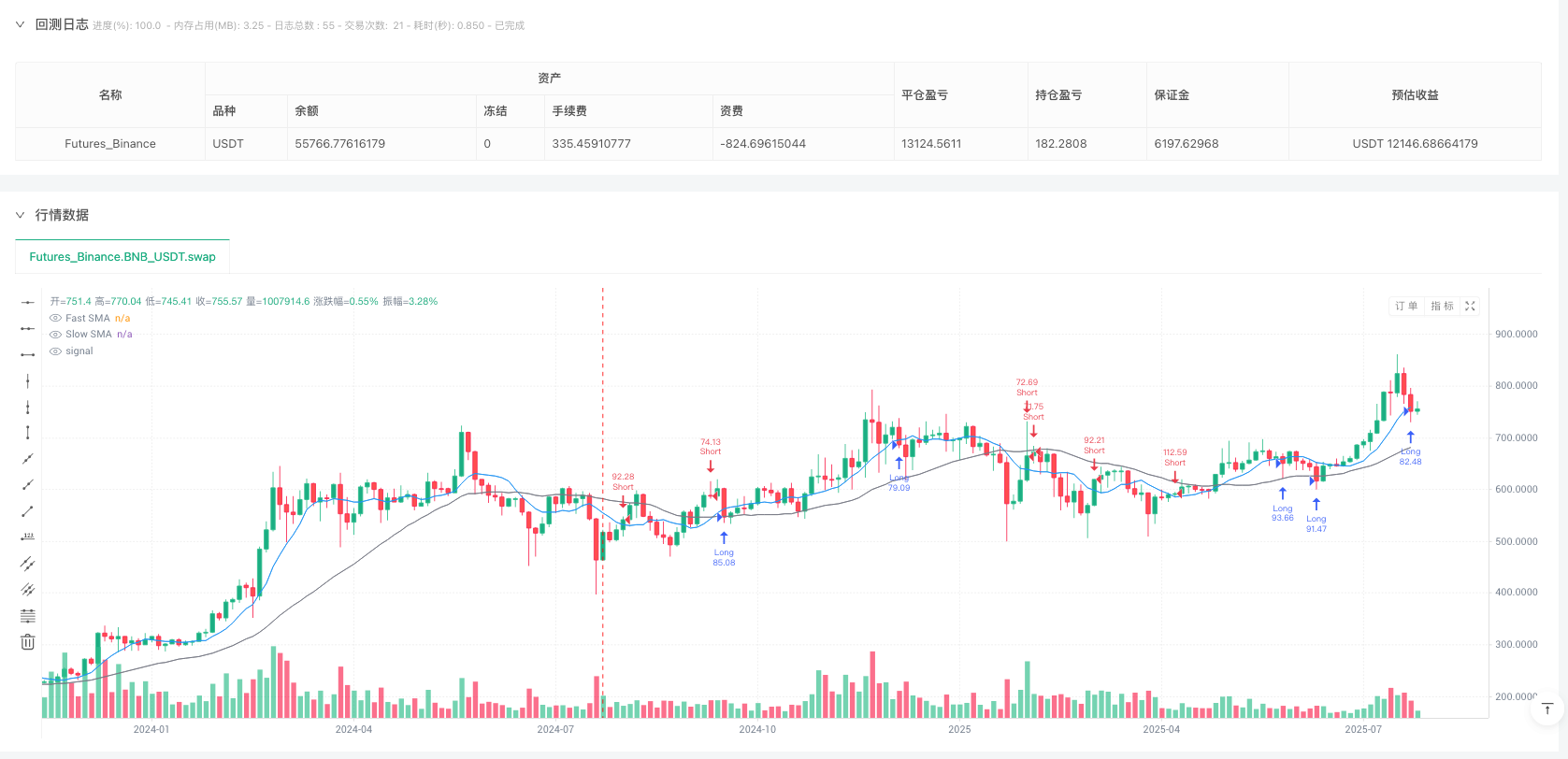
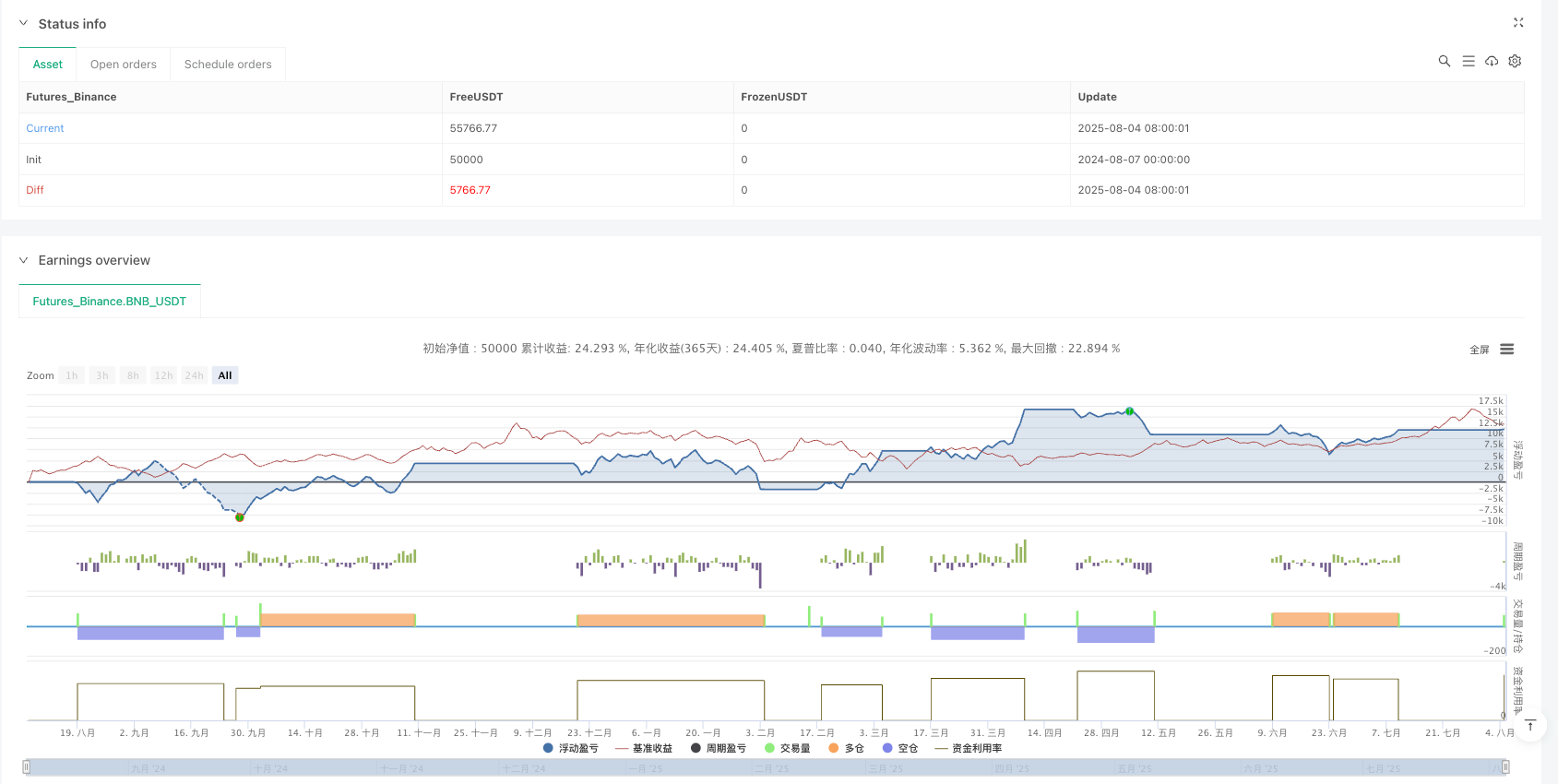
Overview
The Multi-Timeframe SMA Pullback with ATR Dynamic Exit Strategy is a quantitative trading approach that combines short-term and long-term Simple Moving Average (SMA) crossover signals with Average True Range (ATR) dynamic stop-loss and take-profit mechanisms. The core concept focuses on capturing pullback opportunities to the short-term moving average while dynamically setting exit points using ATR to effectively control risk and secure profits. This strategy is primarily designed for cryptocurrency markets, utilizing a moving average system to identify trend direction, capturing entry opportunities through the relationship between price and the fast moving average, and implementing precise exit points using ATR multipliers.
