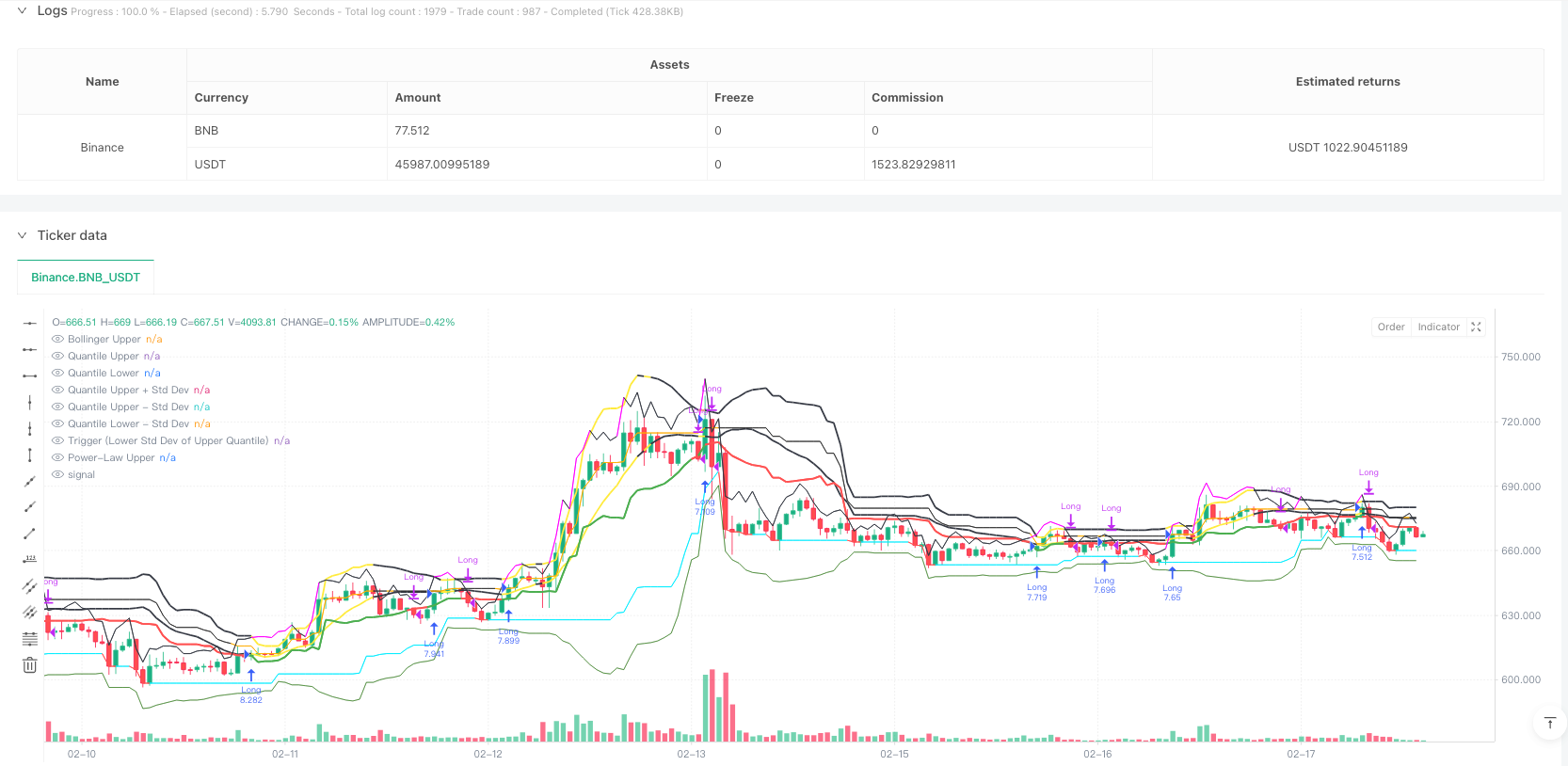
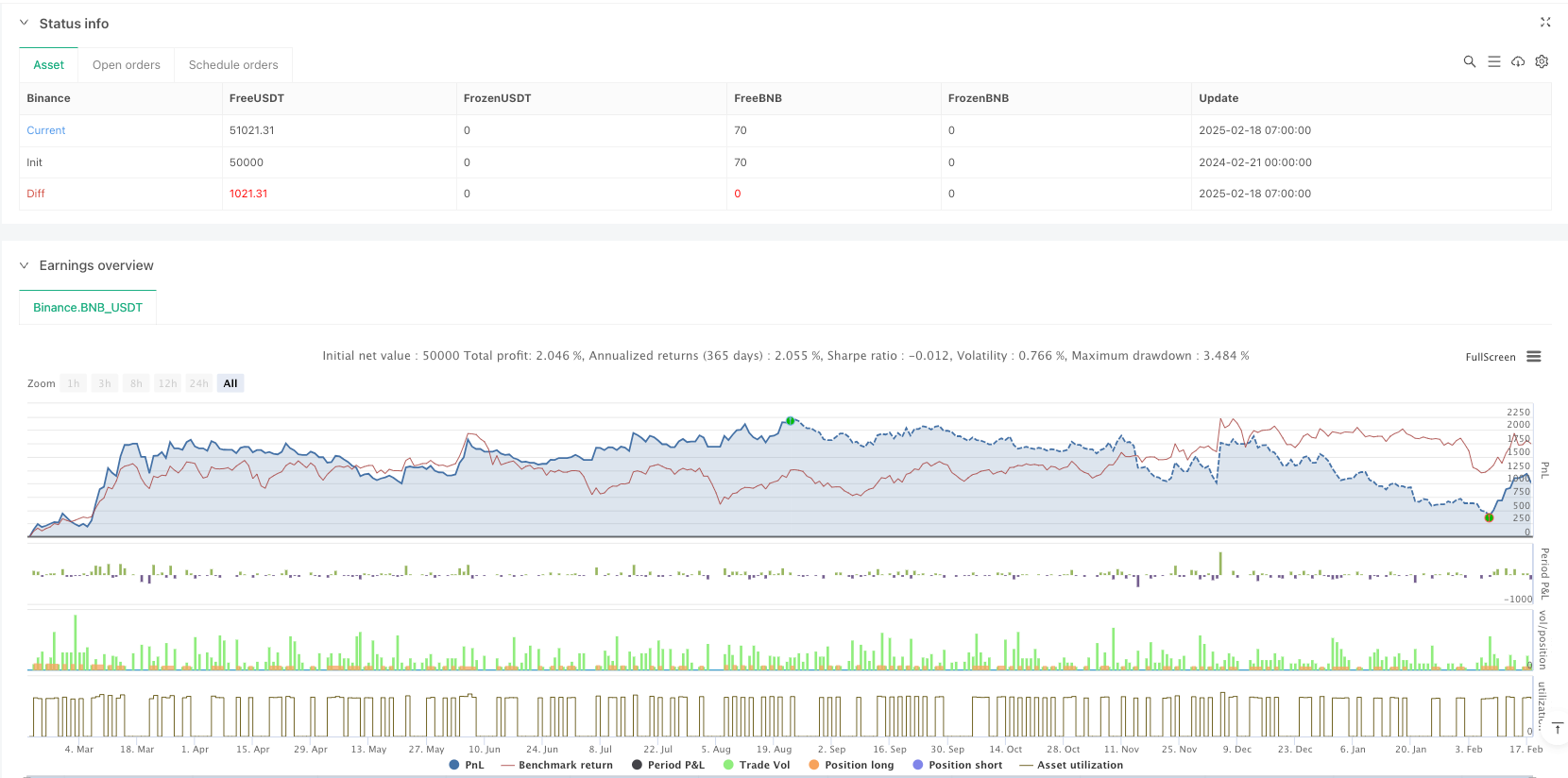
Descripción general
Se trata de una estrategia de negociación basada en el análisis de múltiples bandas estadísticas y tendencias. La estrategia combina el uso de bandas de Brin, bandas de parámetros y la ley de la brecha para identificar las áreas clave de soporte / resistencia, y utiliza la diferencia estándar inferior de las bandas de parámetros superiores como señal de activación para determinar el momento de entrada y salida.
Principio de estrategia
El principio central de la estrategia es capturar las tendencias del mercado a través de la intersección de múltiples bandas estadísticas. La estrategia contiene principalmente los siguientes componentes clave:
- El sistema de bandas de Brin - utilizado para determinar el rango de fluctuación de los precios, se convierte en una alerta amarilla cuando los precios se desvian.
