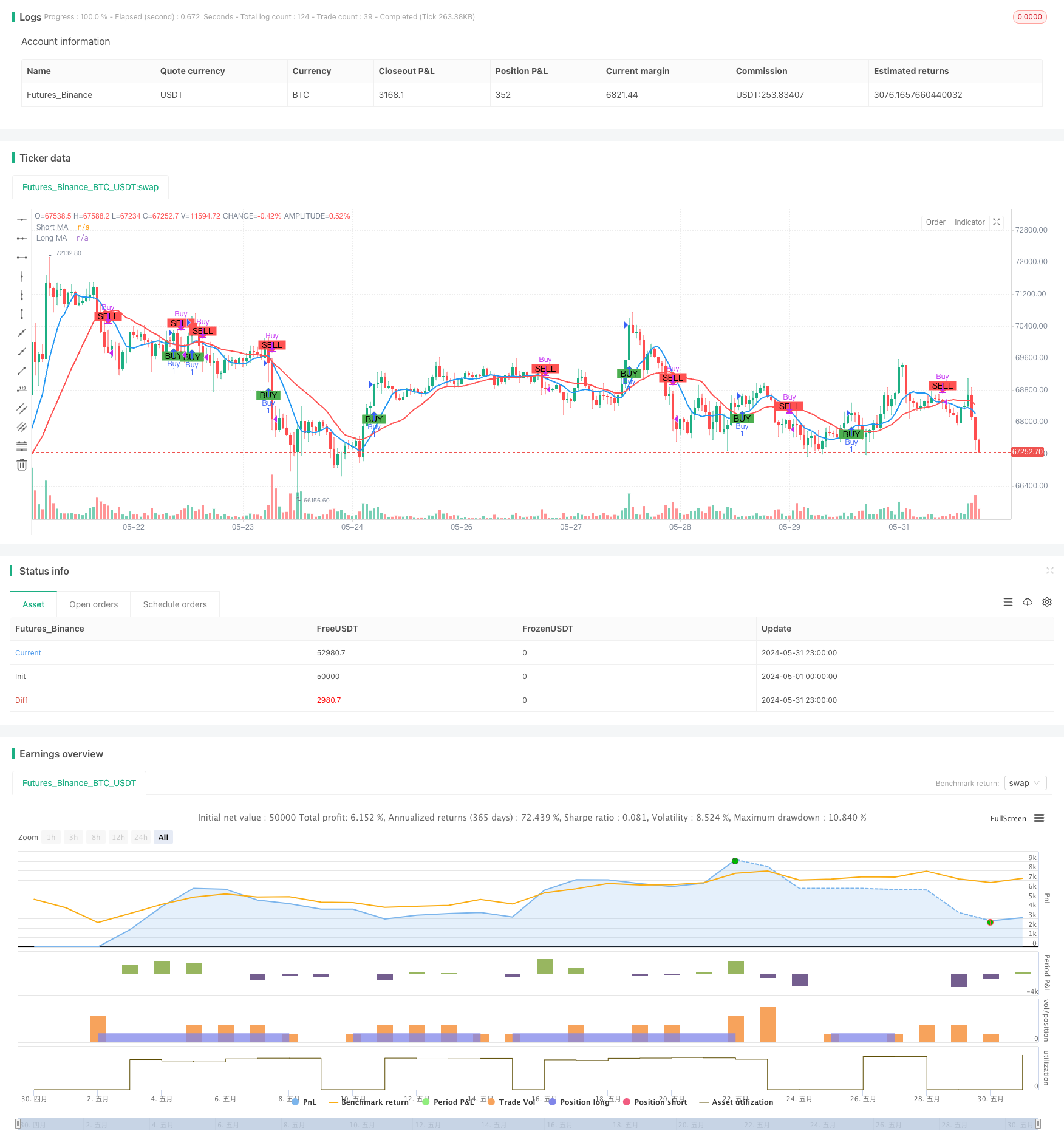
अवलोकन
दो-मध्यम रेखा के क्रॉसिंग पर आधारित एक चलती औसत रणनीति एक सरल और प्रभावी दिन के भीतर व्यापार विधि है, जिसका उद्देश्य बाजार में संभावित खरीद और बिक्री के अवसरों की पहचान करना है, दो अलग-अलग चक्रों में चलती औसत के बीच संबंधों का विश्लेषण करके। यह रणनीति एक अल्पकालिक सरल चलती औसत (एसएमए) और एक दीर्घकालिक सरल चलती औसत का उपयोग करती है, जो एक लंबी अवधि की औसत रेखा को क्रॉस करते समय एक bullish संकेत देता है, संभावित खरीद के अवसरों को इंगित करता है; इसके विपरीत, जब एक लंबी अवधि की औसत रेखा को क्रॉस करता है, तो एक bearish संकेत देता है, संभावित बिक्री के अवसरों को इंगित करता है। यह क्रॉसिंग विधि व्यापारियों को बाजार की रुझान को पकड़ने में मदद करती है, जबकि बाजार के शोर को कम करती है।
रणनीति सिद्धांत
इस रणनीति के मुख्य सिद्धांत का उपयोग करने के लिए प्रवृत्ति की विशेषताओं और विभिन्न अवधि के लिए चलती औसत की विलंबता का उपयोग करें, और यह है कि इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि इस तरह के रूप में इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि इस तरह के रूप में इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि यह इस तरह के रूप में यह इस तरह के रूप में यह है कि
रणनीतिक लाभ
- सरल और समझने में आसानः यह रणनीति क्लासिक चलती औसत सिद्धांत पर आधारित है, तर्क स्पष्ट है, इसे समझना और लागू करना आसान है।
- अनुकूलनशीलताः यह रणनीति कई बाजारों और विभिन्न प्रकार के ट्रेडों के लिए लागू की जा सकती है, जो पैरामीटर सेटिंग्स को समायोजित करके विभिन्न बाजार विशेषताओं के लिए लचीलापन प्रदान करती है।
- ट्रेंड कैप्चरः ट्रेंड की दिशा का आकलन करने के लिए दो समान रेखाओं का उपयोग करें, जिससे व्यापारियों को समय पर मुख्यधारा के रुझानों का पालन करने और मुनाफे की संभावनाओं को बढ़ाने में मदद मिलती है।
- जोखिम नियंत्रणः इस रणनीति में जोखिम प्रबंधन की अवधारणा को पेश किया गया है, जो प्रत्येक व्यापार के जोखिम के छेद को नियंत्रित करने के लिए स्थिति को समायोजित करता है और संभावित नुकसान को प्रभावी ढंग से प्रबंधित करता है।
- कम शोरः औसत रेखा की पिछली विशेषता का लाभ उठाते हुए, बाजार में यादृच्छिक शोर को प्रभावी ढंग से फ़िल्टर करें और ट्रेडिंग सिग्नल की विश्वसनीयता में सुधार करें।
रणनीतिक जोखिम
- पैरामीटर का चयनः विभिन्न पैरामीटर सेटिंग्स का रणनीति के प्रदर्शन पर महत्वपूर्ण प्रभाव पड़ता है। गलत चयन से रणनीति विफल हो सकती है या खराब प्रदर्शन हो सकता है।
- बाजार में रुझानः जब बाजार में उतार-चढ़ाव या रुझान में बदलाव होता है, तो यह रणनीति लगातार नुकसान का कारण बन सकती है।
