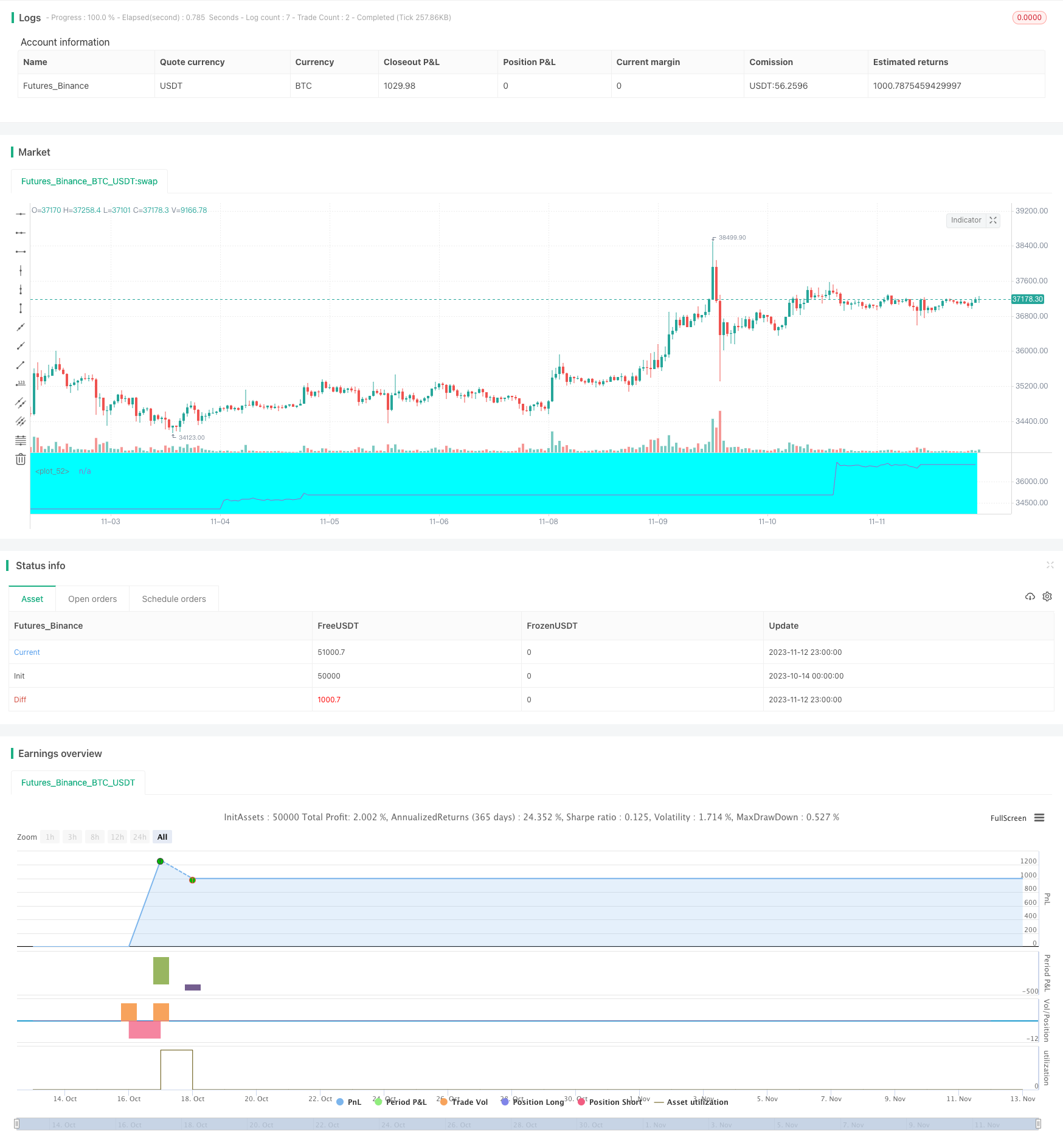
개요
이 전략은 주말에 비트코인을 단선으로 거래하는 전략으로, 10배의 레버리지를 사용하여 거래한다. 전략의 주요 아이디어는 금요일 종결시 가격을 기록하고, 그 다음 토요일과 일요일에는 당일 종결 가격과 금요일 종결 가격의 오락을 비교하고, 낙하값을 초과하면 더 많은 것을 하거나, 월요일에는 평평하게 한다.
전략 원칙
이 전략은 먼저 금요일의 종결 가격을 기록한 다음, 현재 날짜의 금요일로부터의 날 수를 계산한다. 토요일과 일요일에는, 그 날의 종결 가격이 금요일의 종결 가격보다 4.5% 이상 상승하면, 공백을 한다. 그 날의 종결 가격이 금요일의 종결 가격보다 4.5% 이상 떨어지면, 더 많이 한다.
구체적으로, 전략은 금요일의 종결 가격을 가져다가 토요일에는 현재의 종결 가격과 금요일의 종결 가격의 상승과 하락을 비교합니다. 현재의 종결 가격이 금요일의 종결 가격보다 4.5% 이상 상승하면,strategy.short공백; 만약 현재 종결가격이 금요일 종결가격보다 4.5% 이상 하락하면 통과strategy.long더 많이 하세요.leverage이 변수는 10배의 레버리지를 설정합니다. 이윤이 초기 자본의 10%에 도달하면strategy.close_all()월요일, 모든 평지 포지션.strategy.close_all()모든 지점을 평평하게 한다.
우위 분석
- 주말 거래량이 증가하는 비트코인의 특성을 활용하여 주말에 단선 거래를 통해 주말의 단기 트렌드를 잡을 수 있습니다.
