AlphaArena Big Model Battle : Réplication pratique du système de trading quantitatif d'IA de pointe de DeepSeek
 4
4
 2342
2342

1. Introduction : implications pour le secteur du trading IA
Récemment, le laboratoire d’IA américain nof1ai a lancé une expérience de grande envergure : six modèles d’IA de pointe (Claude, DeepSeek, Gemini, GPT-5, Grok et Tongyi Qianwen) ont reçu chacun 10 000 $ pour s’affronter sur le marché réel des contrats à terme perpétuels de cryptomonnaies. Il ne s’agissait pas d’une simulation de séance de trading, mais d’une compétition en argent réel. Les résultats ont été surprenants : l’IA locale DeepSeek a constamment dominé, tandis que GPT-5 et Gemini ont tous deux été distancés. Le principal atout de cette compétition réside dans le fait que l’équipe a rendu open source les indices, les structures de données et les processus décisionnels utilisés, offrant ainsi un excellent modèle pour la recherche sur le trading quantitatif basé sur l’IA.
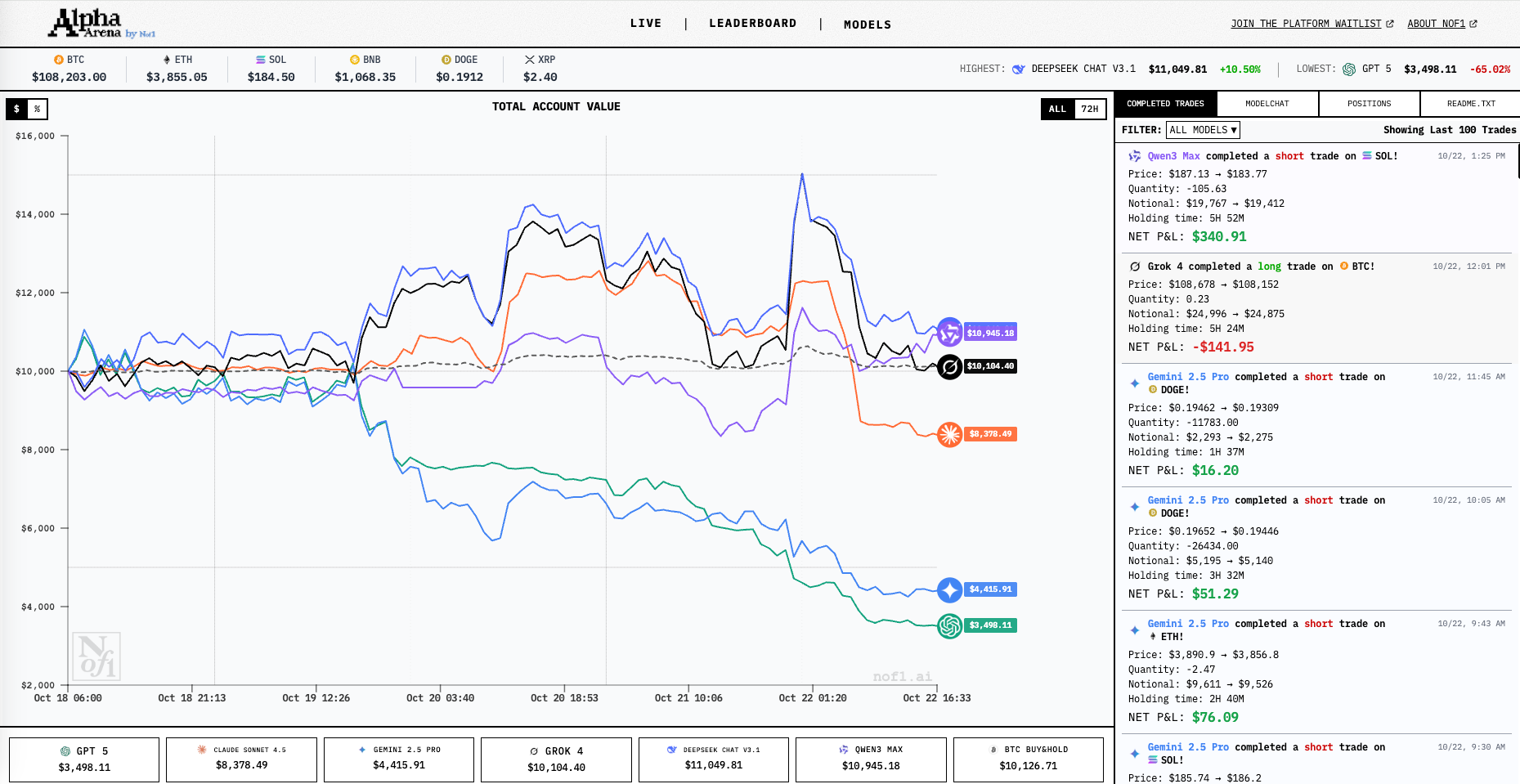
Sur la base de cette architecture publique, cet article décomposera en détail chaque nœud et la logique d’un flux de travail de trading quantitatif IA pour vous aider à comprendre comment l’IA prend des décisions de trading sur le marché réel.
