ガウスチャネル適応移動平均戦略
作成日:
2024-03-28 18:08:18
最終変更日:
2024-03-28 18:08:18
コピー:
2
クリック数:
1244
1
フォロー
1664
フォロワー
概要
高斯通道自己適応均線策略は,高斯波技術と自己適応パラメータ設定を利用した量化取引策策である.この策略は,ジョン・エラーズが提唱した高斯波理論に基づいており,価格データに対する複数の指数移動平均の計算によって,滑らかで自己適応的な取引信号を生成する.この策略の核心は,動的に調整された価格通道を構築し,上下軌道に高斯波の後の価格が加減され,実際の波動幅が得られるものである.価格が突破軌道に上がるときは買取され,突破軌道に上がるときは売り出される.また,この策略は,パラメータの時間を導入し,戦略の動作開始停止時間を柔軟に設定し,戦略の実用性を強化する.
戦略原則
高斯通路は,自己適応均線戦略の原則は以下の通りである.
- 価格の高斯値を計算する. ユーザが設定したサンプリング周期と極点数に応じて,ベータとアルファのパラメータを計算し,価格データに段階的な高斯波をかけて,平らな処理後の価格の序列を得する.
- 真の波動幅の高ステル波の値を計算する.価格の真の波動幅に同じ高ステル波処理を行い,平らな波動幅のシーケンスを得る.
- 高斯通路を構成する.高斯波後の価格を中軌とする.上軌は中軌から実際の波幅とユーザが設定した倍数の倍乗を足し,下軌は中軌からこの値を減算して,動的通路を形成する.
- トレードシグナルを生成する.価格が上方突破チャネル上軌を突破すると,買入シグナルを生成する.価格が下方突破チャネル下軌を突破すると,売出シグナルを生成する.
- 期間パラメータを導入します. ユーザーは,戦略の実行開始時と終了時間を設定できます. この期間中に,戦略は取引信号に基づいて動作します.
優位分析
高斯通路の自己適応均線戦略は以下の利点がある.
- 適応性強. 戦略は動的に調整されるパラメータを採用し,異なる市場状態と取引品種に適応し,頻繁な手動デビューは必要ありません.
- トレンド・トラッキング性が良い.価格チャネルを構築することで,戦略は市場トレンドをうまく捉え,追跡することができ,波動的な市場における偽信号を効果的に回避できます.
- 滑らかさ 価格データを高波技術で何度も滑らかに処理し,市場騒音のほとんどを取り除き,取引信号をより信頼性のあるものにする.
- 柔軟性が高い. ユーザーは,戦略のパフォーマンスを最適化するために,必要に応じて,採取周期,極点数,波動倍数などの戦略パラメータを調整できます.
- 実用性強. タイムスペンダのパラメータが導入され,戦略が指定された時間範囲で動作できるようにし,実地での応用と反省研究が便利である.
リスク分析
ゲースト・チャネルの自己適応型均等線策には多くの利点がありますが,いくつかのリスクがあります.
- パラメータ設定のリスク. 不適切なパラメータ設定は,戦略の失敗や不良なパフォーマンスを引き起こす可能性があるため,実用的なアプリケーションで繰り返しテストおよび最適化が必要である.
- 突発事件のリスク 突発的な重大事件に直面すると,戦略は適切な対応を間に合わせることができず,損失を招く可能性があります.
- 過剰適合のリスク。パラメータが過去データに過度に適合すると,戦略が将来に不良なパフォーマンスを引き起こす可能性があり,サンプル内外のパフォーマンスを考慮する必要がある。
- 利回りリスク 戦略は主にトレンド市場に適用され,波動的な市場で頻繁に取引すると,大きな利回りリスクに直面する可能性があります.
最適化の方向
高斯通路の自律的な戦略の最適化方向は以下の通りです.
- 動的パラメータ最適化. 機械学習などの技術の導入により,戦略パラメータの自動最適化と動的調整を実現し,適応性を向上させる.
- 多因子融合:高位通路と他の有効な技術指標または因子を組み合わせ,より堅牢な取引信号を形成する.
- ポジション管理の最適化. 戦略の基礎に合理的なポジション管理と資金管理の規則を追加し,撤回とリスクを制御する.