- Sistema de bandas de dígitos - para calcular los dígitos superiores y inferiores de los precios, y para evaluar la probabilidad de los valores máximos de los precios.
- El sistema de bandas rectangulares - que calcula el nivel de significancia basado en los retornos históricos - se usa para medir el exceso de compra y venta.
- Sistema de activación - la línea de diferencia estándar inferior de la franja de dígitos superior es la señal de activación principal, y el precio se mantiene por encima de esta línea como una señal de avance.
- Sistema de confirmación - Filtra las señales falsas mediante la configuración de un número de líneas K de confirmación en serie.
Ventajas estratégicas
- La estabilidad de la señal es alta - el uso superpuesto de múltiples bandas estadísticas puede reducir eficazmente las señales falsas.
- Adaptabilidad - Las estrategias pueden adaptarse a diferentes períodos de tiempo y condiciones de mercado.
- Control de riesgos perfecto - Dividir las zonas de riesgo con múltiples estadísticas y un mecanismo de deterioro.
- Flexibilidad de parámetros - Ofrece una gran variedad de opciones de parámetros que se pueden optimizar según las diferentes características del mercado.
- Visualización clara: las líneas de los indicadores son claramente distinguidas en color y las señales de negociación son intuitivas.
Riesgo estratégico
- Riesgo de retraso - Las estadísticas tienen un cierto retraso y pueden perder el mejor punto de entrada.
- Los mercados convulsivos son desfavorables - puede haber demasiadas señales de negociación en los mercados convulsivos horizontales.
- Sensibilidad de los parámetros - Diferentes combinaciones de parámetros tienen una gran diferencia de efecto y requieren una optimización repetida.
- Gran carga de cálculo - El cálculo en tiempo real de múltiples indicadores estadísticos requiere grandes recursos de cálculo.
- Dependencia del entorno de mercado - Las reglas estadísticas pueden fallar en un entorno de mercado extremo.
Dirección de optimización de la estrategia
- Introducción de parámetros dinámicos - ajuste automático de los parámetros en función de la volatilidad del mercado.
- Incrementar el juicio del entorno del mercado - Añadir indicadores de intensidad de tendencia para filtrar las señales de mercado oscilantes.
- Optimización de la eficiencia de la computación - simplificar parte del proceso de computación y reducir la ocupación de recursos.
- Mejora en el control de riesgos - añade más condiciones de stop loss y estrategias de gestión de posiciones.
- Mejorar la adaptabilidad - Desarrollar sistemas de optimización de parámetros de tipo adaptativo.
Resumir
Se trata de una estrategia integral de seguimiento de tendencias que combina varios métodos estadísticos. Gracias a la sinergia de las bandas de Brin, las bandas de dígitos y las bandas de lógica, se puede comprender mejor las tendencias del mercado, al tiempo que se tiene una buena capacidad de control de riesgos. Aunque existe cierto retraso y dificultad para optimizar los parámetros, la estrategia tiene un buen valor práctico y perspectivas de desarrollo mediante la mejora y optimización continuas.
