Estratégia de rompimento de momentum com base em blocos de ordens
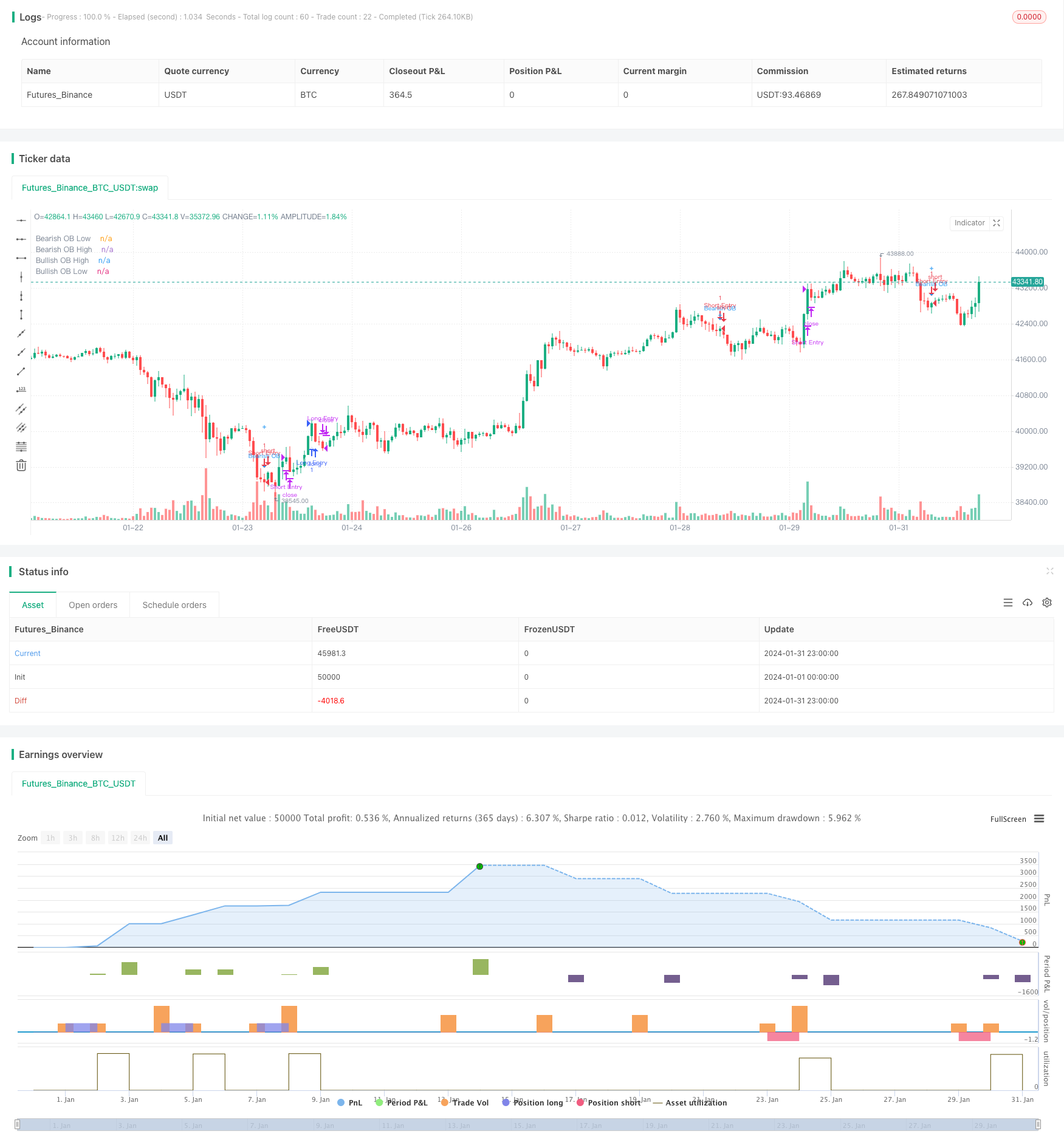
Visão geral
A estratégia identifica blocos de pedidos em preços para encontrar intervalos de preços com um impulso de ruptura e entrar no mercado quando um sinal de compra e venda é apresentado. Os blocos de pedidos marcam as áreas em que as instituições estão envolvidas, o que representa uma maior força do mercado. Portanto, quando o sinal de blocos de pedidos é apresentado, há uma maior probabilidade de ocorrência de mudanças de preços tendenciais.
