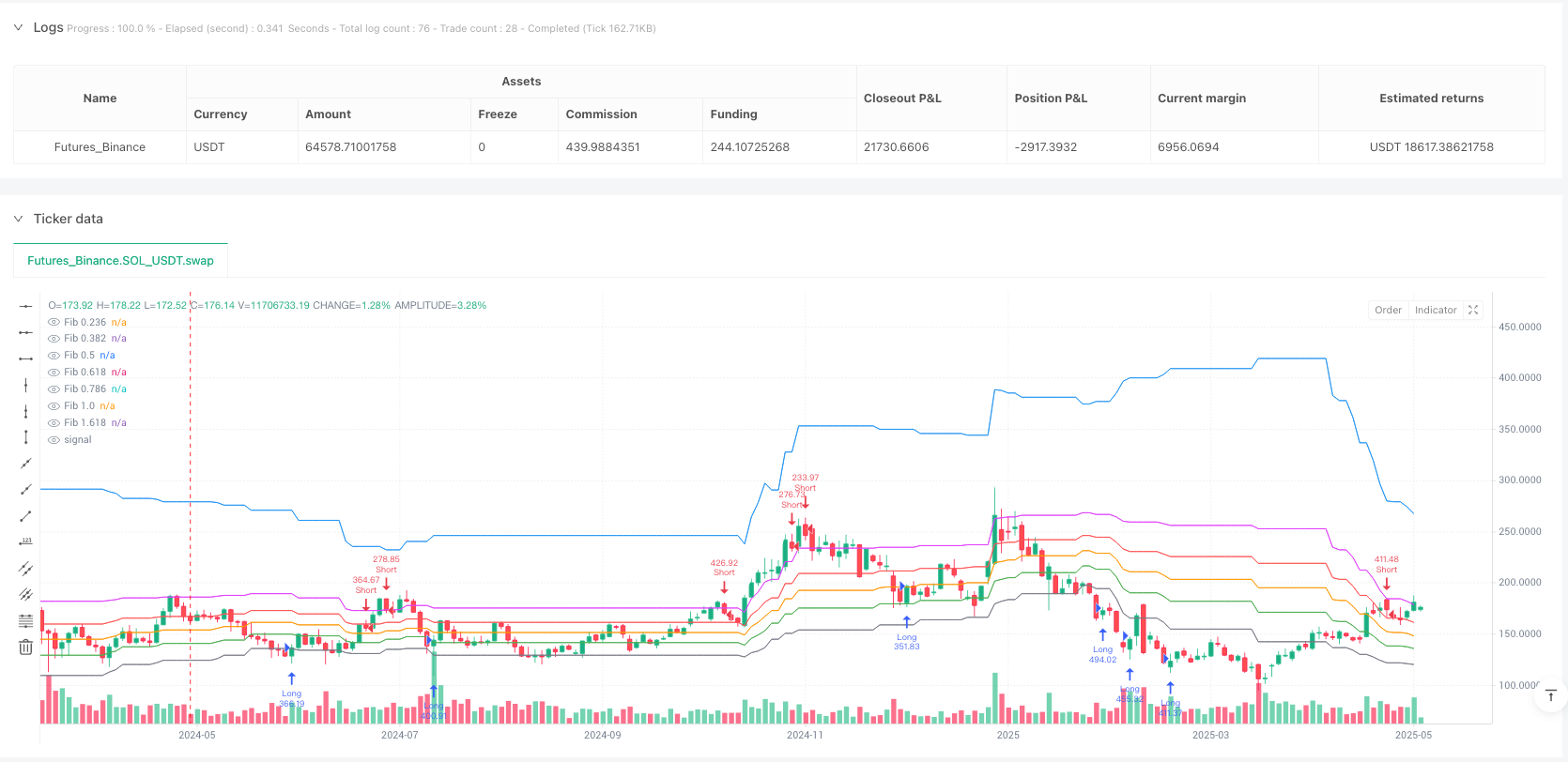
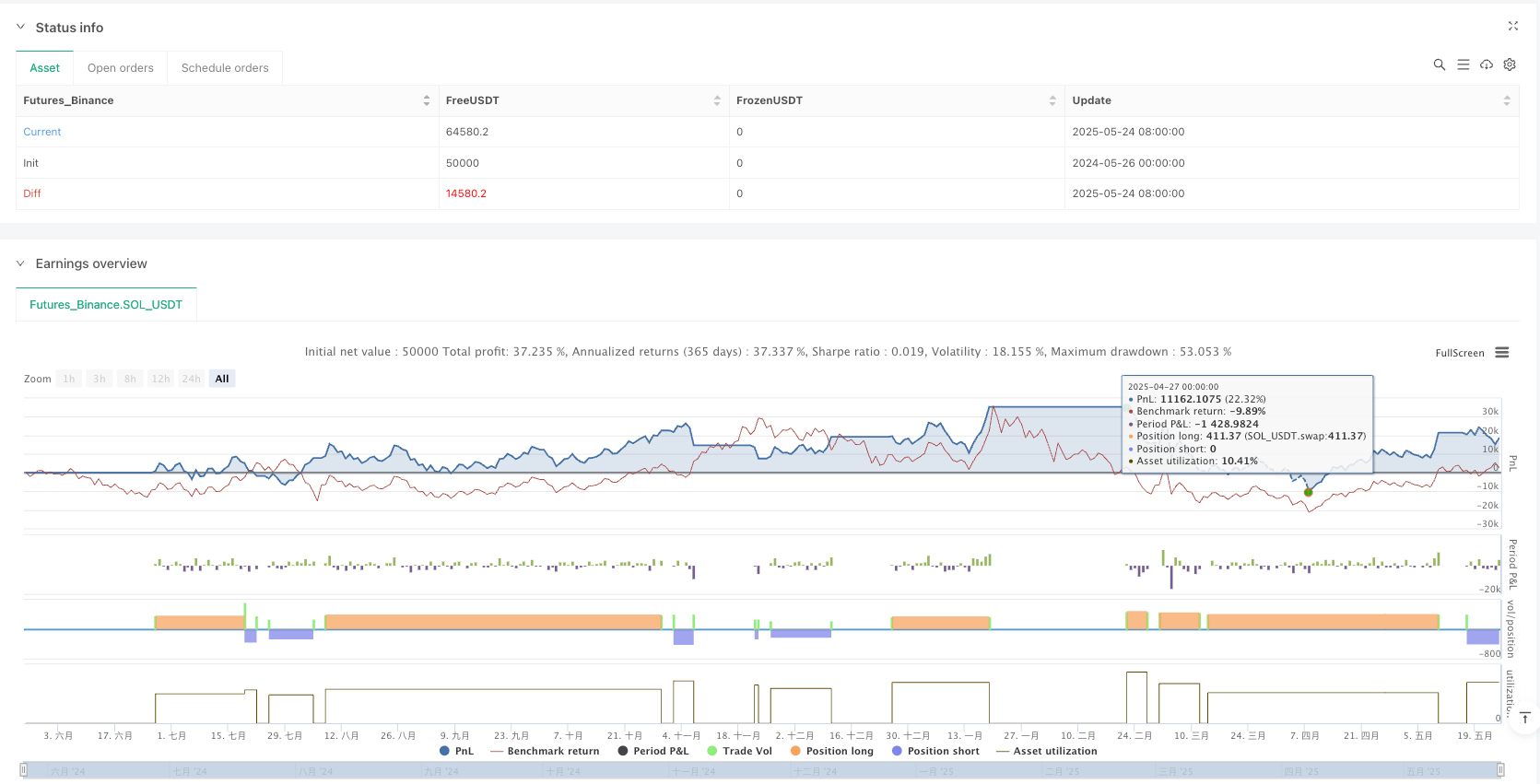
[tran]
개요
다단계 피보나치 트렌드 추적과 헤지 트레이딩 전략 시스템은 여러 가지 기술 분석 지표를 통합한 통합적 수치화 트레이딩 전략이다. 이 전략은 피보나치 회귀 이론을 중심으로 지수 이동 평균 (EMA), 평균 실제 파도 (ATR), 평균 트렌드 지수 (ADX) 및 방향 이동 지표 (DMI) 와 같은 여러 가지 기술 지표를 결합하여 다차원 시장 분석 프레임워크를 구성한다. 전략은 전통적인 트렌드 추적 기능뿐만 아니라 반발 거래 메커니즘과 포지션 기능을 통합하여 다양한 시장에서 수익 기회를 잡고 위험을 효과적으로 제어 할 수 있도록합니다.