- 多品種協調 戦略を複数の異なる取引品種に拡張し,資産配置と関連性分析によってリスクを分散する.
要約する
高斯通道自適応均等線戦略は,高斯波と自適応パラメータに基づく量化取引戦略であり,価格通路を動的に構築することによって,スムーズで信頼性の高い取引信号を生成する.戦略は,自適応性,トレンド追跡性,スムーズ性,柔軟性,実用性などの利点を有しているが,同時に,パラメータ設定,突発事件,過適合およびスレートなどのリスクにも直面する.将来,戦略は,ダイナミックパラメータ最適化,多要素融合,ポジション管理最適化,多種の協同性などの側面からさらに完善および向上することができる.
ストラテジーソースコード
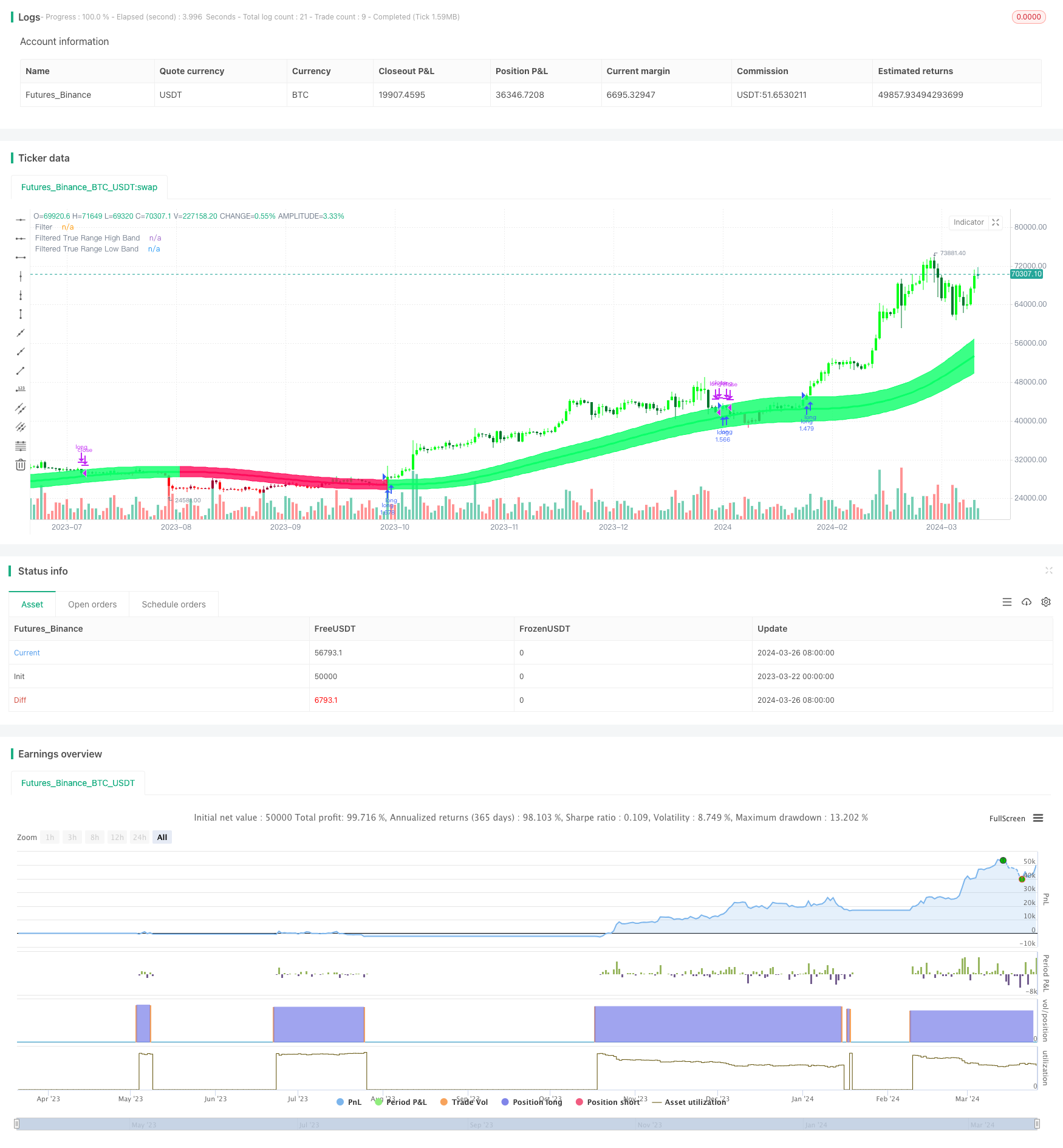
/*backtest
start: 2023-03-22 00:00:00
end: 2024-03-27 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=4
strategy(title="Gaussian Channel Strategy v1.0", overlay=true, calc_on_every_tick=false, initial_capital=10000, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value=100, commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, commission_value=0.1)
// Date condition inputs
startDate = input(title="Date Start", type=input.time, defval=timestamp("1 Jan 2018 00:00 +0000"), group="Dates")
endDate = input(title="Date End", type=input.time, defval=timestamp("31 Dec 2060 23:59 +0000"), group="Dates")
timeCondition = true
// This study is an experiment utilizing the Ehlers Gaussian Filter technique combined with lag reduction techniques and true range to analyze trend activity.
