Lunar Cycle Momentum Quantitative Trading Strategy for Cryptocurrency Markets
Lunar Calendar Cyclical Trading ETHUSDT Fixed Date Entry/Exit Quantitative Strategy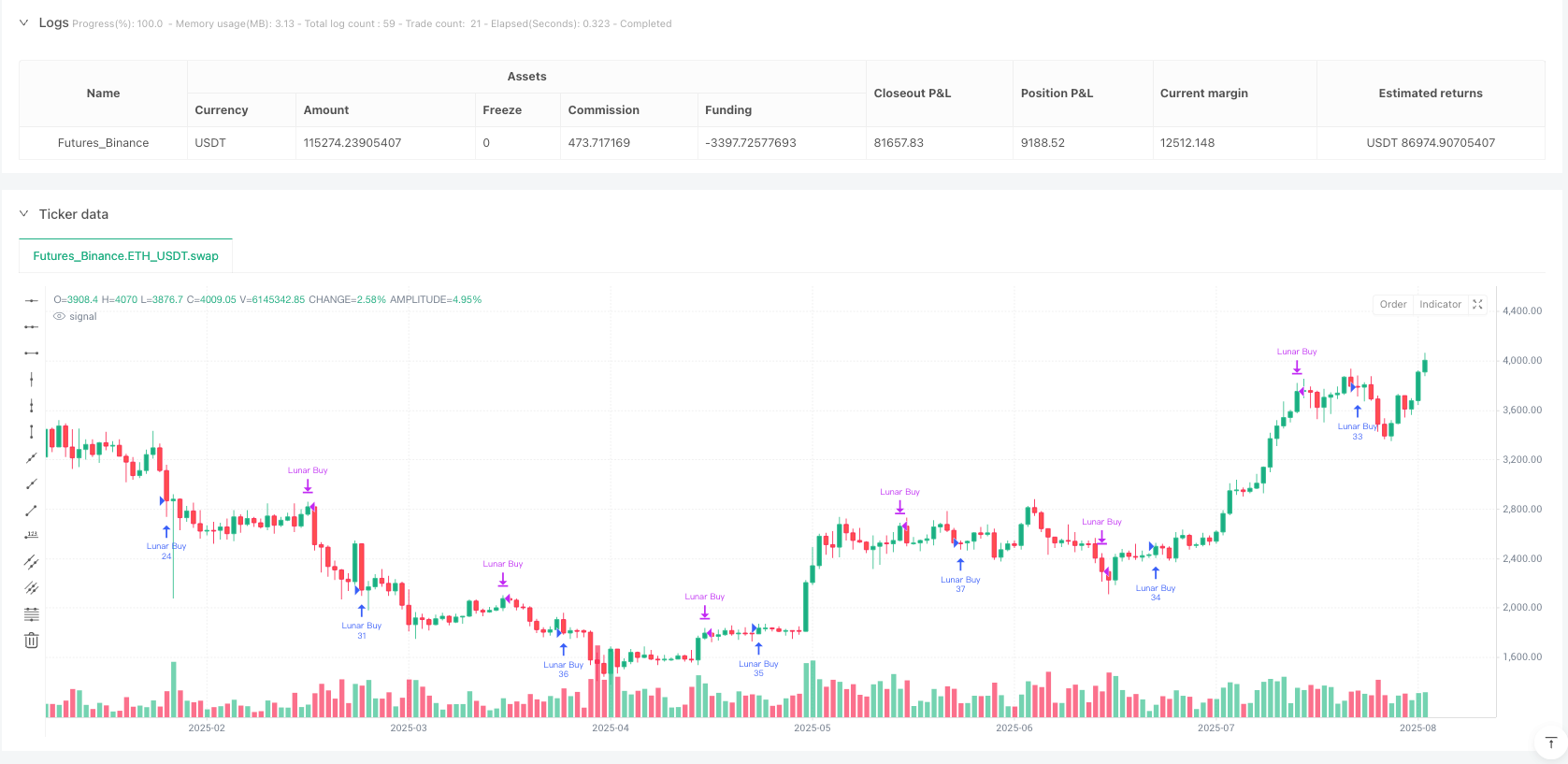
Overview
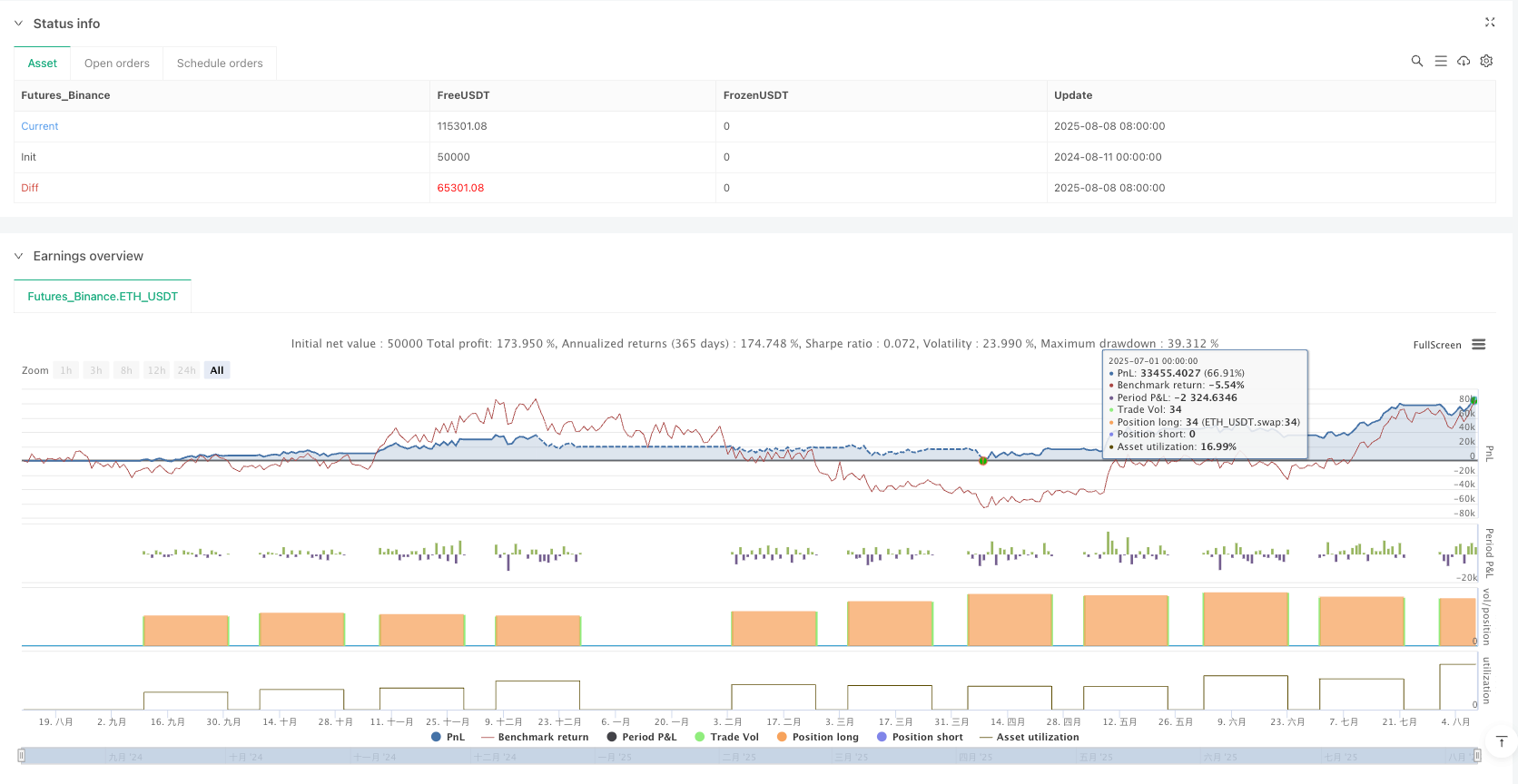
This strategy is a cryptocurrency trading method based on lunar calendar dates, utilizing specific dates in the lunar cycle for buying and selling operations. The strategy begins from the Lunar New Year and continues until the end of December in the solar calendar year, following simple rules: buy on the 5th day of each lunar month and sell on the 26th day. This approach attempts to capture market patterns potentially related to lunar cycles, providing traders with a structured and easy-to-follow trading framework. The strategy accounts for fees and slippage factors, uses 100% of available funds for investment, and is applicable for the timeframe from 2020 to 2026.
Strategy Principles
The core principle of this strategy is based on the potential influence of lunar cycles on cryptocurrency markets. The code implements this concept through the following methods:
- First, it defines the starting dates of the Lunar New Year and the number of days in each month for years 2020 to 2026.
- By calculating the difference in days between the current date and the Lunar New Year, it determines the current lunar month and day.
- When the lunar date is the 5th day and there is no current position, a buy signal is triggered.
- When the lunar date is the 26th day and a position is held, a sell signal is triggered.
- The buy order takes into account slippage and fees, using all available funds to purchase as much cryptocurrency as possible.
- The sell order closes all positions, realizing profit or loss.
The strategy uses precise date calculation methods, storing the number of days for each lunar month in arrays and cumulatively calculating the total days from the Lunar New Year, thereby accurately positioning the current lunar date. This method ensures the accurate triggering of trading signals.