/*backtest
start: 2024-02-21 00:00:00
end: 2025-02-18 08:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Binance","currency":"BNB_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=6
strategy("Multi-Band Comparison Strategy with Separate Entry/Exit Confirmation", overlay=true,
default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value=10,
initial_capital=5000, currency=currency.USD)
// === Inputs ===
// Basic Parameters
length = input.int(20, "Length (SMA)", minval=1)
boll_mult = input.float(1.0, "Bollinger Band Multiplier", minval=0.1, step=0.1)
upper_quantile = input.float(0.95, "Upper Quantile (0.0-1.0)", minval=0.0, maxval=1.0)
lower_quantile = input.float(0.05, "Lower Quantile (0.0-1.0)", minval=0.0, maxval=1.0)
// Separate confirmation inputs
entry_confirmBars = input.int(1, "Entry Confirmation Bars", minval=1, tooltip="Number of consecutive bars the entry condition must hold")
exit_confirmBars = input.int(1, "Exit Confirmation Bars", minval=1, tooltip="Number of consecutive bars the exit condition must hold")
// Toggle Visibility for Bands
show_lower_boll = input.bool(false, "Show Lower Bollinger Band", tooltip="Enable or disable the lower Bollinger Band")
show_upper_boll = input.bool(true, "Show Upper Bollinger Band", tooltip="Enable or disable the upper Bollinger Band")
show_lower_quant = input.bool(true, "Show Lower Quantile Band", tooltip="Enable or disable the lower Quantile Band")
show_upper_quant = input.bool(true, "Show Upper Quantile Band", tooltip="Enable or disable the upper Quantile Band")
show_upper_power = input.bool(true, "Show Upper Power-Law Band", tooltip="Enable or disable the upper Power-Law Band")
show_lower_power = input.bool(false, "Show Lower Power-Law Band", tooltip="Enable or disable the lower Power-Law Band")
show_quant_std = input.bool(true, "Show Standard Deviation around Quantile Bands", tooltip="Enable or disable standard deviation lines around Quantile Bands")
// Individual Toggles for Std Dev Lines
show_upper_quant_std_up = input.bool(true, "Show Upper Quantile + Std Dev", tooltip="Enable or disable the Upper Quantile + Std Dev line")
show_upper_quant_std_down = input.bool(true, "Show Upper Quantile - Std Dev", tooltip="Enable or disable the Upper Quantile - Std Dev line")
show_lower_quant_std_up = input.bool(false, "Show Lower Quantile + Std Dev", tooltip="Enable or disable the Lower Quantile + Std Dev line")
show_lower_quant_std_down = input.bool(true, "Show Lower Quantile - Std Dev", tooltip="Enable or disable the Lower Quantile - Std Dev line")
// Moving Average Toggles
show_ema = input.bool(false, "Show EMA", tooltip="Enable or disable the Exponential Moving Average")
show_sma = input.bool(false, "Show SMA", tooltip="Enable or disable the Simple Moving Average")
// EMA Parameters
ema_length = input.int(50, minval=1, title="EMA Length")
ema_source = input.source(close, title="EMA Source")
// === Data Handling ===
// Create persistent arrays to store data
var float[] data_array = array.new_float()
var float[] return_array = array.new_float()
// Update the data array with the latest close prices
if array.size(data_array) < length
array.push(data_array, close)
else
array.shift(data_array)
array.push(data_array, close)
// Update the return array with the latest returns
returns = close / close[1] - 1
if array.size(return_array) < length
array.push(return_array, returns)
else
array.shift(return_array)
array.push(return_array, returns)
// === Helper Function ===
// Function to calculate a custom percentile
f_percentile(arr, quantile) =>
arr_sorted = array.copy(arr)
array.sort(arr_sorted, order.ascending)
index = math.round((array.size(arr_sorted) - 1) * quantile)
array.get(arr_sorted, index)
// === Calculations ===
// Bollinger Bands Calculation
sma = ta.sma(close, length)
stdev = ta.stdev(close, length)
boll_upper = sma + boll_mult * stdev
boll_lower = sma - boll_mult * stdev
// Power-Law Bands Calculation
var float power_upper = na
var float power_lower = na
if array.size(return_array) == length
power_upper := f_percentile(return_array, upper_quantile)
power_lower := f_percentile(return_array, lower_quantile)
var float power_upper_band = na
var float power_lower_band = na
if not na(power_upper) and not na(power_lower)
power_upper_band := close * (1 + power_upper)
power_lower_band := close * (1 + power_lower)
// Quantile Bands Calculation
var float quant_upper = na
var float quant_lower = na
if array.size(data_array) == length
quant_upper := f_percentile(data_array, upper_quantile)
quant_lower := f_percentile(data_array, lower_quantile)
// Standard Deviation around Quantile Bands
quant_upper_std_up = quant_upper + stdev
quant_upper_std_down = quant_upper - stdev
quant_lower_std_up = quant_lower + stdev
quant_lower_std_down = quant_lower - stdev
// === Color Calculations ===
// For the upper Bollinger band, color it yellow when price is above it, black otherwise.
upper_boll_color = close > boll_upper ? color.yellow : color.black
// The entry/exit trigger is based on the lower std dev band of the upper quantile band.
