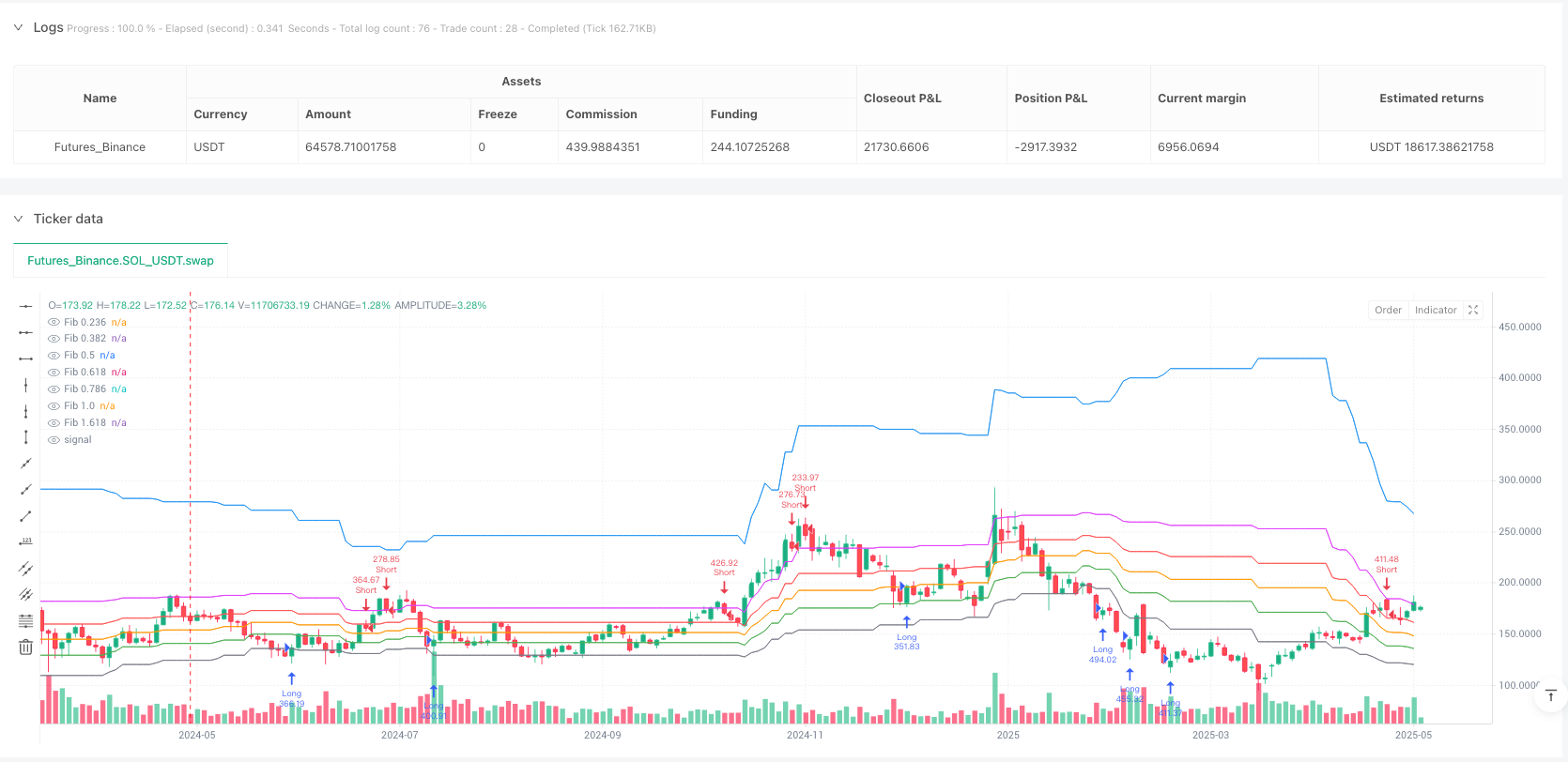
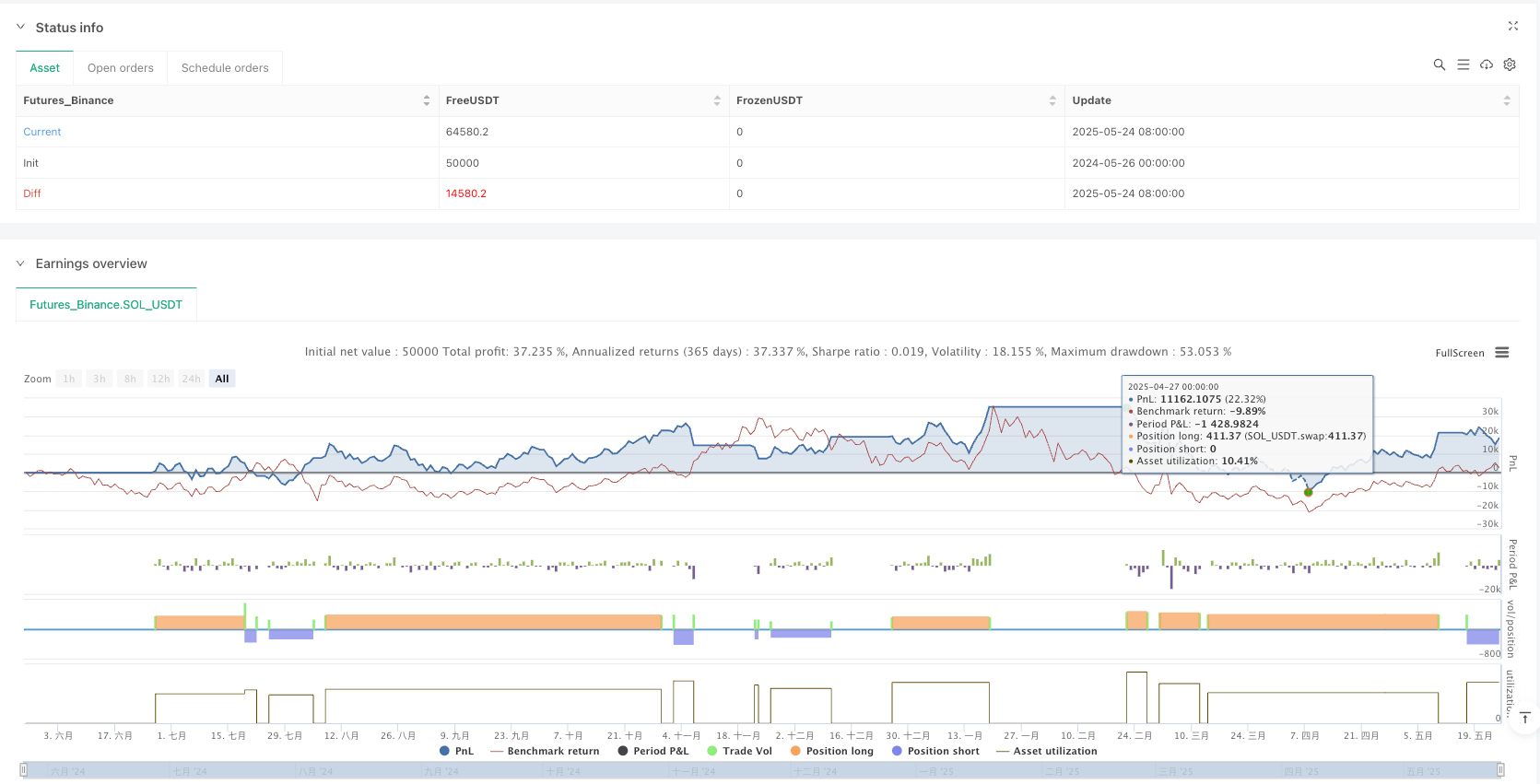
[tran]
概要
多層フィボナッチ・トレンド・トラッキング・アンド・ヘッジ・トレーディング・ストラテジー・システムは,複数の技術分析指標を統合した総合的な量化取引戦略である.この戦略は,フィボナッチ・リトラクション・理論を中心に,指数移動平均 (EMA),平均リアル波幅 (ATR),平均トレンド指数 (ADX) および方向性移動指標 (DMI) などの複数の技術指標を組み合わせて,多次元的な市場分析の枠組みを構築している.この戦略は,伝統的なトレンド・トラッキング機能だけでなく,反弹取引機構とオフショア機能を統合し,異なる市場において利益の機会を捉え,リスクを効果的に制御することを目的としている.
