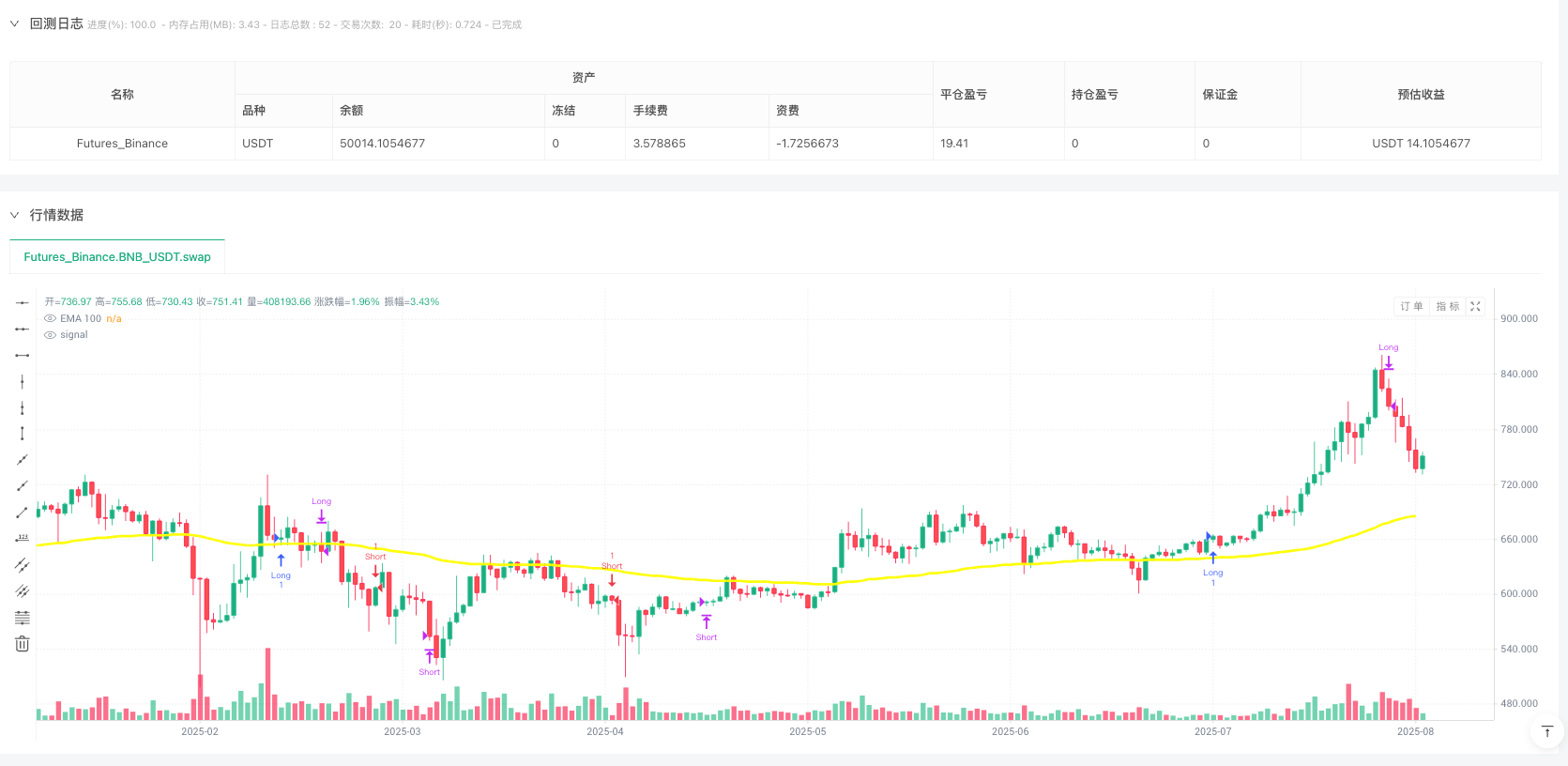
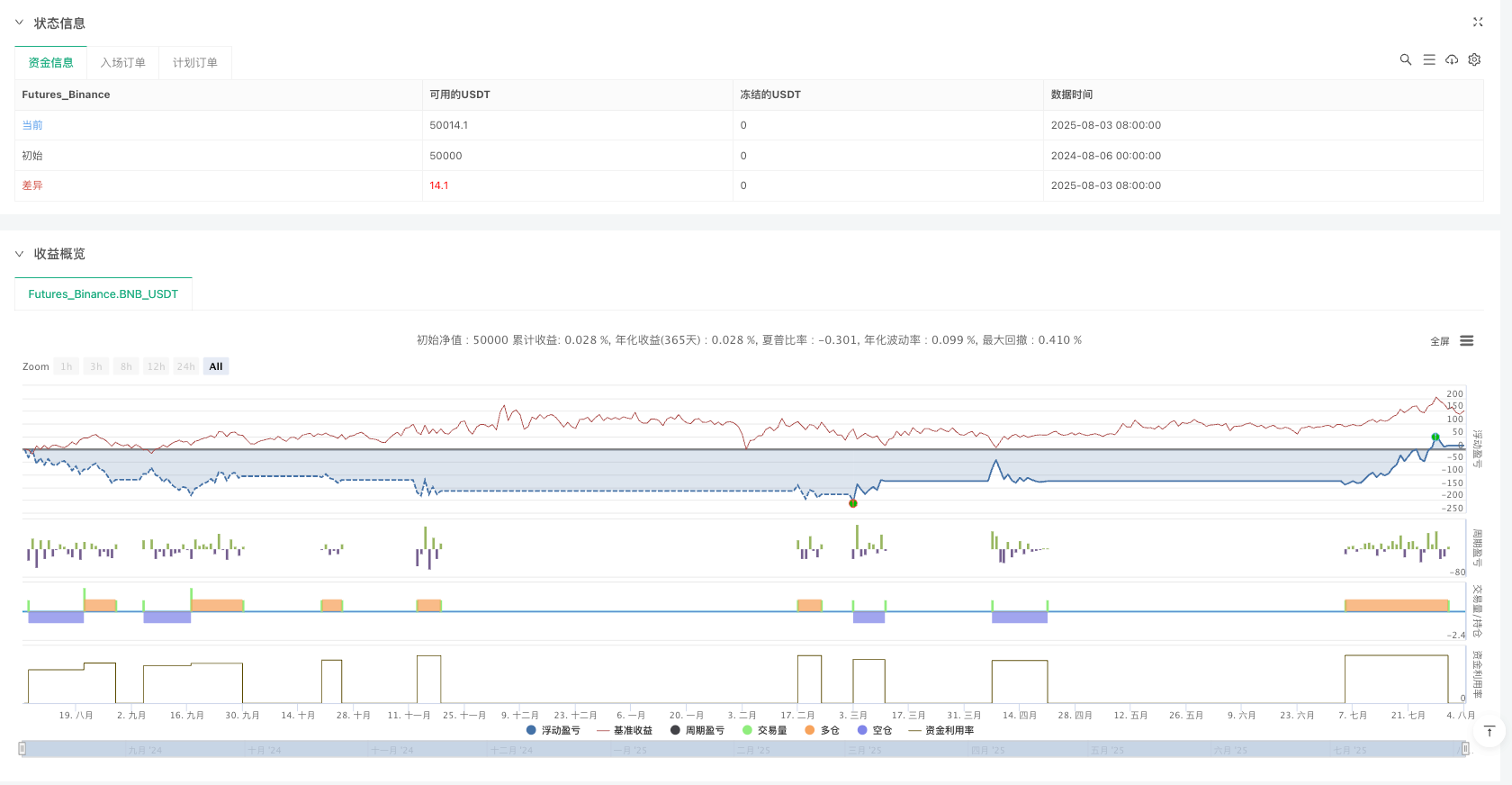
Overview
The Zero-Lag ZLEMA-MACD Multi-Market Quantitative Trading Strategy is a next-generation technical analysis trading system designed for multi-asset classes, aimed at overcoming the lag issues of traditional MACD indicators. This strategy creates a comprehensive trading decision framework by integrating Zero-Lag Exponential Moving Average (ZLEMA), MACD signal lines, trend filters, and RSI momentum confirmation. The strategy is specifically designed for stocks, forex, and cryptocurrency markets, applicable to multiple timeframes from minute to daily charts.
