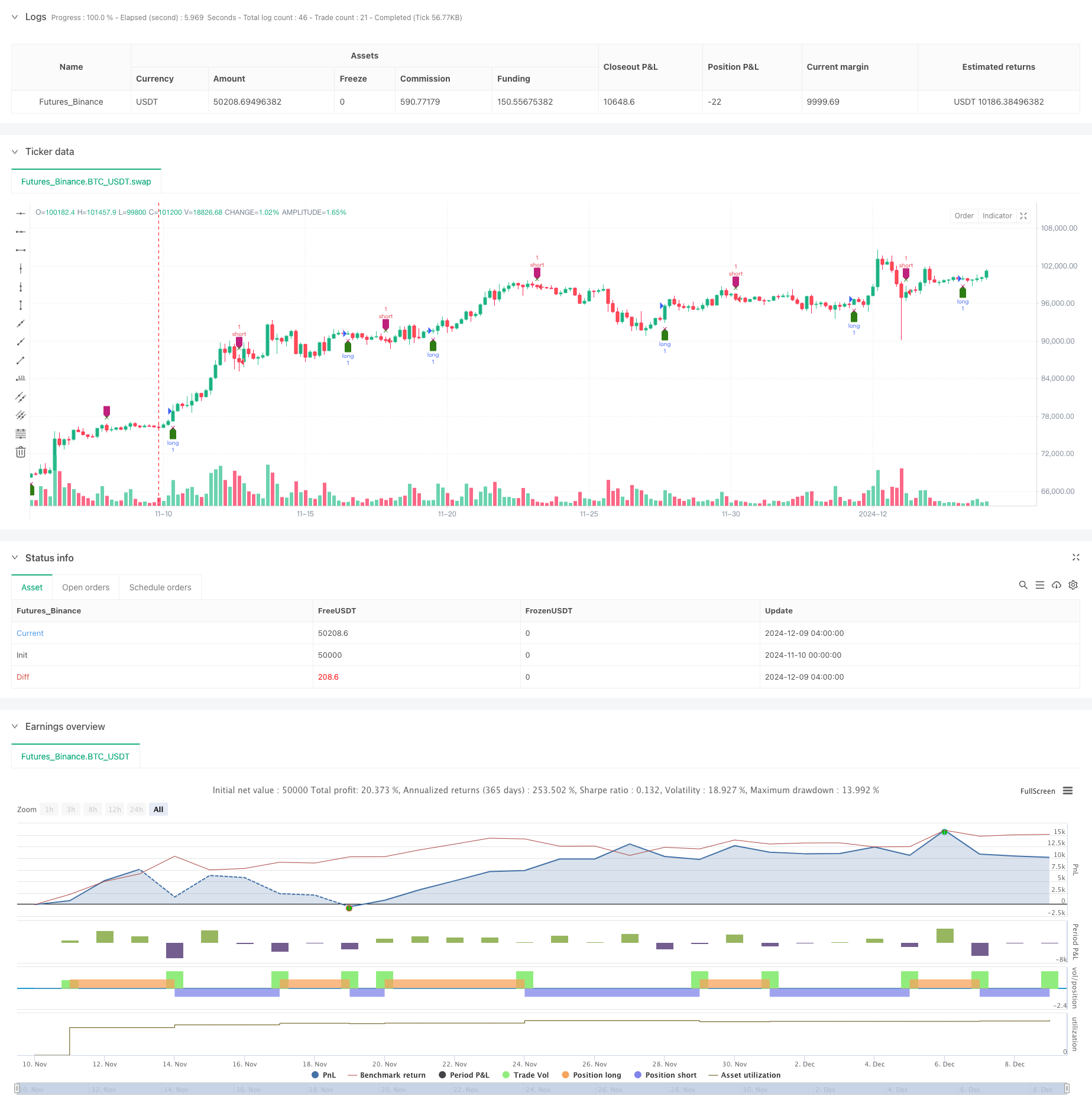
이 전략은 RSI 동적 진동기를 기반으로 한 정량 거래 시스템입니다. RSI 지표에 대한 다중 모형 및 시간 순서 분석을 통해 RSI의 변화율을 계산하여 시장 동력을 포착합니다. 전략은 QR 분해와 같은 고급 수학 방법을 사용하여 신호 처리를 수행하며, 일률 시스템과 결합하여 거래 결정을 수행합니다.