この戦略の特徴は,多層のリスク管理システムと柔軟な取引モデルにある.複数のストップターゲット (TP1とTP2) とATRベースのダイナミック・ストップ・メカニズムを設定することで,戦略は,資本を保護しながら収益の可能性を最大限に発揮できる.さらに,組み込みのヘッジ機能は,戦略に追加のリスク・バッファーを加え,波動的な市場環境でも比較的安定したパフォーマンスを保てる.
戦略原則
戦略の核心的な論理は,フィボナッチ・リターン理論とトレンド分析の組み合わせに基づいています. まず,戦略は,指定された周期内の最高点と最低点を計算することによって,フィボナッチ・リターンレベルを決定します.これは23.6%,38.2%,50%,61.8%,78.6%,100%および161.8%などの重要な位置を含んでいます.これらのレベルは,重要なサポートと抵抗の位置として使用され,取引信号の生成に重要な参照を提供します.
トレンド識別に関しては,戦略は50期指数移動平均を主要なトレンド判断ツールとして使用する.価格が連続した3つのK線がEMA上にあるときは,上昇傾向として認識される;逆に下降傾向である.同時に,戦略は価格構造を分析し,より高い低点とより高い高点を識別して多頭構造を確認し,より低い高点とより低い低点で空頭構造を確認する.
ADXとDMIの指標の導入は,トレンドの強さの判断精度を高めます.ADXの値が20以上は,強いトレンドの基準とみなされ,+DIと-DIの相対的な強さは,トレンドの方向性を決定するために使用されます.取引量分析は,取引量が20期平均の1.2倍を超えると,有効な量確認とみなされ,戦略の重要な構成要素でもあります.
取引信号の生成は,複数の条件を満たすと同時に成立する必要があります:トレンドの方向が明確で,価格が重要なフィボナッチレベルに近い,トレンドの強さが十分で,方向性指標が確認され,取引量が拡大されます.この複数のフィルタリング機構は,信号の信頼性を大幅に高め,偽信号の確率を下げます.
戦略的優位性
この戦略は,総合的な技術的分析の枠組みで,多くの顕著な利点があります.フィボナッチ理論,トレンド分析,動向指標と取引量分析を統合することにより,戦略は,市場状況を複数の次元から評価することができ,より包括的で正確な取引信号を提供します.この複数の指標の融合の方法は,単一の指標によって発生する誤導的な信号を効果的に削減し,全体的な戦略の安定性と信頼性を向上させます.
戦略のリスク管理システムは,そのもう一つの大きな利点である.二重のストップメカニズムは,トレーダーが最初の目標を達成すると,利益の一部をロックし,余剰ポジションを追求し,より大きな利益を保持することを可能にする.ATRベースのダイナミックストップ損失設定は,市場の変動性に応じて,リスク制御のレベルを自動的に調整することができ,低波動時に利益を保護するためにストップを締め,高波動時にストップを緩め,正常な波動から震えを避けるようにすることができる.
反転取引機能は,戦略に追加の収益の機会を増加させます. 価格が重要なサポートまたはレジスタンス地点に反転したとき,戦略は,この短期的な逆転状況を迅速に認識し,参加することができ,その結果,トレンド取引に基づいてより多くの取引機会を増やすことができます. この柔軟性は,戦略が異なる市場条件に適応することを可能にします.
