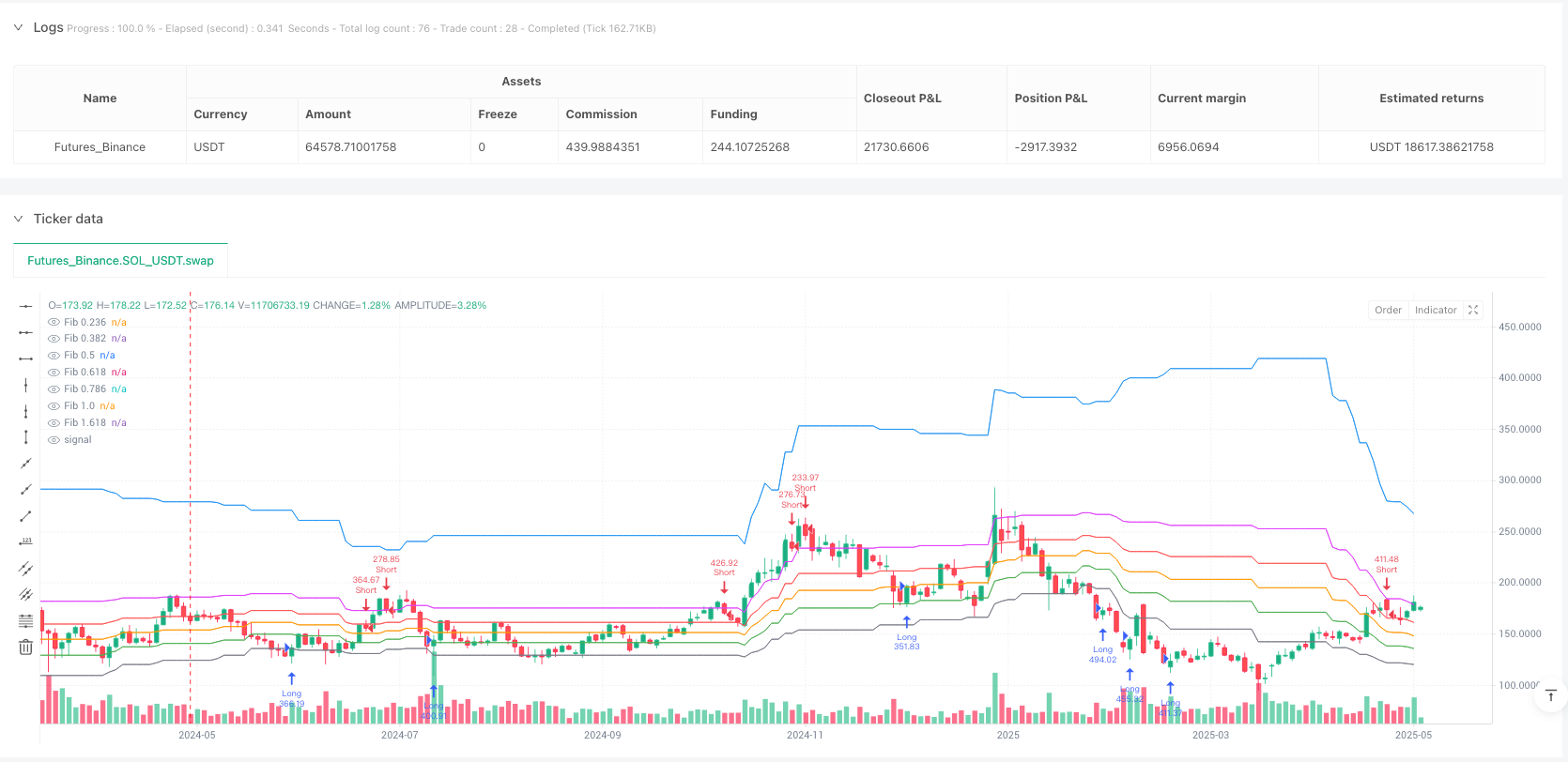
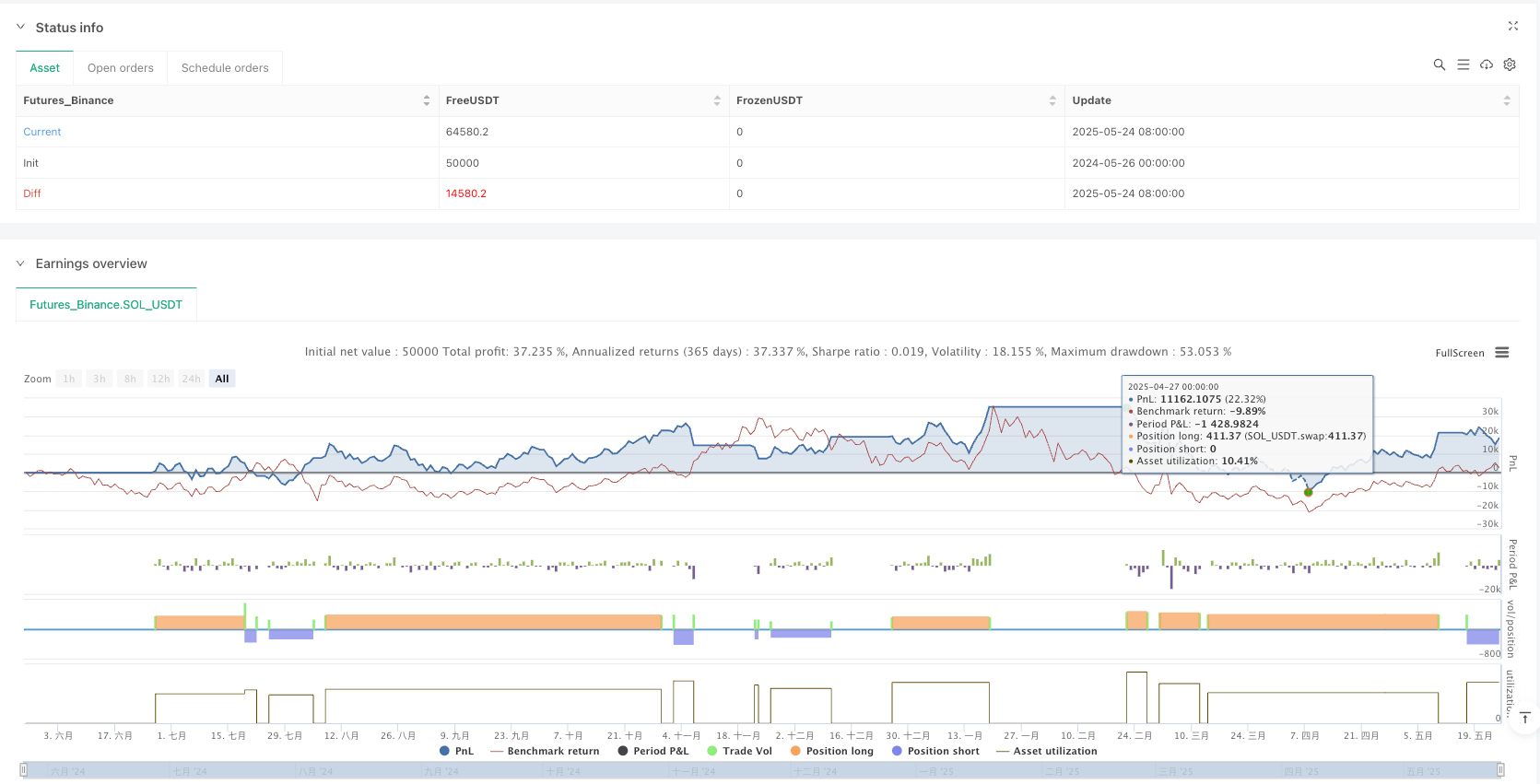
[tran]
جائزہ
ایک کثیر درجے کا فبونیکی رجحان ٹریکنگ اور ہیجنگ ٹریڈنگ اسٹریٹجی سسٹم ایک جامع مقداری تجارتی حکمت عملی ہے جس میں متعدد تکنیکی تجزیہ اشارے شامل ہیں۔ اس حکمت عملی میں فبونیکی ریٹریکشن تھیوری کو مرکزی حیثیت دی گئی ہے ، جس میں متعدد تکنیکی اشارے جیسے انڈیکس منتقل اوسط ((EMA) ، اوسط حقیقی طول و عرض ((ATR) ، اوسط رجحان اشارے ((ADX) ، اور دشاتمک متحرک اشارے ((DMI) شامل ہیں۔ مارکیٹ تجزیہ کا ایک کثیر جہتی فریم ورک تشکیل دیا گیا ہے۔ حکمت عملی میں نہ صرف روایتی رجحان سے باخبر رہنے کی صلاحیتیں ہیں ، بلکہ اس میں باؤنس ٹریڈنگ میکانزم اور شیلنگ کی خصوصیات بھی شامل ہیں ، جس کا مقصد منافع کے مواقع کو پکڑنا اور مختلف مارکیٹوں میں خطرے کو مؤثر طریقے سے کنٹرول کرنا ہے۔
اس حکمت عملی کی خاصیت اس کے کثیر درجے کے خطرے کے انتظام کے نظام اور لچکدار ٹریڈنگ ماڈل میں ہے۔ ایک سے زیادہ اسٹاپ ٹارگٹ (TP1 اور TP2) اور اے ٹی آر پر مبنی متحرک اسٹاپ نقصان کے طریقہ کار کو ترتیب دے کر ، حکمت عملی منافع کی صلاحیت کو زیادہ سے زیادہ کرنے کے قابل بناتی ہے جبکہ سرمایہ کی حفاظت کرتی ہے۔ اس کے علاوہ ، اس میں شامل ہیجنگ فنکشن حکمت عملی میں اضافی رسک بیئرنگ کا اضافہ کرتا ہے ، جس کی وجہ سے یہ مارکیٹ کے زیادہ اتار چڑھاؤ والے ماحول میں بھی نسبتا stable مستحکم کارکردگی کا مظاہرہ کرسکتا ہے۔