// Gaussian filters, as Ehlers explains it, are simply exponential moving averages applied multiple times.
// First, beta and alpha are calculated based on the sampling period and number of poles specified. The maximum number of poles available in this script is 9.
// Next, the data being analyzed is given a truncation option for reduced lag, which can be enabled with "Reduced Lag Mode".
// Then the alpha and source values are used to calculate the filter and filtered true range of the dataset.
// Filtered true range with a specified multiplier is then added to and subtracted from the filter, generating a channel.
// Lastly, a one pole filter with a N pole alpha is averaged with the filter to generate a faster filter, which can be enabled with "Fast Response Mode".
//Custom bar colors are included.
//Note: Both the sampling period and number of poles directly affect how much lag the indicator has, and how smooth the output is.
// Larger inputs will result in smoother outputs with increased lag, and smaller inputs will have noisier outputs with reduced lag.
// For the best results, I recommend not setting the sampling period any lower than the number of poles + 1. Going lower truncates the equation.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Updates:
// Huge shoutout to @e2e4mfck for taking the time to improve the calculation method!
// -> migrated to v4
// -> pi is now calculated using trig identities rather than being explicitly defined.
// -> The filter calculations are now organized into functions rather than being individually defined.
// -> Revamped color scheme.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Functions - courtesy of @e2e4mfck
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Filter function
f_filt9x (_a, _s, _i) =>
int _m2 = 0, int _m3 = 0, int _m4 = 0, int _m5 = 0, int _m6 = 0,
int _m7 = 0, int _m8 = 0, int _m9 = 0, float _f = .0, _x = (1 - _a)
// Weights.
// Initial weight _m1 is a pole number and equal to _i
_m2 := _i == 9 ? 36 : _i == 8 ? 28 : _i == 7 ? 21 : _i == 6 ? 15 : _i == 5 ? 10 : _i == 4 ? 6 : _i == 3 ? 3 : _i == 2 ? 1 : 0
_m3 := _i == 9 ? 84 : _i == 8 ? 56 : _i == 7 ? 35 : _i == 6 ? 20 : _i == 5 ? 10 : _i == 4 ? 4 : _i == 3 ? 1 : 0
_m4 := _i == 9 ? 126 : _i == 8 ? 70 : _i == 7 ? 35 : _i == 6 ? 15 : _i == 5 ? 5 : _i == 4 ? 1 : 0
_m5 := _i == 9 ? 126 : _i == 8 ? 56 : _i == 7 ? 21 : _i == 6 ? 6 : _i == 5 ? 1 : 0
_m6 := _i == 9 ? 84 : _i == 8 ? 28 : _i == 7 ? 7 : _i == 6 ? 1 : 0
_m7 := _i == 9 ? 36 : _i == 8 ? 8 : _i == 7 ? 1 : 0
_m8 := _i == 9 ? 9 : _i == 8 ? 1 : 0
_m9 := _i == 9 ? 1 : 0
// filter
_f := pow(_a, _i) * nz(_s) +
_i * _x * nz(_f[1]) - (_i >= 2 ?
_m2 * pow(_x, 2) * nz(_f[2]) : 0) + (_i >= 3 ?