Princípio da estratégia
Identificação de blocos de pedidos
Os blocos de pedidos são divididos em blocos de pedidos múltiplos e blocos de pedidos em branco. Os blocos de pedidos múltiplos são definidos como uma linha descendente K (linha K vermelha) seguida por uma linha ascendente K (linha K verde). Os blocos de pedidos em branco são definidos como uma linha ascendente K (linha K verde) seguida por uma linha descendente K (linha K vermelha).
Para identificar um bloco de pedidos, é necessário atender simultaneamente às seguintes condições:
Mudança de cor da linha K: uma mudança de cor da linha K anterior para a linha K atual (por exemplo, de vermelho para verde, ou de verde para vermelho). Isso indica que a tendência pode terminar antes que a instituição esteja pronta para iniciar uma nova tendência.
As K-linhas subsequentes são de cor consistente: após atingir o número de raízes especificado pelo parâmetro periodes, as K-linhas subsequentes mantêm a mesma direção de cor ((por exemplo, os blocos de pedidos de múltiplos cabeças são todos K-linhas verdes). Isso indica que a nova tendência é reforçada e confirmada.
Aumento ou queda acima do limiar: O aumento ou queda do preço de abertura do bloco de pedidos para o preço de fechamento da linha K subsequente excede o limite definido para o parâmetro ((default 0)). Isso garante que a nova tendência tenha força e influência suficientes.
Um sinal de bloco de pedidos pode ser identificado quando as três condições acima são satisfeitas simultaneamente.
Geração de sinais de transação
Quando se identifica um bloco de pedidos com várias cabeças, gera-se um sinal de compra; quando se identifica um bloco de pedidos sem cabeça, gera-se um sinal de venda.
Considerando a incerteza do sinal de bloco de pedidos e o possível teste novamente, a estratégia não entra diretamente no mercado quando o sinal de bloco de pedidos aparece, mas avisa o comerciante por meio de linhas de desenho, alarmes, etc. O comerciante pode optar por implantar o preço de limite apropriadamente perto da área de preço do bloco de pedidos e esperar que o preço aumente para entrar na tendência.
Vantagens estratégicas
Utilizando informações de fluxo de pedidos para identificar a dinâmica
Os blocos de pedidos marcam a participação de fundos institucionais e um grande volume de transações, representando a transformação da força do mercado. Assim, os sinais de blocos de pedidos têm uma certa previsibilidade e precisão, podendo capturar antecipadamente a direção de potenciais rupturas. Isso fornece um posicionamento e uma oportunidade favoráveis para a captação de tendências.
Parâmetros de política ajustáveis
Os parâmetros da estratégia, incluindo o número de linhas K históricas, a amplitude da dinâmica de ruptura, etc., podem ser ajustados por meio de parâmetros, o que permite a otimização de diferentes ambientes de mercado e estilos de comerciantes, aumentando a adaptabilidade da estratégia.
Riscos controlados
A estratégia não entra no mercado quando o sinal do bloco de pedidos aparece, mas configura um alarme e constrói posições por meio de uma lista de limites fora do campo. Esta maneira permite que o comerciante controle o ponto de entrada e o risco específicos. Mesmo se o sinal do bloco de pedidos for errado, isso só levará ao fato de que a lista de limites não será acionada, o risco é controlado.
Risco estratégico
A probabilidade de um sinal de bloco de pedidos ser testado novamente é maior
Uma vez que o bloco de pedidos é marcado por um intervalo, a probabilidade de um retorno do preço subsequente para esse intervalo é maior. Portanto, o sinal de bloco de pedidos não pode ser usado como um sinal de entrada padrão, mas como uma mensagem de alerta, o que requer que o próprio comerciante julgue ainda mais o momento da entrada.
Parâmetros mal definidos podem gerar sinais errados
A configuração de parâmetros do bloco de pedidos (número de linhas K históricas, desvalorização de amplitude, etc.) se for inadequada, pode facilmente gerar falsos sinais no intervalo Sideways normal. Isso requer que o comerciante tenha uma certa sensibilidade e julgamento para o mercado e evite a otimização cega dos parâmetros.
