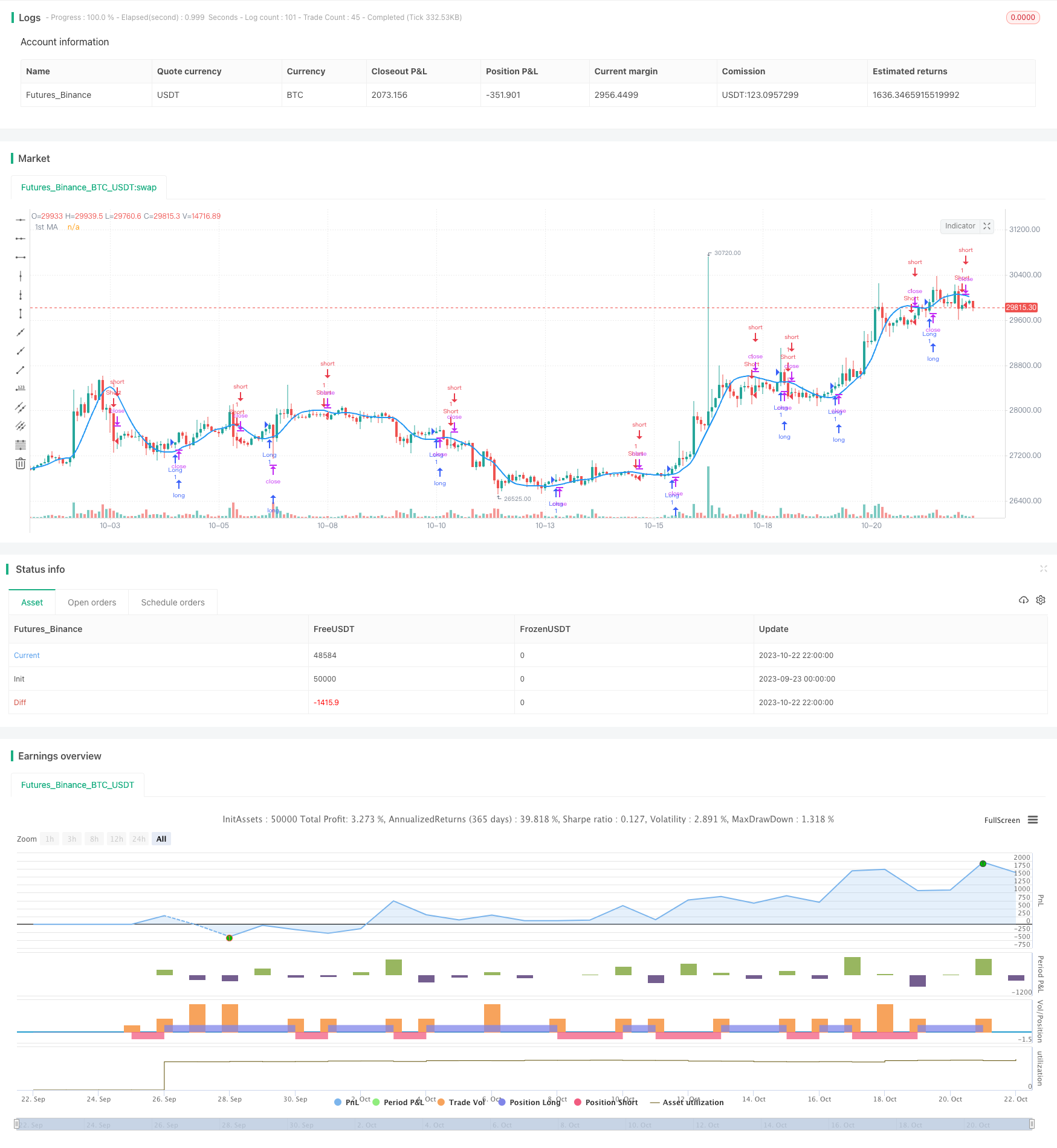
개요
쌍평평선 전환점 거래 전략은 평평선 교차를 기반으로 한 거래 전략이다. 그것은 두 개의 다른 변수 세트의 이동 평균을 사용하여, 그들의 전환 상황에 따라 입문 및 출퇴근 시간을 판단한다. 이 전략은 간단하고 직관적이며, 구현하기 쉽고, 중장선 거래에 적용된다.