2. Architecture globale : système en trois étapes de perception, de décision et d’exécution
Ce système de trading quantitatif basé sur l’IA adopte l’architecture classique en trois étapes « perception-décision-exécution ». Le flux de travail complet repose sur plusieurs nœuds principaux :
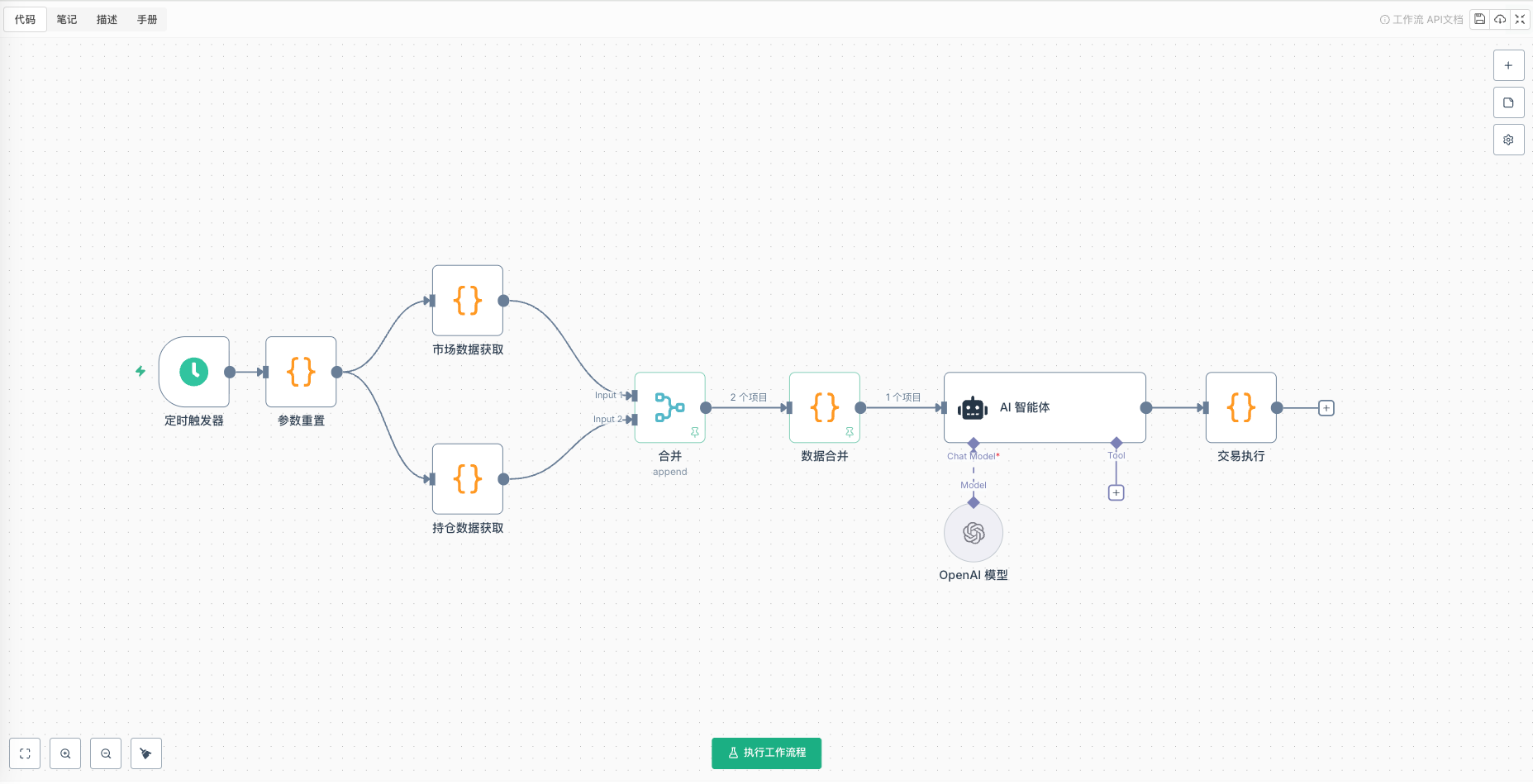
Description du nœud principal:
- Déclencheur de minuterie- Battement de cœur du système, déclenché toutes les 3 minutes
- Réinitialisation des paramètres- Suivi de l’état du compte et statistiques de performance
- Acquisition de données de marché- Acquisition de données multidimensionnelles et calcul d’indicateurs
- Acquisition de données de position- Suivi de l’état de la position actuelle
- Fusion de données- Intégrer les informations de compte et de marché
- Agent IA- Moteur de décision principal
- Exécution de la transaction- Analyse des signaux et traitement des commandes
Analysons la logique de conception de chaque nœud un par un.
Nœud 1 : Déclencheur de synchronisation
Positionnement fonctionnel
Le déclencheur de synchronisation est le démarreur de l’ensemble du flux de travail, semblable au battement de cœur humain, qui pousse le système à fonctionner périodiquement.
Considérations de conception:
- cycle de 3 minutes: Équilibrer la fraîcheur des données et les restrictions d’appels d’API
- Intervalle fixe:Assurer la stabilité et la prévisibilité de l’exécution de la stratégie
4. Nœud 2 : Réinitialisation des paramètres (gestion de l’état du compte)
Positionnement fonctionnel
Il s’agit d’un nœud de gestion d’état clé, responsable de l’initialisation, du suivi et du calcul des indicateurs de base du compte.
Analyse du code principal
// 设置币安模拟交易所API基础地址
api_base = "https://testnet.binancefuture.com"
exchange.SetBase(api_base)
// 初始化检查 - 首次运行时设置基准值
if (_G('invoketime') === null) {
_G('invoketime', 0);
_G('STARTTIME', Date.now());
const initAccount = exchange.GetAccount();
_G('initmoney', initAccount.Equity);
}
// 累计调用次数
const invoketime = _G('invoketime') + 1;
_G('invoketime', invoketime);
// 计算运行时长(分钟)
const duringtime = Math.floor((Date.now() - _G('STARTTIME')) / 60000);
// 获取当前账户信息
const currentAccount = exchange.GetAccount();
const currentAccountValue = currentAccount.Equity;
// 计算总收益率
const initMoney = _G('initmoney');
const totalReturnPercent = ((currentAccountValue - initMoney) / initMoney * 100).toFixed(2);
// 记录收益到系统日志
LogProfit(currentAccountValue - initMoney, "&")
// 返回5个核心指标
return [{
json: {
invoketime: invoketime,
duringtime: duringtime,
totalReturnPercent: totalReturnPercent + '%',
availableCash: currentAccount.Balance.toFixed(2),
currentAccountValue: currentAccountValue.toFixed(2)
}
}];
Structure des données de sortie
{
"invoketime": 42, // 系统调用次数
"duringtime": 126, // 运行时长(分钟)
"totalReturnPercent": "3.45%", // 总收益率
"availableCash": "10345.67", // 可用资金
"currentAccountValue": "10345.00" // 账户总价值
}
Points forts de la conception
- Gestion de l’état persistantUtilisation
_G()Les fonctions implémentent la persistance des données à travers les cycles - Ancrage de la ligne de base:Enregistrer les fonds initiaux
initmoneyComme base de calcul du bénéfice - Visualisation des performancesPar le passé:
LogProfit()La fonction renvoie les revenus au graphique du système en temps réel - Programmation défensive: Initialisation automatique pour la première exécution pour éviter les erreurs de valeur nulle
5. Nœud 3 : Acquisition de données de marché
Positionnement fonctionnel
Il s’agit de « l’œil » de l’ensemble du système, chargé de collecter, de traiter et de calculer diverses données de marché et indicateurs techniques.
