ڈبل موونگ ایوریج ٹرننگ پوائنٹ ٹریڈنگ کی حکمت عملی
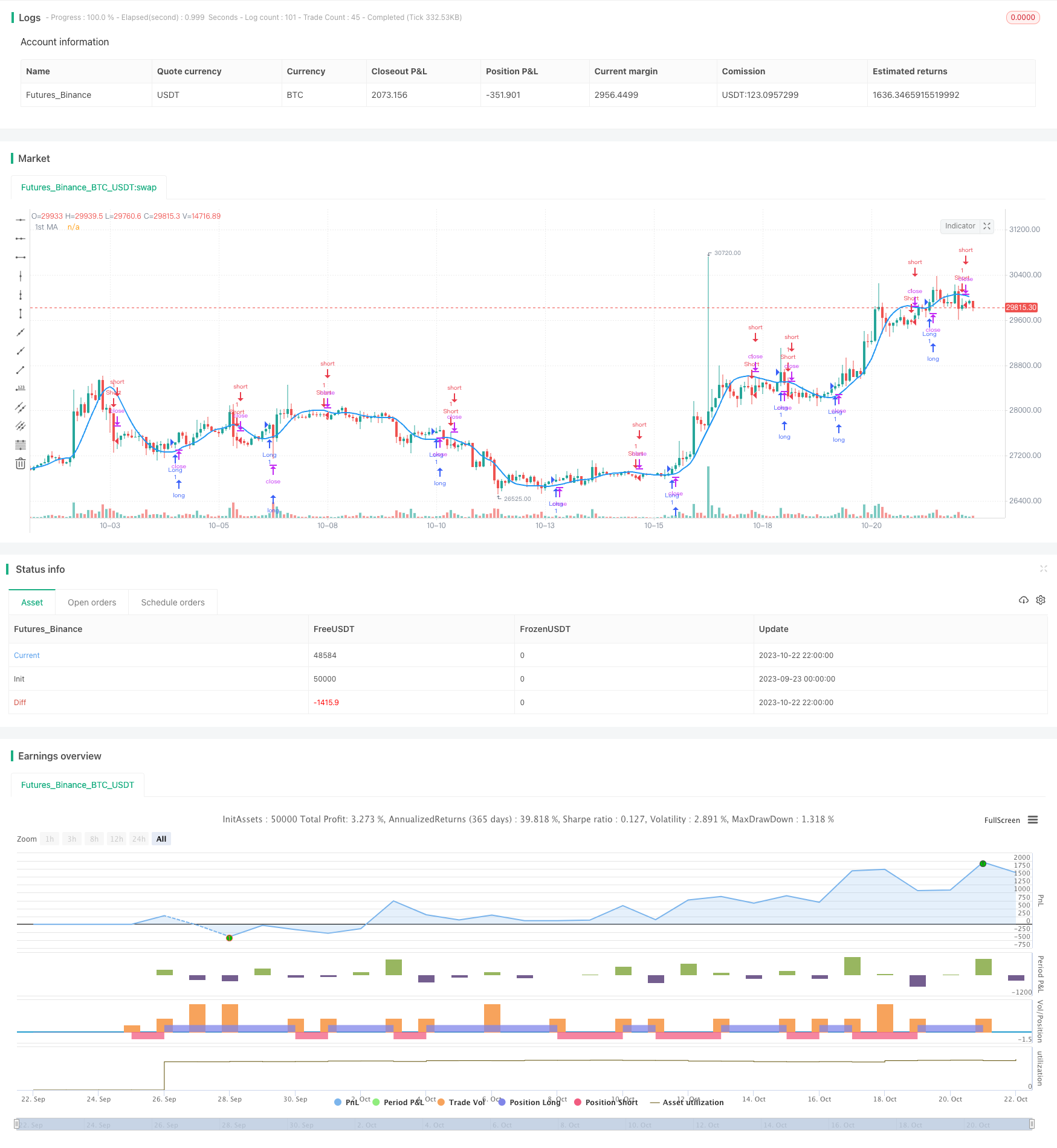
جائزہ
ڈبل مساوی لائن ٹرانسمیشن پوائنٹ ٹریڈنگ حکمت عملی ایک مساوی لائن کراسنگ پر مبنی تجارتی حکمت عملی ہے۔ یہ دو مختلف پیرامیٹرز کے سیٹ کی چلتی اوسط کا استعمال کرتا ہے تاکہ ان کی تبدیلی کی بنیاد پر انٹری اور آؤٹ ٹائم کا فیصلہ کیا جاسکے۔ یہ حکمت عملی آسان ، آسان اور عملی ہے اور درمیانی لمبی لائن ٹریڈنگ کے لئے موزوں ہے۔
حکمت عملی کا اصول
اس حکمت عملی میں قیمت کو قیمت کے ان پٹ کے طور پر استعمال کیا جاتا ہے ، اور دو مختلف پیرامیٹرز ، SMA1 اور SMA2 کے لئے اوسط لائن کا حساب لگایا جاتا ہے۔ حکمت عملی اوسط لائن کی تبدیلی کا فیصلہ کرنے کے لئے ROC اشارے کا استعمال کرتی ہے۔ SMA1 کا ROC قدر ایک مقررہ مثبت حد سے زیادہ ہونے پر ، SMA1 کو اوپر کی طرف موڑنے کے لئے سمجھا جاتا ہے ، اور SMA1 کو اوپر کی طرف اشارہ کیا جاتا ہے۔ جب SMA1 کا ROC قدر ایک مقررہ منفی حد سے کم ہو تو ، SMA1 کو نیچے کی طرف موڑنے کے لئے سمجھا جاتا ہے ، اور SMA1 کو نیچے کی طرف اشارہ کیا جاتا ہے۔ SMA2 کا فیصلہ کرنے کی منطق اسی طرح کی ہے۔
جب SMA1 اوپر کی طرف مڑتا ہے اور اوپر کی K لائن SMA2 نیچے کی طرف مڑتا ہے تو ، خریدنے کا اشارہ ہوتا ہے ، اور زیادہ ہوتا ہے۔ جب SMA1 نیچے کی طرف مڑتا ہے اور اوپر کی K لائن SMA2 اوپر کی طرف مڑتا ہے تو ، فروخت کا اشارہ ہوتا ہے ، اور خالی ہوتا ہے۔