이 전략의 특징은 다단계 위험 관리 시스템과 유연한 거래 모드입니다. 여러 개의 중지 목표 (TP1 및 TP2) 를 설정하고 ATR 기반의 동적 중지 장치를 통해 전략은 자본을 보호하면서 수익 잠재력을 극대화 할 수 있습니다. 또한, 내장된 보호 기능은 전략에 추가적인 위험 완충을 추가하여 불안정한 시장 환경에서 비교적 안정적인 성능을 유지할 수 있습니다.
전략 원칙
전략의 핵심 논리는 피보나치 회귀 이론과 트렌드 분석의 결합에 기초한다. 우선, 전략은 피보나치 회귀 수준을 지정된 주기 내의 최고점과 최저점을 계산하여 결정한다. 이는 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, 78.6%, 100% 및 161.8%와 같은 중요한 위치를 포함한다.
트렌드 식별의 측면에서, 전략은 50 기 지수 이동 평균을 주요 트렌드 판단 도구로 사용합니다. 가격이 연속적으로 3 개의 K 선이 EMA 위에있을 때, 상승 추세로 인식됩니다. 반대로 하향 추세입니다. 동시에, 전략은 가격 구조를 분석하여 더 높은 낮은 점과 더 높은 고점을 식별하여 다중 구조를 확인하고, 더 낮은 높은 점과 더 낮은 낮은 점으로 허공 구조를 확인합니다.
ADX 및 DMI 지표의 도입은 트렌드 강도를 판단하는 정확성을 향상시킵니다. ADX 값이 20보다 크면 강한 트렌드의 기준으로 간주되며, +DI 및 -DI의 상대적으로 약한 것은 트렌드의 방향성을 결정하는 데 사용됩니다. 거래량 분석은 전략의 중요한 구성 요소이기도하며, 거래량이 20 기간 평균의 1.2배를 초과하면 유효한 양을 확인할 수 있습니다.
거래 신호의 생성은 여러 조건을 충족시키는 동시에 설립되어야합니다: 트렌드 방향이 명확하고, 가격이 중요한 피보나치 수준에 가깝고, 트렌드 강도가 충분하고, 방향 지표가 확인되고 거래량이 확대됩니다. 이러한 여러 가지 필터링 메커니즘은 신호의 신뢰성을 크게 향상시키고 가짜 신호의 가능성을 감소시킵니다.
전략적 이점
이 전략은 여러 가지 중요한 장점을 가지고 있으며, 첫째는 포괄적인 기술 분석 프레임워크에 나타납니다. 피보나치 이론, 트렌드 분석, 동력 지표 및 거래량 분석을 통합함으로써 전략은 시장 상황을 여러 차원에서 평가하여 더 포괄적이고 정확한 거래 신호를 제공합니다. 이러한 다중 지표 통합 방식은 단일 지표가 생성 할 수있는 잘못된 신호를 효과적으로 줄여 전체 전략의 안정성과 신뢰성을 향상시킵니다.
이 전략의 위험 관리 시스템은 또 다른 큰 장점이다. 쌍중정지 메커니즘은 상인이 첫 번째 목표를 달성 할 때 수익의 일부를 잠금하는 것을 허용하며, 나머지 포지션을 더 큰 수익을 추구 할 수 있도록 허용한다. ATR 기반의 동적 중지 손실 설정은 시장의 변동성에 따라 자동으로 위험 제어 수준을 조정할 수 있으며, 낮은 변동이있을 때 수익을 보호하기 위해 중지 손실을 강화하고, 높은 변동이있을 때 중지 손실을 완화하여 정상적인 변동이 흔들리지 않도록 할 수 있습니다.
