
Overview
This strategy is an innovative quantitative trading system based on statistical distribution theory, combining the traditional Bull Bear Power (BBP) indicator with adaptive distribution fitting techniques. The core innovation lies in breaking away from the fixed normal distribution assumption of traditional technical analysis. By calculating high-order statistical characteristics (skewness and kurtosis) of market data in real-time, it dynamically adjusts trading thresholds to align signal generation with the market’s true distribution features. The strategy is equipped with a three-level dynamic take-profit system based on ATR and market condition assessment, achieving precise adaptation to different market environments. It is particularly suitable for cryptocurrency markets with distinct distribution characteristics, effectively identifying statistically significant anomalies and avoiding false signals caused by incorrect distribution assumptions.
Strategy Principles
The core operational mechanism includes the following key components:
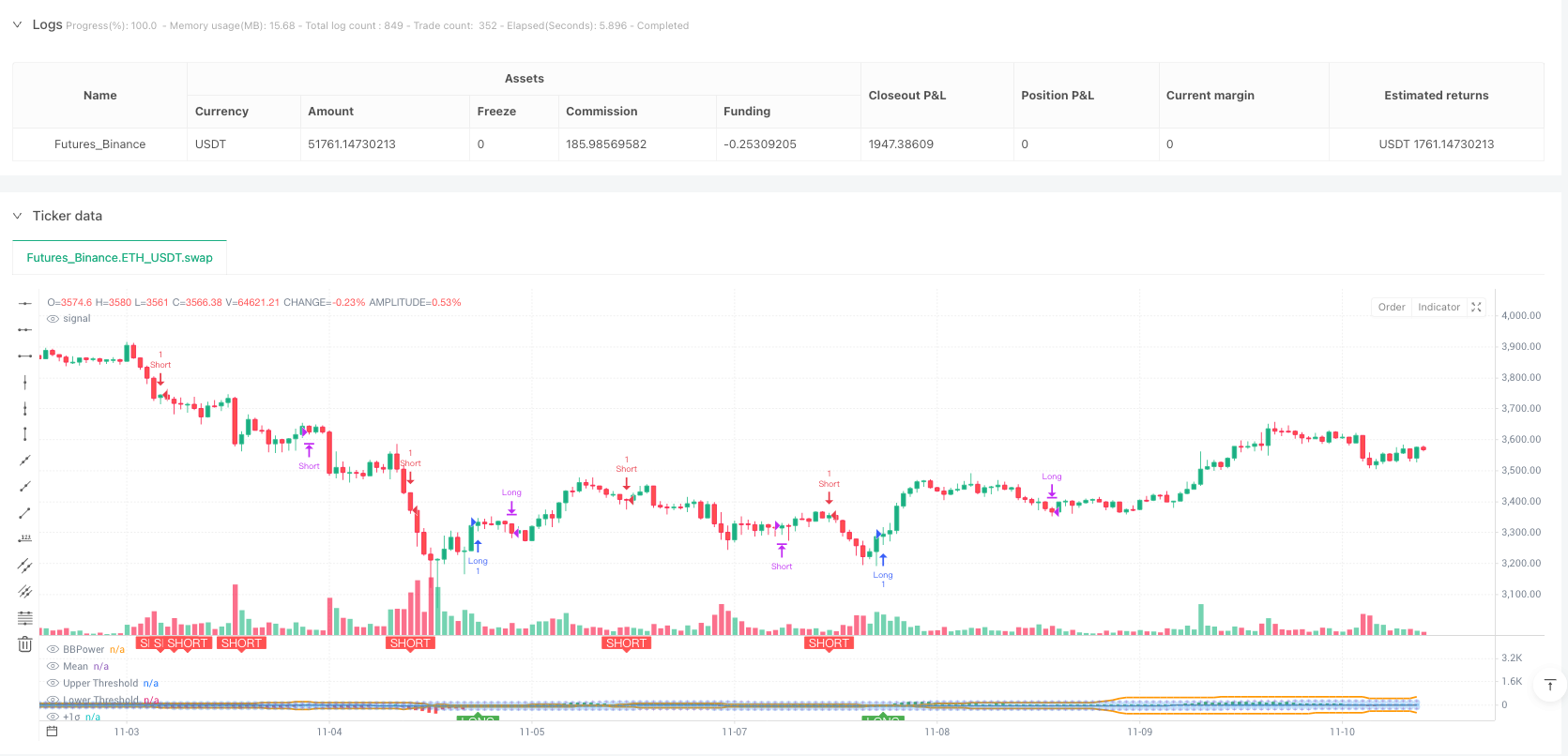
BBP Indicator Calculation: Constructs a fundamental indicator reflecting market bull-bear force comparison by calculating the sum of the difference between high price and EMA (bull power) and the difference between low price and EMA (bear power). Positive values indicate bullish dominance, while negative values indicate bearish dominance.