A qualidade de cada sinal precisa de ser avaliada manualmente.
Como os sinais de bloco de pedidos não são 100% confiáveis, os comerciantes precisam de uma análise mais aprofundada para determinar a credibilidade do sinal atual, o que aumenta um certo volume de trabalho manual. Diferentes julgamentos sobre a qualidade do sinal também podem causar diferenças no desempenho das negociações.
Direção de otimização da estratégia
Combinação com outros indicadores para filtrar falsos sinais
Pode ser combinado com outros indicadores para julgar a direção e a força da tendência, por exemplo, em combinação com o MACD, RSI, etc., filtrando os sinais errados causados pela configuração de parâmetros, melhorando a precisão do sinal.
Optimizar configurações de parâmetros
Diferentes mercados e diferentes variedades de negociação podem testar e otimizar parâmetros, como o número de linhas K, o valor de queda e queda, etc., para que eles estejam mais em sintonia com o ambiente atual do mercado. Também pode ser configurado o recurso de auto-adaptação dos parâmetros, ajustando-se automaticamente de acordo com a volatilidade do mercado e as preferências de risco.
Desenvolvimento de mecanismos de entrada e saída automatizados
Atualmente, a estratégia serve apenas como uma ferramenta de indicação de sinais, e os traders precisam decidir por si mesmos quando entrar. Podemos desenvolver um mecanismo de pedido automático para a faixa de preço do bloco de pedidos, que entra automaticamente quando certas condições são atendidas; e combinar métodos como o stop loss para definir a lógica de saída, reduzir a necessidade de julgamento manual e aumentar o grau de automação da estratégia.
Resumir
A estratégia de bloco de pedidos tem uma certa capacidade de identificação de cabeça e iniciativa em comparação com os métodos de simples rastreamento de tendências. Quando usado em combinação com o método de otimização de parâmetros e controle de vento, pode ser uma estratégia de tendências eficaz. Mas o comerciante precisa estar alerta para a produção de sinais errados e julgar a qualidade dos sinais.
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-01 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-31 23:59:59
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © TradingSecrets and wugamlo
// This experimental Indicator helps identifying instituational Order Blocks.
// Often these blocks signal the beginning of a strong move, but there is a significant probability that these price levels will be revisited at a later point in time again.
// Therefore these are interesting levels to place limit orders (Buy Orders for Bullish OB / Sell Orders for Bearish OB).
//
// A Bullish Order block is defined as the last down candle before a sequence of up candles. (Relevant price range "Open" to "Low" is marked) / Optionally full range "High" to "Low"
// A Bearish Order Block is defined as the last up candle before a sequence of down candles. (Relevant price range "Open" to "High" is marked) / Optionally full range "High" to "Low"
//
// In the settings the number of required sequential candles can be adjusted.
// Furthermore a %-threshold can be entered. It defines which %-change the sequential move needs to achieve in order to identify a relevant Order Block.
// Channels for the last Bullish/Bearish Block can be shown/hidden.
//
// In addition to the upper/lower limits of each Order Block, also the equlibrium (average value) is marked as this is an interesting area for price interaction.
//
// Alerts added: Alerts fire when an Order Block is detected. The delay is based on the "Relevant Periods" input. Means with the default setting "5" the alert will trigger after the
// number of consecutive candles is reached.
//@version=4
strategy("[Backtest] Order Block Finder", overlay = true)
colors = input(title = "Color Scheme", defval="DARK", options=["DARK", "BRIGHT"])
periods = input(5, "Relevant Periods to identify OB") // Required number of subsequent candles in the same direction to identify Order Block
threshold = input(0.0, "Min. Percent move to identify OB", step = 0.1) // Required minimum % move (from potential OB close to last subsequent candle to identify Order Block)
usewicks = input(false, "Use whole range [High/Low] for OB marking?" ) // Display High/Low range for each OB instead of Open/Low for Bullish / Open/High for Bearish
showbull = input(false, "Show latest Bullish Channel?") // Show Channel for latest Bullish OB?
showbear = input(false, "Show latest Bearish Channel?") // Show Channel for latest Bearish OB?
showdocu = input(false, "Show Label for documentation tooltip?") // Show Label which shows documentation as tooltip?
