-profit point, forming a complete position management system. Each trade invests a fixed percentage of capital, and the strategy only allows positions in one direction at a time, which helps control risk and maintain strategy focus.
Strategy Principles
The core principle of this strategy is based on the mean reversion theory in statistics, which suggests that financial market prices may deviate significantly in the short term but tend to revert to their average levels over the long term. The specific implementation is as follows:
Entry Signal Generation:
- The strategy calculates an n-period (default 20) Simple Moving Average (SMA) as the middle band baseline for Bollinger Bands.
- By calculating the standard deviation (STDEV) of prices around the SMA and multiplying by a user-defined multiplier x (default 2.0), it constructs the upper and lower bands for entry signals.
- When the price falls below the lower band, a long entry signal is triggered; when the price rises above the upper band, a short entry signal is triggered.
Exit Mechanism Design:
- Stop Loss Setting: Uses a wider standard deviation multiplier y (default 3.0) to construct a second layer of Bollinger Bands as stop-loss positions.
- Take Profit Strategy: Uses an n-period (default 20) Exponential Moving Average (EMA) as the target profit point. When the price reverts to the EMA, it signifies that mean reversion has completed, at which point the position is closed for profit.
Position Management:
- The strategy adopts a capital proportion allocation method, using a fixed percentage (default 10%) of the account equity for each trade.
- It implements a mutually exclusive position mechanism, ensuring that only one directional position (long or short) can be held at any time.
Strategy Advantages
Through deep analysis of the code, this strategy has the following significant advantages:
Precise Capture of Extreme Price Deviations: Through customizable standard deviation multipliers, the strategy can flexibly adjust sensitivity to market volatility, effectively capturing extreme price movements in the short term.
Comprehensive Risk Control Mechanism: The strategy sets up two lines of defense - a wider standard deviation multiplier as a stop-loss point and the EMA line as a take-profit point, forming a dual risk management system.
Scientific Application of Mean Reversion Theory: The strategy is based on mature statistical principles, utilizing the characteristic of market prices reverting to the mean, with a solid foundation in theory.
Reasonable Capital Management Configuration: Through fixed proportion capital allocation, the strategy achieves dynamic matching of position size with account size, contributing to long-term stable equity growth curves.