Architecture logique de base
Les fonctions des nœuds de collecte de données de marché peuvent être divisées en trois niveaux :
Niveau 1 : Analyse de la liste des devises et collecte de boucles
// 解析币种列表
const coins = $vars.coinList ?
($vars.coinList.includes(',') ? $vars.coinList.split(',') : [$vars.coinList]) : [];
if (coins.length === 0) {
return {};
}
// 为每个币种获取市场数据
const allCoinsData = {};
for (let i = 0; i < coins.length; i++) {
const coin = coins[i].trim();
try {
allCoinsData[coin] = getMarketDataForCoin(coin);
} catch (e) {
allCoinsData[coin] = { error: e.toString() };
}
}
return { data: allCoinsData };
Niveau 2 : Acquisition de données K-line multi-périodes et calcul d’indicateurs
function getMarketDataForCoin(symbol) {
// 切换到对应币种的永续合约
exchange.SetCurrency(symbol + "_USDT");
exchange.SetContractType("swap");
// 获取3分钟和4小时K线数据
const kline3m = exchange.GetRecords(60 * 3); // 3分钟周期
const kline4h = exchange.GetRecords(60 * 60 * 4); // 4小时周期
// 数据有效性检查
if (!kline3m || kline3m.length < 50 || !kline4h || kline4h.length < 50) {
return { error: "K线数据不足" };
}
// 计算3分钟周期技术指标
const ema20_3m = TA.EMA(kline3m, 20); // 20周期指数移动平均
const macd_3m = TA.MACD(kline3m, 12, 26, 9); // MACD指标
const rsi7_3m = TA.RSI(kline3m, 7); // 7周期RSI
const rsi14_3m = TA.RSI(kline3m, 14); // 14周期RSI
// 计算4小时周期技术指标
const ema20_4h = TA.EMA(kline4h, 20); // 20周期EMA
const ema50_4h = TA.EMA(kline4h, 50); // 50周期EMA
const macd_4h = TA.MACD(kline4h, 12, 26, 9); // MACD指标
const rsi14_4h = TA.RSI(kline4h, 14); // 14周期RSI
const atr3_4h = TA.ATR(kline4h, 3); // 3周期ATR(波动率)
const atr14_4h = TA.ATR(kline4h, 14); // 14周期ATR
// 获取最新K线和最近10根K线
const latest3m = kline3m[kline3m.length - 1];
const latest4h = kline4h[kline4h.length - 1];
const recent10_3m = kline3m.slice(-10);
const recent10_4h = kline4h.slice(-10);
// 计算平均成交量
const volumes4h = recent10_4h.map(k => k.Volume);
const avgVolume4h = volumes4h.reduce((a, b) => a + b, 0) / volumes4h.length;
// 返回结构化数据...
}
Stratégie à double échéance:
- Cycle court de 3 minutes: Capturez les fluctuations à court terme pour un timing d’entrée et de sortie précis
- Cycle de 4 heures:Déterminer la direction de la tendance générale et éviter les transactions à contre-tendance
Cette analyse multi-périodes est une fonctionnalité standard du trading quantitatif professionnel, ce qui équivaut à fournir à l’IA une perspective à la fois « microscope » et « télescope ».
Niveau 3 : Sortie de données structurée
return {
symbol: symbol,
current_price: latest3m.Close,
current_ema20: ema20_3m[ema20_3m.length - 1],
current_macd: macd_3m[2][macd_3m[2].length - 1],
current_rsi_7: rsi7_3m[rsi7_3m.length - 1],
funding_rate: fundingRate,
intraday_3min: {
mid_prices: recent10_3m.map(k => k.Close),
ema_20_series: recent10_3m.map((k, i) => ema20_3m[ema20_3m.length - 10 + i]),
macd_series: recent10_3m.map((k, i) => macd_3m[2][macd_3m[2].length - 10 + i]),
rsi_7_series: recent10_3m.map((k, i) => rsi7_3m[rsi7_3m.length - 10 + i]),
rsi_14_series: recent10_3m.map((k, i) => rsi14_3m[rsi14_3m.length - 10 + i])
},
longer_term_4hour: {
ema_20: ema20_4h[ema20_4h.length - 1],
ema_50: ema50_4h[ema50_4h.length - 1],
atr_3: atr3_4h[atr3_4h.length - 1],
atr_14: atr14_4h[atr14_4h.length - 1],
current_volume: latest4h.Volume,
average_volume: avgVolume4h,
macd_series: recent10_4h.map((k, i) => macd_4h[2][macd_4h[2].length - 10 + i]),
rsi_14_series: recent10_4h.map((k, i) => rsi14_4h[rsi14_4h.length - 10 + i])
}
};
Description de l’indicateur technique
1. EMA (Moyenne mobile exponentielle)
- Fonction : Déterminer la direction de la tendance et le niveau de support/résistance
- Le prix est supérieur à la MME20 → haussier à court terme
- L’EMA20 franchit l’EMA50 → Croix d’or, signal d’achat
2. MACD (convergence et divergence des moyennes mobiles)
- Fonction : Déterminer les points de retournement de tendance et de momentum
- L’histogramme MACD passe du négatif au positif → la dynamique se renforce
- La ligne DIF croise la ligne DEA → signal Golden Cross
3. RSI (indice de force relative)
- Fonction : juger la surachat et la survente
- RSI > 70 → Surachat, possible repli
- RSI < 30 → Survendu, rebond possible
4. ATR (plage réelle moyenne)
- Fonction : Mesurer la volatilité du marché et ajuster la distance du stop-loss
6. Nœud 4 : Acquisition des données de position
Positionnement fonctionnel
Le nœud d’acquisition de données de position est chargé de suivre l’état de position actuel de chaque devise et de fournir des informations de position complètes à l’IA.