- 10배의 레버리지를 사용하여 거래하여 수익을 높여라
- 정지 조건을 설정하여 적시에 정지하여 손실을 확대하지 않도록합니다.
- 월요일 상장, 월요일 오픈의 큰 변동의 위험을 피하기
위험 분석
- 비트코인의 주말 가격 변동으로 손실 위험이 있다.
- 10배의 레버리지는 손실을 증가시킬 수 있습니다.
- 부적절한 스톱 손실 설정으로 큰 손실이 발생할 수 있습니다.
- 월요일 오프닝 가격의 급격한 변동으로 인해 모든 거래가 중단되지 않을 수도 있습니다.
위험에 대해 다음과 같은 최적화 조치를 고려할 수 있습니다.
- 스톱로스를 설정하고 단편적 손실을 통제합니다.
- 리버리지 배수를 조정하여 위험을 줄여주세요.
- 정지점 설정을 최적화하여 수익이 일정 비율에 도달했을 때 정지점을 분할한다.
- 월요일 오프닝 전에 거래량이나 시간 정지를 설정하여 월요일 오프닝의 급격한 변동을 피하십시오.
최적화 방향
이 전략은 다음과 같은 부분에서 최적화될 수 있습니다.
다른 지표 판단을 추가하고, 진출 지점 선택을 최적화한다. 이동 평균선, RSI 등의 지표 필터링 진출 시기를 결합하여 진출 정확도를 향상시킬 수 있다.
손해 중지 전략의 최적화, 이동 손해 중지, 분량 중지 등의 방법으로 수익을 잠금하고 위험을 제어한다.
리버리지 크기를 조정하여 위험을 줄이십시오. 리버리지 비율을 동적으로 조정하여 리버리지를 철회할 때 줄일 수 있습니다.
다양한 종류의 거래를 추가한다. 다른 일반적인 암호화폐를 추가하고, 그들의 주말 거래 특성을 활용하여 다양한 종류의 중매 거래를 할 수 있다.
기계학습 알고리즘을 사용하여 최적화 파라미터. 많은 양의 역사 데이터를 수집할 수 있으며, 기계학습 알고리즘을 사용하여 파라미터를 자동으로 최적화하여 파라미터를 동적으로 조정할 수 있다.
요약하다
이 전략은 전형적인 비트코인 주말 거래량 증가를 이용한 단선 거래 전략이다. 전략은 비트코인 주말 거래량 증가를 이용한 특징을 가지고 있으며, 토요일에는 추세를 판단하고, 오버하거나, 비어 있다. 전략은 수익 증대, 위험 제어 등의 장점이 있지만, 또한 약간의 위험도 존재한다. 다음 단계는 입점, 손실 정지, 레버리지 관리, 품종 확장 등의 측면에서 최적화하여 전략을 더 안정적이고 지능적으로 만들 수 있다.
/*backtest
start: 2023-10-14 00:00:00
end: 2023-11-13 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=3
//Copyright Boris Kozak
strategy("XBT Weekend Trade Strategy", overlay=false)
leverage = input(10,"Leverage")
profitTakingPercentThreshold = input(0.10,"Profit Taking Percent Threshold")
//****Code used for setting up backtesting.****///
testStartYear = input(2017, "Backtest Start Year")
testStartMonth = input(12, "Backtest Start Month")
testStartDay = input(10, "Backtest Start Day")
testPeriodStart = timestamp(testStartYear,testStartMonth,testStartDay,0,0)
testStopYear = input(2025, "Backtest Stop Year")
testStopMonth = input(12, "Backtest Stop Month")
testStopDay = input(30, "Backtest Stop Day")
testPeriodStop = timestamp(testStopYear,testStopMonth,testStopDay,0,0)
// A switch to control background coloring of the test period
testPeriodBackground = input(title="Color Background?", type=bool, defval=true)
testPeriodBackgroundColor = testPeriodBackground and (time >= testPeriodStart) and (time <= testPeriodStop) ? #00FFFF : na
bgcolor(testPeriodBackgroundColor, transp=50)
testPeriod() => true
//****END Code used for setting up backtesting.****///
//*** Main entry point is here***//
// Figure out how many days since the Friday close
days_since_friday = if dayofweek == 6
0
else
if dayofweek == 7
1
else
if dayofweek == 1
2
else
if dayofweek == 2
3
else
if dayofweek == 3
4
else
if dayofweek == 4
5
else
6
// Grab the Friday close price
fridaycloseprice = request.security(syminfo.tickerid,'D',close[days_since_friday])
plot(fridaycloseprice)
strategy.initial_capital = 50000
// Only perform backtesting during the window specified
if testPeriod()
// If we've reached out profit threshold, exit all positions
if ((strategy.openprofit/strategy.initial_capital) > profitTakingPercentThreshold)
strategy.close_all()
// Only execute this trade on saturday and sunday (UTC)
if (dayofweek == 7.0 or dayofweek == 1.0)
// Begin - Empty position (no active trades)
if (strategy.position_size == 0)
// If current close price > threshold, go short
if ((close>fridaycloseprice*1.045))
strategy.entry("Short Entry", strategy.short, leverage)
else
// If current close price < threshold, go long
if (close<(fridaycloseprice*0.955))
strategy.entry("Long Entry",strategy.long, leverage)
// Begin - we already have a position
if (abs(strategy.position_size) > 0)
// We are short
if (strategy.position_size < 0)
if ((close>strategy.position_avg_price*1.045))
// Add to the position
strategy.entry("Adding to Short Entry", strategy.short, leverage)
else
strategy.entry("Long Entry",strategy.long,leverage)
// On Monday, if we have any open positions, close them
if (dayofweek==2.0)
strategy.close_all()