info_pan = input(false, "Show Latest OB Panel?") // Show Info Panel with latest OB Stats
//strategy inputs
plot_offset = input( type=input.bool,defval = false, title = 'Plot Offset?')
stoploss_percent = input(type=input.float, defval = 1, title = 'Stop Loss [%]')
takeprofit_percent = input(type=input.float, defval = 2, title = 'Take Profit [%]')
pyramiding = input( type=input.bool,defval = true, title = 'Pyramiding')
ob_period = periods + 1 // Identify location of relevant Order Block candle
absmove = ((abs(close[ob_period] - close[1]))/close[ob_period]) * 100 // Calculate absolute percent move from potential OB to last candle of subsequent candles
relmove = absmove >= threshold // Identify "Relevant move" by comparing the absolute move to the threshold
// Color Scheme
bullcolor = colors == "DARK"? color.white : color.green
bearcolor = colors == "DARK"? color.blue : color.red
// Bullish Order Block Identification
bullishOB = close[ob_period] < open[ob_period] // Determine potential Bullish OB candle (red candle)
int upcandles = 0
for i = 1 to periods
upcandles := upcandles + (close[i] > open[i]? 1 : 0) // Determine color of subsequent candles (must all be green to identify a valid Bearish OB)
OB_bull = bullishOB and (upcandles == (periods)) and relmove // Identification logic (red OB candle & subsequent green candles)
OB_bull_high = OB_bull? usewicks? high[ob_period] : open[ob_period] : na // Determine OB upper limit (Open or High depending on input)
OB_bull_low = OB_bull? low[ob_period] : na // Determine OB lower limit (Low)
OB_bull_avg = (OB_bull_high + OB_bull_low)/2 // Determine OB middle line
// Bearish Order Block Identification
bearishOB = close[ob_period] > open[ob_period] // Determine potential Bearish OB candle (green candle)
int downcandles = 0
for i = 1 to periods
downcandles := downcandles + (close[i] < open[i]? 1 : 0) // Determine color of subsequent candles (must all be red to identify a valid Bearish OB)
OB_bear = bearishOB and (downcandles == (periods)) and relmove // Identification logic (green OB candle & subsequent green candles)
OB_bear_high = OB_bear? high[ob_period] : na // Determine OB upper limit (High)
OB_bear_low = OB_bear? usewicks? low[ob_period] : open[ob_period] : na // Determine OB lower limit (Open or Low depending on input)
OB_bear_avg = (OB_bear_low + OB_bear_high)/2 // Determine OB middle line
//@TradingSecrets: Option to disable the offset in order to allign signals with Backtest
if not plot_offset
ob_period := 0
// Plotting
plotshape(OB_bull, title="Bullish OB", style = shape.triangleup, color = bullcolor, textcolor = bullcolor, size = size.tiny, location = location.belowbar, offset = -ob_period, text = "Bullish OB") // Bullish OB Indicator
bull1 = plot(OB_bull_high, title="Bullish OB High", style = plot.style_linebr, color = bullcolor, offset = -ob_period, linewidth = 3) // Bullish OB Upper Limit
bull2 = plot(OB_bull_low, title="Bullish OB Low", style = plot.style_linebr, color = bullcolor, offset = -ob_period, linewidth = 3) // Bullish OB Lower Limit
fill(bull1, bull2, color=bullcolor, transp = 0, title = "Bullish OB fill") // Fill Bullish OB
plotshape(OB_bull_avg, title="Bullish OB Average", style = shape.cross, color = bullcolor, size = size.normal, location = location.absolute, offset = -ob_period) // Bullish OB Average
plotshape(OB_bear, title="Bearish OB", style = shape.triangledown, color = bearcolor, textcolor = bearcolor, size = size.tiny, location = location.abovebar, offset = -ob_period, text = "Bearish OB") // Bearish OB Indicator
bear1 = plot(OB_bear_low, title="Bearish OB Low", style = plot.style_linebr, color = bearcolor, offset = -ob_period, linewidth = 3) // Bearish OB Lower Limit
bear2 = plot(OB_bear_high, title="Bearish OB High", style = plot.style_linebr, color = bearcolor, offset = -ob_period, linewidth = 3) // Bearish OB Upper Limit