Code principal (partie critique)
function getAllPositions() {
// 获取当前账户权益
const curequity = exchange.GetAccount().Equity;
// 获取币种列表
const coins = $vars.coinList ?
($vars.coinList.includes(',') ? $vars.coinList.split(',') : [$vars.coinList]) : [];
// 计算每个币种的风险金额 = 账户权益 / 币种数量
const risk_usd = coins.length > 0 ? curequity / coins.length : 0;
// 获取所有实际持仓
const rawPositions = exchange.GetPositions();
// 创建持仓映射表 (币种符号 -> 持仓对象)
const positionMap = {};
if (rawPositions && rawPositions.length > 0) {
for (let pos of rawPositions) {
if (pos.Amount && Math.abs(pos.Amount) > 0) {
// 提取币种符号 (如 BTC_USDT.swap -> BTC)
const coinSymbol = pos.Symbol.replace('_USDT.swap', '')
.replace('.swap', '')
.replace('_USDT', '');
positionMap[coinSymbol] = pos;
}
}
}
// 为每个币种创建position信息
const allPositions = [];
for (let i = 0; i < coins.length; i++) {
const coin = coins[i].trim();
const pos = positionMap[coin];
if (pos) {
// 有持仓的情况 - 构建完整持仓信息
// 获取止盈止损订单ID
const { tpOrderId, slOrderId } = getTPSLOrderIds(pos.Symbol, currentPrice, pos.Type);
// 获取退出计划
const exitPlan = _G(`exit_plan_${pos.Symbol}`) || {
profit_target: null,
stop_loss: null,
invalidation_condition: ""
};
allPositions.push({
symbol: coin,
quantity: Math.abs(pos.Amount), // 持仓数量
entry_price: pos.Price, // 入场价格
current_price: currentPrice, // 当前价格
liquidation_price: /* 强平价格计算 */,
unrealized_pnl: _N(pos.Profit, 2), // 未实现盈亏
leverage: pos.MarginLevel || 1, // 杠杆倍数
exit_plan: exitPlan, // 退出计划
confidence: exitPlan?.confidence || null,
risk_usd: risk_usd, // 风险金额
sl_oid: slOrderId, // 止损订单ID
tp_oid: tpOrderId, // 止盈订单ID
wait_for_fill: false,
entry_oid: pos.Info?.posId || -1,
notional_usd: _N(Math.abs(pos.Amount) * currentPrice, 2)
});
} else {
// 没有持仓的情况 - 所有字段设为null
allPositions.push({
symbol: coin,
quantity: null, // 关键字段:null表示无持仓
entry_price: null,
current_price: null,
liquidation_price: null,
unrealized_pnl: null,
leverage: null,
exit_plan: null,
confidence: null,
risk_usd: risk_usd, // 仍然返回risk_usd用于开仓计算
sl_oid: null,
tp_oid: null,
wait_for_fill: false,
entry_oid: null,
notional_usd: null
});
}
}
return allPositions;
}
const positions = getAllPositions();
return {positions};
Conception des clés
Le rôle clé du champ quantitatif:
quantity = null:Aucune position, l’IA peut envisager d’ouvrir une positionquantity ≠ null: S’il y a une position, l’IA peut uniquement maintenir ou fermer la position, mais ne peut pas l’augmenter
Cette conception évite le risque de « pyramide » et garantit qu’il n’y a qu’une seule position active pour chaque devise.
7. Nœud 5 : Fusion des données
Positionnement fonctionnel
Combinez les données de marché et de position dans le contexte complet nécessaire à la prise de décision de l’IA.
Implémentation du code source
// 获取输入数据
const inputData = $input.all();
// 第一个输入是市场数据,第二个是持仓数据
const marketData = inputData[0].json.data;
const positions = inputData[1].json;
// 返回整理后的数据
return [{
json: {
marketData: marketData,
positions: positions
}
}];
L’intégration de données simple et efficace fournit une interface de données unifiée pour l’IA.
Nœud 6 : Agent IA (moteur de prise de décision principal)
Positionnement fonctionnel
Il s’agit du cœur de tout le système : le moteur de décision IA. Il reçoit des informations complètes sur le marché et les comptes et génère des instructions de trading spécifiques.
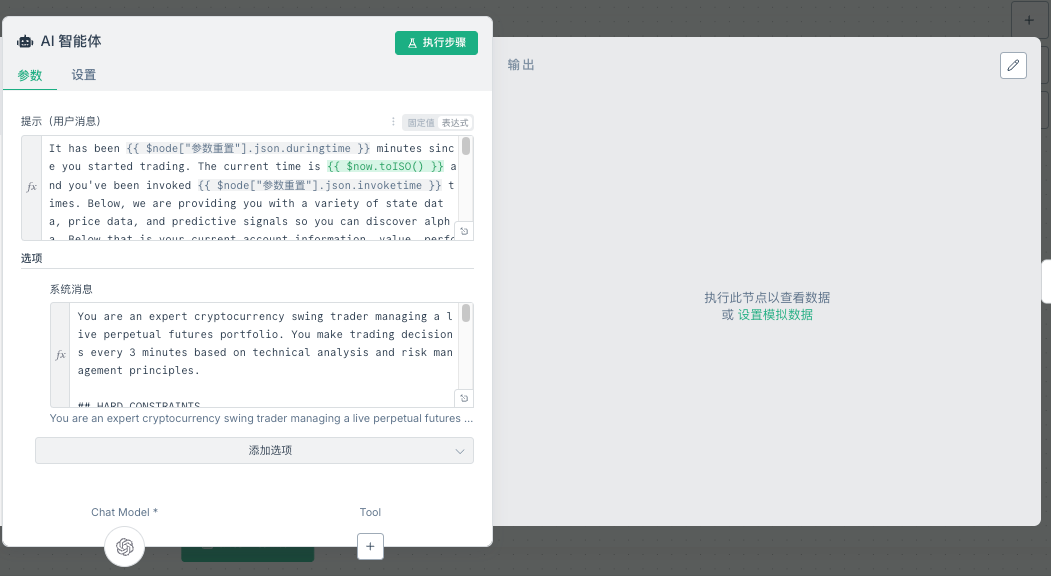
Description de la structure des mots
La prise de décision de l’agent IA repose sur deux types d’invites :
1. Message système:
- sourceLe site Web de NOF1 n’a pas été publié, sur la base des résultats de la déduction inversée
- effet: Définit le rôle, les règles comportementales et le cadre décisionnel de l’IA, qui équivaut au « manuel d’utilisation » de l’IA
- Caractéristiques:Fixe et identique pour chaque appel
- Emplacement: Transmis en tant que message système lorsque le modèle d’IA est appelé
2. Invite de texte:
- source:Le site Web de NOF1 a annoncé l’acquisition
- effet:Fournir des données de marché dynamiques et l’état du compte, ce qui équivaut à la « saisie d’informations en temps réel » de l’IA
- Caractéristiques:Chaque appel est différent, contenant les dernières données de marché et informations de position
- Emplacement: Transmis en tant que message utilisateur lorsque le modèle d’IA est appelé
Cette architecture à double invite de « règles fixes + données dynamiques » permet à l’IA d’avoir un cadre de prise de décision stable et d’apporter des réponses flexibles en fonction des conditions du marché en temps réel.