Strategy Advantages
Analyzing the code of this strategy, we can summarize the following advantages:
- Simple and Clear Rules: Fixed buying and selling dates make the strategy very intuitive, easy to understand and execute, reducing subjective judgment by traders.
- Consideration of Market Friction Factors: The strategy incorporates 0.1% fees and slippage considerations, making the backtesting results closer to actual trading environments.
- High Fund Utilization Efficiency: Each trade uses 100% of available funds, maximizing potential returns.
- Unique Perspective Considering Lunar Cycles: Unlike traditional technical analysis, this strategy introduces the lunar factor, potentially capturing unique patterns related to Asian market investor behavior.
- Long-term Applicability: The strategy provides lunar data from 2020 to 2026, allowing traders to apply this method over an extended period.
- Visual Assistance: By displaying lunar date labels on the chart, it helps traders visually track the strategy execution.
- Avoids Overtrading: Trading only once per lunar month reduces costs and risks associated with excessive trading.
Strategy Risks
Despite the advantages mentioned above, there are also some potential risks:
- Lack of Risk Management Mechanisms: The strategy does not set stop-loss points, which could lead to significant losses if the market falls sharply after buying.
- Ignores Market Trends and Conditions: The strategy trades solely based on dates, without considering the overall market trend, volatility, or other technical indicators.
- Assumes Cyclical Patterns Exist: The strategy assumes there is some correlation between lunar cycles and cryptocurrency prices, but this correlation may be unstable or nonexistent.
- Specific Timeframe Limitations: Although data for 2020-2026 is provided, lunar data for future years needs to be updated, and the strategy may not work outside this range.
- Liquidity Risk: Market liquidity issues may be encountered on specific lunar dates, especially when using large funds.
- Possibility of Date Calculation Errors: Any errors in calculating lunar dates could lead to incorrect trading signals.
- Lack of Adaptability: Fixed trading dates cannot adapt to changing market conditions, potentially missing better buying or selling opportunities.
To mitigate these risks, traders might consider combining other technical indicators for trade confirmation or setting fixed stop-loss positions to limit losses on individual trades.
Strategy Optimization Directions
Through in-depth analysis of the code, the following optimization directions can be proposed:
Introduce Stop-Loss Mechanism: Add percentage or absolute amount stop-loss conditions to automatically close positions when losses reach a specific threshold, avoiding substantial losses. The optimization code could include condition checks like
if strategy.position_size > 0 and close < entry_price * (1 - stop_loss_percent).Incorporate Technical Indicator Confirmation: Combine trend indicators (such as moving averages) or momentum indicators (such as Relative Strength Index RSI) as auxiliary conditions, executing lunar date trades only when technical indicators provide favorable signals. This can improve signal quality.
Optimize Buy and Sell Dates: Through historical data backtesting, analyze which lunar dates actually provide the best buying and selling opportunities for the portfolio, rather than fixed using the 5th and 26th days. Certain specific date combinations may perform better.
Partial Position Management: Modify the strategy to use partial funds rather than 100% for trading, or dynamically adjust position size based on market volatility to diversify risk.
Add Market Condition Filters: Pause strategy execution during extreme market conditions (such as high volatility or obvious bearish trends) to avoid trading in unfavorable environments.
Expand Applicable Time Range: Add lunar data for more years, or develop an automatic function to calculate lunar dates, allowing the strategy to run indefinitely.
Increase Multi-Asset Trading: Extend the strategy to multiple cryptocurrencies or other asset classes, observing differences in lunar cycle performance across different markets.
Implementing these optimization directions can significantly improve the strategy’s robustness and adaptability while maintaining its simple and intuitive core concept.
Summary
The lunar cycle-based cryptocurrency trading strategy provides a unique trading perspective, utilizing specific lunar calendar dates for buying and selling operations. The strategy’s greatest advantages lie in its simple, clear rules and ease of implementation, combining the unique factor of lunar cycles that may capture market patterns overlooked by conventional technical analysis.
However, the strategy also faces challenges such as a lack of risk management and market adaptability. To enhance the strategy’s effectiveness, it is recommended to introduce stop-loss mechanisms, technical indicator confirmation, and optimize buying and selling dates. These improvements can not only reduce potential risks but also enhance the strategy’s adaptability in different market environments.
It is worth noting that any trading strategy requires thorough backtesting and forward testing to verify its performance under actual market conditions. When adopting this strategy, traders should make appropriate adjustments based on their own risk tolerance and investment objectives, and combine it with other analytical methods to make more comprehensive trading decisions.
