Multi-Period Reversal Point Detection and Automated Trading Strategy
MAGIC-9/13 DRP CROSSOVER CONSECUTIVE PATTERNS STOP-LOSS TAKE-PROFIT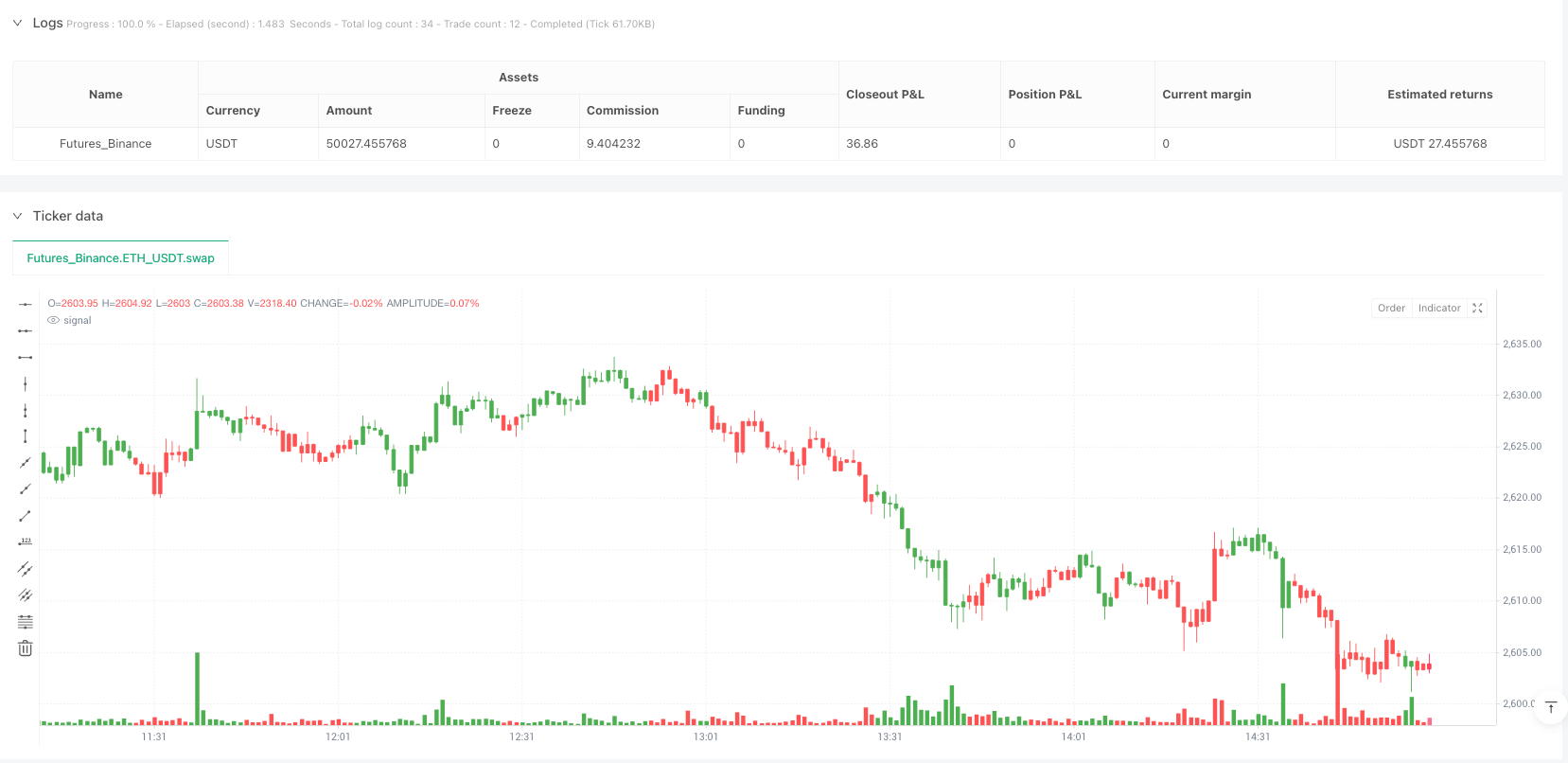
Overview
The Multi-Period Reversal Point Detection and Automated Trading Strategy is a quantitative trading system based on Magic-9⁄13 patterns and Directional Reversal Point (DRP) identification. This strategy captures market reversal signals by identifying consecutive price patterns and momentum change points, and automatically executes trades. The core of the strategy combines traditional technical analysis concepts with modern quantitative methods, analyzing consecutive price behavior to identify potential market turning points, thereby entering the market at the early stages of price reversals. The system integrates automatic stop-loss and take-profit functions to control risk and lock in profits, while providing intuitive trading signal displays through visual indicators (such as labels and candlestick color changes).