전략 원칙
이 전략의 핵심은 델타-RSI 오스컬레이터입니다.
- 먼저 전통적인 RSI를 기본 데이터로 계산합니다.
- RSI를 다중 모음으로 부드럽게 처리하여 소음을 줄인다.
- RSI의 시간 변수를 계산하여 RSI의 변화 속도를 나타내는 델타-RSI를 얻습니다.
- 델타-RSI와 이동 평균을 비교하여 거래 신호를 생성합니다.
- 평방근도 (RMSE) 를 사용하여 적합 품질을 평가하고 필터링
거래 신호는 다음 세 가지 방법으로 생성됩니다.
- 0선을 가로질러: 델타-RSI는 마이너스에서 오른쪽으로 더하고, 긍정적에서 마이너스쪽으로 비로
- 신호선 교차: 델타-RSI는 이동 평균을 상위/하위로 넘어서서 각각 더 많이/더 텅 비게 합니다.
- 방향 변화: 델타-RSI는 마이너스 영역에서 상승하기 시작하면 더 많은 것을하고, 긍정적 영역에서 하락하기 시작하면 더 많은 것을합니다.
전략적 이점
- 수학 기반이 튼튼하다: QR 해독과 같은 고급 수학 방법을 사용하여 신호 처리, 이론 기반이 안정하다
- 신호 부드러움: 다항식 조정이 시장 소음을 효과적으로 필터링하여 신호 품질을 향상시킵니다.
- 유연성: 다양한 시장을 위한 다양한 신호 생성 방식과 변수 선택
- 위험 제어: RMSE 필터링 메커니즘을 포함하여 신뢰성이 높은 신호를 필터링 할 수 있습니다.
- 계산 효율성: 매트릭스 연산은 최적화된 알고리즘을 사용하여 높은 연산 효율을 나타냅니다.
전략적 위험
- 매개 변수 민감성: 여러 개의 핵심 매개 변수가 정교하게 조정되어야 하며, 매개 변수 선택이 잘못되면 전략 성능에 심각한 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
- 지연성: 신호의 부드러운 처리는 약간의 지연을 가져오며, 빠른 동작을 놓칠 수 있다.
- 가짜 돌파구: 불안한 시장에서 가짜 신호를 생성하여 거래 비용을 증가시킬 수 있습니다.
- 계산 복잡성: 더 많은 매트릭스 연산이 포함되며, 고주파 거래에서 성능 병점이 있을 수 있다
- 오버 마칭: 매개 변수를 최적화할 때 주의를 기울여야 합니다.
전략 최적화 방향
- 자기 적응 파라미터: 시장의 변동율 동력에 따라 RSI 주기와 적합 단계 수를 조정할 수 있다
- 다중 시간 주기: 더 많은 시간 주기와 결합된 신호를 교차 검증한다
- 변동률 필터링: ATR과 같은 변동률 지표를 추가하여 신호 필터링
- 시장 분류: 다른 시장 상태에 대한 다른 신호 생성 규칙을 사용함
- 스톱로스 최적화: 지적인 스톱로스 메커니즘을 추가, 예를 들어 저항 지점을 지원하는 동적 스톱로스
요약하다
이것은 구조적으로 완전하고 이론적으로 견고한 양적 거래 전략이다. RSI의 역동적 특성을 분석하고 현대적인 수학적 방법과 결합하여 신호 처리를 함으로써 시장 추세를 더 잘 포착할 수 있다. 특정 파라미터 민감성과 계산 복잡성의 문제가 있지만, 합리적인 파라미터 선택과 최적화 개선을 통해 이 전략은 좋은 응용 가치가 있다. 실장 적용 시 위험 통제에 주의를 기울이고, 합리적인 포지션을 설정하고, 전략의 성능을 지속적으로 모니터링하는 것이 좋습니다.