/*backtest
start: 2024-08-11 00:00:00
end: 2025-08-09 08:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"ETH_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("Lunar ETHUSDT Trading 100% Invest with Fee & Slippage (2020~2026)", overlay=true, commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, commission_value=0.1)
// Fee and slippage settings
feePercent = 0.1 // 0.1%
slippageTicks = 3
tickSize = syminfo.mintick
slippage = slippageTicks * tickSize
// Function for lunar new year start date and monthly lengths by year
f_get_lunar_data() =>
y = year(time)
if y == 2020
[timestamp("Asia/Seoul", 2020, 1, 25, 0, 0), array.from(29,30,29,30,29,30,29,30,29,30,30,29)]
else if y == 2021
[timestamp("Asia/Seoul", 2021, 2, 12, 0, 0), array.from(30,29,30,29,30,29,30,29,30,29,30,30)]
else if y == 2022
[timestamp("Asia/Seoul", 2022, 2, 1, 0, 0), array.from(29,30,29,30,29,30,29,30,30,29,30,29)]
else if y == 2023
[timestamp("Asia/Seoul", 2023, 1, 22, 0, 0), array.from(30,29,30,29,30,29,30,30,29,30,29,30)]
else if y == 2024
[timestamp("Asia/Seoul", 2024, 2, 10, 0, 0), array.from(30,29,30,29,30,29,30,29,30,29,30,30,29)]
else if y == 2025
[timestamp("Asia/Seoul", 2025, 1, 29, 0, 0), array.from(29,30,29,30,29,30,29,30,30,29,30,29)]
else if y == 2026
[timestamp("Asia/Seoul", 2026, 2, 17, 0, 0), array.from(30,29,30,29,30,29,30,30,29,30,29,30)]
else
[na, array.new_int()]
// Function to create cumulative monthly days array
f_get_lunar_md(days_arr) =>
arr = array.new_int()
sum = 0
for i = 0 to array.size(days_arr) - 1
sum += array.get(days_arr, i)
array.push(arr, sum)
arr
// Get lunar start date and monthly lengths
[ts_start, lunar_lengths] = f_get_lunar_data()
valid = not na(ts_start)
days_since = valid ? math.floor((time - ts_start) / 86400000) : na
cumulative = valid ? f_get_lunar_md(lunar_lengths) : na
// Declare lunar month, day, last day variables
var int lunar_month = na
var int lunar_day = na
var int lunar_last_day = na
// Calculate lunar date
if valid and not na(days_since) and days_since >= 0
lunar_month := na
lunar_day := na
lunar_last_day := na
for i = 0 to array.size(cumulative) - 1
cum = array.get(cumulative, i)
prev = i == 0 ? 0 : array.get(cumulative, i - 1)
if days_since < cum
lunar_month := i + 1
lunar_day := days_since - prev + 1
lunar_last_day := array.get(lunar_lengths, i)
break
else
lunar_month := na
lunar_day := na
lunar_last_day := na
// Buy condition: Lunar day 5 and no current position
buy_condition = not na(lunar_day) and lunar_day == 5 and strategy.position_size == 0
// Sell condition: Lunar day 26 and holding position
sell_condition = not na(lunar_day) and lunar_day == 26 and strategy.position_size > 0
// Buy/sell price adjusted for slippage and fee
price_buy = close + slippage
price_buy_with_fee = price_buy * (1 + feePercent * 0.01)
price_sell = close - slippage
price_sell_with_fee = price_sell * (1 - feePercent * 0.01)
// Calculate buy quantity using 100% of equity
qty = math.floor(strategy.equity / price_buy_with_fee)
// Buy order (limit)
if buy_condition and qty > 0
strategy.entry("Lunar Buy", strategy.long, qty, limit=price_buy)
// Sell order (close all)
if sell_condition and strategy.position_size > 0
strategy.close("Lunar Buy")
// True range variable (for label position adjustment)
tr = ta.tr(true)
// Date format creation
yr = year(time)
mo = month(time)
dy = dayofmonth(time)
mo_str = mo < 10 ? "0" + str.tostring(mo) : str.tostring(mo)
dy_str = dy < 10 ? "0" + str.tostring(dy) : str.tostring(dy)
solar_str = str.tostring(yr) + "-" + mo_str + "-" + dy_str
// Display solar and lunar date and position label (on bar close)
if barstate.islastconfirmedhistory and not na(lunar_day)
label.new(bar_index, high - tr * 6, "Solar: " + solar_str + "\nLunar: " + str.tostring(lunar_month) + "-" + str.tostring(lunar_day) ,
style=label.style_label_up, size=size.normal, color=color.new(color.teal, 50), textcolor=color.white)
// Display "15" label at bottom on lunar day 15 (lowest of last 50 bars - 1 true range)
if not na(lunar_day) and lunar_day == 15
low_offset = ta.lowest(low, 50) - tr
label.new(bar_index, low_offset, "15", style=label.style_label_down, color=color.orange, textcolor=color.white, size=size.normal)