策略の革新的な特徴は,ヘッジ機能の統合である.多頭ポジションを保有しているときに空頭シグナルが発生した場合,策略は,空頭ポジションをヘッジし,逆も同様である.このメカニズムは,市場の急速な逆転時に追加の保護を提供し,潜在的な損失を軽減し,新しい利益の機会に変換することができる.
タイムフィルターの設定により,過剰取引の問題を防ぐ.連続信号間には少なくとも5K線の間隔を要求することで,短期間に頻繁にポジション開設を回避し,取引コストを削減し,信号品質を向上させる.
戦略リスク
この戦略は,多くの利点があるにもかかわらず,注意しなければならないいくつかのリスク要因があります. まず,パラメータ依存性のリスクです. 戦略は,フィボナッチ周期,許容度,ATR倍数など,複数のパラメータ設定を伴う.これらのパラメータの選択は,戦略のパフォーマンスに重要な影響を及ぼします.不適切なパラメータ設定は,歴史的データに過度に適合したり,実際の市場で不良なパフォーマンスを引き起こす可能性があります.
市場環境の適応性は,別の潜在的なリスクである.戦略は,主に技術分析に基づいている.技術指標は,基本面が駆動された強い一方的な状況など,特定の市場条件下で不良なパフォーマンスを発揮し,技術指標は失敗する可能性があります.さらに,非常に低波動性または非常に高波動性のある市場環境では,戦略の信号生成頻度と正確さの両方が影響を受けることがあります.
スリップポイントと実行リスクも考慮する必要がある.実際の取引,特に波動性の高い市場条件では,注文実行価格と期待価格の差異がある可能性があります.このスリップポイントコストは,戦略の理論的利益を蝕む可能性があります.特に頻繁に取引する戦略については.
隠蔽機能は,追加の保護を提供しているものの,戦略の複雑さを増している.特定の状況では,隠蔽操作は,空白のポジションの同時損失,または手数料の面で追加のコストを引き起こす可能性があります.したがって,隠蔽機能の実際の効果を慎重に評価し,特定の市場条件下でこの機能を有効にするかどうかを考慮する必要があります.
戦略最適化の方向性
戦略のパフォーマンスをさらに向上させるために,複数の方向から最適化することができる. まず,ダイナミックパラメータ調整メカニズムの導入である.市場の変動性,トレンドの強さなどの要因に応じてフィボナッチ周期,ATR倍数などの重要なパラメータを動的に調整することができる.例えば,高波動の市場でATR倍数を増加させ,より大きなストップロスを提供し,低波動の市場でATR倍数を減少させ,リスクコントロールを厳しくする.
機械学習技術の統合は,もう一つの重要な最適化方向である.機械学習アルゴリズムを使用して,最適な入場時刻を識別したり,歴史的データによる学習パラメータの組み合わせに基づいて最適配置することもできる.さらに,市場情緒やニュースイベントが価格に与える影響を分析するために自然言語処理技術を使用して,戦略に基礎分析の次元を追加することもできる.
多時間枠分析の統合により,より包括的な市場視点を提供することができる.より長い時間枠で大きなトレンドの方向を確認し,より短い時間枠で正確なエントリーポイントを探すことができる.このような多時間枠の協調分析により,信号の質を高め,逆転取引のリスクを減らすことができる.
資金管理の最適化は,戦略のパフォーマンスを向上させる重要な方法でもある.市場条件,戦略の信頼度などの要因に応じて,ポジションサイズを動的に調整することができる.例えば,高い信頼度シグナル時にポジションを増やし,低い信頼度シグナル時にポジションを減らす.さらに,最大引き戻し制御機構を導入し,戦略が大きな損失が発生したときにポジションを自動的に減らすか,取引を一時停止することもできる.