_m3 * pow(_x, 3) * nz(_f[3]) : 0) - (_i >= 4 ?
_m4 * pow(_x, 4) * nz(_f[4]) : 0) + (_i >= 5 ?
_m5 * pow(_x, 5) * nz(_f[5]) : 0) - (_i >= 6 ?
_m6 * pow(_x, 6) * nz(_f[6]) : 0) + (_i >= 7 ?
_m7 * pow(_x, 7) * nz(_f[7]) : 0) - (_i >= 8 ?
_m8 * pow(_x, 8) * nz(_f[8]) : 0) + (_i == 9 ?
_m9 * pow(_x, 9) * nz(_f[9]) : 0)
//9 var declaration fun
f_pole (_a, _s, _i) =>
_f1 = f_filt9x(_a, _s, 1), _f2 = (_i >= 2 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 2) : 0), _f3 = (_i >= 3 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 3) : 0)
_f4 = (_i >= 4 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 4) : 0), _f5 = (_i >= 5 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 5) : 0), _f6 = (_i >= 6 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 6) : 0)
_f7 = (_i >= 2 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 7) : 0), _f8 = (_i >= 8 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 8) : 0), _f9 = (_i == 9 ? f_filt9x(_a, _s, 9) : 0)
_fn = _i == 1 ? _f1 : _i == 2 ? _f2 : _i == 3 ? _f3 :
_i == 4 ? _f4 : _i == 5 ? _f5 : _i == 6 ? _f6 :
_i == 7 ? _f7 : _i == 8 ? _f8 : _i == 9 ? _f9 : na
[_fn, _f1]
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Inputs
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Source
src = input(defval=hlc3, title="Source")
//Poles
int N = input(defval=4, title="Poles", minval=1, maxval=9)
//Period
int per = input(defval=144, title="Sampling Period", minval=2)
//True Range Multiplier
float mult = input(defval=1.414, title="Filtered True Range Multiplier", minval=0)
//Lag Reduction
bool modeLag = input(defval=false, title="Reduced Lag Mode")
bool modeFast = input(defval=false, title="Fast Response Mode")
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Definitions
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Beta and Alpha Components
beta = (1 - cos(4*asin(1)/per)) / (pow(1.414, 2/N) - 1)
alpha = - beta + sqrt(pow(beta, 2) + 2*beta)
//Lag
lag = (per - 1)/(2*N)
//Data
srcdata = modeLag ? src + (src - src[lag]) : src
trdata = modeLag ? tr(true) + (tr(true) - tr(true)[lag]) : tr(true)
//Filtered Values
[filtn, filt1] = f_pole(alpha, srcdata, N)
[filtntr, filt1tr] = f_pole(alpha, trdata, N)
//Lag Reduction
filt = modeFast ? (filtn + filt1)/2 : filtn
filttr = modeFast ? (filtntr + filt1tr)/2 : filtntr
//Bands
hband = filt + filttr*mult
lband = filt - filttr*mult
// Colors
color1 = #0aff68
color2 = #00752d
color3 = #ff0a5a
color4 = #990032
fcolor = filt > filt[1] ? #0aff68 : filt < filt[1] ? #ff0a5a : #cccccc
barcolor = (src > src[1]) and (src > filt) and (src < hband) ? #0aff68 : (src > src[1]) and (src >= hband) ? #0aff1b : (src <= src[1]) and (src > filt) ? #00752d :
(src < src[1]) and (src < filt) and (src > lband) ? #ff0a5a : (src < src[1]) and (src <= lband) ? #ff0a11 : (src >= src[1]) and (src < filt) ? #990032 : #cccccc
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Outputs
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Filter Plot
filtplot = plot(filt, title="Filter", color=fcolor, linewidth=3)
//Band Plots
hbandplot = plot(hband, title="Filtered True Range High Band", color=fcolor)
lbandplot = plot(lband, title="Filtered True Range Low Band", color=fcolor)
//Channel Fill
fill(hbandplot, lbandplot, title="Channel Fill", color=fcolor, transp=80)
//Bar Color
barcolor(barcolor)
longCondition = crossover(close, hband) and timeCondition
closeAllCondition = crossunder(close, hband) and timeCondition
if longCondition
strategy.entry("long", strategy.long)
if closeAllCondition
strategy.close("long")