یہ حکمت عملی تجارت کی سمت کا تعین کرنے کے لئے دو یکساں لائنوں کے موڑ کا استعمال کرتی ہے ، ایک یکساں لائن کا موڑ داخلے کے وقت کی تصدیق کرتا ہے ، اور دو یکساں لائنوں کا کراس اس بات کو یقینی بناتا ہے کہ داخلے کے وقت کا رجحان تبدیل ہوجائے ، جس سے جعلی توڑ کو مؤثر طریقے سے فلٹر کیا جاسکے۔
طاقت کا تجزیہ
ڈبل مساوی لائن کراس اور ٹرننگ فیصلے کا استعمال کرتے ہوئے ، جعلی توڑ کو مؤثر طریقے سے فلٹر کیا جاسکتا ہے ، اور داخلے کی درستگی کو بہتر بنایا جاسکتا ہے۔
اوسط لائن ٹرانسمیشن کے ساتھ آر او سی اشارے کے ساتھ ٹرانسمیشن ٹائمنگ کو واضح طور پر سمجھا جاتا ہے اور بار بار تجارت سے بچا جاتا ہے۔
اس کے علاوہ، یہ ایک طویل اور درمیانے درجے کی لائن ہے، جس میں آپ کو اہم رجحانات کی پیروی کر سکتے ہیں اور اس سے زیادہ منافع حاصل کر سکتے ہیں.
حکمت عملی کی منطق سادہ اور واضح ہے ، اس پر عمل درآمد آسان ہے ، اور یہ مقدار میں تجارت کرنے والے ابتدائی افراد کے لئے موزوں ہے۔
اپنی مرضی کے مطابق پیرامیٹرز ، مختلف مارکیٹ کے حالات کے مطابق ڈھالنے کے لئے ، مضبوط موافقت پذیری
خطرے کا تجزیہ
ڈبل مساوی لائن کراسنگ ہلچل کے حالات میں غلط سگنل کی ایک بڑی تعداد پیدا کر سکتا ہے، جس کے نتیجے میں نقصان ہوتا ہے.