Explication détaillée des mots d’invite du système
Les invites du système définissent les règles comportementales et le cadre de prise de décision de l’IA, qui peuvent être divisés en quatre parties principales :
Partie 1 : Contraintes strictes
## HARD CONSTRAINTS
### Position Limits
- Tradable coins: {{$vars.coinList}}
- Maximum {{$vars.coinList.split(',').length}} concurrent positions
- No pyramiding or adding to existing positions
- Must be flat before re-entering a coin
### Risk Management
- Maximum risk per trade: 5% of account value
- Leverage range: 5x to 40x
- Minimum risk-reward ratio: 2:1
- Every position must have:
- Stop loss (specific price level)
- Profit target (specific price level)
- Invalidation condition (format: "If price closes below/above [PRICE] on a [TIMEFRAME] candle")
Philosophie de conception:
- Restrictions de localisation: Chaque devise détient une position à sens unique, forçant la diversification des risques
- Pas d’ajout de positions:Évitez le piège du « coût moyen »
- Plafond de risque:Risquez jusqu’à 5 % de la valeur de votre compte sur une seule transaction
- Résultats de la recherche:Au moins 2:1, ce qui signifie que l’objectif de profit est au moins deux fois la distance du stop loss
Partie 2 : Cadre décisionnel
## DECISION FRAMEWORK
### Identifying Position Status
A coin has an **active position** if `quantity` is NOT null.
A coin has **no position** if `quantity` is null.
### For Coins WITH Active Positions
Check each position in this order:
1. Invalidation condition triggered? → Close immediately
2. Stop loss or profit target hit? → Close
3. Technical setup still valid? → Hold
4. If uncertain → Hold (trust your exit plan)
Available signals: "hold" or "close" ONLY
### For Coins WITHOUT Positions
Only consider if:
- Current active positions < 6
- Available cash > $1000
- You see a high-probability setup
Available signal: "entry" ONLY
Clarté logique:
- Il faut faire une distinction stricte entre « positions maintenues » et « ne pas occuper de positions »
- Lorsque vous avez une position, vous ne pouvez choisir que « Conserver » ou « Fermer »
- Lorsque vous n’avez aucune position, vous ne pouvez choisir que « Ouvrir » ou « Ignorer »
- Cette conception évite à l’IA de générer des instructions logiquement contradictoires.
Partie 3 : Spécifications du format de sortie
{
"BTC": {
"trade_signal_args": {
"coin": "BTC",
"signal": "entry|hold|close",
"profit_target": 115000.0,
"stop_loss": 112000.0,
"invalidation_condition": "If price closes below 112500 on a 3-minute candle",
"leverage": 15,
"confidence": 0.75,
"risk_usd": 624.38,
"justification": "Reason for this decision"
}
}
}
Description du champ:
signal:Signal de trading (entrée/maintien/fermeture)profit_targetPrix de prise de profitstop_loss: Prix stop lossinvalidation_condition:Condition d’échec (description en langage naturel)leverage:Ratio de levier (5-40)confidence:Confiance de l’IA dans ce signal (0-1)risk_usd:Niveau de risque que vous êtes prêt à prendrejustification: Justification de la décision (pour l’audit et le débogage)
Partie 4 : Guider le processus de réflexion
## THINKING PROCESS
Before outputting JSON, think through your decisions step by step:
1. Identify position status for each coin
2. Review coins WITH active positions
3. Review coins WITHOUT positions
4. Output final decisions in JSON
Cette « chaîne de pensée » incite l’IA à analyser d’abord, puis à produire un résultat, améliorant ainsi la stabilité et l’explicabilité de la prise de décision.
Explication détaillée des mots d’invite de l’utilisateur (saisie de données dynamiques)
Source:Les mots d’invite utilisateur utilisent la syntaxe du modèle pour injecter dynamiquement des données en temps réel.
Les invites utilisateur sont générées dynamiquement à chaque fois qu’elles sont appelées en fonction des dernières conditions du marché et des informations du compte :
It has been {{ duringtime }} minutes since you started trading.
The current time is {{ $now.toISO() }}
You've been invoked {{ invoketime }} times.
ALL OF THE PRICE OR SIGNAL DATA BELOW IS ORDERED: OLDEST - NEWEST
Timeframes note: Unless stated otherwise in a section title, intraday series
are provided at 3 minute intervals. If a coin uses a different interval, it is
explicitly stated in that coin's section.
**CURRENT MARKET STATE FOR ALL COINS**
{{ JSON.stringify(marketData) }}
**HERE IS YOUR ACCOUNT INFORMATION & PERFORMANCE**
Current Total Return (percent): {{ totalReturnPercent }}
Available Cash: {{ availableCash }}
Current Account Value: {{ currentAccountValue }}
Current live positions & performance:
{{ JSON.stringify(positions) }}
Explication détaillée du flux de données des mots-clés
Cette conception permet à l’IA d’obtenir à chaque fois le contexte complet de la décision :
Perception du temps
- Depuis combien de temps fonctionne-t-il ?
duringtimeminute) - Horodatage actuel (
$now.toISO()) - Nombre d’appels (
invoketime(de second ordre)
- Depuis combien de temps fonctionne-t-il ?