// It "turns green" (i.e. favorable for entry) when the price is above this level,
// and "turns red" (i.e. unfavorable, triggering an exit) when price is below it.
triggerCondition = close > quant_upper_std_down
// For plotting purposes, define the color of the lower std dev band of the upper quantile band:
triggerColor = triggerCondition ? color.green : color.red
// (Other color definitions remain for the additional bands.)
upper_power_color = (not na(power_upper_band) and not na(quant_upper_std_up) and power_upper_band > quant_upper_std_up) ? color.new(#FF00FF, 0) : color.black
upper_quant_color = (not na(quant_upper) and not na(power_upper_band) and power_upper_band > quant_upper) ? color.new(#FFAE00, 0) : color.rgb(50, 50, 50)
upper_quant_std_down_color = (not na(quant_upper_std_down) and close > quant_upper_std_down) ? color.green : color.red
lower_quant_std_down_color = (not na(quant_lower_std_down) and close > quant_lower_std_down) ? color.rgb(24, 113, 0, 44) : color.red
lower_quant_color = (ta.cross(close, quant_lower) or close == quant_lower) ? color.red : color.rgb(0, 238, 255)
// For demonstration, a variable to toggle a color on the Bollinger crossover.
var color upper_quant_std_up_color = color.black
if ta.crossover(close, boll_upper)
upper_quant_std_up_color := color.yellow
if ta.crossunder(close, boll_upper)
upper_quant_std_up_color := color.black
// === Confirmation Bars Logic with Separate Counters Based on Trigger Condition ===
// Use the trigger condition (based on the lower std dev band of the upper quantile band)
// for entry/exit confirmation.
var int entryCounter = 0
var int exitCounter = 0
// When triggerCondition is true (price above quant_upper_std_down) the "green" state holds.
entryCounter := triggerCondition ? entryCounter + 1 : 0
// When triggerCondition is false (price below quant_upper_std_down) the "red" state holds.
exitCounter := not triggerCondition ? exitCounter + 1 : 0
// === Strategy Orders ===
// Enter long when triggerCondition has been true for at least entry_confirmBars bars and no position is active.
if (entryCounter >= entry_confirmBars) and (strategy.position_size <= 0)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
// Exit long when triggerCondition has been false for at least exit_confirmBars bars and a long position is active.
if (exitCounter >= exit_confirmBars) and (strategy.position_size > 0)
strategy.close("Long")
// === Plotting ===
// Plot Bollinger Bands
plot(show_upper_boll ? boll_upper : na, color=upper_boll_color, title="Bollinger Upper", linewidth=2)
plot(show_lower_boll ? boll_lower : na, color=color.red, title="Bollinger Lower", linewidth=1)
// Plot Power-Law Bands
plot(show_upper_power ? power_upper_band : na, color=upper_power_color, title="Power-Law Upper", linewidth=1)
plot(show_lower_power ? power_lower_band : na, color=color.rgb(255, 59, 248), title="Power-Law Lower", linewidth=1)
// Plot Quantile Bands
plot(show_upper_quant ? quant_upper : na, color=upper_quant_color, title="Quantile Upper", linewidth=1)
plot(show_lower_quant ? quant_lower : na, color=lower_quant_color, title="Quantile Lower", linewidth=1)
// Plot Standard Deviation around Quantile Bands
plot(show_quant_std and show_upper_quant and show_upper_quant_std_up ? quant_upper_std_up : na, color=upper_quant_std_up_color, title="Quantile Upper + Std Dev", linewidth=2)
plot(show_quant_std and show_upper_quant and show_upper_quant_std_down ? quant_upper_std_down : na, color=upper_quant_std_down_color, title="Quantile Upper - Std Dev", linewidth=2)
plot(show_quant_std and show_lower_quant and show_lower_quant_std_up ? quant_lower_std_up : na, color=color.green, title="Quantile Lower + Std Dev", linewidth=1)
plot(show_quant_std and show_lower_quant and show_lower_quant_std_down ? quant_lower_std_down : na, color=lower_quant_std_down_color, title="Quantile Lower - Std Dev", linewidth=1)
// Also plot the trigger line (lower std dev band of upper quantile band) with its own color
plot(show_quant_std ? quant_upper_std_down : na, color=triggerColor, title="Trigger (Lower Std Dev of Upper Quantile)", linewidth=2)
// Plot SMA for reference
plot(show_sma ? sma : na, color=color.rgb(0, 24, 132), title="SMA", linewidth=3)
// Plot EMA for reference
ema_value = ta.ema(ema_source, ema_length)
plot(show_ema ? ema_value : na, color=color.rgb(147, 0, 0), title="EMA", linewidth=2)