반발 거래 기능은 전략에 추가적인 수익 기회를 제공합니다. 가격이 중요한 지원 또는 저항 지점에서 반발 할 때, 전략은 이러한 단기 반향 상황을 신속하게 인식하고 참여할 수 있으므로 추세 거래에 따라 더 많은 거래 기회를 얻을 수 있습니다. 이러한 유연성은 전략이 다른 시장 조건에 적응할 수있게 해줍니다.
포장 기능의 통합은 이 전략의 혁신적인 특징이다. 다중 상점 포지션을 보유할 때 공백 신호가 발생하면 전략이 공백 포지션을 포장한다. 그 반대의 경우도 마찬가지이다. 이 메커니즘은 시장의 급격한 역전시 추가적인 보호를 제공하여 잠재적인 손실을 줄이고 새로운 수익 기회로 변환할 수 있다.
시간 필터의 설정은 과도한 거래의 문제를 방지한다. 연속적인 신호 사이에 최소 5개의 K선 간격을 요구함으로써, 전략은 짧은 시간에 자주 포지션을 열기를 피하고, 거래 비용을 낮추고, 신호 품질을 향상시킨다.
전략적 위험
이 전략은 여러 장점이 있음에도 불구하고, 주의해야 할 몇 가지 위험 요소가 있습니다. 첫째, 변수 의존성 위험입니다. 전략은 피보나치 사이클, 관용, ATR 배수 등과 같은 여러 변수 설정을 포함합니다. 이러한 변수 설정을 선택하는 것은 전략의 성과에 중요한 영향을 미칩니다.
시장 환경의 적응성은 또 다른 잠재적인 위험이다. 전략은 주로 기술 분석에 기반하고 있으며, 특정 시장 조건에서 좋지 않은 성과를 낼 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 강렬한 일방적 인 기본 요소가있는 상황에서 기술 지표가 실패 할 수 있습니다. 또한, 전략의 신호 생성 빈도와 정확성은 매우 낮은 변동성 또는 매우 높은 변동성 시장 환경에서 영향을받을 수 있습니다.
슬라이드 포인트와 실행 위험도 고려해야 한다. 실제 거래에서, 특히 변동성이 높은 시장 조건에서, 주문 실행 가격과 기대 가격 사이의 차이가 있을 수 있다. 이러한 슬라이드 포인트 비용은 전략의 이론적 수익을 손상시킬 수 있다. 특히 자주 거래하는 전략에 대해서는.
보호 기능은 추가적인 보호를 제공하지만, 전략의 복잡성을 증가시킵니다. 일부 경우에, 보호 동작은 여분의 포지션을 동시에 손실하거나 수수료에 대한 추가 비용을 초래할 수 있습니다. 따라서, 보호 기능의 실제 효과를 신중하게 평가하고 특정 시장 조건에서 기능을 활성화하는 것을 고려해야합니다.
전략 최적화 방향
전략의 성능을 더욱 향상시키기 위해 여러 방향으로 최적화 할 수 있습니다. 첫째는 동적 변수 조정 메커니즘의 도입입니다. 시장의 변동성, 트렌드 강도와 같은 요인에 따라 피보나치 사이클, ATR 배수와 같은 핵심 변수를 동적으로 조정할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 높은 변동성 시장에서 ATR 배수를 증가시켜 더 큰 손실 공간을 제공하거나, 낮은 변동성 시장에서 ATR 배수를 감소시켜 위험 제어를 강화합니다.
기계 학습 기술의 통합은 또 다른 중요한 최적화 방향이다. 기계 학습 알고리즘을 사용하여 최적의 진입 시점을 식별하거나, 역사적 데이터 학습 파라미트 콤비에 따라 최적의 구성을 할 수 있다. 또한, 시장 감정과 뉴스 이벤트의 가격에 대한 영향을 분석하는 자연 언어 처리 기술을 사용하여 전략에 기본 분석 차원을 추가할 수 있다.
다중 시간 프레임 분석의 통합은 더 포괄적인 시장 관점을 제공할 수 있다. 더 긴 시간 프레임에서 큰 트렌드 방향을 확인하고, 더 짧은 시간 프레임에서 정확한 입구 지점을 찾을 수 있다. 이러한 다중 시간 프레임의 조율 분석은 신호 품질을 높이고 역동 거래의 위험을 줄일 수 있다.
