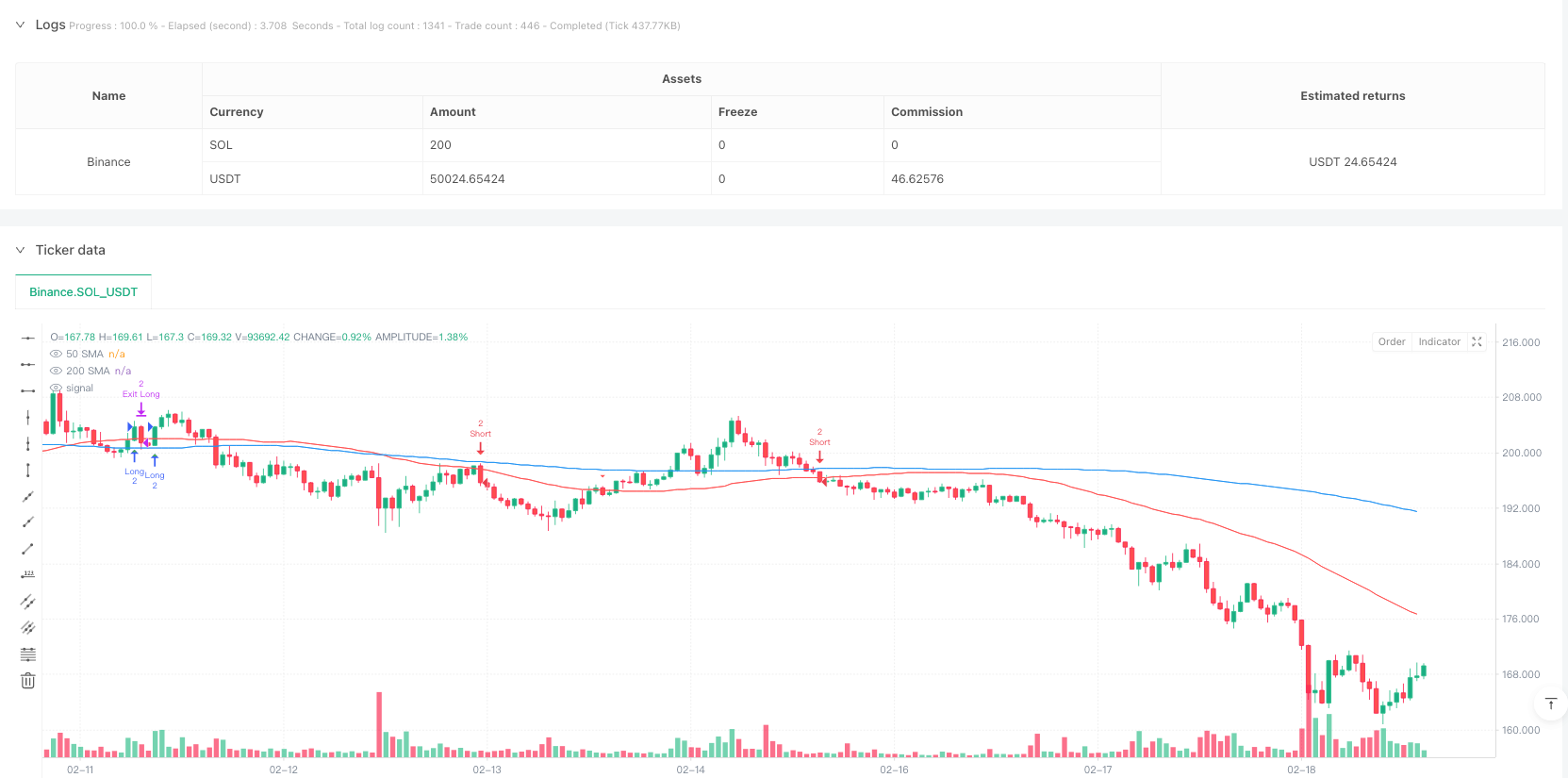
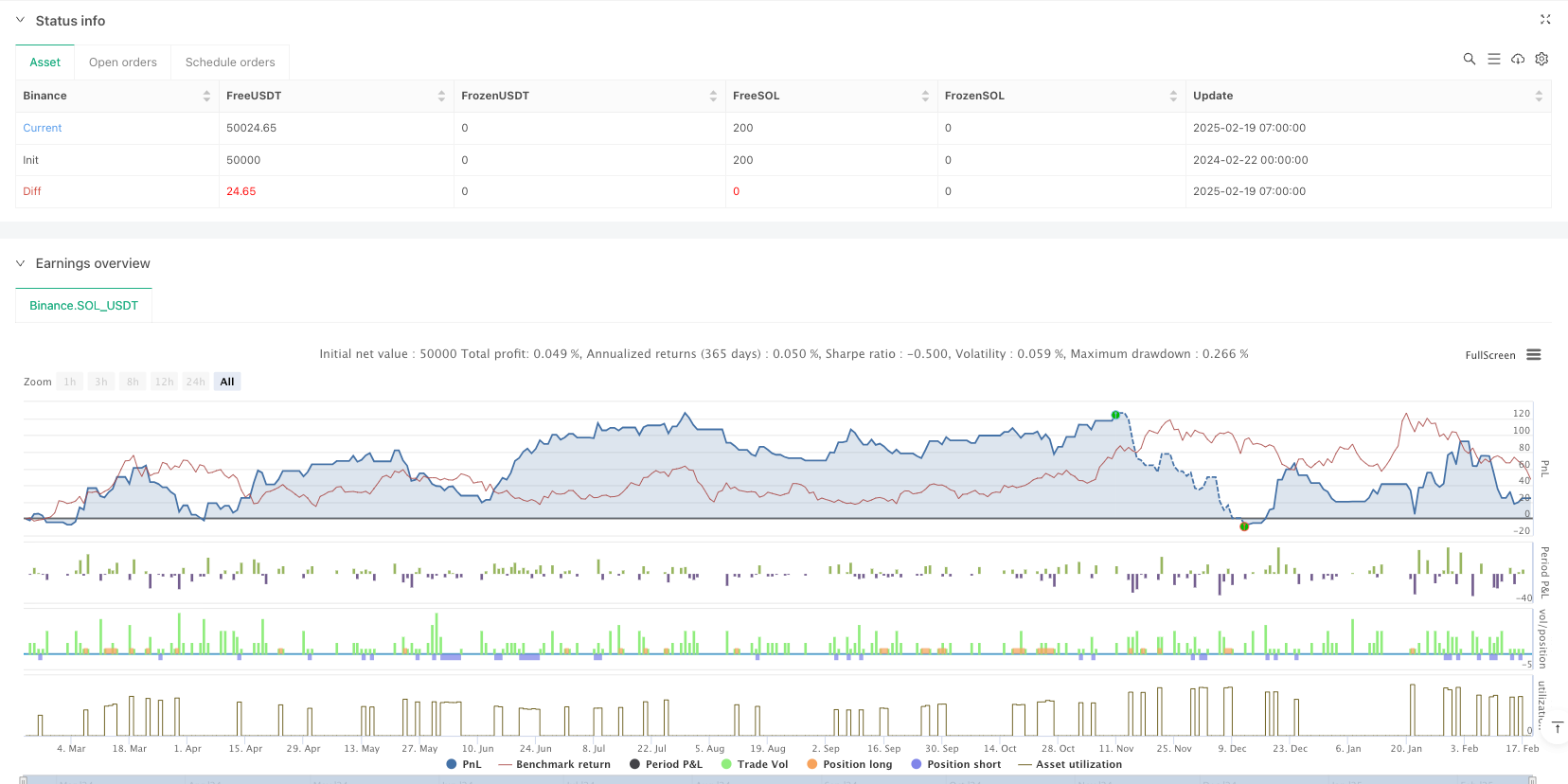
Descripción general
Esta estrategia es un sistema de negociación automatizado basado en el cruce de líneas y la gestión de posiciones dinámicas. Utiliza el promedio móvil simple de 50 y 200 días (SMA) como indicador principal, combinado con el ajuste de posiciones dinámicas y el mecanismo de seguimiento de las paradas, para buscar oportunidades de negociación en las tendencias del mercado. El núcleo de la estrategia es determinar la dirección del mercado a través de la relación entre el precio y la línea de equilibrio, mientras que se aplica la gestión de fondos y el control de riesgos para garantizar la estabilidad de las transacciones.