Through deep analysis of the source code, we can see that the core of this strategy uses a 34-period ZLEMA for smoothed inputs, combined with a 100-period EMA as a trend filter, while using the RSI indicator as a sentinel against false breakouts. Additionally, the strategy integrates an automatic risk management mechanism, implementing a 3:1 risk-reward ratio.
Strategy Principles
The core principle of this strategy is based on the MACD indicator improved with ZLEMA (Zero-Lag Exponential Moving Average). ZLEMA is an advanced moving average that reduces the lag in price movement responses through a special formula. The strategy calculation process is as follows:
ZLEMA Calculation: First calculates a regular EMA, then eliminates lag through the formula
2 * ema1 - ema2, where ema1 is the EMA of price, and ema2 is the EMA of ema1.Enhanced MACD: Calculates fast line (12-period) and slow line (26-period) based on ZLEMA, then computes their difference as the MACD line, with the signal line being a 9-period simple moving average of the MACD line.
Trend Confirmation: Uses a 100-period EMA as the primary trend indicator, only considering entry when price is aligned with the trend direction.
Entry Conditions:
- Long: Price above EMA100, MACD line crosses above signal line, and the two lines are not parallel
- Short: Price below EMA100, MACD line crosses below signal line, and the two lines are not parallel
RSI Filtering: Uses 14-period RSI to monitor overbought and oversold conditions, setting 70 and 30 as thresholds for exit decision assistance.
Exit Mechanisms:
- MACD signal reversal (crossover or histogram decline)
- RSI retracement after threshold breakthrough
Risk Management: Automatically sets fixed percentage stop-loss (default 0.3%), and calculates profit targets based on a set risk-reward ratio (default 3:1).
This design eliminates the lag inherent in traditional MACD indicators while reducing false signals through multiple filters, forming a more precise trading decision system.
Strategy Advantages
Through in-depth analysis of the code, this strategy has the following significant advantages:
Reduced Lag Signal Generation: By using ZLEMA instead of traditional EMA to calculate MACD, the strategy significantly reduces signal lag, enabling traders to capture trend reversal points earlier.
Multiple Confirmation Mechanisms: The strategy requires triple alignment of price, MACD, and trend filter (EMA100), greatly reducing the possibility of false signals.
Intelligent Linear Relationship Detection: The
linesParallelcondition in the code detects whether the MACD line and signal line are parallel (difference less than 0.03), avoiding trading when MACD oscillates without a clear direction.Dynamic Exit Strategy: Combines MACD reversal signals and RSI threshold breakout retracements to form a dual exit mechanism that both protects profits and avoids prematurely exiting strong trends.
Visual Risk Management: The strategy automatically calculates and displays stop-loss and profit target levels, helping traders intuitively understand the risk and reward of each trade.
Adaptive Multi-Market Design: Parameter settings are suitable for various asset classes, allowing the strategy to maintain consistent performance across stock, forex, and cryptocurrency markets.
Complete Trade Lifecycle Management: From entry signal identification, position management to exit strategy, the strategy provides complete trade lifecycle management, reducing the need for manual decision-making.
Strategy Risks
Despite the strategy’s sophisticated design, the following potential risks exist:
Delay in Trend Reversals: Although ZLEMA is used to reduce lag, any system based on moving averages will have some degree of lag during severe market reversals, potentially leading to losses in the early stages of reversals. The solution is to consider adding volatility filters to adjust strategy parameters or pause trading when market volatility suddenly increases.