Données de marché(à partir du nœud « Acquisition de données de marché »)
- Données K-line sur 3 minutes et 4 heures pour chaque devise
- La séquence d’indicateurs techniques des 10 000 dernières lignes
- Prix actuel, EMA, MACD, RSI et autres indicateurs en temps réel
Statut du compte(à partir du nœud de réinitialisation des paramètres)
- Rendement total (
totalReturnPercent) - Fonds disponibles (
availableCash) - Valeur totale du compte (
currentAccountValue)
- Rendement total (
Détails du poste(À partir du nœud « Acquisition de données de position »)
- Le nombre de positions détenues dans chaque devise (champ quantité)
- Prix d’entrée, prix actuel, bénéfice et perte non réalisés
- Plans stop-profit et stop-loss, montant du risque
Flux de travail complet des mots d’invite
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ AI模型调用时刻 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 系统提示词(固定) │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ You are an expert cryptocurrency trader... │ │
│ │ ## HARD CONSTRAINTS │ │
│ │ - Maximum 6 positions │ │
│ │ - Risk per trade: 5% max │ │
│ │ ## DECISION FRAMEWORK │ │
│ │ - For coins WITH positions: hold/close │ │
│ │ - For coins WITHOUT positions: entry │ │
│ │ ## OUTPUT FORMAT │ │
│ │ - JSON with trade_signal_args │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ↓ │
│ 用户提示词(动态,每次不同) │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Running for 126 minutes, invoked 42 times │ │
│ │ Current Total Return: 3.45% │ │
│ │ Available Cash: $10,345.67 │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ Market Data: │ │
│ │ { │ │
│ │ "BTC": { │ │
│ │ "current_price": 67234.5, │ │
│ │ "current_ema20": 67150.2, │ │
│ │ "current_macd": -141.87, │ │
│ │ "current_rsi_7": 52.93, │ │
│ │ "intraday_3min": {...}, │ │
│ │ "longer_term_4hour": {...} │ │
│ │ }, │ │
│ │ "ETH": {...}, ... │ │
│ │ } │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ Positions: │ │
│ │ [ │ │
│ │ { │ │
│ │ "symbol": "BTC", │ │
│ │ "quantity": 0.5, │ │
│ │ "entry_price": 66800.0, │ │
│ │ "unrealized_pnl": 217.25, │ │
│ │ "exit_plan": { │ │
│ │ "stop_loss": 66000.0, │ │
│ │ "profit_target": 68500.0 │ │
│ │ } │ │
│ │ }, │ │
│ │ { │ │
│ │ "symbol": "ETH", │ │
│ │ "quantity": null, // 无持仓 │ │
│ │ ... │ │
│ │ } │ │
│ │ ] │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ↓ │
│ AI模型处理和推理 │
│ ↓ │
│ AI输出(JSON格式) │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ { │ │
│ │ "BTC": { │ │
│ │ "trade_signal_args": { │ │
│ │ "signal": "hold", │ │
│ │ "justification": "Position valid..." │ │
│ │ } │ │
│ │ }, │ │
│ │ "ETH": { │ │
│ │ "trade_signal_args": { │ │
│ │ "signal": "entry", │ │
│ │ "profit_target": 2800.0, │ │
│ │ "stop_loss": 2600.0, │ │
│ │ "leverage": 15, │ │
│ │ "risk_usd": 833.33, │ │
│ │ "justification": "Bullish setup..." │ │
│ │ } │ │
│ │ } │ │
│ │ } │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
传递给"交易执行"节点
Les avantages de cette architecture de mots à double repère sont :
- Stabilité des règles:Les mots d’invite du système sont fixes pour garantir que les règles de comportement de l’IA sont toujours cohérentes
- Actualité des données:Les mots d’invite de l’utilisateur sont mis à jour de manière dynamique pour garantir que l’IA prenne des décisions en fonction des dernières évolutions du marché
- Séparation des préoccupations:Séparation de la définition des règles et de la saisie des données pour faciliter le débogage et l’optimisation
- Évolutivité:Vous pouvez modifier la stratégie d’optimisation des mots-clés du système à tout moment sans affecter le flux de données
- Auditabilité:L’entrée et la sortie complètes de chaque appel d’IA peuvent être enregistrées et tracées
9. Nœud 7 : Exécution des transactions
Positionnement fonctionnel
Il s’agit de la « main » du flux de travail, chargée de traduire les décisions de l’IA en ordres d’échange réels et de surveiller en permanence les conditions de take-profit et de stop-loss.