حکمت عملی کا اصول
حکمت عملی کا بنیادی منطق فبونیکی ریٹریس تھیوری اور رجحان تجزیہ کے امتزاج پر مبنی ہے۔ سب سے پہلے ، حکمت عملی فبونیکی ریٹریس کی سطح کا تعین کرتی ہے جس میں 23.6٪ ، 38.2٪ ، 50٪ ، 61.8٪ ، 78.6٪ ، 100٪ اور 161.8٪ جیسے اہم مقامات شامل ہیں۔ یہ سطحیں اہم حمایت اور مزاحمت کی سطح کے طور پر استعمال کی جاتی ہیں ، جو تجارتی سگنل کی تخلیق کے لئے ایک اہم حوالہ فراہم کرتی ہیں۔
رجحانات کی نشاندہی کرنے کے لئے ، حکمت عملی 50 مدت کی اشاریہ کی حرکت پذیری اوسط کو رجحانات کا تعین کرنے کے لئے ایک اہم ٹول کے طور پر استعمال کرتی ہے۔ جب قیمت کی تینوں K لائنیں ای ایم اے کے اوپر ہوتی ہیں تو ، اس کو اوپر کی طرف رجحان سمجھا جاتا ہے۔ اس کے برعکس ، یہ ایک نیچے کی طرف رجحان ہے۔ اس کے علاوہ ، حکمت عملی قیمت کی ساخت کا تجزیہ کرتی ہے ، جس میں ایک سے زیادہ ڈوبنے والی ساخت کی نشاندہی کی جاتی ہے جس میں ایک سے زیادہ اونچائی اور ایک سے زیادہ اونچائی کی نشاندہی کی جاتی ہے ، جس میں ایک سے زیادہ اونچائی اور ایک سے کم اونچائی کی نشاندہی کی جاتی ہے۔
ADX اور DMI کے اشارے متعارف کرانے سے رجحان کی طاقت کا تعین کرنے کی درستگی میں اضافہ ہوا ہے۔ 20 سے زیادہ ADX اقدار کو مضبوط رجحان کا معیار سمجھا جاتا ہے ، جبکہ + DI اور -DI کی نسبتا weak کمزوری کو رجحان کی سمت کا تعین کرنے کے لئے استعمال کیا جاتا ہے۔ حجم تجزیہ بھی حکمت عملی کا ایک اہم جزو ہے۔ جب حجم 20 مدت کی اوسط سے 1.2 گنا سے زیادہ ہوتا ہے تو ، اسے موثر مقدار کی تصدیق کے طور پر سمجھا جاتا ہے۔
