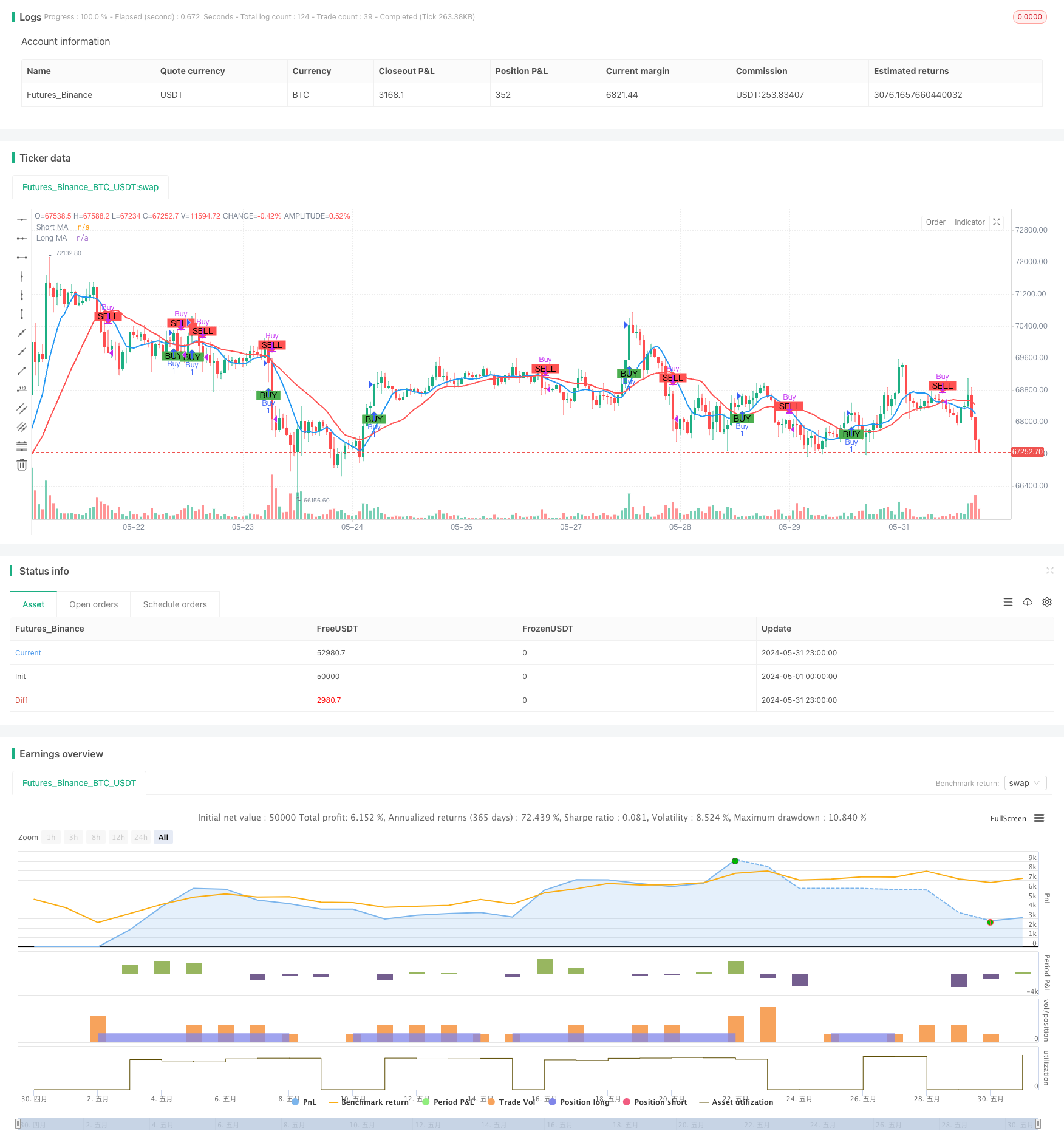
Descripción general
La estrategia de promedio móvil basada en el cruce de dos medias es un método de negociación simple y eficaz para identificar oportunidades de compra y venta potenciales en el mercado mediante el análisis de la relación entre dos promedios móviles de diferentes períodos. La estrategia utiliza una media móvil simple a corto plazo (SMA) y una media móvil simple a largo plazo, que indica una señal de ganancia cuando cruza la media a largo plazo en la media a corto plazo, lo que sugiere una oportunidad de compra potencial; por el contrario, cuando cruza la media a corto plazo por debajo de la media a largo plazo, indica una señal de bajada, lo que sugiere una oportunidad de venta potencial.