전략 원칙
이 전략은 가격 입력을 사용하여 각각 두 가지 다른 변수의 평균선을 계산한다. SMA1과 SMA2이다. 전략은 ROC 지표를 사용하여 평균선의 전환 상황을 판단한다. SMA1의 ROC 값이 설정된 긍정적 인 경계를 초과하면 SMA1이 상향으로 전환되었다고 간주하고 SMA1의 상향 신호를 기록한다.
SMA1이 위쪽으로 돌고 상위 K선 SMA2가 아래로 돌면, 구매 신호를 발생시키고, 더 많은 것을 한다. SMA1이 아래로 돌고 상위 K선 SMA2가 위쪽으로 돌면, 판매 신호를 발생시키고, 공백을 한다.
이 전략은 거래 방향을 결정하는 두 개의 평행선 전환을 사용하며, 하나의 평행선 전환은 입시 시점을 확인하고, 두 개의 평행선 교차는 입시 시점 트렌드에 변화가 발생하도록 보장하며, 가짜 돌파구를 효과적으로 필터링 할 수 있습니다.
우위 분석
쌍평선 교차와 돌림 판단을 사용하여 가짜 돌파를 효과적으로 필터링하여 진입의 정확성을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
평균선 전환은 ROC 지표와 결합하여 전환 시기를 명확하게 판단하여 자주 거래되는 것을 피할 수 있습니다.
중·장선 쌍평선으로, 주 트렌드를 추적하여 큰 트렌드 수익을 얻을 수 있다.
전략 논리는 간단하고 명확하며, 이해하기 쉬운 구현으로, 양자 거래 초보자에게 적합하다.
사용자 정의 가능한 매개 변수, 다양한 시장 환경에 적응할 수 있으며, 강한 적응력을 가지고 있다.
위험 분석
양평선 교차는 진동상태에서 많은 양의 가짜 신호를 생성하여 손실을 초래할 수 있다.
ROC 매개 변수는 정밀 최적화가 필요합니다. 그렇지 않으면 인식으로 전환하면 오류가 발생하여 전략 성능에 영향을 미칩니다.
대주기적 변동시장은 여러 번의 스톱을 유발할 수 있으며, 스톱의 폭을 넓혀서 이를 방지할 수 있다.
“일반적인 지표만으로는, 중요한 뉴스와 같은 급격한 사건에 대응하기 어렵고, 손실을 초래할 수 있다”.
매개 변수 최적화 과 적합 문제, 테스트 사이클이 충분히 길고, 다양한 상황을 포함할 필요가 있다.
최적화 방향
이동 평균 변수를 최적화하여 최적의 평균 선주기 조합을 찾습니다.
ROC 매개 변수를 최적화하여 회전 인식 정확도를 향상시킵니다.
사용자 정의 가격 레벨을 돌파하는 동적 상쇄를 적용할 수 있는 상쇄 메커니즘을 추가
거래량 지표 트리거와 같은 추가 조건을 추가하여 가짜 브레이크를 피하십시오.
MACD, BOLL 등과 결합하여 의사결정 효과를 높이는 방법
기계 학습과 같은 방법을 사용하여 변수를 자동으로 최적화하여 시장 변화에 적응합니다.
요약하다
쌍평선 전환점 전략은 전반적으로 간단하고 실용적인 트렌드 추적 전략이다. 그것은 기본 평선 지표만 필요로하며, 논리가 명확하고 이해하기 쉽으며, 양자 거래 초보자에게 학습하고 연습하기에 적합하다. 매개 변수 최적화 및 중지 손실 메커니즘 최적화를 통해 전략의 안정성을 크게 향상시킬 수 있다. 다른 보조 지표와 결합하여 사용하면 전략의 효과를 더욱 향상시킬 수 있다. 이 전략은 사용자 정의가 높고, 다양한 시장 환경에서 적용할 수 있는 유연성이 있으며, 추천할 만한 쌍평선 거래 전략이다.
Overview
The Dual Moving Average Turning Point strategy is a trend following strategy based on moving average crossovers. It uses two moving averages with different parameter settings and determines entry and exit points according to their turning directions. This strategy is simple and intuitive, easy to implement, and suitable for medium-to-long term trading.