- स्लाइडिंग लागतः बार-बार ट्रेड करने से स्लाइडिंग लागत अधिक हो सकती है, जो रणनीति के समग्र लाभ को प्रभावित करती है।
- ब्लैक स्क्वैम: यह रणनीति चरम स्थितियों के लिए अनुकूल नहीं है, और ब्लैक स्क्वैम से रणनीति को भारी नुकसान हो सकता है।
- ओवरफिट जोखिमः यदि पैरामीटर अनुकूलन ऐतिहासिक डेटा पर बहुत अधिक निर्भर करता है, तो यह रणनीति को वास्तविक लेनदेन में खराब प्रदर्शन करने का कारण बन सकता है।
रणनीति अनुकूलन दिशा
- गतिशील पैरामीटर अनुकूलन: बाजार की स्थिति के अनुसार परिवर्तन, गतिशील रूप से रणनीति पैरामीटर को समायोजित करना, अनुकूलनशीलता में सुधार करना।
- प्रवृत्ति की पुष्टिः ट्रेडिंग सिग्नल उत्पन्न करने के बाद, संकेत की विश्वसनीयता बढ़ाने के लिए प्रवृत्ति की पुष्टि करने के लिए अन्य संकेतकों या मूल्य व्यवहार पैटर्न को पेश करना।
- स्टॉप लॉस स्टॉपः एक उचित स्टॉप लॉस स्टॉप तंत्र की शुरूआत, जो एकल लेनदेन के लिए जोखिम को और अधिक नियंत्रित करता है।
- पोजीशन मैनेजमेंट: पोजीशन समायोजन को अनुकूलित करने के तरीके, जैसे कि अस्थिरता दर संकेतक की शुरूआत, बाजार में उतार-चढ़ाव के स्तर के आधार पर पोजीशन को गतिशील रूप से समायोजित करना।
- मल्टी हेड फोर्स आकलनः मल्टी हेड और हेड फोर्स के बीच तुलनात्मक संबंधों का आकलन करना, प्रवृत्ति की शुरुआत में हस्तक्षेप करना, प्रवृत्ति को पकड़ने की सटीकता में सुधार करना।
संक्षेप
दो-समान रेखाओं को पार करने पर आधारित चलती औसत रणनीति एक सरल और व्यावहारिक दिन के भीतर व्यापार विधि है, विभिन्न आवधिक औसत रेखाओं के स्थान संबंधों की तुलना करके बाजार की प्रवृत्ति दिशा का न्याय करने के लिए, व्यापार संकेत उत्पन्न करती है। रणनीति तर्क स्पष्ट है, अनुकूलनशील है, और बाजार की प्रवृत्ति को प्रभावी ढंग से पकड़ सकती है, जबकि जोखिम प्रबंधन उपायों को संभावित नुकसान को नियंत्रित करने के लिए पेश किया जाता है। हालांकि, इस रणनीति में पैरामीटर, प्रवृत्ति परिवर्तन, लगातार व्यापार जैसे संभावित जोखिम भी हैं। गतिशील अनुकूलन, सिग्नल पुष्टिकरण, स्थिति प्रबंधन आदि के माध्यम से रणनीति की स्थिरता और लाभप्रदता को और बढ़ाने की आवश्यकता है। कुल मिलाकर, एक क्लासिक तकनीकी विश्लेषण सूचक के रूप में चलती औसत, इसके मूल सिद्धांतों और वास्तविक अनुप्रयोगों के मूल्य को बाजार में व्यापक रूप से परीक्षण किया गया है, जो लगातार गहन शोध और अनुकूलित ट्रेडिंग रणनीतियों के लिए योग्य है।
Overview