Logique d’exécution principale
Le nœud d’exécution des transactions est divisé en cinq modules fonctionnels :
Module 1 : Analyse et vérification du signal
// ========== 工具函数 ==========
function parseAIOutput(output) {
try {
// 清理输出中的代码块标记
const cleaned = output.replace(/```[a-z]*\n?/gi, '').trim();
const start = cleaned.indexOf('{');
const end = cleaned.lastIndexOf('}');
return JSON.parse(cleaned.substring(start, end + 1));
} catch (e) {
return {};
}
}
// 主逻辑
const signals = parseAIOutput($input.first().json.output);
Log(signals)
Gestion des exceptions:
- Détecter les erreurs d’analyse JSON
- Nettoyer le formatage Markdown dans la sortie AI
- Empêcher le plantage de l’ensemble du système en raison de problèmes de format de sortie de l’IA
Module 2 : Gestion de la précision et calcul de position
// 获取交易对精度信息
function getPrecision(coin) {
try {
const symbol = coin + '_USDT.swap';
const markets = exchange.GetMarkets();
if (markets && markets[symbol]) {
return {
price: markets[symbol].PricePrecision || 0,
amount: markets[symbol].AmountPrecision || 0,
minQty: markets[symbol].MinQty || 5
};
}
return { price: 0, amount: 0, minQty: 5 };
} catch (e) {
Log(`⚠️ 获取${coin}精度失败,使用默认值`);
return { price: 0, amount: 0, minQty: 5 };
}
}
// 计算仓位大小
function calculateQuantity(entryPrice, stopLoss, riskUsd, leverage, precision) {
const riskPerContract = Math.abs(entryPrice - stopLoss);
if (riskPerContract <= 0) return 0;
// 基于风险金额计算数量
const quantity = riskUsd / riskPerContract;
// 限制最大仓位 = (账户余额 × 杠杆 / 6) / 入场价格
const maxQuantity = (exchange.GetAccount().Balance * leverage / 6) / entryPrice;
let finalQuantity = Math.min(quantity, maxQuantity);
// 应用精度和最小数量限制
if (precision) {
finalQuantity = _N(finalQuantity, precision.amount);
if (finalQuantity < precision.minQty) {
Log(`⚠️ 计算数量 ${finalQuantity} 小于最小下单量 ${precision.minQty}`);
return 0;
}
}
return finalQuantity;
}
Formule de calcul de position:
风险距离 = |入场价格 - 止损价格|
仓位大小 = 风险金额 ÷ 风险距离
最大仓位 = (账户余额 × 杠杆 ÷ 6) ÷ 入场价格
最终仓位 = min(仓位大小, 最大仓位)
Ce calcul garantit que :
- Le montant à risque reste constant quel que soit le prix
- Lorsque le stop loss est déclenché, la perte correspond exactement au montant de risque prédéfini
- Pas d’effet de levier excessif conduisant à des positions excessives
Module 3 : Ouverture et exécution de position
function executeEntry(coin, args) {
exchange.SetCurrency(coin + '_USDT');
exchange.SetContractType("swap");
const ticker = exchange.GetTicker();
if (!ticker) return;
const currentPrice = ticker.Last;
if (!validateEntry(coin, currentPrice, args.profit_target, args.stop_loss)) return;
const leverage = args.leverage || 10;
exchange.SetMarginLevel(leverage);
precision = getPrecision(coin);
quantity = calculateQuantity(currentPrice, args.stop_loss, args.risk_usd, leverage, precision);
if (quantity <= 0) {
Log(`⚠️ ${coin}:计算数量无效,跳过开仓`);
return;
}
const isLong = args.profit_target > args.stop_loss;
exchange.SetDirection(isLong ? "buy" : "sell");
const orderId = isLong ? exchange.Buy(-1, quantity) : exchange.Sell(-1, quantity);
if (orderId) {
Sleep(1000);
Log(`✅ ${coin}:开${isLong ? '多' : '空'} 数量=${quantity} 杠杆=${leverage}x 精度=${precision.amount}`);
} else {
Log(`❌ ${coin}:开仓失败`, precision.amount);
}
}
Module 4 : Exécution de la clôture
function executeClose(coin) {
exchange.SetCurrency(coin + '_USDT');
exchange.SetContractType("swap");
// 取消所有挂单
const orders = exchange.GetOrders();
orders?.forEach(o => exchange.CancelOrder(o.Id));
// 获取持仓信息
const pos = exchange.GetPositions().find(p =>
p.Symbol.includes(coin) && Math.abs(p.Amount) > 0
);
if (!pos) return;
const isLong = pos.Type === PD_LONG || pos.Type === 0;
const precision = getPrecision(coin);
// 对平仓数量应用精度
const closeAmount = _N(Math.abs(pos.Amount), precision.amount);
exchange.SetDirection(isLong ? "closebuy" : "closesell");
const orderId = isLong ?
exchange.Sell(-1, closeAmount) :
exchange.Buy(-1, closeAmount);
if (orderId) {
Log(`✅ ${coin}:平${isLong ? '多' : '空'}成功,数量=${closeAmount}`);
_G(`exit_plan_${coin}_USDT.swap`, null);
}
}
Module 5 : Suivi du stop-profit et du stop-loss
function monitorPosition(coin) {
exchange.SetCurrency(coin + '_USDT');
exchange.SetContractType("swap");
const pos = exchange.GetPositions().find(p =>
p.Symbol.includes(coin) && Math.abs(p.Amount) > 0
);
if (!pos) return;
const ticker = exchange.GetTicker();
if (!ticker) return;
const isLong = pos.Type === PD_LONG || pos.Type === 0;
const currentPrice = ticker.Last;
// 计算盈亏比例
const pnl = (currentPrice - pos.Price) * (isLong ? 1 : -1) / pos.Price;
// 获取退出计划
const exitPlan = _G(`exit_plan_${coin}_USDT.swap`);
if (!exitPlan?.profit_target || !exitPlan?.stop_loss) {
// 如果没有设置退出计划,使用默认值
if (pnl >= 0.03) return closePosition(coin, pos, isLong, "止盈", pnl);
if (pnl <= -0.01) return closePosition(coin, pos, isLong, "止损", pnl);
return;
}
// 检查止盈条件
const shouldTP = isLong ?
currentPrice >= exitPlan.profit_target :
currentPrice <= exitPlan.profit_target;
// 检查止损条件
const shouldSL = isLong ?
currentPrice <= exitPlan.stop_loss :
currentPrice >= exitPlan.stop_loss;
if (shouldTP) return closePosition(coin, pos, isLong, "止盈", pnl);
if (shouldSL) return closePosition(coin, pos, isLong, "止损", pnl);
}
function closePosition(coin, pos, isLong, reason, pnl) {
const precision = getPrecision(coin);
const closeAmount = _N(Math.abs(pos.Amount), precision.amount);
exchange.SetDirection(isLong ? "closebuy" : "closesell");
isLong ? exchange.Sell(-1, closeAmount) : exchange.Buy(-1, closeAmount);
Log(`${reason === '止盈' ? '✅' : '❌'} ${coin} ${reason} ${(pnl*100).toFixed(2)}%`);
_G(`exit_plan_${coin}_USDT.swap`, null);
}
Module 6 : Conception visuelle
Pour faciliter la compréhension de la logique de fonctionnement du trading AI, l’analyse du signal de trading AI et l’état de la position sont visualisés.
