Strategi ini adalah sistem perdagangan kuantitatif yang berasaskan pengayun dinamik RSI. Dengan melakukan analisa susunan dan urutan masa yang berlainan terhadap indikator RSI, ia dikira untuk menangkap pergerakan pasaran. Strategi ini menggunakan kaedah matematik canggih seperti pemisahan QR untuk pemprosesan isyarat, dan membuat keputusan perdagangan dalam kombinasi dengan sistem linear.
Prinsip Strategi
Pusat strategi ini adalah Delta-RSI Oscillator, yang dilaksanakan melalui langkah-langkah berikut:
- Mulakan dengan mengira RSI tradisional sebagai data asas.
- RSI ditangani dengan lancar menggunakan kecocokan pelbagai untuk mengurangkan kebisingan
- Mengira derivatif masa RSI dengan Delta-RSI, yang mencerminkan kadar perubahan RSI
- Membandingkan Delta-RSI dengan purata bergerak untuk menghasilkan isyarat perdagangan
- Penilaian dan penapisan kualiti yang sesuai menggunakan kesilapan akar sama rata (RMSE)
Isyarat perdagangan boleh dihasilkan dengan tiga cara:
- Melalui garis sifar: Delta-RSI lebih banyak daripada nilai negatif dan kosong daripada nilai positif
- Talian isyarat bersalin: Delta-RSI naik/turun semasa bergerak rata-rata
- Pergeseran arah: Delta-RSI melakukan lebih banyak apabila kawasan negatif mula naik, melakukan lebih sedikit apabila kawasan positif mula turun
Kelebihan Strategik
- Dasar matematik yang kukuh: menggunakan kaedah matematik canggih seperti pemisahan QR untuk pemprosesan isyarat, asas teori yang kukuh
- Sinyal halus: gabungan pelbagai jenis dapat menyaring bunyi pasaran dengan berkesan dan meningkatkan kualiti isyarat
- Fleksibiliti yang tinggi: menyediakan pelbagai cara penjanaan isyarat dan pilihan parameter untuk menyesuaikan diri dengan keadaan pasaran yang berbeza
- Risiko terkawal: mengandungi mekanisme penapisan RMSE, yang boleh memfilterkan isyarat yang lebih dipercayai