ストップストップの論理のさらなる精細化も考慮に値する. ストップストップを追跡するメカニズムを導入し,価格の動きに応じてストップポジションを調整して,より多くの利益をロックすることができる. 同時に,市場構造の特徴に応じて,よりスマートなストップ目標を設定することができる. 例えば,重要な抵抗点の近くで早期にストップストップを行う.
要約する
多層のフィボナッチ・トレンド・トラッキングとヘッジ・トレーディング・ストラテジー・システムは,近代的な量化取引技術の重要な発展の方向を表している.このストラテジーは,クラシックな技術分析の複数のツールを巧妙に統合して,堅牢で柔軟な取引の枠組みを構築している.その多層のフィルタリング機構は,信号の質を保証し,多層のリスク管理システムは,効果的な資本保護を提供し,ヘッジ機能は,ストラテジーの追加的なセキュリティ・マージンを加えている.
戦略の成功実施には,その基本原理と動作メカニズムを十分に理解し,特定の取引環境に応じて適切なパラメータの調整と最適化を行う必要があります.戦略は理論的には良好な設計ですが,実際のアプリケーションでは,市場の微細構造,取引コスト,滑り点などの現実的な要因の影響を考慮する必要があります.
人工知能と機械学習技術の進歩に伴い,この戦略には大きな最適化余地があります.より高度なデータ分析技術と自適化メカニズムを導入することにより,戦略の性能がさらに向上する見込みがあります.このような総合的な戦略は,市場動態とリスク管理の重要性を深く理解するための貴重な学習と改善のプラットフォームを提供する. ||
Overview
The Multi-Level Fibonacci Trend Following and Hedging Trading Strategy System is a comprehensive quantitative trading strategy that integrates multiple technical analysis indicators. This strategy centers on Fibonacci retracement theory, combining Exponential Moving Average (EMA), Average True Range (ATR), Average Directional Index (ADX), and Directional Movement Indicator (DMI) to construct a multi-dimensional market analysis framework. The strategy not only features traditional trend-following capabilities but also integrates bounce trading mechanisms and hedging functionality, aiming to capture profitable opportunities under different market conditions while effectively controlling risk.
The unique aspect of this strategy lies in its multi-layered risk management system and flexible trading modes. By setting multiple take-profit targets (TP1 and TP2) and dynamic stop-loss mechanisms based on ATR, the strategy can maximize profit potential while protecting capital. Additionally, the built-in hedging function adds an extra risk buffer to the strategy, enabling it to maintain relatively stable performance even in highly volatile market environments.
Strategy Principles
The core logic of the strategy is based on the combination of Fibonacci retracement theory and trend analysis. First, the strategy calculates the highest and lowest points within a specified period to determine Fibonacci retracement levels, including key positions at 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, 78.6%, 100%, and 161.8%. These levels serve as important support and resistance zones, providing crucial references for trading signal generation.
For trend identification, the strategy employs a 50-period Exponential Moving Average as the primary trend determination tool. When prices remain above the EMA for three consecutive candlesticks, it’s identified as an uptrend; conversely, it’s considered a downtrend. Simultaneously, the strategy analyzes price structure by identifying higher lows and higher highs to confirm bullish structure, and lower highs and lower lows to confirm bearish structure.
The introduction of ADX and DMI indicators enhances the precision of trend strength assessment. An ADX value greater than 20 is considered the standard for a strong trend, while the relative strength of +DI and -DI is used to determine trend direction. Volume analysis is also an important component of the strategy, where volume exceeding 1.2 times the 20-period average is considered effective volume confirmation.
Trade signal generation requires multiple conditions to be met simultaneously: clear trend direction, price proximity to key Fibonacci levels, sufficient trend strength, directional indicator confirmation, and volume expansion. This multi-filter mechanism significantly improves signal reliability and reduces the probability of false signals.