Parameter Optimization Risk: The strategy relies on multiple parameters (ZLEMA, MACD, EMA periods, etc.), and the optimal values for these parameters may differ in different market environments. To mitigate this risk, regularly backtest different parameter combinations or consider implementing an adaptive parameter system.
False Breakout Risk: Despite multiple filters, false breakout signals may still occur in range-bound markets. This can be improved by adding volume confirmation or volatility filters.
Fixed Percentage Stop-Loss Limitation: The current strategy uses a fixed percentage stop-loss (default 0.3%), which may be too small in highly volatile markets and too large in low volatility markets. Consider using dynamic stop-losses based on ATR (Average True Range) to address this issue.
Limitations of RSI Thresholds: In strong trend markets, RSI may remain in overbought or oversold zones for extended periods, leading to premature exits from good trends. Consider dynamically adjusting RSI thresholds based on market conditions or combining with other indicators for confirmation.
Lack of Volume Analysis: The current strategy is based solely on price action without considering volume factors, which may lead to lower quality signals in low volume environments. Adding volume confirmation can improve signal quality.
Strategy Optimization Directions
Based on in-depth analysis of the code, here are directions for strategy optimization:
Dynamic Parameter Adaptation: Implement a mechanism for dynamically adjusting parameters based on market volatility, for example, lengthening ZLEMA periods when volatility increases and shortening periods when volatility decreases. This will make the strategy better adapt to different market environments.
Add Volume Confirmation: Include volume filters in entry conditions, only entering when volume supports price movements, using relative volume indicators such as OBV or volume-weighted moving averages.
Improve Stop-Loss Mechanism: Replace fixed percentage stop-losses with dynamic ATR-based stop-losses to better reflect actual market volatility. The formula could be
stopLoss = close - (multiplier * ATR(14)), where multiplier is the risk tolerance coefficient.Add Market State Recognition: Incorporate a market state recognition module into the strategy to distinguish between trending and oscillating markets, using different trading rules in different market states. ADX or similar indicators can be used to measure trend strength.
Time Filters: Add time filters to avoid known low liquidity or high volatility periods, such as earnings release periods, important economic data release times, etc.
Partial Profit Mechanism: Implement a partial profit-taking mechanism instead of closing the entire position at once, for example, closing 50% of the position when a 1:1 risk-reward ratio is achieved, and holding the remainder until higher targets are met or other exit conditions are triggered.
Indicator Correlation Analysis: Reduce potentially redundant indicators in the strategy, for example, MACD and RSI may provide similar signals in certain situations. Optimize indicator combinations through correlation analysis.
Machine Learning Enhancement: Consider using machine learning techniques to optimize entry and exit decisions, such as using random forests or support vector machines to predict the reliability of MACD signals.
Summary
The Zero-Lag ZLEMA-MACD Multi-Market Quantitative Trading Strategy is a technically advanced and practical trading system that effectively reduces the lag of traditional technical indicators while maintaining signal reliability through innovative combinations of ZLEMA technology, MACD momentum signals, EMA trend filtering, and RSI confirmation.
The strategy’s main advantages lie in its reduced lag signal generation mechanism, multiple confirmation systems, and automatic risk management functions, making it applicable to various asset classes and timeframes. However, potential parameter optimization risks, false breakout risks, and limitations of fixed stop-losses need to be considered during application.
By implementing the suggested optimization directions, such as dynamic parameter adjustment, volume confirmation, and improved stop-loss mechanisms, the performance and robustness of this strategy can be further enhanced. Particularly, introducing machine learning techniques for signal quality assessment and market state recognition holds promise for maintaining technical advantages in today’s highly competitive quantitative trading field.