- Kecekapan tinggi: Operasi matriks menggunakan algoritma yang dioptimumkan, dengan kecekapan yang lebih tinggi
Risiko Strategik
- Sensitiviti parameter: beberapa parameter utama memerlukan penyesuaian yang teliti, pilihan parameter yang salah boleh menjejaskan prestasi strategi
- Laggity: Pemprosesan isyarat yang lancar akan membawa kepada kelewatan tertentu, mungkin kehilangan pergerakan yang cepat
- Penembusan palsu: mungkin menghasilkan isyarat palsu dalam pasaran yang bergolak, meningkatkan kos dagangan
- Kompleksiti pengiraan: melibatkan lebih banyak operasi matriks, kemungkinan terdapat masalah prestasi dalam perdagangan frekuensi tinggi
- Overfitting: perlu berhati-hati dalam mengoptimumkan parameter untuk mengelakkan overfitting data sejarah
Arah pengoptimuman strategi
- Parameter penyesuaian diri: RSI kitaran dan tahap penyesuaian boleh disesuaikan dengan pergerakan kadar turun naik pasaran
- Tempoh berganda: sinyal yang menggabungkan lebih banyak tempoh masa untuk disahkan silang
- Penapisan kadar lonjakan: penapisan isyarat dengan penunjuk kadar lonjakan seperti ATR
- Klasifikasi pasaran: menggunakan peraturan penjanaan isyarat yang berbeza untuk keadaan pasaran yang berbeza (trend / goyah)
- Pengoptimuman Hentikan Kerosakan: Menambah mekanisme hentikan yang lebih pintar, seperti hentikan dinamik berdasarkan kedudukan rintangan sokongan
ringkaskan
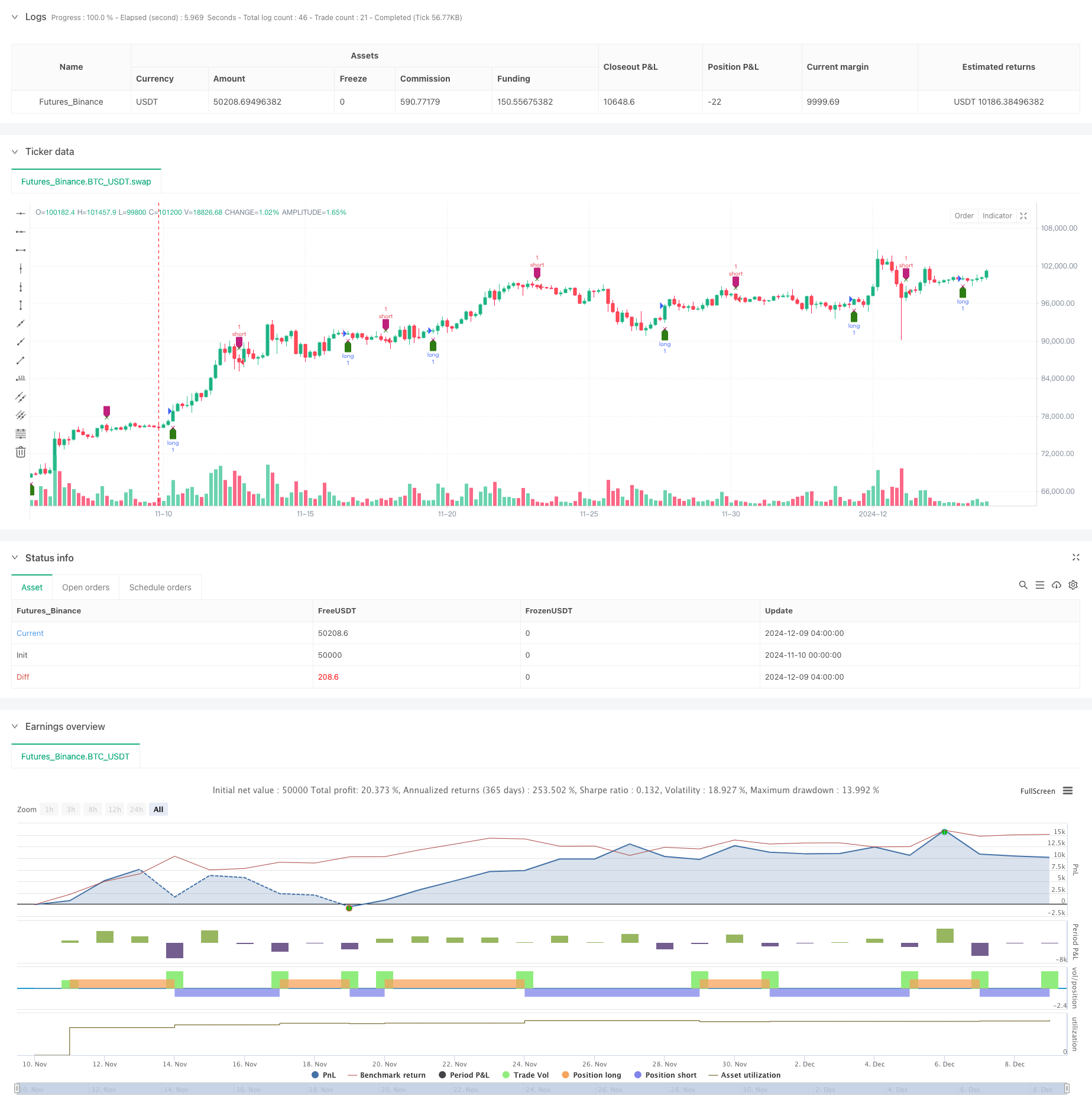
Ini adalah strategi perdagangan kuantitatif yang lengkap dan berasaskan teori yang kukuh. Dengan analisis ciri dinamik RSI, pemprosesan isyarat yang digabungkan dengan kaedah matematik moden, dapat menangkap trend pasaran dengan lebih baik. Walaupun terdapat beberapa masalah kepekaan parameter dan kerumitan pengiraan, strategi ini mempunyai nilai aplikasi yang baik dengan pemilihan parameter yang munasabah dan penambahbaikan pengoptimuman.