ROC پیرامیٹرز کو درست طریقے سے بہتر بنانے کی ضرورت ہے ، ورنہ شناخت کی طرف رجوع کرنے میں غلطیاں ہوسکتی ہیں ، جو حکمت عملی کی کارکردگی کو متاثر کرتی ہیں۔
بڑے دورانیہ کے جھٹکے سے مارکیٹ میں متعدد اسٹاپ نقصانات کا سبب بن سکتا ہے ، جس سے روک تھام کی حد کو بڑھا کر بچا جاسکتا ہے۔
اس کے نتیجے میں ، اس طرح کی خبروں کے بارے میں ردعمل دینے میں دشواری کا سامنا کرنا پڑتا ہے ، جس سے نقصان ہوسکتا ہے۔
پیرامیٹرز کو زیادہ سے زیادہ فٹ ہونے کے مسئلے پر دھیان دیں ، ٹیسٹ کا دورانیہ کافی لمبا ہونا چاہئے ، جس میں مختلف حالات شامل ہوں۔
اصلاح کی سمت
بہترین اوسطاً دورانیہ کا مجموعہ تلاش کرنے کے لئے منتقل اوسط پیرامیٹرز کو بہتر بنائیں
ROC پیرامیٹرز کو بہتر بنانے کے لئے موڑ کی شناخت کی درستگی میں اضافہ
ایک متحرک روک تھام کے ساتھ اپنی مرضی کے مطابق قیمت کی سطح کو توڑنے کے لئے روک تھام کے طریقہ کار میں اضافہ کریں
اضافی شرائط شامل کریں ، جیسے ٹریڈنگ حجم اشارے کو ٹرگر کریں ، جھوٹے بریک سے بچیں۔
دیگر اشارے جیسے MACD، BOLL وغیرہ کے ساتھ مل کر، فیصلہ سازی کو بہتر بنانا
مارکیٹ میں تبدیلیوں کے مطابق پیرامیٹرز کو خودکار طور پر بہتر بنانے کے لئے مشین لرننگ جیسے طریقوں کا استعمال کرنا
خلاصہ کریں۔
ڈبل مساوی لائن ٹرانسمیشن پوائنٹ حکمت عملی ایک سادہ عملی رجحان کی پیروی کرنے والی حکمت عملی ہے۔ اس میں صرف بنیادی مساوی اشارے کی ضرورت ہوتی ہے ، اس کی منطق واضح اور سمجھنے میں آسان ہے ، اور یہ سیکھنے اور مشق کرنے کے لئے کوانٹم ٹریڈنگ کے ابتدائی افراد کے لئے بہت موزوں ہے۔ پیرامیٹرز کو بہتر بنانے اور اسٹاپ نقصان کے طریقہ کار کو بہتر بنانے کے ذریعے حکمت عملی کی استحکام میں نمایاں اضافہ کیا جاسکتا ہے۔ دوسرے معاون اشارے کے ساتھ مل کر استعمال کرنے سے حکمت عملی کی تاثیر کو مزید بڑھا دیا جاسکتا ہے۔ یہ حکمت عملی انتہائی مرضی کے مطابق ہے ، اور مختلف مارکیٹ کے ماحول میں لچکدار اطلاق کے قابل ہے ، اور یہ ایک تجویز کردہ دو طرفہ مساوی لائن ٹریڈنگ حکمت عملی ہے۔
Overview
The Dual Moving Average Turning Point strategy is a trend following strategy based on moving average crossovers. It uses two moving averages with different parameter settings and determines entry and exit points according to their turning directions. This strategy is simple and intuitive, easy to implement, and suitable for medium-to-long term trading.