Strategy Principles
The core principle of this strategy is based on the interrelationship between two SMAs of different periods and price action, combined with ATR for dynamic risk management:
Entry Logic:
- Long entry: When price falls below the 8-period SMA (fast line) while the fast line is above the 30-period SMA (slow line)
- Short entry: When price rises above the 8-period SMA (fast line) while the fast line is below the 30-period SMA (slow line)
Exit Mechanism:
- Uses 14-period ATR indicator to calculate market volatility
- Long stop-loss: Entry price minus 1.2 times ATR value
- Long take-profit: Entry price plus 2.0 times ATR value
- Short stop-loss: Entry price plus 1.2 times ATR value
- Short take-profit: Entry price minus 2.0 times ATR value
The strategy’s logic combines trend following and mean reversion concepts. When the fast moving average is above the slow moving average, the market is in an uptrend; when the fast moving average is below the slow moving average, the market is in a downtrend. Price pullbacks to the fast moving average provide opportunities for trend-aligned entries, allowing the strategy to enter the market at more favorable prices when the trend is established.
The ATR-based dynamic exit mechanism adjusts according to actual market volatility, automatically widening stop-loss and take-profit ranges when volatility increases and narrowing them when volatility decreases, making it more flexible and market-adaptive than fixed-point exits.
Strategy Advantages
Trend and Pullback Combination: Uses two SMAs to confirm trend direction while leveraging price pullbacks to the fast moving average for better entry prices, ensuring both trend direction accuracy and optimized entry timing.
Dynamic Risk Management: Implements ATR-based stop-loss and take-profit levels that automatically adjust to actual market volatility, avoiding stops that are too tight during high volatility or too wide during low volatility periods.
Optimized Risk-Reward Ratio: The ATR take-profit multiplier (2.0) is greater than the stop-loss multiplier (1.2), ensuring a favorable risk-reward ratio with a theoretical profit-to-loss ratio of 1.67:1 per trade.
Simple Parameter Structure: Contains only 4 key parameters (fast SMA period, slow SMA period, ATR stop-loss multiplier, ATR take-profit multiplier), making it easy to understand and optimize.
High Adaptability: The strategy can adapt to different market conditions, performing well in trending markets while reducing losses in ranging markets through dynamic stops.
Full Position Efficiency: The strategy uses position management set to 100% of account equity, fully utilizing capital efficiency when confident signals appear.
Strategy Risks
Moving Average Lag: SMAs are inherently lagging indicators that may lead to delayed signals in rapidly changing markets, resulting in suboptimal entry points or missed key turning points. Solution: Consider using EMAs (Exponential Moving Averages) instead of SMAs to reduce lag.
False Breakout Risk: Markets may exhibit short-term breakouts followed by quick reversals, leading to frequent stop-losses. Solution: Add confirmation signals such as volume confirmation or momentum indicator filtering.
Parameter Sensitivity: Strategy performance is sensitive to SMA periods and ATR multiplier settings, with different parameter combinations performing differently under various market conditions. Solution: Optimize parameters for different market conditions through backtesting.
Consecutive Loss Risk: In highly volatile ranging markets, consecutive stop-losses may occur, eroding account capital. Solution: Implement market environment filtering mechanisms to reduce trading frequency or pause trading during high-volatility sideways markets.
Full Position Risk: The strategy uses 100% equity for trading, increasing risk exposure per trade. Solution: Consider scaling into positions or reducing position size, especially during periods of high market uncertainty.
Fixed ATR Calculation Period: The code uses a fixed 14-period ATR, which may not fully adapt to all market states. Solution: Make the ATR period an adjustable parameter to adapt to different market conditions.
Strategy Optimization Directions
Add Trend Strength Filtering: Incorporate ADX (Average Directional Index) or similar indicators to measure trend strength, entering only when trends are clearly defined to avoid false signals in ranging markets. This optimization can significantly improve strategy performance in trending markets while reducing losing trades in ranging conditions.