ٹریڈنگ سگنل کی تخلیق کو متعدد شرائط کو پورا کرنے کی ضرورت ہوتی ہے: رجحان کی سمت واضح ہے ، قیمت اہم فبونیکی سطح کے قریب ہے ، رجحان کی طاقت کافی ہے ، دشاتمک اشارے کی تصدیق اور حجم میں اضافہ ہوا ہے۔ اس کثیر فلٹرنگ میکانزم سے سگنل کی وشوسنییتا میں بہتری آتی ہے اور جھوٹے سگنل کا امکان کم ہوجاتا ہے۔
اسٹریٹجک فوائد
اس حکمت عملی میں متعدد نمایاں فوائد ہیں ، سب سے پہلے اس کی جامع تکنیکی تجزیہ کے فریم ورک میں۔ فبونیکی نظریہ ، رجحانات کا تجزیہ ، متحرک اشارے اور حجم تجزیہ کو مربوط کرکے ، حکمت عملی مارکیٹ کی صورتحال کا متعدد جہتوں سے جائزہ لینے کے قابل ہے ، جس سے زیادہ جامع اور درست تجارتی سگنل فراہم کیے جاسکتے ہیں۔ اس طرح کے متعدد اشارے کے امتزاج کا یہ طریقہ مؤثر طریقے سے گمراہ کن سگنل کو کم کرتا ہے جو ایک ہی اشارے سے پیدا ہوسکتا ہے ، اور مجموعی حکمت عملی کی استحکام اور وشوسنییتا کو بڑھاتا ہے۔
حکمت عملی کا خطرہ مینجمنٹ سسٹم اس کا ایک اور بڑا فائدہ ہے۔ ڈبل اسٹاپ میکانزم تاجر کو پہلے ہدف تک پہنچنے پر کچھ منافع کو لاک کرنے کی اجازت دیتا ہے ، جبکہ باقی پوزیشنوں کو زیادہ سے زیادہ منافع کے حصول کے لئے برقرار رکھتا ہے۔ اے ٹی آر پر مبنی متحرک اسٹاپ نقصان کی ترتیب مارکیٹ میں اتار چڑھاؤ کے مطابق خود بخود خطرے کے کنٹرول کی سطح کو ایڈجسٹ کرنے کی صلاحیت رکھتی ہے ، جو منافع کی حفاظت کے لئے کم اتار چڑھاؤ کے دوران اسٹاپ نقصان کو سخت کرتی ہے اور عام اتار چڑھاؤ سے بچنے کے لئے اعلی اتار چڑھاؤ کے دوران اسٹاپ نقصان کو کم کرتی ہے۔
باؤنس ٹریڈنگ کی خصوصیت حکمت عملی کے لئے اضافی منافع کے مواقع میں اضافہ کرتی ہے۔ جب قیمتوں میں اہم حمایت یا مزاحمت کی سطح پر باؤنس ہوتا ہے تو ، حکمت عملی تیزی سے شناخت کرسکتی ہے اور اس قلیل مدتی الٹ رویے میں حصہ لے سکتی ہے ، اور اس طرح رجحان کی تجارت کی بنیاد پر تجارت کے مزید مواقع پیدا کرتی ہے۔ اس لچک کی وجہ سے حکمت عملی مختلف مارکیٹ کے حالات کے مطابق ڈھال سکتی ہے ، چاہے وہ مضبوط رجحان کی منڈی ہو یا زون کے زلزلے کی منڈی میں مناسب تجارتی مواقع تلاش کریں۔
ہیجنگ فنکشن کی انٹیگریشن اس حکمت عملی کی ایک جدید خصوصیت ہے۔ جب ایک سے زیادہ پوزیشنیں ہوتی ہیں تو ، حکمت عملی کو کھول دیا جاتا ہے اگر خالی سر کا اشارہ ہوتا ہے۔ اور اس کے برعکس۔ یہ میکانزم مارکیٹ میں تیزی سے الٹ جانے پر اضافی تحفظ فراہم کرنے ، ممکنہ نقصان کو کم کرنے اور ممکنہ طور پر نئے منافع کے مواقع میں تبدیل کرنے کے قابل ہے۔
ٹائم فلٹرز کی ترتیب سے زیادہ تجارت کے مسائل کو روکا جاتا ہے۔ اس حکمت عملی نے کم سے کم 5 K لائنوں کو مسلسل سگنل کے درمیان وقفے کی ضرورت سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے سے بچنے اور سگنل کی کیفیت کو بہتر بنانے کے لۓ.