자금 관리 최적화는 전략의 성능을 향상시키는 중요한 방법이다. 시장 조건, 전략의 신뢰도 등의 요인에 따라 포지션 크기를 동적으로 조정할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 높은 신뢰도 신호 때 포지션을 증가시키고 낮은 신뢰도 신호 때 포지션을 감소시킨다. 또한, 최대 회수 제어 장치를 도입하여 전략이 큰 손실이 발생했을 때 포지션을 자동으로 감소시키거나 거래를 일시 중지 할 수 있다.
스톱 스톱 손실 논리의 추가 정교화는 고려할 가치가 있습니다. 가격 움직임에 따라 스톱 손실 위치를 조정하여 더 많은 수익을 잠금 할 수있는 추적 스톱 메커니즘을 도입 할 수 있습니다. 동시에, 시장 구조 특성에 따라 더 지능적인 스톱 목표를 설정 할 수 있습니다.
요약하다
다단계 피보나치 트렌드 추적과 헤지 트레이딩 전략 시스템은 현대적인 양적 거래 기술의 중요한 발전 방향을 나타냅니다. 이 전략은 여러 가지 고전적 기술 분석 도구를 능숙하게 통합하여 안정적이고 유연한 거래 프레임 워크를 구축합니다. 다중 필터링 메커니즘은 신호 품질을 보장하고, 다단계 위험 관리 시스템은 효과적인 자본 보호를 제공하며, 헤지 기능은 전략에 추가적인 안전 한계를 제공합니다.
전략의 성공적인 실행은 그것의 기본 원리 및 작동 메커니즘을 충분히 이해하고, 특정 거래 환경에 따라 적절한 매개 변수를 조정하고 최적화해야합니다. 전략은 이론적으로 잘 설계되었지만 실제 적용에서는 시장의 미시 구조, 거래 비용, 슬라이드 포인트와 같은 실제 요소의 영향을 고려해야합니다.
인공지능과 기계학습 기술의 지속적인 발전과 함께, 이 전략에는 엄청난 최적화 공간이 있습니다. 더 진보된 데이터 분석 기술과 적응 메커니즘을 도입함으로써 전략의 성능이 더욱 향상될 것으로 예상됩니다. 이러한 종합 전략은 정량 거래자에게는 시장 역동성과 위험 관리의 중요성을 깊이 이해하는 데 도움이되는 귀중한 학습 및 개선 플랫폼을 제공합니다. ||
Overview
The Multi-Level Fibonacci Trend Following and Hedging Trading Strategy System is a comprehensive quantitative trading strategy that integrates multiple technical analysis indicators. This strategy centers on Fibonacci retracement theory, combining Exponential Moving Average (EMA), Average True Range (ATR), Average Directional Index (ADX), and Directional Movement Indicator (DMI) to construct a multi-dimensional market analysis framework. The strategy not only features traditional trend-following capabilities but also integrates bounce trading mechanisms and hedging functionality, aiming to capture profitable opportunities under different market conditions while effectively controlling risk.
The unique aspect of this strategy lies in its multi-layered risk management system and flexible trading modes. By setting multiple take-profit targets (TP1 and TP2) and dynamic stop-loss mechanisms based on ATR, the strategy can maximize profit potential while protecting capital. Additionally, the built-in hedging function adds an extra risk buffer to the strategy, enabling it to maintain relatively stable performance even in highly volatile market environments.
Strategy Principles
The core logic of the strategy is based on the combination of Fibonacci retracement theory and trend analysis. First, the strategy calculates the highest and lowest points within a specified period to determine Fibonacci retracement levels, including key positions at 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, 78.6%, 100%, and 161.8%. These levels serve as important support and resistance zones, providing crucial references for trading signal generation.
For trend identification, the strategy employs a 50-period Exponential Moving Average as the primary trend determination tool. When prices remain above the EMA for three consecutive candlesticks, it’s identified as an uptrend; conversely, it’s considered a downtrend. Simultaneously, the strategy analyzes price structure by identifying higher lows and higher highs to confirm bullish structure, and lower highs and lower lows to confirm bearish structure.