전략 소스 코드
/*backtest
start: 2024-11-10 00:00:00
end: 2024-12-09 08:00:00
period: 4h
basePeriod: 4h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © tbiktag
//
// Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy
//
// A strategy that uses Delta-RSI Oscillator (© tbiktag) as a stand-alone indicator:
// https://www.tradingview.com/script/OXQVFTQD-Delta-RSI-Oscillator/
//
// Delta-RSI is a smoothed time derivative of the RSI, plotted as a histogram
// and serving as a momentum indicator.
//
// Input parameters:
// RSI Length: The timeframe of the RSI that serves as an input to D-RSI.
// Length: The length of the lookback frame used for local regression.
// Polynomial Order: The order of the local polynomial function used to interpolate the RSI.
// Signal Length: The length of a EMA of the D-RSI series that is used as a signal line.
// Trade signals are generated based on three optional conditions:
// - Zero-crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses zero from negative to positive values (bearish otherwise)
// - Signal Line Crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses from below to above the signal line (bearish otherwise)
// - Direction Change: bullish when D-RSI was negative and starts ascending (bearish otherwise)
//
// Since D-RSI oscillator is based on polynomial fitting of the RSI curve, there is also an option
// to filter trade signal by means of the root mean-square error of the fit (normalized by the sample average).
//
//@version=5
strategy(title='Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy-QuangVersion', shorttitle='D-RSI-Q', overlay=true)
// ---Subroutines---
matrix_get(_A, _i, _j, _nrows) =>
// Get the value of the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.get(_A, _i + _nrows * _j)
matrix_set(_A, _value, _i, _j, _nrows) =>
// Set a value to the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array, changed on output: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _value :: float: the new value to be set
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.set(_A, _i + _nrows * _j, _value)
transpose(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
// Transpose an implied 2d matrix
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _AT :: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions: _ncolums x _nrows
var _AT = array.new_float(_nrows * _ncolumns, 0)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_AT, matrix_get(_A, i, j, _nrows), j, i, _ncolumns)
_AT
multiply(_A, _B, _nrowsA, _ncolumnsA, _ncolumnsB) =>
// Calculate scalar product of two matrices
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _B :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _nrowsA :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumnsA :: integer: number of columns in _A
// _ncolumnsB :: integer: number of columns in _B
// output:
// _C:: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions _nrowsA x _ncolumnsB
var _C = array.new_float(_nrowsA * _ncolumnsB, 0)
int _nrowsB = _ncolumnsA
float elementC = 0.0
for i = 0 to _nrowsA - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _ncolumnsB - 1 by 1
elementC := 0
for k = 0 to _ncolumnsA - 1 by 1
elementC += matrix_get(_A, i, k, _nrowsA) * matrix_get(_B, k, j, _nrowsB)
elementC
matrix_set(_C, elementC, i, j, _nrowsA)
_C
vnorm(_X, _n) =>
//Square norm of vector _X with size _n
float _norm = 0.0
for i = 0 to _n - 1 by 1
_norm += math.pow(array.get(_X, i), 2)
_norm
math.sqrt(_norm)
qr_diag(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
//QR Decomposition with Modified Gram-Schmidt Algorithm (Column-Oriented)
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _Q: unitary matrix, implied dimenstions _nrows x _ncolumns
// _R: upper triangular matrix, implied dimansions _ncolumns x _ncolumns
var _Q = array.new_float(_nrows * _ncolumns, 0)
var _R = array.new_float(_ncolumns * _ncolumns, 0)
var _a = array.new_float(_nrows, 0)
var _q = array.new_float(_nrows, 0)
float _r = 0.0
float _aux = 0.0
//get first column of _A and its norm:
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
array.set(_a, i, matrix_get(_A, i, 0, _nrows))
_r := vnorm(_a, _nrows)
//assign first diagonal element of R and first column of Q