اسٹریٹجک رسک
اگرچہ اس حکمت عملی کے بہت سارے فوائد ہیں ، لیکن اس میں کچھ خطرات بھی ہیں جن پر توجہ دینے کی ضرورت ہے۔ سب سے پہلے ، پیرامیٹر پر انحصار کا خطرہ ہے۔ حکمت عملی میں متعدد پیرامیٹرز کی ترتیبات شامل ہیں ، بشمول فبونیکی دورانیہ ، رواداری ، اے ٹی آر ضرب ، وغیرہ۔ ان پیرامیٹرز کا انتخاب حکمت عملی کی کارکردگی پر اہم اثر ڈالتا ہے۔ پیرامیٹرز کی غلط ترتیب سے تاریخی اعداد و شمار کو زیادہ سے زیادہ فٹ ہونے یا حقیقی مارکیٹ میں خراب کارکردگی کا سبب بن سکتا ہے۔ لہذا ، مناسب مارکیٹ اور وقت کے فریم کے لئے بہترین پیرامیٹرز کا مجموعہ تلاش کرنے کے لئے کافی بیک اپ اور پیرامیٹرز کی اصلاح کی ضرورت ہے۔
مارکیٹ کے ماحول کی موافقت ایک اور ممکنہ خطرہ ہے۔ حکمت عملی بنیادی طور پر تکنیکی تجزیہ پر مبنی ہوتی ہے ، جو بعض مارکیٹ کے حالات میں خراب کارکردگی کا مظاہرہ کرسکتی ہے ، جیسے کہ بنیادی طور پر چلنے والے ایک طرفہ سخت حالات میں ، تکنیکی اشارے ناکام ہوسکتے ہیں۔ اس کے علاوہ ، انتہائی کم اتار چڑھاؤ یا انتہائی اتار چڑھاؤ والے مارکیٹ کے ماحول میں حکمت عملی کی سگنل جنریشن کی تعدد اور درستگی دونوں متاثر ہوسکتی ہیں۔
اسکیلپنگ اور عملدرآمد کے خطرات کو بھی مدنظر رکھنا چاہئے۔ اصل تجارت میں ، خاص طور پر زیادہ اتار چڑھاؤ والی مارکیٹ کے حالات میں ، آرڈر کی عملدرآمد کی قیمت اور متوقع قیمت کے مابین فرق ہوسکتا ہے۔ اسکیلپنگ کی یہ قیمت حکمت عملی کے نظریاتی منافع کو ختم کرسکتی ہے ، خاص طور پر اس حکمت عملی کے لئے جو کثرت سے تجارت کرتی ہے۔
اگرچہ ہیجنگ کی خصوصیت اضافی تحفظ فراہم کرتی ہے ، لیکن اس سے حکمت عملی کی پیچیدگی میں اضافہ ہوتا ہے۔ کچھ معاملات میں ، ہیجنگ کے آپریشن سے ایک ہی وقت میں زیادہ کھلی پوزیشنوں کو نقصان پہنچ سکتا ہے ، یا فیسوں کے معاملے میں اضافی لاگت آسکتی ہے۔ لہذا ، ہیجنگ کی خصوصیت کی اصل تاثیر کا محتاط اندازہ لگانے کی ضرورت ہے ، اور اس پر غور کرنے کی ضرورت ہے کہ آیا اس خصوصیت کو مخصوص مارکیٹ کے حالات میں چالو کیا جائے۔
حکمت عملی کی اصلاح کی سمت