Strategy Principles
The core principles of this strategy are based on two main technical indicators: Magic-9⁄13 patterns and Directional Reversal Points (DRP).
Magic-9⁄13 Pattern Recognition:
- The system monitors price behavior over 9 consecutive periods, looking for consistent price patterns
- High point pattern (high_9): Formed when prices are higher than their closing prices from 4 periods ago for 9 consecutive times, but not for the 10th time
- Low point pattern (low_9): Formed when prices are lower than their closing prices from 4 periods ago for 9 consecutive times, but not for the 10th time
Directional Reversal Point (DRP) Calculation:
- Analyzes the relationship between current prices and prices from lookback_length periods ago within a specified length (length_input)
- Calculates up_count: The number of times current prices are higher than prices during the lookback period
- Calculates down_count: The number of times current prices are lower than prices during the lookback period
- When down_count equals the set length, it marks an upward reversal point (value 1)
- When up_count equals the set length, it marks a downward reversal point (value -1)
Trade Signal Generation:
- Buy signal: Triggered when a low_9 pattern is detected and the directional reversal point crosses above from a negative or zero value
- Sell signal: Triggered when a high_9 pattern is detected and the directional reversal point crosses below from a positive or zero value
Risk Management Mechanism:
- Automatic stop-loss: Set at 10 points in the opposite direction of the entry price
- Automatic take-profit: Set at 10 points in the opposite direction of the entry price
Auxiliary Functions:
- get_first_non_na_value: Function to obtain non-NA values
- count_consecutive_occurrences: Calculates the number of consecutive occurrences of conditions
- check_condition_occurrence: Checks if a condition occurs within a given period
- filter_occurrences: Filters occurrences based on lookback periods
Strategy Advantages
Early Identification of Market Reversals: By combining Magic-9⁄13 patterns with directional reversal points, the strategy can capture signals in the early stages of market reversals, providing good entry timing.