Strategy Advantages
This strategy possesses multiple significant advantages, first manifested in its comprehensive technical analysis framework. By integrating Fibonacci theory, trend analysis, momentum indicators, and volume analysis, the strategy can evaluate market conditions from multiple dimensions, providing more comprehensive and accurate trading signals. This multi-indicator fusion approach effectively reduces misleading signals that might be generated by single indicators, improving the overall stability and reliability of the strategy.
The strategy’s risk management system represents another major advantage. The dual take-profit mechanism allows traders to lock in partial profits upon reaching the first target while maintaining remaining positions to pursue greater returns. ATR-based dynamic stop-loss settings can automatically adjust risk control levels according to market volatility, tightening stops during low volatility to protect profits and relaxing stops during high volatility to avoid being stopped out by normal fluctuations.
The bounce trading functionality adds additional profit opportunities to the strategy. When prices bounce at key support or resistance levels, the strategy can quickly identify and participate in such short-term reversal movements, thereby adding more trading opportunities beyond trend trading. This flexibility enables the strategy to adapt to different market conditions, finding suitable trading opportunities whether in strong trending markets or range-bound markets.
The integration of hedging functionality is an innovative feature of this strategy. When holding long positions and a short signal appears, the strategy will open a hedge short position; vice versa. This mechanism can provide additional protection during rapid market reversals, reducing potential losses and possibly converting them into new profit opportunities.
The time filter setting prevents overtrading issues. By requiring at least 5 candlesticks between consecutive signals, the strategy avoids frequent position opening within short periods, reducing trading costs and improving signal quality.
Strategy Risks
Despite the strategy’s multiple advantages, several risk factors require attention. First is parameter dependency risk. The strategy involves multiple parameter settings, including Fibonacci period, tolerance, ATR multipliers, etc. The selection of these parameters significantly impacts strategy performance. Inappropriate parameter settings may lead to overfitting historical data or poor performance in actual markets. Therefore, sufficient backtesting and parameter optimization are needed to find the most suitable parameter combinations for specific markets and timeframes.
Market environment adaptability represents another potential risk. The strategy is primarily based on technical analysis and may underperform in certain market conditions, such as during fundamental-driven strong unidirectional moves where technical indicators might fail. Additionally, in extremely low or high volatility market environments, both signal generation frequency and accuracy may be affected.
Slippage and execution risks also need consideration. In actual trading, particularly during high volatility market conditions, there may be differences between order execution prices and expected prices. This slippage cost could erode the strategy’s theoretical returns, especially for frequently trading strategies.
While the hedging function provides additional protection, it also increases strategy complexity. In certain situations, hedging operations might result in simultaneous losses on both long and short positions, or generate additional costs in terms of commissions. Therefore, careful evaluation of the hedging function’s actual effectiveness is needed, along with consideration of whether to enable this function under specific market conditions.
Strategy Optimization Directions
To further enhance strategy performance, optimization can be pursued in multiple directions. First is the introduction of dynamic parameter adjustment mechanisms. Key parameters such as Fibonacci period and ATR multipliers can be dynamically adjusted based on market volatility, trend strength, and other factors. For example, increasing ATR multipliers in high volatility markets to provide larger stop-loss space, and decreasing ATR multipliers in low volatility markets to tighten risk control.
Integration of machine learning technology represents another important optimization direction. Machine learning algorithms can be used to identify optimal entry timing or learn optimal parameter combination configurations based on historical data. Additionally, natural language processing technology can be utilized to analyze market sentiment and news event impacts on prices, adding fundamental analysis dimensions to the strategy.
Integration of multi-timeframe analysis can provide a more comprehensive market perspective. Larger timeframes can be used to confirm major trend direction, while shorter timeframes can be used to find precise entry points. This coordinated multi-timeframe analysis can improve signal quality and reduce counter-trend trading risks.
Money management optimization is also an important avenue for enhancing strategy performance. Position sizes can be dynamically adjusted based on market conditions, strategy confidence levels, and other factors. For example, increasing positions during high-confidence signals and reducing positions during low-confidence signals. Additionally, maximum drawdown control mechanisms can be introduced to automatically reduce positions or pause trading when the strategy experiences significant losses.