The introduction of ADX and DMI indicators enhances the precision of trend strength assessment. An ADX value greater than 20 is considered the standard for a strong trend, while the relative strength of +DI and -DI is used to determine trend direction. Volume analysis is also an important component of the strategy, where volume exceeding 1.2 times the 20-period average is considered effective volume confirmation.
Trade signal generation requires multiple conditions to be met simultaneously: clear trend direction, price proximity to key Fibonacci levels, sufficient trend strength, directional indicator confirmation, and volume expansion. This multi-filter mechanism significantly improves signal reliability and reduces the probability of false signals.
Strategy Advantages
This strategy possesses multiple significant advantages, first manifested in its comprehensive technical analysis framework. By integrating Fibonacci theory, trend analysis, momentum indicators, and volume analysis, the strategy can evaluate market conditions from multiple dimensions, providing more comprehensive and accurate trading signals. This multi-indicator fusion approach effectively reduces misleading signals that might be generated by single indicators, improving the overall stability and reliability of the strategy.
The strategy’s risk management system represents another major advantage. The dual take-profit mechanism allows traders to lock in partial profits upon reaching the first target while maintaining remaining positions to pursue greater returns. ATR-based dynamic stop-loss settings can automatically adjust risk control levels according to market volatility, tightening stops during low volatility to protect profits and relaxing stops during high volatility to avoid being stopped out by normal fluctuations.
The bounce trading functionality adds additional profit opportunities to the strategy. When prices bounce at key support or resistance levels, the strategy can quickly identify and participate in such short-term reversal movements, thereby adding more trading opportunities beyond trend trading. This flexibility enables the strategy to adapt to different market conditions, finding suitable trading opportunities whether in strong trending markets or range-bound markets.
The integration of hedging functionality is an innovative feature of this strategy. When holding long positions and a short signal appears, the strategy will open a hedge short position; vice versa. This mechanism can provide additional protection during rapid market reversals, reducing potential losses and possibly converting them into new profit opportunities.
The time filter setting prevents overtrading issues. By requiring at least 5 candlesticks between consecutive signals, the strategy avoids frequent position opening within short periods, reducing trading costs and improving signal quality.
Strategy Risks
Despite the strategy’s multiple advantages, several risk factors require attention. First is parameter dependency risk. The strategy involves multiple parameter settings, including Fibonacci period, tolerance, ATR multipliers, etc. The selection of these parameters significantly impacts strategy performance. Inappropriate parameter settings may lead to overfitting historical data or poor performance in actual markets. Therefore, sufficient backtesting and parameter optimization are needed to find the most suitable parameter combinations for specific markets and timeframes.
Market environment adaptability represents another potential risk. The strategy is primarily based on technical analysis and may underperform in certain market conditions, such as during fundamental-driven strong unidirectional moves where technical indicators might fail. Additionally, in extremely low or high volatility market environments, both signal generation frequency and accuracy may be affected.
Slippage and execution risks also need consideration. In actual trading, particularly during high volatility market conditions, there may be differences between order execution prices and expected prices. This slippage cost could erode the strategy’s theoretical returns, especially for frequently trading strategies.
While the hedging function provides additional protection, it also increases strategy complexity. In certain situations, hedging operations might result in simultaneous losses on both long and short positions, or generate additional costs in terms of commissions. Therefore, careful evaluation of the hedging function’s actual effectiveness is needed, along with consideration of whether to enable this function under specific market conditions.
Strategy Optimization Directions
To further enhance strategy performance, optimization can be pursued in multiple directions. First is the introduction of dynamic parameter adjustment mechanisms. Key parameters such as Fibonacci period and ATR multipliers can be dynamically adjusted based on market volatility, trend strength, and other factors. For example, increasing ATR multipliers in high volatility markets to provide larger stop-loss space, and decreasing ATR multipliers in low volatility markets to tighten risk control.
Integration of machine learning technology represents another important optimization direction. Machine learning algorithms can be used to identify optimal entry timing or learn optimal parameter combination configurations based on historical data. Additionally, natural language processing technology can be utilized to analyze market sentiment and news event impacts on prices, adding fundamental analysis dimensions to the strategy.