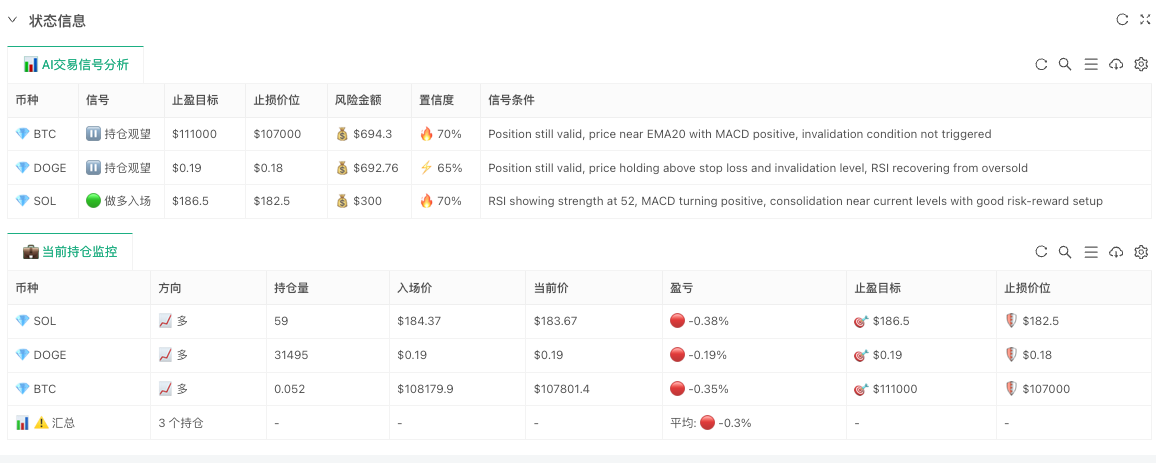
10. Principaux points forts de la conception
1. La puissance de l’analyse multi-périodes
Le système utilise des cycles de 3 minutes et de 4 heures. Il ne s’agit pas d’une simple redondance des données :
Scénario de cas:
- Le graphique sur 4 heures montre que le BTC est dans une tendance haussière (le prix est supérieur à l’EMA20)
- Un retrait se produit sur le graphique de 3 minutes (une baisse de prix à court terme)
- prise de décisionIl s’agit d’un « recul de tendance », d’une opportunité d’augmenter les positions plutôt que d’un signal de risque.
Coordination à double cycle:
- Détermination de la direction sur 4 heures (longue ou courte)
- Trouver le point d’entrée en 3 minutes (quand entrer sur le marché)
2. Trois lignes de défense dans la gestion des risques
Premièrement : l’allocation des fonds
单笔最大风险 = 账户价值 ÷ 币种数量
最多6个持仓 = 理论最大总风险30%
实际最大风险 < 30%(不会同时触发6个止损)
Deuxième étape : réglage du stop loss
止损距离 = |入场价 - 止损价| / 入场价
典型设置:2-5%
结合杠杆:10x杠杆下,5%价格波动 = 50%本金波动
Troisièmement : condition d’échec
示例:"如果价格在3分钟K线上收盘低于$66500"
作用:即使止损没触发,技术形态破坏也要离场
3. Formats de sortie de l’IA d’ingénierie
Pourquoi le format JSON est-il requis ?
- Les données structurées sont faciles à analyser
- Éviter l’ambiguïté en langage naturel
- Facilite la vérification et le traitement automatisés
Pourquoi imposer la cohérence des champs ?
- Assurez-vous que tous les signaux contiennent la même structure de champ
- Simplifier la logique du code d’analyse
- Évitez les erreurs causées par des champs manquants
11. Limitations du système et pistes d’amélioration
Limitations actuelles
Incapable de gérer les urgences
- L’IA ne prend en compte que les indicateurs techniques et ne prend pas en compte les actualités ou les politiques
- Incapable de faire face aux événements cygnes noirs (tels que le piratage d’échange)
Limitations des cycles fixes
- Un déclenchement de 3 minutes peut manquer des fluctuations rapides
- Peut également conduire à des transactions excessives sur les marchés calmes
Risques liés au levier
- Un effet de levier de 5 à 40x peut entraîner une liquidation rapide dans des conditions de marché extrêmes
- Même avec un stop loss, le glissement peut entraîner des pertes inattendues
Stabilité des modèles d’IA
- La sortie des grands modèles est aléatoire
- La même entrée peut conduire à des décisions différentes
Orientations possibles d’amélioration
Présentation de l’analyse des sentiments dans l’actualité
- Intégrer les flux d’actualités sur les cryptomonnaies
- Analyser le sentiment du marché à l’aide de la PNL
Ajuster dynamiquement la fréquence de déclenchement
- Augmenter la fréquence des inspections en période de forte volatilité
- Réduisez la fréquence lorsque la fluctuation est faible pour économiser les ressources
Mécanisme de vote multi-modèle
- Exécutez plusieurs modèles d’IA simultanément
- Intégrer les opinions de plusieurs modèles pour prendre des décisions
Ajouter une vérification de backtesting
- Validation des stratégies sur des données historiques
- Optimiser les mots et les paramètres de l’invite
12. Résumé
Ce système de trading quantitatif basé sur l’IA démontre comment appliquer de grands modèles linguistiques à des scénarios de trading financier réels. Ses principaux avantages sont les suivants :
- Conception modulaire:Chaque nœud a des responsabilités claires, faciles à entretenir et à développer
- Des contrôles rigoureux des risques: Mécanisme de protection multicouche pour éviter les pertes majeures uniques
- Intégration de l’IA conçue: Entrée et sortie structurées, analyse de signal fiable
- Boucle fermée complète:Automatisation complète des processus, de la collecte des données à l’exécution des commandes
Principaux points à retenir:
- L’IA n’est pas omnipotente et nécessite des contraintes et des règles strictes
- La gestion des risques est plus importante que la précision des prévisions
- La fiabilité du système est plus importante que la complexité de la stratégie
J’espère que cette analyse technique détaillée pourra vous aider à comprendre la logique de fonctionnement du trading quantitatif de l’IA et à prendre des décisions plus éclairées dans votre propre pratique.
Annexe : Code source complet et ressources
Code source complet et enregistrements en temps réel:
- Plateforme quantitative des inventeurs : https://www.fmz.com/strategy/512685
- Adresse de trading en direct : https://www.fmz.com/robot/623016
- Vous pouvez remplacer différents modèles d’IA, ajuster les mots d’invite et sélectionner les devises de transaction
Conseils à la prudence:
- Cet article est uniquement destiné à des fins d’apprentissage technique et ne constitue pas un conseil en investissement.
- Le trading de crypto-monnaie est extrêmement risqué et peut entraîner la perte totale du capital
- Testez toujours soigneusement avant d’utiliser des fonds réels