Multiple Confirmation Mechanism: The strategy requires simultaneous satisfaction of two independent conditions (Magic pattern and directional reversal point crossing), reducing the possibility of false signals and improving trade quality.
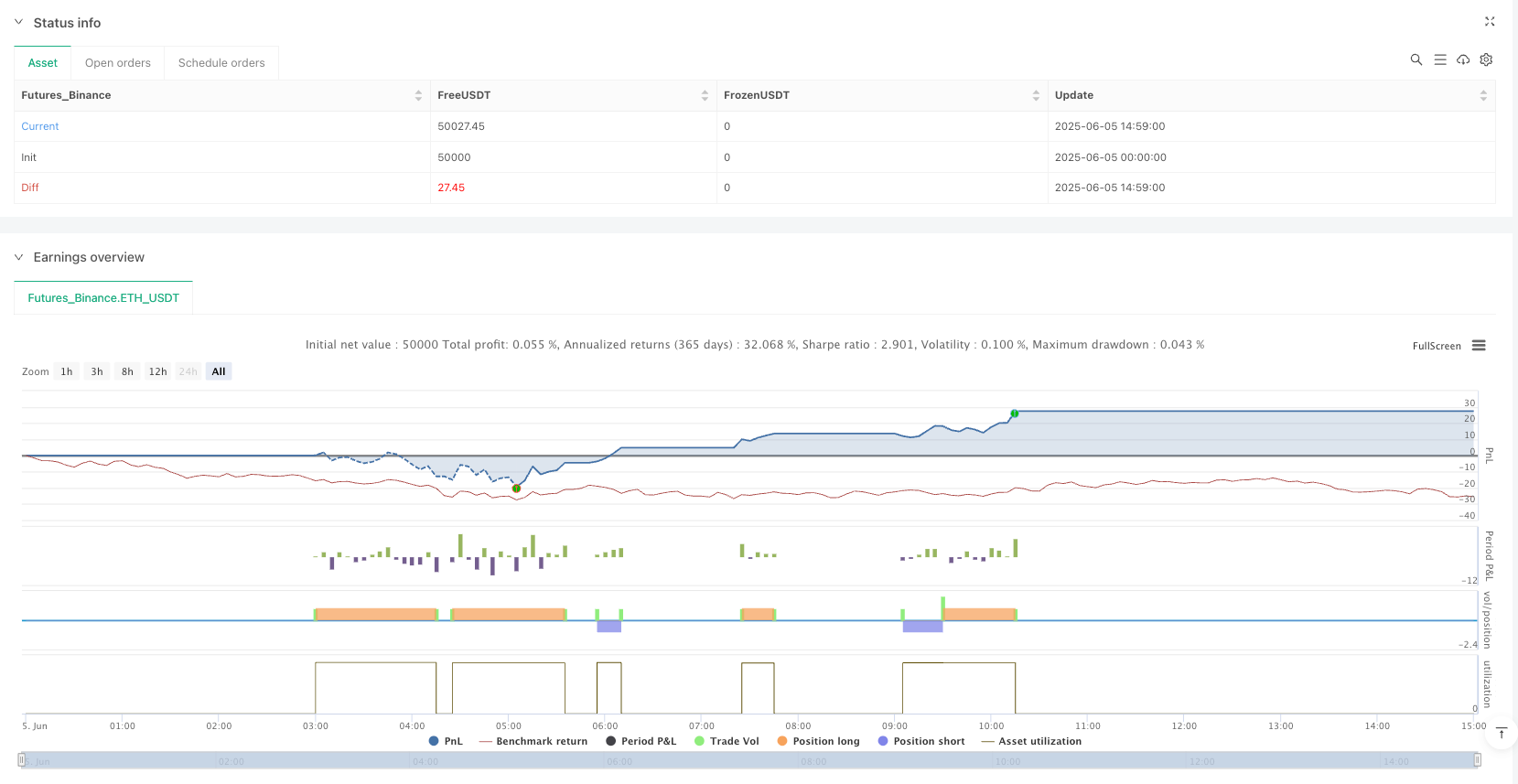
Automated Risk Control: Integrated stop-loss and take-profit functions control single-trade risk without manual intervention, preventing emotional trading decisions.
Visualized Trading Signals: Trading signals are visually displayed through labels and candlestick color changes, allowing traders to quickly identify potential trading opportunities.
Parameter Adjustability: The strategy offers adjustment options for two key parameters - length and lookback length - enabling traders to optimize according to different market environments and trading instruments.
Data Processing Robustness: Includes mechanisms for handling NA values, enhancing strategy stability under various data conditions.
Timeframe Adaptability: The strategy can be applied to charts of different timeframes, from minute charts to daily charts, providing flexible trading timeframe options.
Strategy Risks
Parameter Sensitivity: Strategy performance is highly dependent on length and lookback length parameter settings. Different market environments may require different parameter combinations, and incorrect parameter settings may lead to overtrading or missed trading opportunities. Solution: Conduct comprehensive historical backtesting and establish parameter optimization matrices for different market conditions.
Market Volatility Risk: In highly volatile markets, setting stop-loss points at a fixed 10 points may be too small, leading to frequent triggering; in low-volatility markets, this setting may be too large. Solution: Set stop-loss points as dynamic values based on market volatility (such as ATR) rather than fixed points.
Trend Market Performance: This strategy is primarily designed for reversal points and may generate frequent false signals in strong trend markets. Solution: Add trend filters to only trigger trade signals when confirming the market is not in a strong trend state.