Integration of multi-timeframe analysis can provide a more comprehensive market perspective. Larger timeframes can be used to confirm major trend direction, while shorter timeframes can be used to find precise entry points. This coordinated multi-timeframe analysis can improve signal quality and reduce counter-trend trading risks.
Money management optimization is also an important avenue for enhancing strategy performance. Position sizes can be dynamically adjusted based on market conditions, strategy confidence levels, and other factors. For example, increasing positions during high-confidence signals and reducing positions during low-confidence signals. Additionally, maximum drawdown control mechanisms can be introduced to automatically reduce positions or pause trading when the strategy experiences significant losses.
Further refinement of take-profit and stop-loss logic is also worth considering. Trailing stop mechanisms can be introduced to dynamically adjust stop-loss positions based on price movements to lock in more profits. Simultaneously, more intelligent take-profit targets can be set based on market structure characteristics, such as taking profits early near key resistance levels.
Conclusion
The Multi-Level Fibonacci Trend Following and Hedging Trading Strategy System represents an important development direction in modern quantitative trading technology. This strategy cleverly integrates multiple classic technical analysis tools to construct a trading framework that is both robust and flexible. Its multi-filter mechanism ensures signal quality, the multi-layered risk management system provides effective capital protection, and the hedging function adds an additional safety margin to the strategy.
Successful implementation of this strategy requires thorough understanding of its fundamental principles and operational mechanisms, along with appropriate parameter adjustments and optimizations based on specific trading environments. While the strategy has excellent theoretical design, practical application still requires consideration of real-world factors such as market microstructure, trading costs, and slippage.
With the continuous development of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, this strategy still has enormous optimization potential. Through the introduction of more advanced data analysis techniques and adaptive mechanisms, strategy performance is expected to be further enhanced. For quantitative traders, such comprehensive strategies provide a valuable learning and improvement platform, helping to deepen understanding of market dynamics and the importance of risk management.[/trans]
/*backtest
start: 2024-05-26 00:00:00
end: 2025-05-25 00:00:00
period: 2d
basePeriod: 2d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"SOL_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("Fibonacci Trend v6.4 - TP/SL Labels", overlay=true, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value=100)
// === Parameters ===
fibLen = input.int(50, "Fibonacci Range")
fibTol = input.float(0.01, "Fib Proximity Tolerance (%)", step=0.001)
slMult = input.float(1.5, "SL - ATR", step=0.1)
tp2Mult = input.float(2.0, "TP2 - ATR", step=0.1)
srLookback = input.int(20, "Support/Resistance Lookback Bars")
useBounce = input.bool(true, "Enable Bounce Entry")
// === Indicators ===
ema50 = ta.ema(close, 50)
atr = ta.atr(14)
volAvg = ta.sma(volume, 20)
volHigh = volume > volAvg * 1.2
// === Fibonacci Levels ===
lowWick = ta.lowest(low, fibLen)
highWick = ta.highest(high, fibLen)
rangeWick = highWick - lowWick
fib236 = lowWick + 0.236 * rangeWick
fib382 = lowWick + 0.382 * rangeWick
fib5 = lowWick + 0.5 * rangeWick
fib618 = lowWick + 0.618 * rangeWick
fib786 = lowWick + 0.786 * rangeWick
fib1 = highWick
fib1618 = lowWick + 1.618 * rangeWick
nearSupport = math.abs(low - fib382)/close < fibTol or math.abs(low - fib5)/close < fibTol
nearResist = math.abs(high - fib618)/close < fibTol
// === Trend Structure ===
higherLow = low > low[1] and low[1] > low[2]
higherHigh = high > high[1]
lowerHigh = high < high[1] and high[1] < high[2]
lowerLow = low < low[1]
longStruct = higherLow and higherHigh
shortStruct = lowerHigh and lowerLow