Further refinement of take-profit and stop-loss logic is also worth considering. Trailing stop mechanisms can be introduced to dynamically adjust stop-loss positions based on price movements to lock in more profits. Simultaneously, more intelligent take-profit targets can be set based on market structure characteristics, such as taking profits early near key resistance levels.
Conclusion
The Multi-Level Fibonacci Trend Following and Hedging Trading Strategy System represents an important development direction in modern quantitative trading technology. This strategy cleverly integrates multiple classic technical analysis tools to construct a trading framework that is both robust and flexible. Its multi-filter mechanism ensures signal quality, the multi-layered risk management system provides effective capital protection, and the hedging function adds an additional safety margin to the strategy.
Successful implementation of this strategy requires thorough understanding of its fundamental principles and operational mechanisms, along with appropriate parameter adjustments and optimizations based on specific trading environments. While the strategy has excellent theoretical design, practical application still requires consideration of real-world factors such as market microstructure, trading costs, and slippage.
With the continuous development of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, this strategy still has enormous optimization potential. Through the introduction of more advanced data analysis techniques and adaptive mechanisms, strategy performance is expected to be further enhanced. For quantitative traders, such comprehensive strategies provide a valuable learning and improvement platform, helping to deepen understanding of market dynamics and the importance of risk management.[/trans]
/*backtest
start: 2024-05-26 00:00:00
end: 2025-05-25 00:00:00
period: 2d
basePeriod: 2d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"SOL_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("Fibonacci Trend v6.4 - TP/SL Labels", overlay=true, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value=100)
// === Parameters ===
fibLen = input.int(50, "Fibonacci Range")
fibTol = input.float(0.01, "Fib Proximity Tolerance (%)", step=0.001)
slMult = input.float(1.5, "SL - ATR", step=0.1)
tp2Mult = input.float(2.0, "TP2 - ATR", step=0.1)
srLookback = input.int(20, "Support/Resistance Lookback Bars")
useBounce = input.bool(true, "Enable Bounce Entry")
// === Indicators ===
ema50 = ta.ema(close, 50)
atr = ta.atr(14)
volAvg = ta.sma(volume, 20)
volHigh = volume > volAvg * 1.2
// === Fibonacci Levels ===
lowWick = ta.lowest(low, fibLen)
highWick = ta.highest(high, fibLen)
rangeWick = highWick - lowWick
fib236 = lowWick + 0.236 * rangeWick
fib382 = lowWick + 0.382 * rangeWick
fib5 = lowWick + 0.5 * rangeWick
fib618 = lowWick + 0.618 * rangeWick
fib786 = lowWick + 0.786 * rangeWick
fib1 = highWick
fib1618 = lowWick + 1.618 * rangeWick
nearSupport = math.abs(low - fib382)/close < fibTol or math.abs(low - fib5)/close < fibTol
nearResist = math.abs(high - fib618)/close < fibTol
// === Trend Structure ===
higherLow = low > low[1] and low[1] > low[2]
higherHigh = high > high[1]
lowerHigh = high < high[1] and high[1] < high[2]
lowerLow = low < low[1]
longStruct = higherLow and higherHigh
shortStruct = lowerHigh and lowerLow
// === ADX / DMI ===
dmiLen = 14
upMove = high - high[1]
downMove = low[1] - low
plusDM = (upMove > downMove and upMove > 0) ? upMove : 0
minusDM = (downMove > upMove and downMove > 0) ? downMove : 0
tr = ta.tr(true)
tr14 = ta.rma(tr, dmiLen)
plusDI = 100 * ta.rma(plusDM, dmiLen) / tr14
minusDI = 100 * ta.rma(minusDM, dmiLen) / tr14
dx = 100 * math.abs(plusDI - minusDI) / (plusDI + minusDI)
adx = ta.rma(dx, dmiLen)