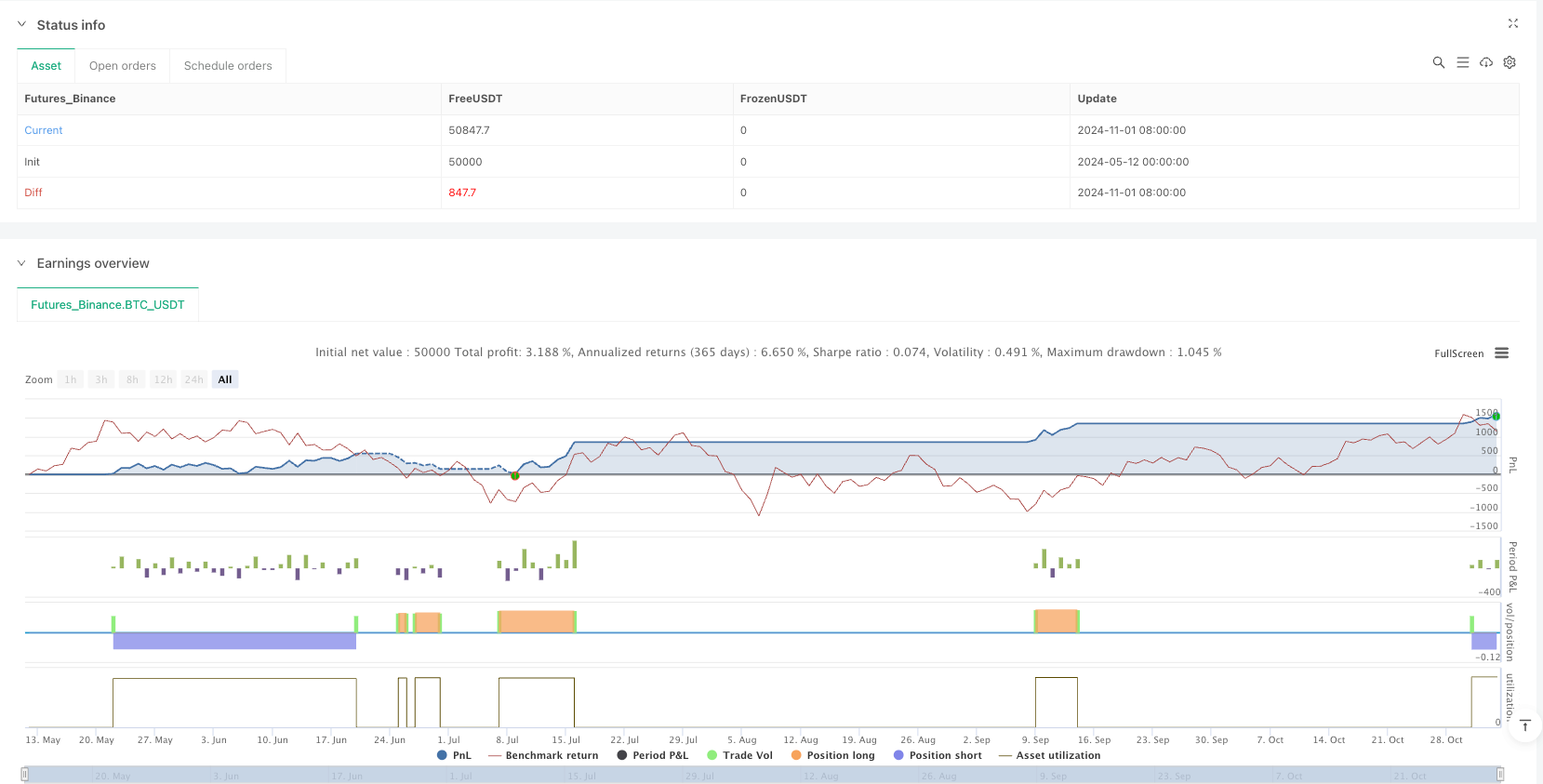
Comprehensive Performance Monitoring System: The strategy has a built-in comprehensive performance tracking mechanism, including key indicators such as net profit, maximum drawdown, win rate, and total number of trades, facilitating real-time evaluation and optimization.
Strong Adaptability: Through adjustable parameter settings, the strategy can adapt to the characteristics of different market environments and trading instruments.
Strategy Risks
Despite the reasonable design of this strategy, there are still the following potential risks:
Risk of Mean Reversion Assumption Failure: In strong trending markets, prices may continue to deviate from the mean without reverting, leading to increased frequency of stop-losses being triggered. The solution is to pause strategy operation in clear trending environments or add trend filters.
Parameter Sensitivity Risk: Strategy performance highly depends on parameter settings such as Bollinger Band length, standard deviation multipliers, and EMA periods. Different markets and timeframes may require different parameter combinations. It is recommended to find the optimal parameter combination through historical backtesting.
Slippage and Trading Cost Risk: The strategy has considered a 0.1% commission in backtesting, but in actual trading, higher trading costs and slippage may be faced, which could erode strategy profits. These factors should be conservatively estimated in live trading.
Liquidity Risk: In low liquidity markets, it may not be possible to execute entry and exit orders at ideal prices. It is recommended to apply this strategy in high liquidity markets or timeframes.
Overfitting Risk: If parameters are overly optimized to fit historical data, the strategy may perform poorly in future markets. Sufficient historical data and different out-of-sample tests should be used to verify strategy robustness.
Strategy Optimization Directions
By analyzing the code structure and logic, this strategy can be optimized in the following aspects:
Add Trend Filters: Combine longer-period moving averages or trend indicators like ADX to filter out counter-trend signals in strong trending environments. This can reduce the frequency of stop-losses being triggered in one-directional trending markets, as mean reversion strategies typically perform poorly in strong trending markets.
Dynamic Standard Deviation Multipliers: Currently, the strategy uses fixed standard deviation multipliers; consider dynamically adjusting this parameter based on changes in market volatility. For example, use smaller multipliers in low volatility environments and larger multipliers in high volatility environments to adapt to different market states.