The Moving Average Crossover Strategy based on dual moving averages is a straightforward and effective intraday trading approach designed to identify potential buy and sell opportunities in the market by analyzing the relationship between two moving averages of different periods. This strategy utilizes a short-term simple moving average (SMA) and a long-term simple moving average. When the short-term moving average crosses above the long-term moving average, it indicates a bullish signal, suggesting a potential buying opportunity. Conversely, when the short-term moving average crosses below the long-term moving average, it indicates a bearish signal, suggesting a potential selling opportunity. This crossover method helps traders capture trending moves in the market while minimizing market noise interference.
Strategy Principle
The core principle of this strategy is to utilize the trend characteristics and lag of moving averages with different periods. By comparing the relative position relationship between the short-term moving average and the long-term moving average, it determines the current market trend direction and makes corresponding trading decisions. When an upward trend emerges in the market, the price will first break through the long-term moving average, and the short-term moving average will subsequently cross above the long-term moving average, forming a golden cross and generating a buy signal. When a downward trend emerges in the market, the price will first break below the long-term moving average, and the short-term moving average will subsequently cross below the long-term moving average, forming a death cross and generating a sell signal. In the parameter settings of this strategy, the period of the short-term moving average is set to 9, and the period of the long-term moving average is set to 21. These two parameters can be adjusted based on market characteristics and personal preferences. Additionally, this strategy introduces the concept of money management by setting the initial capital and risk percentage per trade, using position sizing to control the risk exposure of each trade.
Strategy Advantages
- Simplicity: This strategy is based on the classic moving average theory, with clear logic and easy to understand and implement.
- Adaptability: This strategy can be applied to multiple markets and different trading instruments. By adjusting parameter settings, it can flexibly adapt to different market characteristics.