Slippage and Liquidity Risk: In markets with poor liquidity, execution prices may differ significantly from signal prices. Solution: Add liquidity filtering conditions or consider slippage factors when executing orders.
Overfitting Risk: The strategy uses multiple conditions and parameters, which may risk overfitting to historical data. Solution: Use out-of-sample testing and forward testing to verify the robustness of the strategy.
Consecutive Signal Accumulation: Under certain market conditions, multiple signals in the same direction may be produced consecutively, leading to excessive positions. Solution: Implement signal filtering mechanisms to limit the number of same-direction signal executions within a short time.
Fixed Take-Profit and Stop-Loss Limitations: Fixed point take-profit and stop-loss may not be suitable for all market environments, potentially ending profitable trades too early or stopping losses too late. Solution: Implement dynamic take-profit and stop-loss mechanisms based on market volatility, or adopt trailing stop strategies.
Strategy Optimization Directions
Dynamic Parameter Adjustment:
- Implement mechanisms to automatically adjust length_input and lookback_length parameters based on market volatility
- Rationale: Different volatility environments require parameters with different sensitivities; dynamic adjustment can improve strategy adaptability
- Implementation method: Design parameter adjustment formulas based on ATR values from recent N periods
Add Trend Filters:
- Integrate trend recognition indicators (such as moving averages, ADX) and only execute trades consistent with the trend direction
- Rationale: Reversal strategies typically perform poorly in markets with obvious trends; trend filtering can reduce false signals
- Implementation method: Add long-term moving averages as trend direction references, only going long when prices are above the average line and short when below
Optimize Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Mechanisms:
- Replace fixed point settings with dynamic stop-loss and take-profit based on volatility
- Rationale: Market volatility varies greatly across different periods; fixed points cannot adapt to all market environments
- Implementation method: Set stop-loss and take-profit levels using multiples of ATR, such as 1.5 times ATR for stop-loss and 3 times ATR for take-profit
Add Volume Filtering:
- Consider trading volume factors and only execute signals when confirmed by volume
- Rationale: Volume is an important confirmation factor for the validity of price movements and can reduce false breakouts
- Implementation method: Check if the volume at signal occurrence is higher than the average volume of the previous N periods
Implement Time Filtering:
- Avoid trading during specific time periods (such as market opening/closing times or before/after important economic data releases)
- Rationale: Some time periods have abnormal volatility or unclear direction, with higher trading risks
- Implementation method: Add time condition judgments to prohibit new signal generation during high-risk periods
Add Position Management Functions:
- Dynamically adjust position size based on market volatility and account risk levels
- Rationale: Fixed positions cannot adapt to different risk environments; dynamic positions can control risk while maintaining expected returns
- Implementation method: Design position calculation formulas based on maximum drawdown percentages
Implement Signal Strength Scoring:
- Assign strength scores to each trade signal and only execute signals above a threshold
- Rationale: Not all signals that meet conditions are of equal quality; a scoring mechanism can screen for high-quality signals
- Implementation method: Calculate comprehensive scores based on factors such as distance between price and moving averages, clarity of Magic patterns, and reversal point strength
Add Related Market Confirmation:
- Introduce related market or index data as additional confirmation conditions
- Rationale: Consistent confirmation from related markets can increase signal reliability
- Implementation method: Check if major indices or related markets also show similar reversal indications
Summary
The Multi-Period Reversal Point Detection and Automated Trading Strategy is a quantitative trading system based on a combination of technical indicators, capturing potential market reversal opportunities through the combination of Magic-9⁄13 pattern recognition and directional reversal point analysis. The core advantages of this strategy lie in its multiple confirmation mechanisms and integrated risk management functions, which can provide relatively reliable trading signals in the early stages of market reversals while controlling risk through automated stop-loss and take-profit.
However, the strategy also faces limitations such as parameter sensitivity, market environment adaptability, and fixed stop-loss and take-profit. By implementing dynamic parameter adjustments, adding trend filters, optimizing stop-loss and take-profit mechanisms, and adding volume confirmation, the adaptability and performance stability of the strategy can be significantly enhanced.