matrix_set(_R, _r, 0, 0, _ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Q, array.get(_a, i) / _r, i, 0, _nrows)
if _ncolumns != 1
//repeat for the rest of the columns
for k = 1 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
array.set(_a, i, matrix_get(_A, i, k, _nrows))
for j = 0 to k - 1 by 1
//get R_jk as scalar product of Q_j column and A_k column:
_r := 0
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
_r += matrix_get(_Q, i, j, _nrows) * array.get(_a, i)
_r
matrix_set(_R, _r, j, k, _ncolumns)
//update vector _a
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
_aux := array.get(_a, i) - _r * matrix_get(_Q, i, j, _nrows)
array.set(_a, i, _aux)
//get diagonal R_kk and Q_k column
_r := vnorm(_a, _nrows)
matrix_set(_R, _r, k, k, _ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Q, array.get(_a, i) / _r, i, k, _nrows)
[_Q, _R]
pinv(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
//Pseudoinverse of matrix _A calculated using QR decomposition
// Input:
// _A:: array: implied as a (_nrows x _ncolumns) matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(_ncolumns-1)]]
// Output:
// _Ainv:: array implied as a (_ncolumns x _nrows) matrix _A = [[row_0],[row_1],...,[row_(_nrows-1)]]
// ----
// First find the QR factorization of A: A = QR,
// where R is upper triangular matrix.
// Then _Ainv = R^-1*Q^T.
// ----
[_Q, _R] = qr_diag(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns)
_QT = transpose(_Q, _nrows, _ncolumns)
// Calculate Rinv:
var _Rinv = array.new_float(_ncolumns * _ncolumns, 0)
float _r = 0.0
matrix_set(_Rinv, 1 / matrix_get(_R, 0, 0, _ncolumns), 0, 0, _ncolumns)
if _ncolumns != 1
for j = 1 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
for i = 0 to j - 1 by 1
_r := 0.0
for k = i to j - 1 by 1
_r += matrix_get(_Rinv, i, k, _ncolumns) * matrix_get(_R, k, j, _ncolumns)
_r
matrix_set(_Rinv, _r, i, j, _ncolumns)
for k = 0 to j - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Rinv, -matrix_get(_Rinv, k, j, _ncolumns) / matrix_get(_R, j, j, _ncolumns), k, j, _ncolumns)
matrix_set(_Rinv, 1 / matrix_get(_R, j, j, _ncolumns), j, j, _ncolumns)
//
_Ainv = multiply(_Rinv, _QT, _ncolumns, _ncolumns, _nrows)
_Ainv
norm_rmse(_x, _xhat) =>
// Root Mean Square Error normalized to the sample mean
// _x. :: array float, original data
// _xhat :: array float, model estimate
// output
// _nrmse:: float
float _nrmse = 0.0
if array.size(_x) != array.size(_xhat)
_nrmse := na
_nrmse
else
int _N = array.size(_x)
float _mse = 0.0
for i = 0 to _N - 1 by 1
_mse += math.pow(array.get(_x, i) - array.get(_xhat, i), 2) / _N
_mse
_xmean = array.sum(_x) / _N
_nrmse := math.sqrt(_mse) / _xmean
_nrmse
_nrmse
diff(_src, _window, _degree) =>
// Polynomial differentiator
// input:
// _src:: input series
// _window:: integer: wigth of the moving lookback window
// _degree:: integer: degree of fitting polynomial
// output:
// _diff :: series: time derivative
// _nrmse:: float: normalized root mean square error
//
// Vandermonde matrix with implied dimensions (window x degree+1)
// Linear form: J = [ [z]^0, [z]^1, ... [z]^degree], with z = [ (1-window)/2 to (window-1)/2 ]
var _J = array.new_float(_window * (_degree + 1), 0)
for i = 0 to _window - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _degree by 1
matrix_set(_J, math.pow(i, j), i, j, _window)
// Vector of raw datapoints:
var _Y_raw = array.new_float(_window, na)
for j = 0 to _window - 1 by 1
array.set(_Y_raw, j, _src[_window - 1 - j])
// Calculate polynomial coefficients which minimize the loss function
_C = pinv(_J, _window, _degree + 1)
_a_coef = multiply(_C, _Y_raw, _degree + 1, _window, 1)
// For first derivative, approximate the last point (i.e. z=window-1) by
float _diff = 0.0
for i = 1 to _degree by 1
_diff += i * array.get(_a_coef, i) * math.pow(_window - 1, i - 1)
_diff
// Calculates data estimate (needed for rmse)
_Y_hat = multiply(_J, _a_coef, _window, _degree + 1, 1)
float _nrmse = norm_rmse(_Y_raw, _Y_hat)
[_diff, _nrmse]
/// --- main ---
degree = input.int(title='Polynomial Order', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar1', defval=2, minval=1)
rsi_l = input.int(title='RSI Length', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar1', defval=21, minval=1, tooltip='The period length of RSI that is used as input.')