- Trend Capture: By using the dual moving average crossover to determine the trend direction, it helps traders timely follow the mainstream trend and increase profit opportunities.
- Risk Control: This strategy introduces the concept of risk management, using position sizing to control the risk exposure of each trade, effectively managing potential losses.
- Noise Reduction: By utilizing the lag characteristic of moving averages, it effectively filters out random noise in the market, improving the reliability of trading signals.
Strategy Risks
- Parameter Selection: Different parameter settings can have a significant impact on strategy performance. Improper selection may lead to strategy failure or poor performance.
- Market Trend: In ranging markets or trend turning points, this strategy may experience consecutive losses.
- Slippage Costs: Frequent trading may result in higher slippage costs, affecting the overall profitability of the strategy.
- Black Swan Events: This strategy has poor adaptability to extreme market conditions, and black swan events may cause significant losses to the strategy.
- Overfitting Risk: If parameter optimization relies too heavily on historical data, it may lead to poor performance of the strategy in actual trading.
Strategy Optimization Directions
- Dynamic Parameter Optimization: Dynamically adjust strategy parameters based on changes in market conditions to improve adaptability.
- Trend Confirmation: After generating trading signals, introduce other indicators or price behavior patterns to confirm the trend, improving signal reliability.
- Stop-Loss and Take-Profit: Introduce reasonable stop-loss and take-profit mechanisms to further control the risk exposure of each trade.
- Position Management: Optimize the position sizing method, such as introducing volatility indicators to dynamically adjust positions based on market volatility levels.
- Long-Short Strength Assessment: Assess the comparative relationship between bullish and bearish strengths, entering at the early stage of a trend to improve the accuracy of trend capture.
Summary
The Moving Average Crossover Strategy based on dual moving averages is a simple and practical intraday trading method. By comparing the position relationship of moving averages with different periods, it determines the market trend direction and generates trading signals. This strategy has clear logic, strong adaptability, and can effectively capture market trends while introducing risk management measures to control potential losses. However, this strategy also has potential risks such as parameter selection, trend reversal, frequent trading, etc. It needs to be further improved through dynamic optimization, signal confirmation, position management, and other methods to enhance the robustness and profitability of the strategy. In general, as a classic technical analysis indicator, the basic principles and practical application value of moving averages have been widely verified by the market. It is a trading strategy worthy of in-depth research and continuous optimization.
/*backtest
start: 2024-05-01 00:00:00
end: 2024-05-31 23:59:59
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("Moving Average Crossover Strategy", overlay=true)
// Input parameters
shortLength = input.int(9, title="Short Moving Average Length")
longLength = input.int(21, title="Long Moving Average Length")
capital = input.float(100000, title="Initial Capital")
risk_per_trade = input.float(1.0, title="Risk Per Trade (%)")
// Calculate Moving Averages
shortMA = ta.sma(close, shortLength)
longMA = ta.sma(close, longLength)
// Plot Moving Averages
plot(shortMA, title="Short MA", color=color.blue, linewidth=2)
plot(longMA, title="Long MA", color=color.red, linewidth=2)
// Generate Buy/Sell signals
longCondition = ta.crossover(shortMA, longMA)
shortCondition = ta.crossunder(shortMA, longMA)
// Plot Buy/Sell signals
plotshape(series=longCondition, title="Buy Signal", location=location.belowbar, color=color.green, style=shape.labelup, text="BUY")
plotshape(series=shortCondition, title="Sell Signal", location=location.abovebar, color=color.red, style=shape.labeldown, text="SELL")
// Risk management: calculate position size
risk_amount = capital * (risk_per_trade / 100)
position_size = risk_amount / close
// Execute Buy/Sell orders with position size
if (longCondition)
strategy.entry("Buy", strategy.long, qty=1, comment="Buy")
if (shortCondition)
strategy.close("Buy", comment="Sell")
// Display the initial capital and risk per trade on the chart
var label initialLabel = na
if (na(initialLabel))
initialLabel := label.new(x=bar_index, y=high, text="Initial Capital: " + str.tostring(capital) + "\nRisk Per Trade: " + str.tostring(risk_per_trade) + "%", style=label.style_label_down, color=color.white, textcolor=color.black)
else
label.set_xy(initialLabel, x=bar_index, y=high)