Optimize Position Management: Implement a volatility-based position adjustment mechanism, increasing position size in low volatility environments and reducing position size in high volatility environments, to balance risk and reward.
Add Time Filters: Some markets may conform more to mean reversion characteristics during specific time periods, while behaving as trending markets during others. By adding time filters, the strategy can be run during the most favorable time periods.
Implement Partial Take Profit Mechanism: Currently, the strategy adopts a full position closing approach; consider implementing batch closing, such as closing part of the position when the price reverts to a certain percentage of the EMA, and continuing to hold the remaining position for more potential profit.
Integrate Multi-Timeframe Analysis: By combining market structure analysis from higher timeframes, the quality of entry signals can be improved. For example, only enter in directions supported by higher timeframe analysis.
Summary
The Bollinger Bands and EMA Multi-Standard Deviation Mean Reversion Trading Strategy is a well-designed, logically clear mean reversion trading system. It identifies extreme market volatility through multiple standard deviation breakouts of Bollinger Bands and uses the EMA line as a profit target, forming a complete trading loop. The strategy has built-in comprehensive risk management mechanisms, including stop-loss settings, position control, and single-direction position limits, helping to control drawdowns and maintain stable account growth.
While the strategy performs excellently in mean-reverting markets, it may face challenges in strong trending environments. By adding trend filters, dynamically adjusting parameters, and optimizing position management, the robustness and adaptability of the strategy can be further enhanced. Particularly in different market conditions, flexibly adjusting standard deviation multipliers and implementing volatility-based position management will be key to improving strategy performance.
Overall, this is a quantitative trading strategy that combines statistical foundations with practicality, suitable for traders who have confidence in mean reversion theory and seek to capture opportunities in volatile markets. Through continuous monitoring and optimization, this strategy has the potential to remain competitive in various market environments.
/*backtest
start: 2024-05-12 00:00:00
end: 2024-11-03 00:00:00
period: 2d
basePeriod: 2d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy(title = "Bollinger + EMA Strategy with Stats",overlay = true,default_qty_type = strategy.percent_of_equity,default_qty_value = 10,initial_capital = 100000,commission_type = strategy.commission.percent,commission_value = 0.1)
// === 参数设置 ===
length = input.int(20, "BB Length")
mult_entry = input.float(2.0, "Entry StdDev Multiplier (x)", step=0.1)
mult_stop = input.float(3.0, "Stop StdDev Multiplier (y)", step=0.1)
ema_period = input.int(20, "EMA Exit Period")
show_stats = input.bool(true, "Show Performance Label")
// === 指标计算 ===
basis = ta.sma(close, length)
dev_entry = mult_entry * ta.stdev(close, length)
dev_stop = mult_stop * ta.stdev(close, length)
upper_entry = basis + dev_entry
lower_entry = basis - dev_entry
upper_stop = basis + dev_stop
lower_stop = basis - dev_stop
ema_exit = ta.ema(close, ema_period)
// === 入场 & 出场条件 ===
long_entry = close < lower_entry
short_entry = close > upper_entry
long_exit = close >= ema_exit
short_exit = close <= ema_exit
// === 只允许一个方向持仓 ===
if long_entry and strategy.position_size == 0
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
strategy.exit("Exit Long", from_entry="Long", stop=lower_stop, limit=ema_exit)
if short_entry and strategy.position_size == 0
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
strategy.exit("Exit Short", from_entry="Short", stop=upper_stop, limit=ema_exit)
// === 画图 ===
plot(basis, "BB Basis", color=color.gray)
plot(upper_entry, "BB Upper", color=color.red)
plot(lower_entry, "BB Lower", color=color.green)
plot(ema_exit, "EMA Exit", color=color.orange)
// === 资金曲线 & 回撤 ===
equity = strategy.equity
plot(equity, "Equity Curve", color=color.teal)
var float peak = na
var float max_dd = na
peak := na(peak) ? equity : math.max(peak, equity)
dd = (equity - peak) / peak
max_dd := na(max_dd) ? dd : math.min(max_dd, dd)
plot(dd * 100, title="Drawdown (%)", color=color.red)