trendStrong = adx > 20
// === EMA Momentum Break ===
emaBreakLong = close > ema50 and close[1] < ema50 and volume > volAvg
emaBreakShort = close < ema50 and close[1] > ema50 and volume > volAvg
// === Time Filter ===
var int lastLongBar = na
var int lastShortBar = na
canLong = na(lastLongBar) or (bar_index - lastLongBar > 5)
canShort = na(lastShortBar) or (bar_index - lastShortBar > 5)
priceAboveEMA = close > ema50 and close[1] > ema50 and close[2] > ema50
priceBelowEMA = close < ema50 and close[1] < ema50 and close[2] < ema50
// === Support / Resistance ===
support = ta.lowest(low, srLookback)
resist = ta.highest(high, srLookback)
// === Entry Conditions ===
longTrend = priceAboveEMA and nearSupport and trendStrong and plusDI > minusDI and longStruct and (volHigh or emaBreakLong) and canLong
shortTrend = priceBelowEMA and nearResist and trendStrong and minusDI > plusDI and shortStruct and (volHigh or emaBreakShort) and canShort
bounceLong = useBounce and math.abs(low - support)/close < fibTol and close > open and close > close[1]
bounceShort = useBounce and math.abs(high - resist)/close < fibTol and close < open and close < close[1]
longSignal = longTrend or bounceLong
shortSignal = shortTrend or bounceShort
// === TP/SL Calculations ===
tp1Long = resist
tp2Long = close + atr * tp2Mult
slLong = close - atr * slMult
tp1Short = support
tp2Short = close - atr * tp2Mult
slShort = close + atr * slMult
tp1ColorLong = bounceLong ? color.blue : color.yellow
tp1ColorShort = bounceShort ? color.blue : color.yellow
// === Long Entry ===
if (longSignal and strategy.position_size <= 0)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
strategy.exit("TP1", from_entry="Long", limit=tp1Long, stop=slLong, qty_percent=50)
strategy.exit("TP2", from_entry="Long", limit=tp2Long, stop=slLong)
lastLongBar := bar_index
label.new(bar_index, close, text="ENTRY: " + str.tostring(close, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=color.green, textcolor=color.white)
label.new(bar_index, tp1Long, text="TP1: " + str.tostring(tp1Long, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=tp1ColorLong)
label.new(bar_index, tp2Long, text="TP2: " + str.tostring(tp2Long, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=color.green)
label.new(bar_index, slLong, text="SL: " + str.tostring(slLong, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=color.red)
// === Short Entry ===
if (shortSignal and strategy.position_size >= 0)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
strategy.exit("TP1", from_entry="Short", limit=tp1Short, stop=slShort, qty_percent=50)
strategy.exit("TP2", from_entry="Short", limit=tp2Short, stop=slShort)
lastShortBar := bar_index
label.new(bar_index, close, text="ENTRY: " + str.tostring(close, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=color.red, textcolor=color.white)
label.new(bar_index, tp1Short, text="TP1: " + str.tostring(tp1Short, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=tp1ColorShort)
label.new(bar_index, tp2Short, text="TP2: " + str.tostring(tp2Short, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=color.green)
label.new(bar_index, slShort, text="SL: " + str.tostring(slShort, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=color.red)
// === Hedge Orders ===
if (strategy.position_size > 0 and shortSignal)
strategy.entry("HedgeShort", strategy.short)
if (strategy.position_size < 0 and longSignal)
strategy.entry("HedgeLong", strategy.long)
// === Fibonacci Plotting ===
plot(fib236, "Fib 0.236", color=color.gray)
plot(fib382, "Fib 0.382", color=color.green)
plot(fib5, "Fib 0.5", color=color.orange)
plot(fib618, "Fib 0.618", color=color.red)
plot(fib786, "Fib 0.786", color=color.fuchsia)
plot(fib1, "Fib 1.0", color=color.white)
plot(fib1618, "Fib 1.618", color=color.blue)