Strategy Logic
The strategy uses Price as the price input source and calculates two moving averages, SMA1 and SMA2, with different parameters. It uses the ROC indicator to determine the turning directions of the moving averages. When SMA1’s ROC value exceeds the positive threshold, it is considered an upward turn of SMA1 and an upward signal is recorded. When SMA1’s ROC value breaks the negative threshold, it is considered a downward turn of SMA1 and a downward signal is recorded. The judgment logic for SMA2 is similar.
When SMA1 turns upward and the previous bar’s SMA2 turns downward, a buy signal is generated to go long. When SMA1 turns downward and the previous bar’s SMA2 turns upward, a sell signal is generated to go short.
The strategy uses the turning directions of two moving averages to determine the trading direction and the turning of one moving average to confirm entry timing. The dual moving average crossover ensures the trend has changed when entering the market, which helps avoid false breakouts.
Advantage Analysis
Using dual moving average crossover and turning points can effectively filter out false breakouts and improve entry accuracy.
Combining moving average turning points with the ROC indicator can clearly identify turning points and avoid frequent trading.
Adopting medium-to-long-term dual moving averages can track the main trend and achieve sizable trend profits.
The strategy logic is simple and clear, easy to understand and implement, suitable for quant trading beginners.
Customizable parameters suit different market environments with strong adaptability.
Risk Analysis
Dual moving average crossovers may generate many false signals in ranging markets, leading to losses.
The ROC parameters need precise optimization, otherwise turn recognition will have errors, affecting strategy performance.
Large periodic ranging markets may trigger stop loss multiple times. Expanding stop loss range can avoid it.
Relying solely on moving averages, it’s hard to respond to sudden events like major news, which may lead to losses.
Note the overfitting problem in parameter optimization. Test period should be long enough to include different market conditions.
Optimization Directions
Optimize moving average parameters to find the best moving average period combination.
Optimize ROC parameters to improve turning point recognition accuracy.
Add stop loss mechanisms such as dynamic stop loss based on breaking customized price levels.
Add additional conditions like volume indicators to avoid false breakouts.
Incorporate other indicators like MACD, BOLL to improve decision making.
Use machine learning etc. to auto optimize parameters and adapt to market changes.
Summary
In summary, the Dual Moving Average Turning Point strategy is a simple and practical trend following strategy. It can be implemented with basic moving average indicators and has clear, easy-to-understand logic, making it very suitable for quant trading beginners to learn and practice. With parameter optimization and stop loss optimization, the strategy stability can be greatly improved. Combining with other auxiliary indicators can further enhance the strategy. The highly customizable strategy can be flexibly applied to different market environments and is a recommended dual moving average trading strategy.
[/trans]
/*backtest
start: 2023-09-23 00:00:00
end: 2023-10-23 00:00:00
period: 2h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=3
strategy("MA Turning Point Strategy", overlay=true)
src = input(close, title="Source")
price = request.security(syminfo.tickerid, timeframe.period, src)
ma1 = input(25, title="1st MA Length")
type1 = input("HMA", "1st MA Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "HMA", "VWMA"])
f_hma(_src, _length)=>
_return = wma((2*wma(_src, _length/2))-wma(_src, _length), round(sqrt(_length)))
price1 = if (type1 == "SMA")
sma(price, ma1)
else
if (type1 == "EMA")
ema(price, ma1)
else
if (type1 == "VWMA")
vwma(price, ma1)
else
f_hma(price, ma1)
plot(series=price1, style=line, title="1st MA", color=blue, linewidth=2, transp=0)
lookback1 = input(1, "Lookback 1")
roc1 = roc(price1, lookback1)
ma1up = false
ma1down = false
ma2up = false
ma2down = false
ma1up := nz(ma1up[1])
ma1down := nz(ma1down[1])
ma2up := nz(ma2up[1])
ma2down := nz(ma2down[1])
trendStrength1 = input(2.5, title="Minimum slope magnitude * 100", type=float) * 0.01
if crossover(roc1, trendStrength1)
ma1up := true
ma1down := false
if crossunder(roc1, -trendStrength1)
ma1up := false
ma1down := true
longCondition = ma1up and ma1down[1]
if (longCondition)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
shortCondition = ma1down and ma1up[1]
if (shortCondition)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)