Distribution Characteristic Analysis: Employs high-order moment calculation methods to perform statistical analysis on the BBP sequence, outputting four key statistics: mean, standard deviation, skewness (third-order central moment), and excess kurtosis (fourth-order central moment minus 3), comprehensively depicting the distribution shape of market data. Skewness reflects distribution asymmetry, while kurtosis reflects tail thickness and extreme event frequency.
Adaptive Threshold Generation:
- Calculates standard normal quantile as baseline Z-value based on significance level
- Applies t-distribution approximation correction when excess kurtosis exceeds threshold, deriving degrees of freedom from kurtosis and expanding tolerance range
- Applies Cornish-Fisher expansion for asymmetry correction when skewness exceeds threshold
- Generates upper and lower threshold lines dynamically adjusted according to market’s true distribution characteristics
Market Condition Assessment:
- Volume dimension: Quantifies market participation into high, medium, and low levels through the ratio of current volume to period average
- Price position dimension: Locates price’s relative position in historical range through percentile ranking algorithm
- Composite scoring mechanism: Averages scores from both dimensions to form take-profit adjustment coefficient
Dynamic Take-Profit System:
- Adopts three-level take-profit design with multipliers based on golden ratio (1.618, 2.382, 3.618)
- Each take-profit level distance = ATR × fixed multiplier × dynamic adjustment coefficient
- Expands take-profit targets in strong trends with high volume and high percentiles, tightens take-profit distance in low participation scenarios
Signal Generation and Execution:
- Long signal: Opens long when BBP crosses above adaptive upper threshold
- Short signal: Opens short when BBP crosses below adaptive lower threshold
- Exit signal: Closes position when BBP reverts to mean line, following mean reversion principle
Strategy Advantages
Solid Statistical Theory Foundation: Breaks away from traditional strategies’ fixed normal distribution assumption, dynamically adjusting decision criteria based on market’s true distribution characteristics. Reconstructs signal generation logic from a statistical perspective with rigorous theoretical support.
Outstanding Adaptive Capability: Through real-time monitoring of skewness and kurtosis, the strategy automatically identifies changes in market distribution characteristics. Raises upper threshold in positively skewed markets to avoid chasing highs, expands threshold range in fat-tailed markets to avoid overreacting to normal fluctuations, truly achieving “strategy adapts to market.”
Multi-Dimensional Comprehensive Assessment: Combines three dimensions - price momentum, volume activity, and price relative position - to construct a comprehensive market condition assessment system, avoiding one-dimensional judgment bias.
Dynamic Risk Management: Three-level take-profit system with dynamic adjustment mechanism adaptively optimizes take-profit distances based on market heat. Fully captures profit space in trending markets while quickly realizing gains in weak markets.
High Signal Quality: Through statistical significance testing, triggers trades only at true distribution anomalies, effectively reducing false signal rate and improving statistical validity of trades.
Intuitive Visualization: Through dynamic threshold lines, standard deviation reference lines, and signal markers, clearly displays the strategy’s adaptive adjustment process, facilitating understanding and monitoring.
Strategy Risks
High Parameter Optimization Complexity: The strategy contains multiple parameters (significance level, skewness threshold, kurtosis threshold, take-profit multipliers, etc.). Optimal parameter combinations vary significantly across different market environments, requiring systematic parameter optimization and backtesting validation.