window = input.int(title='Length ( > Order)', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar2', defval=21, minval=2)
signalLength = input.int(title='Signal Length', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar2', defval=9, tooltip='The signal line is a EMA of the D-RSI time series.')
islong = input.bool(title='Buy', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
isshort = input.bool(title='Sell', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
showendlabels = input.bool(title='Exit', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
buycond = input.string(title='Buy', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
sellcond = input.string(title='Sell', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
endcond = input.string(title='Exit', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
usenrmse = input.bool(title='', group='Filter by Means of Root-Mean-Square Error of RSI Fitting:', inline='linermse', defval=false)
rmse_thrs = input.float(title='RSI fitting Error Threshold, %', group='Filter by Means of Root-Mean-Square Error of RSI Fitting:', inline='linermse', defval=10, minval=0.0) / 100
src = ta.rsi(close, rsi_l)
[drsi, nrmse] = diff(src, window, degree)
signalline = ta.ema(drsi, signalLength)
// Conditions and filters
filter_rmse = usenrmse ? nrmse < rmse_thrs : true
dirchangeup = drsi > drsi[1] and drsi[1] < drsi[2] and drsi[1] < 0.0
dirchangedw = drsi < drsi[1] and drsi[1] > drsi[2] and drsi[1] > 0.0
crossup = ta.crossover(drsi, 0.0)
crossdw = ta.crossunder(drsi, 0.0)
crosssignalup = ta.crossover(drsi, signalline)
crosssignaldw = ta.crossunder(drsi, signalline)
//Signals
golong = (buycond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangeup : buycond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossup : crosssignalup) and filter_rmse
goshort = (sellcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangedw : sellcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossdw : crosssignaldw) and filter_rmse
endlong = (endcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangedw : endcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossdw : crosssignaldw) and filter_rmse
endshort = (endcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangeup : endcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossup : crosssignalup) and filter_rmse
plotshape(golong and islong ? low : na, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.labelup, color=color.new(#2E7C13, 0), size=size.small, title='Buy')
plotshape(goshort and isshort ? high : na, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.labeldown, color=color.new(#BF217C, 0), size=size.small, title='Sell')
plotshape(showendlabels and endlong and islong ? high : na, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.xcross, color=color.new(#2E7C13, 0), size=size.tiny, title='Exit Long')
plotshape(showendlabels and endshort and isshort ? low : na, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.xcross, color=color.new(#BF217C, 0), size=size.tiny, title='Exit Short')
alertcondition(golong, title='Long Signal', message='D-RSI: Long Signal')
alertcondition(goshort, title='Short Signal', message='D-RSI: Short Signal')
alertcondition(endlong, title='Exit Long Signal', message='D-RSI: Exit Long')
alertcondition(endshort, title='Exit Short Signal', message='D-RSI: Exit Short')
strategy.entry('long', strategy.long, when=golong and islong)
strategy.entry('short', strategy.short, when=goshort and isshort)
strategy.close('long', when=endlong and islong)
strategy.close('short', when=endshort and isshort)