Introduce Momentum Confirmation: Integrate RSI or MACD as auxiliary confirmation signals to increase entry condition stringency. Momentum indicators can help confirm price movement strength and reduce losses from false breakouts.
Develop Parameter Adaptive Mechanisms: Create mechanisms that dynamically adjust SMA periods and ATR multipliers based on market volatility or trend strength. This would allow the strategy to better adapt to different market environments and improve overall stability.
Add Time Filters: Implement time filtering functionality to avoid known low-liquidity or high-volatility periods, such as important data releases or cross-session trading hours. This can reduce unnecessary stop-losses caused by abnormal market volatility.
Implement Position Sizing Strategy: Adjust position size based on market conditions, account equity changes, or signal strength, rather than fixed 100% equity usage. This will improve capital efficiency while reducing single-trade risk.
Develop Partial Profit-Taking Mechanism: Allow partial position closure to secure profits when certain profit targets are reached, with trailing stops for remaining positions. This optimization can effectively reduce drawdown magnitude while maintaining profit potential.
Integrate Multi-Timeframe Analysis: Combine higher timeframe trend confirmation, trading only when higher and lower timeframe trends align. Multi-timeframe analysis can effectively filter low-quality signals and improve trade success rates.
Summary
The Multi-Timeframe SMA Pullback with ATR Dynamic Exit Strategy is a quantitative trading system that combines fundamental technical analysis principles, identifying market trends through the interplay of 8-period and 30-period SMAs, finding entry opportunities through price pullbacks to the fast moving average, and controlling risk using ATR-based dynamic exits. The strategy design is concise, with clear logic and few parameters that are easy to understand, making it particularly suitable for highly volatile markets like cryptocurrencies.
The main advantages of this strategy lie in the combination of trend confirmation with pullback entries, and dynamic risk management based on actual market volatility. By setting reasonable stop-loss and take-profit multiplier ratios, the strategy can theoretically maintain a favorable risk-reward profile. However, the strategy also faces risks such as moving average lag, high parameter sensitivity, and potential frequent stop-losses in ranging markets.
Future optimization directions primarily focus on adding trend strength and momentum confirmation, developing parameter adaptive mechanisms, optimizing position management, and integrating multi-timeframe analysis. Through these improvements, the strategy has the potential to maintain its original simplicity while further enhancing stability and profitability, better adapting to various market environments.
/*backtest
start: 2024-08-07 00:00:00
end: 2025-08-05 08:00:00
period: 3d
basePeriod: 3d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BNB_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=6
strategy("8/30 SMA Pullback + ATR Exits (Crypto)", overlay=true,
default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity,
default_qty_value=100, initial_capital=200)
// === Inputs === //
smaFastLen = input.int(8, "Fast SMA", minval=1)
smaSlowLen = input.int(30, "Slow SMA", minval=1)
atrMultSL = input.float(1.2, "ATR Multiplier SL", step=0.1)
atrMultTP = input.float(2.0, "ATR Multiplier TP", step=0.1)
// === Core Series === //
smaFast = ta.sma(close, smaFastLen)
smaSlow = ta.sma(close, smaSlowLen)
atr = ta.atr(14)
// === Entry Conditions === //
longCond = close < smaFast and smaFast > smaSlow
shortCond = close > smaFast and smaFast < smaSlow
if longCond
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
if shortCond
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
// === ATR-based TP / SL === //
if strategy.position_size > 0
longSL = strategy.position_avg_price - atr * atrMultSL
longTP = strategy.position_avg_price + atr * atrMultTP
strategy.exit(id="Exit Long", from_entry="Long",
stop=longSL, limit=longTP)
if strategy.position_size < 0
shortSL = strategy.position_avg_price + atr * atrMultSL
shortTP = strategy.position_avg_price - atr * atrMultTP
strategy.exit(id="Exit Short", from_entry="Short",
stop=shortSL, limit=shortTP)
// === Visuals === //
plot(smaFast, "Fast SMA", color=color.blue)
plot(smaSlow, "Slow SMA", color=color.gray)