Lack of Clear Stop-Loss Mechanism: The strategy primarily relies on mean reversion exits, lacking hard stop-loss based on price or ATR. In extreme trending markets, if BBP continues to deviate from mean without reverting, it may cause significant unrealized losses and capital tie-up.
Poor Adaptability in Ranging Markets: In prolonged narrow-range consolidation, BBP values hover around the mean, difficult to reach adaptive thresholds, resulting in scarce trading opportunities and limited strategy performance.
Strong Data Dependency: Distribution characteristic analysis requires sufficient historical data to obtain stable and reliable statistical results. For newly listed coins or instruments with insufficient data, statistics may be unstable in early usage, affecting strategy performance.
High Computational Complexity: Real-time calculation of high-order moments, percentile rankings, and dynamic thresholds requires traversing historical data, potentially facing performance bottlenecks in resource-constrained trading environments.
Extreme Market Risk: In extreme rapid one-directional moves like flash crashes or surges, BBP may instantly break through thresholds and quickly revert, leading to suboptimal entry points or missed optimal timing.
Optimization Directions
Introduce Dynamic Stop-Loss Mechanism:
- ATR-based trailing stop-loss with distance dynamically adjusted based on holding time and profit status
- Technical stop-loss incorporating support and resistance levels
- Adaptive stop-loss based on Maximum Adverse Excursion (MAE)
Enhanced Market Environment Recognition:
- Introduce trend strength filter (e.g., ADX), suspending trades when no clear trend exists
- Add volatility state classification to identify and avoid extreme volatility periods
- Incorporate market microstructure indicators to preemptively identify liquidity exhaustion states
Parameter Adaptive Optimization:
- Apply rolling window backtesting to dynamically adjust analysis period length
- Introduce machine learning methods (e.g., genetic algorithms, particle swarm optimization) for parameter optimization
- Implement parameter switching mechanism based on market states
Signal Quality Enhancement:
- Add volume confirmation condition requiring signal triggers to be accompanied by volume expansion
- Incorporate key technical levels (e.g., previous highs/lows, Fibonacci retracements) for multiple confirmations
- Introduce signal strength scoring system to adjust position size based on score
Position Management Optimization:
- Dynamic position allocation based on Kelly Criterion
- Adjust opening ratio according to signal strength and market condition scores
- Implement pyramid scaling in/out strategies
Multi-Timeframe Integration:
- Determine major trend direction on higher timeframes, trading only with the trend
- Seek precise entry points on lower timeframes
- Build multi-period resonance confirmation mechanism
Summary
The BBP Adaptive Distribution Strategy represents an innovative attempt at combining technical analysis with modern statistics, fundamentally solving traditional strategies’ dependence on normal distribution assumptions through adaptive distribution fitting techniques. The strategy’s core value lies in its theoretical innovation and respect for market’s true distribution characteristics, maintaining reasonable signal quality across markets with different distribution shapes. The three-level dynamic take-profit system further enhances the strategy’s practicality, achieving a good balance between returns and risk.
However, the strategy also has obvious room for improvement. The lack of a clear stop-loss mechanism is the biggest shortcoming and needs priority supplementation in practical application. The complexity of parameter optimization and adaptability issues in ranging markets also need to be addressed by introducing market environment recognition and parameter adaptive mechanisms.
For quantitative traders pursuing theoretical depth and willing to conduct in-depth research, this strategy provides an excellent learning and improvement framework. Recommendations before live trading: 1. Conduct thorough historical backtesting and parameter optimization for specific trading instruments 2. Add hard stop-loss protection based on ATR or percentage 3. Combine with trend filters to avoid trading in unfavorable market environments 4. Start with small positions and gradually validate strategy performance in live trading
Overall, this is an innovative strategy with solid theoretical foundation, rigorous design logic, and high research and application value, worthy of in-depth exploration and continuous optimization by quantitative traders.