fill(bear1, bear2, color=bearcolor, transp = 0, title = "Bearish OB fill") // Fill Bearish OB
plotshape(OB_bear_avg, title="Bearish OB Average", style = shape.cross, color = bearcolor, size = size.normal, location = location.absolute, offset = -ob_period) // Bullish OB Average
var line linebull1 = na // Bullish OB average
var line linebull2 = na // Bullish OB open
var line linebull3 = na // Bullish OB low
var line linebear1 = na // Bearish OB average
var line linebear2 = na // Bearish OB high
var line linebear3 = na // Bearish OB open
if OB_bull and showbull
line.delete(linebull1)
linebull1 := line.new(x1 = bar_index, y1 = OB_bull_avg, x2 = bar_index - 1, y2 = OB_bull_avg, extend = extend.left, color = bullcolor, style = line.style_solid, width = 1)
line.delete(linebull2)
linebull2 := line.new(x1 = bar_index, y1 = OB_bull_high, x2 = bar_index - 1, y2 = OB_bull_high, extend = extend.left, color = bullcolor, style = line.style_dashed, width = 1)
line.delete(linebull3)
linebull3 := line.new(x1 = bar_index, y1 = OB_bull_low, x2 = bar_index - 1, y2 = OB_bull_low, extend = extend.left, color = bullcolor, style = line.style_dashed, width = 1)
if OB_bear and showbear
line.delete(linebear1)
linebear1 := line.new(x1 = bar_index, y1 = OB_bear_avg, x2 = bar_index - 1, y2 = OB_bear_avg, extend = extend.left, color = bearcolor, style = line.style_solid, width = 1)
line.delete(linebear2)
linebear2 := line.new(x1 = bar_index, y1 = OB_bear_high, x2 = bar_index - 1, y2 = OB_bear_high, extend = extend.left, color = bearcolor, style = line.style_dashed, width = 1)
line.delete(linebear3)
linebear3 := line.new(x1 = bar_index, y1 = OB_bear_low, x2 = bar_index - 1, y2 = OB_bear_low, extend = extend.left, color = bearcolor, style = line.style_dashed, width = 1)
// Alerts for Order Blocks Detection
alertcondition(OB_bull, title='New Bullish OB detected', message='New Bullish OB detected - This is NOT a BUY signal!')
alertcondition(OB_bear, title='New Bearish OB detected', message='New Bearish OB detected - This is NOT a SELL signal!')
// Print latest Order Blocks in Data Window
var latest_bull_high = 0.0 // Variable to keep latest Bull OB high
var latest_bull_avg = 0.0 // Variable to keep latest Bull OB average
var latest_bull_low = 0.0 // Variable to keep latest Bull OB low
var latest_bear_high = 0.0 // Variable to keep latest Bear OB high
var latest_bear_avg = 0.0 // Variable to keep latest Bear OB average
var latest_bear_low = 0.0 // Variable to keep latest Bear OB low
// Assign latest values to variables
if OB_bull_high > 0
latest_bull_high := OB_bull_high
if OB_bull_avg > 0
latest_bull_avg := OB_bull_avg
if OB_bull_low > 0
latest_bull_low := OB_bull_low
if OB_bear_high > 0
latest_bear_high := OB_bear_high
if OB_bear_avg > 0
latest_bear_avg := OB_bear_avg
if OB_bear_low > 0
latest_bear_low := OB_bear_low
// Plot invisible characters to be able to show the values in the Data Window
plotchar(latest_bull_high, char = ' ', location = location.abovebar, color = #777777, transp = 100, size = size.tiny, title = "Latest Bull High")
plotchar(latest_bull_avg, char = ' ', location = location.abovebar, color = #777777, transp = 100, size = size.tiny, title = "Latest Bull Avg")
plotchar(latest_bull_low, char = ' ', location = location.abovebar, color = #777777, transp = 100, size = size.tiny, title = "Latest Bull Low")
plotchar(latest_bear_high, char = ' ', location = location.abovebar, color = #777777, transp = 100, size = size.tiny, title = "Latest Bear High")
plotchar(latest_bear_avg, char = ' ', location = location.abovebar, color = #777777, transp = 100, size = size.tiny, title = "Latest Bear Avg")
plotchar(latest_bear_low, char = ' ', location = location.abovebar, color = #777777, transp = 100, size = size.tiny, title = "Latest Bear Low")
//InfoPanel for latest Order Blocks
draw_InfoPanel(_text, _x, _y, font_size)=>