Principio de estrategia
El principio central de esta estrategia es utilizar las características de la tendencia y el atraso de los diferentes promedios móviles de período, para determinar la dirección de la tendencia del mercado actual mediante la comparación de la media a corto plazo y la media a largo plazo, para tomar decisiones de negociación correspondientes. Cuando hay una tendencia ascendente en el mercado, los precios rompen primero la media a largo plazo, la media a corto plazo cruza la media a largo plazo y se forma un tenedor de oro para generar una señal de compra; cuando hay una tendencia descendente en el mercado, los precios rompen primero la media a largo plazo, la media a corto plazo cruza la media a largo plazo y se forma un tenedor de oro para generar una señal de venta. En la configuración de los parámetros de esta estrategia, la media a corto plazo es de 9 períodos y la media a largo plazo es de 21 períodos, los dos parámetros pueden ajustarse según las características y preferencias individuales del mercado.
Ventajas estratégicas
- Sencilla y fácil de entender: La estrategia se basa en la teoría clásica de las medias móviles, tiene una lógica clara, es fácil de entender y de implementar.
- Adaptabilidad: La estrategia puede aplicarse a varios mercados y diferentes variedades de operaciones, y puede responder con flexibilidad a diferentes características del mercado mediante el ajuste de la configuración de los parámetros.
- Captura de tendencias: la dirección de las tendencias se determina mediante el cruce de dos líneas equidistantes, lo que ayuda a los comerciantes a seguir las tendencias principales a tiempo y mejorar las oportunidades de ganancias.
- Control de riesgos: La estrategia introduce el concepto de gestión de riesgos, controlando el riesgo de cada operación mediante el ajuste de posiciones y administrando de manera efectiva los posibles pérdidas.
- Reducción del ruido: aprovecha las características de retraso de la línea media para filtrar eficazmente el ruido aleatorio en el mercado y mejorar la fiabilidad de las señales de negociación.
Riesgo estratégico
- Selección de parámetros: los diferentes ajustes de parámetros tienen un impacto importante en el rendimiento de la estrategia, y la elección incorrecta puede causar el fracaso o el mal rendimiento de la estrategia.
- Tendencias del mercado: la estrategia puede tener pérdidas continuas en mercados convulsivos o en puntos de cambio de tendencia.
- Costos de deslizamiento: la frecuencia de las transacciones puede generar costos de deslizamiento más altos que afectan a los beneficios generales de la estrategia.
- Incidentes de cisnes negros: La estrategia es poco adaptada a situaciones extremas, y los eventos de cisnes negros pueden causar grandes pérdidas para la estrategia.
- Riesgo de sobreajuste: Si la optimización de los parámetros depende demasiado de los datos históricos, puede causar que la estrategia no funcione bien en las operaciones reales.
Dirección de optimización de la estrategia
- Optimización de parámetros dinámicos: ajuste dinámico de los parámetros de la estrategia según los cambios en el estado del mercado, mejora de la adaptabilidad.
- Confirmación de tendencias: después de generar una señal de negociación, se introducen otros indicadores o patrones de comportamiento de precios para confirmar tendencias y mejorar la fiabilidad de la señal.
- Bloqueo de pérdidas: Introducción de un mecanismo de bloqueo de pérdidas razonable para controlar aún más el umbral de riesgo de las operaciones individuales.
- Gestión de posiciones: métodos para optimizar los ajustes de posiciones, como la introducción de indicadores de volatilidad y el ajuste dinámico de las posiciones en función de los niveles de fluctuación del mercado.
- Evaluación de la fuerza múltiple: evalúa la relación entre la fuerza múltiple y la fuerza no múltiple, interviene en el inicio de la tendencia y mejora la precisión de la captura de tendencias.
Resumir
La estrategia de promedio móvil basada en el cruce de dos líneas de medias es un método de negociación diaria simple y práctico para determinar la dirección de la tendencia del mercado y generar señales de negociación mediante la comparación de la posición de las diferentes líneas de medias periódicas. La lógica de la estrategia es clara, adaptable y puede capturar efectivamente la tendencia del mercado, al tiempo que introduce medidas de gestión de riesgos para controlar las pérdidas potenciales.
Overview
The Moving Average Crossover Strategy based on dual moving averages is a straightforward and effective intraday trading approach designed to identify potential buy and sell opportunities in the market by analyzing the relationship between two moving averages of different periods. This strategy utilizes a short-term simple moving average (SMA) and a long-term simple moving average. When the short-term moving average crosses above the long-term moving average, it indicates a bullish signal, suggesting a potential buying opportunity. Conversely, when the short-term moving average crosses below the long-term moving average, it indicates a bearish signal, suggesting a potential selling opportunity. This crossover method helps traders capture trending moves in the market while minimizing market noise interference.
Strategy Principle
The core principle of this strategy is to utilize the trend characteristics and lag of moving averages with different periods. By comparing the relative position relationship between the short-term moving average and the long-term moving average, it determines the current market trend direction and makes corresponding trading decisions. When an upward trend emerges in the market, the price will first break through the long-term moving average, and the short-term moving average will subsequently cross above the long-term moving average, forming a golden cross and generating a buy signal. When a downward trend emerges in the market, the price will first break below the long-term moving average, and the short-term moving average will subsequently cross below the long-term moving average, forming a death cross and generating a sell signal. In the parameter settings of this strategy, the period of the short-term moving average is set to 9, and the period of the long-term moving average is set to 21. These two parameters can be adjusted based on market characteristics and personal preferences. Additionally, this strategy introduces the concept of money management by setting the initial capital and risk percentage per trade, using position sizing to control the risk exposure of each trade.