//@version=5
strategy("BBP Adaptive Distribution Strategy [presentTrading]")
//========================================
// BBP策略参数设置
//========================================
lengthInput = input.int(20, "EMA Length");//EMA周期长度
zLength = input.int(150, "Distribution Analysis Period");//分布分析周期
//自适应分布参数组
dist_group = "Distribution Fitting";
//统计显著性水平,0.05表示95%置信度
significance_level = input.float(0.05, "Significance Level", minval=0.01, maxval=0.1, step=0.01,
group=dist_group, tooltip="统计显著性水平,0.05=95%置信度");
//是否启用自适应分布拟合,禁用则使用传统Z-score
auto_fit = input.bool(true, "Auto Fit Distribution", group=dist_group,
tooltip="启用自适应分布拟合,禁用则使用传统Z-score");
//偏度阈值,超过此值考虑使用偏态分布
skew_threshold = input.float(0.5, "Skewness Threshold", minval=0.1, maxval=2.0, group=dist_group,
tooltip="超过此值考虑偏态分布");
//峰度阈值,超过此值考虑使用厚尾分布
kurt_threshold = input.float(1.0, "Kurtosis Threshold", minval=0.3, maxval=3.0, group=dist_group,
tooltip="超过此值考虑厚尾分布");
//========================================
// 止盈参数设置
//========================================
tp_group = "Take Profit Settings";//止盈参数组
useTP = input.bool(true, "Use Take Profit", group=tp_group);//是否启用止盈
baseAtrLength = input.int(20, "ATR Period", minval=1, group=tp_group);//ATR计算周期
atrMult1 = input.float(1.618, "TP1 ATR Multiplier", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=tp_group);//第一止盈位ATR倍数
atrMult2 = input.float(2.382, "TP2 ATR Multiplier", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=tp_group);//第二止盈位ATR倍数
atrMult3 = input.float(3.618, "TP3 ATR Multiplier", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=tp_group);//第三止盈位ATR倍数
tp1_size = input.float(13, "TP1 Position %", minval=1, maxval=100, group=tp_group);//第一止盈位仓位百分比
tp2_size = input.float(13, "TP2 Position %", minval=1, maxval=100, group=tp_group);//第二止盈位仓位百分比
tp3_size = input.float(13, "TP3 Position %", minval=1, maxval=100, group=tp_group);//第三止盈位仓位百分比
//========================================
// 成交量分析参数设置
//========================================
vol_group = "Volume Analysis Settings";//成交量分析参数组
vol_period = input.int(100, "Volume MA Period", minval=1, group=vol_group);//成交量均线周期
vol_high = input.float(2.0, "High Volume Multiplier", minval=1.0, step=0.1, group=vol_group);//高成交量倍数
vol_med = input.float(1.5, "Medium Volume Multiplier", minval=1.0, step=0.1, group=vol_group);//中成交量倍数
vol_low = input.float(1.0, "Low Volume Multiplier", minval=0.5, step=0.1, group=vol_group);//低成交量倍数
vol_high_mult = input.float(1.5, "High Volume Factor", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=vol_group);//高成交量系数
vol_med_mult = input.float(1.3, "Medium Volume Factor", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=vol_group);//中成交量系数
vol_low_mult = input.float(1.0, "Low Volume Factor", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=vol_group);//低成交量系数
//========================================
// 百分位分析参数设置
//========================================
perc_group = "Percentile Analysis Settings";//百分位分析参数组
perc_period = input.int(100, "Percentile Period", minval=20, group=perc_group);//百分位计算周期
perc_high = input.float(90, "High Percentile", minval=50, maxval=100, group=perc_group);//高百分位阈值
perc_med = input.float(80, "Medium Percentile", minval=50, maxval=100, group=perc_group);//中百分位阈值
perc_low = input.float(70, "Low Percentile", minval=0, maxval=100, group=perc_group);//低百分位阈值