Principio de estrategia
La estrategia se basa en los siguientes principios centrales:
- Las señales de entrada se basan en el cruce de precios con la línea media de 50 días, mientras que se hace referencia a la posición relativa de la línea media de 50 días con la línea media de 200 días para determinar la tendencia general
- Cuando el precio se rompe por debajo de la línea media, se activa la señal de más; a la inversa, se activa la señal de menos
- La gestión de posiciones adopta un mecanismo de ajuste dinámico, que aumenta el número de posiciones cuando la ganancia de la cuenta supera los 4000
- El Stop Loss utiliza un mecanismo de seguimiento de stop loss, que ajusta dinámicamente la posición de stop loss a medida que aumenta la ganancia
- El riesgo-beneficio se establece en una proporción de 1:2,5, lo que garantiza que los beneficios esperados de cada transacción sean mayores que el riesgo
Ventajas estratégicas
- La lógica de negociación es clara y clara, combinada con indicadores técnicos y comportamiento de precios para determinar el momento de entrada
- La administración de posiciones dinámicas permite aumentar el tamaño de las operaciones y la eficiencia de la utilización de los fondos cuando se obtienen ganancias.
- El mecanismo de trazabilidad de los stop-losses es eficaz para bloquear las ganancias y evitar retiros masivos.
- Se ha configurado un filtro de horario para operar solo durante las horas de mayor actividad, evitando el riesgo de periodos de baja liquidez
- Controles de riesgo adecuados, incluidos objetivos de pérdidas y ganancias y gestión de posiciones
Riesgo estratégico
- Puede desencadenar falsas brechas frecuentes en mercados convulsionados, lo que lleva a paros continuos
- La gestión dinámica de posiciones puede generar grandes pérdidas en el caso de cambios bruscos en el mercado
- La dependencia de un sistema lineal puede retrasarse en un mercado con rápidas fluctuaciones
- El riesgo-beneficio fijo puede perder algunas oportunidades potenciales de grandes tendencias
- Las restricciones de horario podrían perder oportunidades importantes de mercado
Dirección de optimización de la estrategia
- Puede introducir indicadores de volatilidad para ajustar los parámetros de forma dinámica en diferentes entornos de mercado
- Considere agregar un indicador de sentimiento en el mercado para mejorar la precisión de las señales de entrada
- Optimizar el seguimiento de los parámetros de stop loss para adaptarlos mejor a diferentes entornos del mercado
- Aumentar el análisis de múltiples ciclos de tiempo y mejorar la estabilidad de los sistemas de negociación
- Introducción de análisis de tráfico para mejorar la fiabilidad de la señal
Resumir
La estrategia combina un sistema de línea uniforme, gestión dinámica de posiciones y un mecanismo de seguimiento de los estancamientos para construir un sistema de negociación relativamente completo. La estrategia tiene la ventaja de tener una lógica de negociación clara y un mecanismo de control de riesgo completo, pero también hay algunas áreas que necesitan ser optimizadas.
/*backtest
start: 2024-02-22 00:00:00
end: 2025-02-19 08:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Binance","currency":"SOL_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("15m - Rebound 50SMA with Dynamic Lots & Trailing Stop, RRR 2:1, Date Filter (Closed Bars Only)",
overlay=true,
initial_capital=50000,
default_qty_type=strategy.fixed,
default_qty_value=1,
pyramiding=0,
calc_on_order_fills=true)
// ===== INPUTS =====
sma50Period = input.int(50, "50 SMA Period", minval=1)
sma200Period = input.int(200, "200 SMA Period", minval=1)
// ===== CALCULATE SMAs =====
sma50 = ta.sma(close, sma50Period)
sma200 = ta.sma(close, sma200Period)
// ===== PLOT SMAs =====
plot(sma50, color=color.red, title="50 SMA")
plot(sma200, color=color.blue, title="200 SMA")
// ===== DEFINE TRADING SESSIONS =====
// Trading is allowed 15 minutes after market open:
// - New York: 09:45–16:00 (America/New_York)
// - London: 08:15–16:00 (Europe/London)
nySession = not na(time("15", "0945-1600", "America/New_York"))
londonSession = not na(time("15", "0815-1600", "Europe/London"))
inSession = nySession or londonSession
// ===== DEFINE DATE RANGE =====
// Only allow orders on or after January 1, 2024.