var label la_panel = na
label.delete(la_panel)
la_panel := label.new(
x=_x, y=_y,
text=_text, xloc=xloc.bar_time, yloc=yloc.price,
color=color.new(#383838, 5), style=label.style_label_left, textcolor=color.white, size=font_size)
info_panel_x = time_close + round(change(time) * 100)
info_panel_y = close
title = "LATEST ORDER BLOCKS"
row0 = "-----------------------------------------------------"
row1 = ' Bullish - High: ' + tostring(latest_bull_high, '#.##')
row2 = ' Bullish - Avg: ' + tostring(latest_bull_avg, '#.##')
row3 = ' Bullish - Low: ' + tostring(latest_bull_low, '#.##')
row4 = "-----------------------------------------------------"
row5 = ' Bearish - High: ' + tostring(latest_bear_high, '#.##')
row6 = ' Bearish - Avg: ' + tostring(latest_bear_avg, '#.##')
row7 = ' Bearish - Low: ' + tostring(latest_bear_low, '#.##')
panel_text = '\n' + title + '\n' + row0 + '\n' + row1 + '\n' + row2 + '\n' + row3 + '\n' + row4 + '\n\n' + row5 + '\n' + row6 + '\n' + row7 + '\n'
if info_pan
draw_InfoPanel(panel_text, info_panel_x, info_panel_y, size.normal)
// === Label for Documentation/Tooltip ===
chper = time - time[1]
chper := change(chper) > 0 ? chper[1] : chper
// === Tooltip text ===
var vartooltip = "Indicator to help identifying instituational Order Blocks. Often these blocks signal the beginning of a strong move, but there is a high probability, that these prices will be revisited at a later point in time again and therefore are interesting levels to place limit orders. \nBullish Order block is the last down candle before a sequence of up candles. \nBearish Order Block is the last up candle before a sequence of down candles. \nIn the settings the number of required sequential candles can be adjusted. \nFurthermore a %-threshold can be entered which the sequential move needs to achieve in order to validate a relevant Order Block. \nChannels for the last Bullish/Bearish Block can be shown/hidden."
// === Print Label ===
var label l_docu = na
label.delete(l_docu)
if showdocu
l_docu := label.new(x = time + chper * 35, y = close, text = "DOCU OB", color=color.gray, textcolor=color.white, style=label.style_label_center, xloc = xloc.bar_time, yloc=yloc.price, size=size.tiny, textalign = text.align_left, tooltip = vartooltip)
// @TradingSecrets: Generate entry and exit orders based on the signals
entryLongSignal = OB_bull
entryShortSignal = OB_bear
if not pyramiding
entryLongSignal := entryLongSignal and not strategy.position_size
entryShortSignal := entryShortSignal and not strategy.position_size
if entryLongSignal
strategy.entry("Long Entry", strategy.long)
//strategy.exit("Long Exit Loss", "Long Entry", stop = close * (1 - stoploss_percent*0.01))
if entryShortSignal
strategy.entry("Short Entry", strategy.short)
//strategy.exit("Short Exit Loss", "Short Entry", stop = close * (1 + stoploss_percent*0.01))
strategy.initial_capital = 50000
//Close Position by market order
if strategy.position_size > 0 and strategy.openprofit/nz(strategy.initial_capital + strategy.netprofit) >= takeprofit_percent*0.01
//If I m in a long position and my take profit got hit close it by market order
strategy.close("Long Entry", comment = "Long Exit Profit")
if strategy.position_size < 0 and strategy.openprofit/nz(strategy.initial_capital + strategy.netprofit) >= takeprofit_percent*0.01
strategy.close("Short Entry", comment = "Short Exit Profit")
if strategy.position_size > 0 and strategy.openprofit/nz(strategy.initial_capital + strategy.netprofit) <= -stoploss_percent*0.01
//If I m in a long position and my take profit got hit close it by market order
strategy.close("Long Entry", comment = "Long Exit Loss")
if strategy.position_size < 0 and strategy.openprofit/nz(strategy.initial_capital + strategy.netprofit) <= -stoploss_percent*0.01
strategy.close("Short Entry", comment = "Short Exit Loss")