For traders, this strategy provides a systematic framework for capturing market reversal points, but still requires reasonable parameter adjustments and optimization combined with personal risk preferences and market understanding. In practical application, it is recommended to first conduct sufficient testing in a simulated environment to understand the performance characteristics of the strategy in different market environments before gradually applying it to live trading. Through continuous optimization and improvement, this strategy can become an effective tool in a trader’s toolbox, especially in capturing market turning points.
/*backtest
start: 2025-06-05 00:00:00
end: 2025-06-05 15:00:00
period: 1m
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"ETH_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy('L3 Magic-9/13 Strategy', overlay=true, max_bars_back=4000, max_labels_count=500)
// 输入参数
length_input = input.int(title='Length', defval=9, minval=1)
lookback_length = input.int(title='Lookback Length', defval=4, minval=1)
// 获取第一个非 NA 值的函数
get_first_non_na_value(values, length) =>
result = float(na)
if length >= 1
for i = 0 to length - 1
if na(result) or not na(values[i])
result := values[i]
result
// 计算连续条件出现次数的函数
count_consecutive_occurrences(condition, length) =>
count = 0
for i = 1 to length
if condition[i - 1]
count += 1
count
// 检查条件是否在给定周期内出现的函数
check_condition_occurrence(condition, length) =>
occurrence = count_consecutive_occurrences(condition, length) != 0 ? 1 : 0
occurrence
// 基于回溯周期过滤出现次数的函数
filter_occurrences(condition, lookback_period) =>
output = 0.0
temp = 0
for i = lookback_period to 0
if temp > 0
output := 0.0
temp := temp[1] - 1
else
if not condition[i]
output := 0.0
else
output := 1.0
temp := lookback_period + 1
output_bool = output == 1 ? true : false
output_bool
// Magic-9/13 逻辑
high_9 = count_consecutive_occurrences(close > get_first_non_na_value(close, 4), 9) == 9 and count_consecutive_occurrences(close > get_first_non_na_value(close, 4), 10) == 9
low_9 = count_consecutive_occurrences(close < get_first_non_na_value(close, 4), 9) == 9 and count_consecutive_occurrences(close < get_first_non_na_value(close, 4), 10) == 9
// 计算方向反转点
up_count = 0
down_count = 0
for i = 0 to length_input - 1
up_count += (nz(close[i]) > nz(close[i + lookback_length]) ? 1 : 0)
down_count += (nz(close[i]) < nz(close[i + lookback_length]) ? 1 : 0)
directional_reversal_point = down_count == length_input ? 1 : up_count == length_input ? -1 : 0
// 定义交易信号
buy_signal = check_condition_occurrence(low_9, 2) and ta.crossover(directional_reversal_point, 0)
sell_signal = check_condition_occurrence(high_9, 2) and ta.crossunder(directional_reversal_point, 0)
// 执行交易
if (buy_signal)
strategy.entry("Buy", strategy.long)
strategy.exit("Take Profit", "Buy", limit=close + 10 * syminfo.pointvalue, stop=close - 10 * syminfo.pointvalue)
if (sell_signal)
strategy.entry("Sell", strategy.short)
strategy.exit("Take Profit", "Sell", limit=close - 10 * syminfo.pointvalue, stop=close + 10 * syminfo.pointvalue)
// 绘制标签
labels = buy_signal ? label.new(bar_index, low, 'B', color=color.new(color.red, 40), textcolor=color.white, style=label.style_label_up, yloc=yloc.price, size=size.small) : sell_signal ? label.new(bar_index, high, 'S', color=color.new(color.lime, 40), textcolor=color.white, style=label.style_label_down, yloc=yloc.price, size=size.small) : na
// 绘制蜡烛图颜色
signal = directional_reversal_point > 0 or up_count > down_count ? 1 : directional_reversal_point < 0 or down_count > up_count ? -1 : 0
drp_color = signal > 0 ? color.green : signal < 0 ? color.red : color.black
barcolor(drp_color)