// === ADX / DMI ===
dmiLen = 14
upMove = high - high[1]
downMove = low[1] - low
plusDM = (upMove > downMove and upMove > 0) ? upMove : 0
minusDM = (downMove > upMove and downMove > 0) ? downMove : 0
tr = ta.tr(true)
tr14 = ta.rma(tr, dmiLen)
plusDI = 100 * ta.rma(plusDM, dmiLen) / tr14
minusDI = 100 * ta.rma(minusDM, dmiLen) / tr14
dx = 100 * math.abs(plusDI - minusDI) / (plusDI + minusDI)
adx = ta.rma(dx, dmiLen)
trendStrong = adx > 20
// === EMA Momentum Break ===
emaBreakLong = close > ema50 and close[1] < ema50 and volume > volAvg
emaBreakShort = close < ema50 and close[1] > ema50 and volume > volAvg
// === Time Filter ===
var int lastLongBar = na
var int lastShortBar = na
canLong = na(lastLongBar) or (bar_index - lastLongBar > 5)
canShort = na(lastShortBar) or (bar_index - lastShortBar > 5)
priceAboveEMA = close > ema50 and close[1] > ema50 and close[2] > ema50
priceBelowEMA = close < ema50 and close[1] < ema50 and close[2] < ema50
// === Support / Resistance ===
support = ta.lowest(low, srLookback)
resist = ta.highest(high, srLookback)
// === Entry Conditions ===
longTrend = priceAboveEMA and nearSupport and trendStrong and plusDI > minusDI and longStruct and (volHigh or emaBreakLong) and canLong
shortTrend = priceBelowEMA and nearResist and trendStrong and minusDI > plusDI and shortStruct and (volHigh or emaBreakShort) and canShort
bounceLong = useBounce and math.abs(low - support)/close < fibTol and close > open and close > close[1]
bounceShort = useBounce and math.abs(high - resist)/close < fibTol and close < open and close < close[1]
longSignal = longTrend or bounceLong
shortSignal = shortTrend or bounceShort
// === TP/SL Calculations ===
tp1Long = resist
tp2Long = close + atr * tp2Mult
slLong = close - atr * slMult
tp1Short = support
tp2Short = close - atr * tp2Mult
slShort = close + atr * slMult
tp1ColorLong = bounceLong ? color.blue : color.yellow
tp1ColorShort = bounceShort ? color.blue : color.yellow
// === Long Entry ===
if (longSignal and strategy.position_size <= 0)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
strategy.exit("TP1", from_entry="Long", limit=tp1Long, stop=slLong, qty_percent=50)
strategy.exit("TP2", from_entry="Long", limit=tp2Long, stop=slLong)
lastLongBar := bar_index
label.new(bar_index, close, text="ENTRY: " + str.tostring(close, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=color.green, textcolor=color.white)
label.new(bar_index, tp1Long, text="TP1: " + str.tostring(tp1Long, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=tp1ColorLong)
label.new(bar_index, tp2Long, text="TP2: " + str.tostring(tp2Long, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=color.green)
label.new(bar_index, slLong, text="SL: " + str.tostring(slLong, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=color.red)
// === Short Entry ===
if (shortSignal and strategy.position_size >= 0)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
strategy.exit("TP1", from_entry="Short", limit=tp1Short, stop=slShort, qty_percent=50)
strategy.exit("TP2", from_entry="Short", limit=tp2Short, stop=slShort)
lastShortBar := bar_index
label.new(bar_index, close, text="ENTRY: " + str.tostring(close, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=color.red, textcolor=color.white)
label.new(bar_index, tp1Short, text="TP1: " + str.tostring(tp1Short, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=tp1ColorShort)
label.new(bar_index, tp2Short, text="TP2: " + str.tostring(tp2Short, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=color.green)
label.new(bar_index, slShort, text="SL: " + str.tostring(slShort, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=color.red)
// === Hedge Orders ===
if (strategy.position_size > 0 and shortSignal)
strategy.entry("HedgeShort", strategy.short)
if (strategy.position_size < 0 and longSignal)
strategy.entry("HedgeLong", strategy.long)
// === Fibonacci Plotting ===
plot(fib236, "Fib 0.236", color=color.gray)
plot(fib382, "Fib 0.382", color=color.green)
plot(fib5, "Fib 0.5", color=color.orange)
plot(fib618, "Fib 0.618", color=color.red)
plot(fib786, "Fib 0.786", color=color.fuchsia)
plot(fib1, "Fib 1.0", color=color.white)
plot(fib1618, "Fib 1.618", color=color.blue)