For traders looking to implement a unified trading system across different markets and timeframes, this strategy provides a solid technical foundation and clear decision-making framework that, with appropriate parameter adjustments and risk management, can effectively adapt to different trading environments and individual risk preferences.
/*backtest
start: 2024-08-06 00:00:00
end: 2025-08-04 08:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BNB_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=6
strategy("Neo IMACD Strategy", overlay=true, default_qty_type=strategy.fixed, default_qty_value=1)
// === INPUTS === //
zlemaSrc = close
zlemaLen = input.int(34, title="ZLEMA Length")
shortLen = input.int(12, title="MACD Short Length")
longLen = input.int(26, title="MACD Long Length")
signalLen = input.int(9, title="MACD Signal Smoothing")
emaLen100 = input.int(100, title="EMA 100 Length")
emaColor = input.color(color.yellow, title="EMA 100 Color")
emaWidth = input.int(3, title="EMA 100 Line Width", minval=1, maxval=5)
riskReward = input.float(3.0, title="Risk-Reward Ratio (TP:SL)", minval=1.0)
stopLossPerc = input.float(0.3, title="Stop Loss %", minval=0.1, step=0.1)
// === CALCULOS ZLEMA + MACD === //
ema100 = ta.ema(close, emaLen100)
plot(ema100, title="EMA 100", color=emaColor, linewidth=emaWidth)
ema1 = ta.ema(zlemaSrc, zlemaLen)
ema2 = ta.ema(ema1, zlemaLen)
zlema = 2 * ema1 - ema2
fastMA = ta.ema(zlema, shortLen)
slowMA = ta.ema(zlema, longLen)
macdLine = fastMA - slowMA
signal = ta.sma(macdLine, signalLen)
hist = macdLine - signal
// === CONDICIONES DE CRUCE Y TENDENCIA === //
macdCrossUp = ta.crossover(macdLine, signal)
macdCrossDown = ta.crossunder(macdLine, signal)
histFalling = hist < hist[1] and hist[1] > hist[2]
linesParallel = math.abs(macdLine - signal) < 0.03 and math.abs(macdLine[1] - signal[1]) < 0.03
// === CONDICIONES DE ENTRADA === //
longCondition = close > ema100 and macdCrossUp and not linesParallel
shortCondition = close < ema100 and macdCrossDown and not linesParallel
// === RSI === //
rsi = ta.rsi(close, 14)
rsiUpper = 70
rsiLower = 30
// === FLAGS RSI === //
var bool wasRSIAbove70 = false
var bool wasRSIBelow30 = false
wasRSIAbove70 := (rsi > rsiUpper) ? true : (rsi < rsiUpper ? false : wasRSIAbove70)
wasRSIBelow30 := (rsi < rsiLower) ? true : (rsi > rsiLower ? false : wasRSIBelow30)
// === GESTIÓN TP/SL + ENTRADA === //
if (longCondition)
stopLoss = close * (1 - stopLossPerc / 100)
takeProfit = close + (close - stopLoss) * riskReward
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
if (shortCondition)
stopLoss = close * (1 + stopLossPerc / 100)
takeProfit = close - (stopLoss - close) * riskReward
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
// === CIERRE POR MACD / HISTOGRAMA === //
exitLongMACD = strategy.position_size > 0 and (macdCrossDown or histFalling)
exitShortMACD = strategy.position_size < 0 and (macdCrossUp or histFalling)
if exitLongMACD
strategy.close("Long", comment="Exit Long by MACD/Hist")
if exitShortMACD
strategy.close("Short", comment="Exit Short by MACD/Hist")
// === CIERRE POR RSI 70 / 30 === //
exitLongRSI = strategy.position_size > 0 and wasRSIAbove70 and rsi < rsiUpper
exitShortRSI = strategy.position_size < 0 and wasRSIBelow30 and rsi > rsiLower
if exitLongRSI
strategy.close("Long", comment="Exit Long by RSI < 70")
if exitShortRSI
strategy.close("Short", comment="Exit Short by RSI > 30")