Strategy Logic
The strategy uses Price as the price input source and calculates two moving averages, SMA1 and SMA2, with different parameters. It uses the ROC indicator to determine the turning directions of the moving averages. When SMA1’s ROC value exceeds the positive threshold, it is considered an upward turn of SMA1 and an upward signal is recorded. When SMA1’s ROC value breaks the negative threshold, it is considered a downward turn of SMA1 and a downward signal is recorded. The judgment logic for SMA2 is similar.
When SMA1 turns upward and the previous bar’s SMA2 turns downward, a buy signal is generated to go long. When SMA1 turns downward and the previous bar’s SMA2 turns upward, a sell signal is generated to go short.
The strategy uses the turning directions of two moving averages to determine the trading direction and the turning of one moving average to confirm entry timing. The dual moving average crossover ensures the trend has changed when entering the market, which helps avoid false breakouts.
Advantage Analysis
Using dual moving average crossover and turning points can effectively filter out false breakouts and improve entry accuracy.
Combining moving average turning points with the ROC indicator can clearly identify turning points and avoid frequent trading.
Adopting medium-to-long-term dual moving averages can track the main trend and achieve sizable trend profits.
The strategy logic is simple and clear, easy to understand and implement, suitable for quant trading beginners.
Customizable parameters suit different market environments with strong adaptability.
Risk Analysis
Dual moving average crossovers may generate many false signals in ranging markets, leading to losses.
The ROC parameters need precise optimization, otherwise turn recognition will have errors, affecting strategy performance.
Large periodic ranging markets may trigger stop loss multiple times. Expanding stop loss range can avoid it.
Relying solely on moving averages, it’s hard to respond to sudden events like major news, which may lead to losses.
Note the overfitting problem in parameter optimization. Test period should be long enough to include different market conditions.
Optimization Directions
Optimize moving average parameters to find the best moving average period combination.
Optimize ROC parameters to improve turning point recognition accuracy.
Add stop loss mechanisms such as dynamic stop loss based on breaking customized price levels.
Add additional conditions like volume indicators to avoid false breakouts.
Incorporate other indicators like MACD, BOLL to improve decision making.
Use machine learning etc. to auto optimize parameters and adapt to market changes.
Summary
In summary, the Dual Moving Average Turning Point strategy is a simple and practical trend following strategy. It can be implemented with basic moving average indicators and has clear, easy-to-understand logic, making it very suitable for quant trading beginners to learn and practice. With parameter optimization and stop loss optimization, the strategy stability can be greatly improved. Combining with other auxiliary indicators can further enhance the strategy. The highly customizable strategy can be flexibly applied to different market environments and is a recommended dual moving average trading strategy.
[/trans]
/*backtest
start: 2023-09-23 00:00:00
end: 2023-10-23 00:00:00
period: 2h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=3
strategy("MA Turning Point Strategy", overlay=true)
src = input(close, title="Source")
price = request.security(syminfo.tickerid, timeframe.period, src)
ma1 = input(25, title="1st MA Length")
type1 = input("HMA", "1st MA Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "HMA", "VWMA"])
f_hma(_src, _length)=>
_return = wma((2*wma(_src, _length/2))-wma(_src, _length), round(sqrt(_length)))
price1 = if (type1 == "SMA")
sma(price, ma1)
else
if (type1 == "EMA")
ema(price, ma1)
else
if (type1 == "VWMA")
vwma(price, ma1)
else
f_hma(price, ma1)
plot(series=price1, style=line, title="1st MA", color=blue, linewidth=2, transp=0)
lookback1 = input(1, "Lookback 1")
roc1 = roc(price1, lookback1)
ma1up = false
ma1down = false
ma2up = false
ma2down = false
ma1up := nz(ma1up[1])
ma1down := nz(ma1down[1])
ma2up := nz(ma2up[1])
ma2down := nz(ma2down[1])
trendStrength1 = input(2.5, title="Minimum slope magnitude * 100", type=float) * 0.01
if crossover(roc1, trendStrength1)
ma1up := true
ma1down := false
if crossunder(roc1, -trendStrength1)
ma1up := false
ma1down := true
longCondition = ma1up and ma1down[1]
if (longCondition)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
shortCondition = ma1down and ma1up[1]
if (shortCondition)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)