/*backtest
start: 2024-11-10 00:00:00
end: 2024-12-09 08:00:00
period: 4h
basePeriod: 4h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © tbiktag
//
// Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy
//
// A strategy that uses Delta-RSI Oscillator (© tbiktag) as a stand-alone indicator:
// https://www.tradingview.com/script/OXQVFTQD-Delta-RSI-Oscillator/
//
// Delta-RSI is a smoothed time derivative of the RSI, plotted as a histogram
// and serving as a momentum indicator.
//
// Input parameters:
// RSI Length: The timeframe of the RSI that serves as an input to D-RSI.
// Length: The length of the lookback frame used for local regression.
// Polynomial Order: The order of the local polynomial function used to interpolate the RSI.
// Signal Length: The length of a EMA of the D-RSI series that is used as a signal line.
// Trade signals are generated based on three optional conditions:
// - Zero-crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses zero from negative to positive values (bearish otherwise)
// - Signal Line Crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses from below to above the signal line (bearish otherwise)
// - Direction Change: bullish when D-RSI was negative and starts ascending (bearish otherwise)
//
// Since D-RSI oscillator is based on polynomial fitting of the RSI curve, there is also an option
// to filter trade signal by means of the root mean-square error of the fit (normalized by the sample average).
//
//@version=5
strategy(title='Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy-QuangVersion', shorttitle='D-RSI-Q', overlay=true)
// ---Subroutines---
matrix_get(_A, _i, _j, _nrows) =>
// Get the value of the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.get(_A, _i + _nrows * _j)
matrix_set(_A, _value, _i, _j, _nrows) =>
// Set a value to the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array, changed on output: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _value :: float: the new value to be set
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.set(_A, _i + _nrows * _j, _value)
transpose(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
// Transpose an implied 2d matrix
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _AT :: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions: _ncolums x _nrows
var _AT = array.new_float(_nrows * _ncolumns, 0)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_AT, matrix_get(_A, i, j, _nrows), j, i, _ncolumns)
_AT
multiply(_A, _B, _nrowsA, _ncolumnsA, _ncolumnsB) =>
// Calculate scalar product of two matrices
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _B :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _nrowsA :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumnsA :: integer: number of columns in _A
// _ncolumnsB :: integer: number of columns in _B
// output:
// _C:: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions _nrowsA x _ncolumnsB
var _C = array.new_float(_nrowsA * _ncolumnsB, 0)
int _nrowsB = _ncolumnsA
float elementC = 0.0
for i = 0 to _nrowsA - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _ncolumnsB - 1 by 1
elementC := 0
for k = 0 to _ncolumnsA - 1 by 1
elementC += matrix_get(_A, i, k, _nrowsA) * matrix_get(_B, k, j, _nrowsB)
elementC
matrix_set(_C, elementC, i, j, _nrowsA)
_C
vnorm(_X, _n) =>
//Square norm of vector _X with size _n
float _norm = 0.0
for i = 0 to _n - 1 by 1
_norm += math.pow(array.get(_X, i), 2)
_norm
math.sqrt(_norm)
qr_diag(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
//QR Decomposition with Modified Gram-Schmidt Algorithm (Column-Oriented)
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _Q: unitary matrix, implied dimenstions _nrows x _ncolumns
// _R: upper triangular matrix, implied dimansions _ncolumns x _ncolumns
var _Q = array.new_float(_nrows * _ncolumns, 0)
var _R = array.new_float(_ncolumns * _ncolumns, 0)
var _a = array.new_float(_nrows, 0)
var _q = array.new_float(_nrows, 0)
float _r = 0.0
float _aux = 0.0
//get first column of _A and its norm:
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
array.set(_a, i, matrix_get(_A, i, 0, _nrows))
_r := vnorm(_a, _nrows)
//assign first diagonal element of R and first column of Q