perc_high_mult = input.float(1.5, "High Percentile Factor", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=perc_group);//高百分位系数
perc_med_mult = input.float(1.3, "Medium Percentile Factor", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=perc_group);//中百分位系数
perc_low_mult = input.float(1.0, "Low Percentile Factor", minval=0.1, step=0.1, group=perc_group);//低百分位系数
//========================================
// 核心多空力量计算
//========================================
//计算价格的指数移动平均
emaClose = ta.ema(close, lengthInput);
//多头力量:最高价与EMA的差值
bullPower = high - emaClose;
//空头力量:最低价与EMA的差值
bearPower = low - emaClose;
//多空力量平衡:多头力量加上空头力量
bbp = bullPower + bearPower;
//计算分布的高阶矩:均值、标准差、偏度、峰度
calcDistributionMoments(src, length) =>
mean = ta.sma(src, length);//计算均值
variance = ta.variance(src, length);//计算方差
stddev = math.sqrt(variance);//计算标准差
//初始化偏度和峰度累加变量
skew_sum = 0.0;
kurt_sum = 0.0;
//当标准差大于0时,计算偏度和峰度
if stddev > 0
for i = 0 to math.min(length - 1, 100)
z = (src[i] - mean) / stddev;//计算标准化值
z2 = z * z;//计算Z的平方
skew_sum += z * z2;//累加偏度项
kurt_sum += z2 * z2;//累加峰度项
n = math.min(length, 100);//取样本数
skewness = skew_sum / n;//计算偏度
excess_kurtosis = kurt_sum / n - 3.0;//计算超额峰度
[mean, stddev, skewness, excess_kurtosis];//返回四个统计量
//自适应阈值计算:根据分布特征动态调整阈值
calcAdaptiveThreshold(mu, sigma, skew, kurt, alpha, use_adaptive) =>
//计算标准正态分位数(基础Z值)
z_base = math.sqrt(-2.0 * math.log(alpha / 2.0));
z_adjusted = z_base;//初始化调整后的Z值
//如果启用自适应拟合,则进行分布修正
if use_adaptive
//厚尾修正:使用t分布近似,当峰度超过阈值时调整
if math.abs(kurt) > kurt_threshold
df = math.max(6.0 / math.abs(kurt) + 4.0, 5.0);//计算自由度
z_adjusted := z_adjusted * math.sqrt(df / (df - 2.0));//调整Z值
//偏度修正:使用Cornish-Fisher展开式,当偏度超过阈值时调整
if math.abs(skew) > skew_threshold
z_adjusted := z_adjusted + skew * (z_adjusted * z_adjusted - 1.0) / 6.0;//应用偏度修正
//计算上下阈值
upper_threshold = mu + sigma * z_adjusted;
lower_threshold = mu - sigma * z_adjusted;
[upper_threshold, lower_threshold];//返回上下阈值
//执行分布分析:计算BBP的均值、标准差、偏度和峰度
[mu, sigma, skewness, kurtosis] = calcDistributionMoments(bbp, zLength);
//计算自适应阈值:基于统计特征动态确定交易阈值
[upper_threshold, lower_threshold] = calcAdaptiveThreshold(mu, sigma, skewness, kurtosis,
significance_level, auto_fit);
//========================================
// 成交量与百分位分析
//========================================
vol_sma = ta.sma(volume, vol_period);//计算成交量简单移动平均
vol_mult = volume / vol_sma;//计算当前成交量相对于均值的倍数
//计算百分位排名:返回当前值在历史数据中的百分位位置
calcPercentile(src) =>
var values = array.new_float(0);//初始化数组
array.unshift(values, src);//将新值插入数组头部
if array.size(values) > perc_period
array.pop(values);//超过周期长度时删除尾部元素
//计算百分位排名
array.size(values) > 0 ? array.percentrank(values, array.size(values)-1) * 100 : 50;
price_perc = calcPercentile(close);//计算价格百分位
vol_perc = calcPercentile(volume);//计算成交量百分位
//计算止盈系数:综合成交量和价格百分位评分
getTpFactor() =>
//根据成交量倍数评分
vol_score = vol_mult > vol_high ? vol_high_mult : vol_mult > vol_med ? vol_med_mult : vol_mult > vol_low ? vol_low_mult : 0.8;
//根据价格百分位评分
price_score = price_perc > perc_high ? perc_high_mult : price_perc > perc_med ? perc_med_mult : price_perc > perc_low ? perc_low_mult : 0.8;
math.avg(vol_score, price_score);//返回两个评分的平均值
//========================================
// 入场出场逻辑
//========================================
//多头入场条件:BBP向上突破上阈值