Strategy Advantages
- Simplicity: This strategy is based on the classic moving average theory, with clear logic and easy to understand and implement.
- Adaptability: This strategy can be applied to multiple markets and different trading instruments. By adjusting parameter settings, it can flexibly adapt to different market characteristics.
- Trend Capture: By using the dual moving average crossover to determine the trend direction, it helps traders timely follow the mainstream trend and increase profit opportunities.
- Risk Control: This strategy introduces the concept of risk management, using position sizing to control the risk exposure of each trade, effectively managing potential losses.
- Noise Reduction: By utilizing the lag characteristic of moving averages, it effectively filters out random noise in the market, improving the reliability of trading signals.
Strategy Risks
- Parameter Selection: Different parameter settings can have a significant impact on strategy performance. Improper selection may lead to strategy failure or poor performance.
- Market Trend: In ranging markets or trend turning points, this strategy may experience consecutive losses.
- Slippage Costs: Frequent trading may result in higher slippage costs, affecting the overall profitability of the strategy.
- Black Swan Events: This strategy has poor adaptability to extreme market conditions, and black swan events may cause significant losses to the strategy.
- Overfitting Risk: If parameter optimization relies too heavily on historical data, it may lead to poor performance of the strategy in actual trading.
Strategy Optimization Directions
- Dynamic Parameter Optimization: Dynamically adjust strategy parameters based on changes in market conditions to improve adaptability.
- Trend Confirmation: After generating trading signals, introduce other indicators or price behavior patterns to confirm the trend, improving signal reliability.
- Stop-Loss and Take-Profit: Introduce reasonable stop-loss and take-profit mechanisms to further control the risk exposure of each trade.
- Position Management: Optimize the position sizing method, such as introducing volatility indicators to dynamically adjust positions based on market volatility levels.
- Long-Short Strength Assessment: Assess the comparative relationship between bullish and bearish strengths, entering at the early stage of a trend to improve the accuracy of trend capture.
Summary
The Moving Average Crossover Strategy based on dual moving averages is a simple and practical intraday trading method. By comparing the position relationship of moving averages with different periods, it determines the market trend direction and generates trading signals. This strategy has clear logic, strong adaptability, and can effectively capture market trends while introducing risk management measures to control potential losses. However, this strategy also has potential risks such as parameter selection, trend reversal, frequent trading, etc. It needs to be further improved through dynamic optimization, signal confirmation, position management, and other methods to enhance the robustness and profitability of the strategy. In general, as a classic technical analysis indicator, the basic principles and practical application value of moving averages have been widely verified by the market. It is a trading strategy worthy of in-depth research and continuous optimization.
/*backtest
start: 2024-05-01 00:00:00
end: 2024-05-31 23:59:59
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("Moving Average Crossover Strategy", overlay=true)
// Input parameters
shortLength = input.int(9, title="Short Moving Average Length")
longLength = input.int(21, title="Long Moving Average Length")
capital = input.float(100000, title="Initial Capital")
risk_per_trade = input.float(1.0, title="Risk Per Trade (%)")
// Calculate Moving Averages
shortMA = ta.sma(close, shortLength)
longMA = ta.sma(close, longLength)
// Plot Moving Averages
plot(shortMA, title="Short MA", color=color.blue, linewidth=2)
plot(longMA, title="Long MA", color=color.red, linewidth=2)
// Generate Buy/Sell signals
longCondition = ta.crossover(shortMA, longMA)
shortCondition = ta.crossunder(shortMA, longMA)
// Plot Buy/Sell signals
plotshape(series=longCondition, title="Buy Signal", location=location.belowbar, color=color.green, style=shape.labelup, text="BUY")
plotshape(series=shortCondition, title="Sell Signal", location=location.abovebar, color=color.red, style=shape.labeldown, text="SELL")
// Risk management: calculate position size
risk_amount = capital * (risk_per_trade / 100)
position_size = risk_amount / close
// Execute Buy/Sell orders with position size
if (longCondition)
strategy.entry("Buy", strategy.long, qty=1, comment="Buy")
if (shortCondition)
strategy.close("Buy", comment="Sell")
// Display the initial capital and risk per trade on the chart
var label initialLabel = na
if (na(initialLabel))
initialLabel := label.new(x=bar_index, y=high, text="Initial Capital: " + str.tostring(capital) + "\nRisk Per Trade: " + str.tostring(risk_per_trade) + "%", style=label.style_label_down, color=color.white, textcolor=color.black)
else
label.set_xy(initialLabel, x=bar_index, y=high)