// (We include seconds in the timestamp for proper parsing.)
startDate = timestamp("UTC", 2024, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0)
inDateRange = time >= startDate
// ===== DEFINE ENTRY CONDITIONS =====
// ----- LONG ENTRY CONDITION -----
// A long entry is triggered when:
// - The previous candle closed below the 50 SMA and the current candle closes above it,
// - And the 50 SMA is above the 200 SMA.
longCondition = (close[1] < sma50[1]) and (close > sma50) and (sma50 > sma200)
// ----- SHORT ENTRY CONDITION -----
// A short entry is triggered when:
// - The previous candle closed above the 50 SMA and the current candle closes below it,
// - And the 50 SMA is below the 200 SMA.
shortCondition = (close[1] > sma50[1]) and (close < sma50) and (sma50 < sma200)
// ===== DEBUG PLOTS =====
plotshape(longCondition and barstate.isconfirmed, title="Long Signal", location=location.belowbar, color=color.green, style=shape.triangleup, size=size.tiny)
plotshape(shortCondition and barstate.isconfirmed, title="Short Signal", location=location.abovebar, color=color.red, style=shape.triangledown, size=size.tiny)
// ===== VARIABLES FOR STOP LOSS MANAGEMENT =====
// For long positions.
var float initialLongStop = na // Set at entry: low of the rebound candle.
var float trailStopLong = na // Updated trailing stop for long.
// For short positions.
var float initialShortStop = na // Set at entry: high of the rebound candle.
var float trailStopShort = na // Updated trailing stop for short.
// ===== DYNAMIC LOT SIZE =====
// If current profit (strategy.equity - 50000) exceeds 4000, lot size becomes 3; otherwise, 2.
lotSize = (strategy.equity - 50000 > 4000) ? 3 : 2
// ===== ENTRY LOGIC (EXECUTED ON CONFIRMED BARS) =====
if barstate.isconfirmed and inSession and inDateRange and longCondition and strategy.position_size <= 0
initialLongStop := low
trailStopLong := initialLongStop
if strategy.position_size < 0
strategy.close("Short", comment="Close Short before Long")
// Submit a market order entry (no offset).
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long, qty=lotSize, comment="Enter Long")
if barstate.isconfirmed and inSession and inDateRange and shortCondition and strategy.position_size >= 0
initialShortStop := high
trailStopShort := initialShortStop
if strategy.position_size > 0
strategy.close("Long", comment="Close Long before Short")
// Submit a market order entry (no offset).
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short, qty=lotSize, comment="Enter Short")
// ===== TRAILING STOP LOGIC & EXIT ORDERS (ON CLOSED BARS) =====
if barstate.isconfirmed and strategy.position_size > 0
// For Long Positions:
floatingProfitLong = (close - strategy.position_avg_price) / syminfo.mintick
newTrailLong = trailStopLong // Default: no change.
if floatingProfitLong >= 20 and floatingProfitLong < 30
newTrailLong := initialLongStop + 5 * syminfo.mintick
else if floatingProfitLong >= 31 and floatingProfitLong < 40
newTrailLong := initialLongStop + 10 * syminfo.mintick
else if floatingProfitLong >= 41 and floatingProfitLong < 50
newTrailLong := initialLongStop + 15 * syminfo.mintick
// Update trailing stop only if the new value is more favorable.
trailStopLong := math.max(trailStopLong, newTrailLong)
longRisk = strategy.position_avg_price - trailStopLong
tpLong = strategy.position_avg_price + 2.5 * longRisk
strategy.exit("Exit Long", from_entry="Long", stop=trailStopLong, limit=tpLong)
if barstate.isconfirmed and strategy.position_size < 0
// For Short Positions:
floatingProfitShort = (strategy.position_avg_price - close) / syminfo.mintick
newTrailShort = trailStopShort // Default: no change.
if floatingProfitShort >= 20 and floatingProfitShort < 30
newTrailShort := initialShortStop - 5 * syminfo.mintick
else if floatingProfitShort >= 31 and floatingProfitShort < 40
newTrailShort := initialShortStop - 10 * syminfo.mintick
else if floatingProfitShort >= 41 and floatingProfitShort < 50
newTrailShort := initialShortStop - 15 * syminfo.mintick
// Update trailing stop only if the new value is more favorable.
trailStopShort := math.min(trailStopShort, newTrailShort)
shortRisk = trailStopShort - strategy.position_avg_price
tpShort = strategy.position_avg_price - 2.5 * shortRisk
strategy.exit("Exit Short", from_entry="Short", stop=trailStopShort, limit=tpShort)