matrix_set(_R, _r, 0, 0, _ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Q, array.get(_a, i) / _r, i, 0, _nrows)
if _ncolumns != 1
//repeat for the rest of the columns
for k = 1 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
array.set(_a, i, matrix_get(_A, i, k, _nrows))
for j = 0 to k - 1 by 1
//get R_jk as scalar product of Q_j column and A_k column:
_r := 0
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
_r += matrix_get(_Q, i, j, _nrows) * array.get(_a, i)
_r
matrix_set(_R, _r, j, k, _ncolumns)
//update vector _a
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
_aux := array.get(_a, i) - _r * matrix_get(_Q, i, j, _nrows)
array.set(_a, i, _aux)
//get diagonal R_kk and Q_k column
_r := vnorm(_a, _nrows)
matrix_set(_R, _r, k, k, _ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Q, array.get(_a, i) / _r, i, k, _nrows)
[_Q, _R]
pinv(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
//Pseudoinverse of matrix _A calculated using QR decomposition
// Input:
// _A:: array: implied as a (_nrows x _ncolumns) matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(_ncolumns-1)]]
// Output:
// _Ainv:: array implied as a (_ncolumns x _nrows) matrix _A = [[row_0],[row_1],...,[row_(_nrows-1)]]
// ----
// First find the QR factorization of A: A = QR,
// where R is upper triangular matrix.
// Then _Ainv = R^-1*Q^T.
// ----
[_Q, _R] = qr_diag(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns)
_QT = transpose(_Q, _nrows, _ncolumns)
// Calculate Rinv:
var _Rinv = array.new_float(_ncolumns * _ncolumns, 0)
float _r = 0.0
matrix_set(_Rinv, 1 / matrix_get(_R, 0, 0, _ncolumns), 0, 0, _ncolumns)
if _ncolumns != 1
for j = 1 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
for i = 0 to j - 1 by 1
_r := 0.0
for k = i to j - 1 by 1
_r += matrix_get(_Rinv, i, k, _ncolumns) * matrix_get(_R, k, j, _ncolumns)
_r
matrix_set(_Rinv, _r, i, j, _ncolumns)
for k = 0 to j - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Rinv, -matrix_get(_Rinv, k, j, _ncolumns) / matrix_get(_R, j, j, _ncolumns), k, j, _ncolumns)
matrix_set(_Rinv, 1 / matrix_get(_R, j, j, _ncolumns), j, j, _ncolumns)
//
_Ainv = multiply(_Rinv, _QT, _ncolumns, _ncolumns, _nrows)
_Ainv
norm_rmse(_x, _xhat) =>
// Root Mean Square Error normalized to the sample mean
// _x. :: array float, original data
// _xhat :: array float, model estimate
// output
// _nrmse:: float
float _nrmse = 0.0
if array.size(_x) != array.size(_xhat)
_nrmse := na
_nrmse
else
int _N = array.size(_x)
float _mse = 0.0
for i = 0 to _N - 1 by 1
_mse += math.pow(array.get(_x, i) - array.get(_xhat, i), 2) / _N
_mse
_xmean = array.sum(_x) / _N
_nrmse := math.sqrt(_mse) / _xmean
_nrmse
_nrmse
diff(_src, _window, _degree) =>
// Polynomial differentiator
// input:
// _src:: input series
// _window:: integer: wigth of the moving lookback window
// _degree:: integer: degree of fitting polynomial
// output:
// _diff :: series: time derivative
// _nrmse:: float: normalized root mean square error
//
// Vandermonde matrix with implied dimensions (window x degree+1)
// Linear form: J = [ [z]^0, [z]^1, ... [z]^degree], with z = [ (1-window)/2 to (window-1)/2 ]
var _J = array.new_float(_window * (_degree + 1), 0)
for i = 0 to _window - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _degree by 1
matrix_set(_J, math.pow(i, j), i, j, _window)
// Vector of raw datapoints:
var _Y_raw = array.new_float(_window, na)
for j = 0 to _window - 1 by 1
array.set(_Y_raw, j, _src[_window - 1 - j])
// Calculate polynomial coefficients which minimize the loss function
_C = pinv(_J, _window, _degree + 1)
_a_coef = multiply(_C, _Y_raw, _degree + 1, _window, 1)
// For first derivative, approximate the last point (i.e. z=window-1) by
float _diff = 0.0
for i = 1 to _degree by 1
_diff += i * array.get(_a_coef, i) * math.pow(_window - 1, i - 1)
_diff
// Calculates data estimate (needed for rmse)
_Y_hat = multiply(_J, _a_coef, _window, _degree + 1, 1)
float _nrmse = norm_rmse(_Y_raw, _Y_hat)
[_diff, _nrmse]
/// --- main ---
degree = input.int(title='Polynomial Order', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar1', defval=2, minval=1)
rsi_l = input.int(title='RSI Length', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar1', defval=21, minval=1, tooltip='The period length of RSI that is used as input.')