longCondition = ta.crossover(bbp, upper_threshold);
//空头入场条件:BBP向下跌破下阈值
shortCondition = ta.crossunder(bbp, lower_threshold);
//多头出场条件:BBP向下跌破均值
exitLongCondition = ta.crossunder(bbp, mu);
//空头出场条件:BBP向上突破均值
exitShortCondition = ta.crossover(bbp, mu);
//========================================
// 交易执行逻辑
//========================================
//在K线确认后执行交易
if (barstate.isconfirmed)
if longCondition
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long);//开多头仓位
if shortCondition
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short);//开空头仓位
if exitLongCondition
strategy.close("Long");//平多头仓位
if exitShortCondition
strategy.close("Short");//平空头仓位
//========================================
// 止盈执行逻辑
//========================================
//当启用止盈且持有仓位时执行止盈逻辑
if useTP and strategy.position_size != 0
base_move = ta.atr(baseAtrLength);//计算基础ATR值
tp_factor = getTpFactor();//获取止盈系数
is_long = strategy.position_size > 0;//判断是否为多头仓位
entry_price = strategy.position_avg_price;//获取入场均价
//多头止盈设置
if is_long
tp1_price = entry_price + (base_move * atrMult1 * tp_factor);//计算第一止盈价
tp2_price = entry_price + (base_move * atrMult2 * tp_factor);//计算第二止盈价
tp3_price = entry_price + (base_move * atrMult3 * tp_factor);//计算第三止盈价
strategy.exit("TP1", "Long", qty_percent=tp1_size, limit=tp1_price);//设置第一止盈
strategy.exit("TP2", "Long", qty_percent=tp2_size, limit=tp2_price);//设置第二止盈
strategy.exit("TP3", "Long", qty_percent=tp3_size, limit=tp3_price);//设置第三止盈
else
//空头止盈设置
tp1_price = entry_price - (base_move * atrMult1 * tp_factor);//计算第一止盈价
tp2_price = entry_price - (base_move * atrMult2 * tp_factor);//计算第二止盈价
tp3_price = entry_price - (base_move * atrMult3 * tp_factor);//计算第三止盈价
strategy.exit("TP1", "Short", qty_percent=tp1_size, limit=tp1_price);//设置第一止盈
strategy.exit("TP2", "Short", qty_percent=tp2_size, limit=tp2_price);//设置第二止盈
strategy.exit("TP3", "Short", qty_percent=tp3_size, limit=tp3_price);//设置第三止盈
//========================================
// 图表绘制
//========================================
//绘制BBP柱状图:多头力量为绿色,空头力量为红色
plot(bbp, color=bbp >= mu ? color.new(color.green, 0) : color.new(color.red, 0),
title="BBPower", style=plot.style_columns);
//绘制均值线
plot(mu, "Mean", color=color.gray, linewidth=1, style=plot.style_line);
//绘制上阈值线
plot(upper_threshold, "Upper Threshold", color=color.orange, linewidth=2);
//绘制下阈值线
plot(lower_threshold, "Lower Threshold", color=color.orange, linewidth=2);
//绘制参考线:正负1倍标准差
plot(mu + sigma, "+1σ", color=color.new(color.blue, 70), linewidth=1, style=plot.style_circles);
plot(mu - sigma, "-1σ", color=color.new(color.blue, 70), linewidth=1, style=plot.style_circles);
//绘制参考线:正负2倍标准差
plot(mu + 2*sigma, "+2σ", color=color.new(color.purple, 70), linewidth=1, style=plot.style_cross);
plot(mu - 2*sigma, "-2σ", color=color.new(color.purple, 70), linewidth=1, style=plot.style_cross);
//========================================
// 信号标记
//========================================
//绘制多头信号标记
plotshape(longCondition, title="Long Signal", location=location.bottom,
color=color.new(color.green, 0), style=shape.labelup, text="LONG",
textcolor=color.white, size=size.small);
//绘制空头信号标记
plotshape(shortCondition, title="Short Signal", location=location.top,
color=color.new(color.red, 0), style=shape.labeldown, text="SHORT",
textcolor=color.white, size=size.small);