window = input.int(title='Length ( > Order)', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar2', defval=21, minval=2)
signalLength = input.int(title='Signal Length', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar2', defval=9, tooltip='The signal line is a EMA of the D-RSI time series.')
islong = input.bool(title='Buy', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
isshort = input.bool(title='Sell', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
showendlabels = input.bool(title='Exit', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
buycond = input.string(title='Buy', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
sellcond = input.string(title='Sell', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
endcond = input.string(title='Exit', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
usenrmse = input.bool(title='', group='Filter by Means of Root-Mean-Square Error of RSI Fitting:', inline='linermse', defval=false)
rmse_thrs = input.float(title='RSI fitting Error Threshold, %', group='Filter by Means of Root-Mean-Square Error of RSI Fitting:', inline='linermse', defval=10, minval=0.0) / 100
src = ta.rsi(close, rsi_l)
[drsi, nrmse] = diff(src, window, degree)
signalline = ta.ema(drsi, signalLength)
// Conditions and filters
filter_rmse = usenrmse ? nrmse < rmse_thrs : true
dirchangeup = drsi > drsi[1] and drsi[1] < drsi[2] and drsi[1] < 0.0
dirchangedw = drsi < drsi[1] and drsi[1] > drsi[2] and drsi[1] > 0.0
crossup = ta.crossover(drsi, 0.0)
crossdw = ta.crossunder(drsi, 0.0)
crosssignalup = ta.crossover(drsi, signalline)
crosssignaldw = ta.crossunder(drsi, signalline)
//Signals
golong = (buycond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangeup : buycond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossup : crosssignalup) and filter_rmse
goshort = (sellcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangedw : sellcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossdw : crosssignaldw) and filter_rmse
endlong = (endcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangedw : endcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossdw : crosssignaldw) and filter_rmse
endshort = (endcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangeup : endcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossup : crosssignalup) and filter_rmse
plotshape(golong and islong ? low : na, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.labelup, color=color.new(#2E7C13, 0), size=size.small, title='Buy')
plotshape(goshort and isshort ? high : na, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.labeldown, color=color.new(#BF217C, 0), size=size.small, title='Sell')
plotshape(showendlabels and endlong and islong ? high : na, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.xcross, color=color.new(#2E7C13, 0), size=size.tiny, title='Exit Long')
plotshape(showendlabels and endshort and isshort ? low : na, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.xcross, color=color.new(#BF217C, 0), size=size.tiny, title='Exit Short')
alertcondition(golong, title='Long Signal', message='D-RSI: Long Signal')
alertcondition(goshort, title='Short Signal', message='D-RSI: Short Signal')
alertcondition(endlong, title='Exit Long Signal', message='D-RSI: Exit Long')
alertcondition(endshort, title='Exit Short Signal', message='D-RSI: Exit Short')
strategy.entry('long', strategy.long, when=golong and islong)
strategy.entry('short', strategy.short, when=goshort and isshort)
strategy.close('long', when=endlong and islong)
strategy.close('short', when=endshort and isshort)