حکمت عملی کی کارکردگی کو مزید بڑھانے کے ل several ، اس کو متعدد سمتوں سے بہتر بنایا جاسکتا ہے۔ پہلا ، متحرک پیرامیٹر ایڈجسٹمنٹ میکانزم کا تعارف۔ اہم پیرامیٹرز جیسے فبونیکی چکر ، اے ٹی آر ضرب ، مارکیٹ میں اتار چڑھاؤ ، رجحان کی طاقت اور اسی طرح کے عوامل کے مطابق متحرک طور پر ایڈجسٹ کیا جاسکتا ہے۔ مثال کے طور پر ، اعلی اتار چڑھاؤ والے بازاروں میں اے ٹی آر ضرب کو بڑھانا تاکہ زیادہ سے زیادہ نقصان کی گنجائش فراہم کی جاسکے ، اور کم اتار چڑھاؤ والے بازاروں میں اے ٹی آر ضرب کو کم کرنا تاکہ خطرے پر قابو پانا مشکل ہوجائے۔
مشین لرننگ ٹکنالوجی کا انضمام ایک اور اہم اصلاحی سمت ہے۔ مشین لرننگ الگورتھم کا استعمال بہترین انٹری ٹائمنگ کی شناخت کے لئے کیا جاسکتا ہے ، یا تاریخی اعداد و شمار کے سیکھنے والے پیرامیٹرز کے مجموعے پر مبنی بہترین ترتیب۔ اس کے علاوہ ، مارکیٹ کے جذبات اور خبروں کے واقعات کے اثر کو قیمتوں پر تجزیہ کرنے کے لئے قدرتی زبان کی پروسیسنگ ٹکنالوجی کا استعمال کیا جاسکتا ہے ، تاکہ حکمت عملی میں بنیادی تجزیہ کی جہت کو شامل کیا جاسکے۔
ملٹی ٹائم فریم تجزیہ کا انضمام مارکیٹ کا ایک جامع نقطہ نظر فراہم کرسکتا ہے۔ بڑے رجحانات کی سمت کو طویل ٹائم فریم پر تسلیم کیا جاسکتا ہے ، اور مختصر ٹائم فریم پر عین مطابق داخلے کے مقامات کی تلاش کی جاسکتی ہے۔ اس طرح کے ملٹی ٹائم فریم کے ہم آہنگ تجزیے سے سگنل کے معیار کو بہتر بنایا جاسکتا ہے اور اس کے برعکس تجارت کا خطرہ کم ہوسکتا ہے۔
فنڈ مینجمنٹ کو بہتر بنانا حکمت عملی کی کارکردگی کو بہتر بنانے کا ایک اہم طریقہ ہے۔ مارکیٹ کے حالات ، حکمت عملی کے اعتماد اور دیگر عوامل کے مطابق پوزیشن کا سائز متحرک طور پر ایڈجسٹ کیا جاسکتا ہے۔ مثال کے طور پر ، اعلی اعتماد کے اشارے پر پوزیشن میں اضافہ ، کم اعتماد کے اشارے پر پوزیشن میں کمی۔ اس کے علاوہ ، زیادہ سے زیادہ واپسی کنٹرول کا طریقہ کار متعارف کرایا جاسکتا ہے ، جب حکمت عملی میں زیادہ نقصان ہوتا ہے تو پوزیشن کو خود بخود کم کیا جاسکتا ہے یا تجارت کو روک دیا جاسکتا ہے۔
اسٹاپ نقصان کی روک تھام کی منطق کو مزید بہتر بنانے کے بارے میں بھی غور کیا جاسکتا ہے۔ اس میں ٹریکنگ اسٹاپ میکانزم متعارف کرایا جاسکتا ہے ، جس میں زیادہ منافع کو مقفل کرنے کے لئے قیمت کی نقل و حرکت کے مطابق اسٹاپ نقصان کی پوزیشن کو ایڈجسٹ کیا جاسکتا ہے۔ اس کے ساتھ ہی ، مارکیٹ کی ساخت کی خصوصیات کے مطابق زیادہ ذہین اسٹاپ ہدف طے کیا جاسکتا ہے ، جیسے کہ اہم مزاحمت کی سطح کے قریب اسٹاپ کو آگے بڑھانا۔
خلاصہ کریں۔
ایک کثیر پرت فیبونیکی رجحان ٹریکنگ اور ہیجنگ ٹریڈنگ اسٹریٹجی سسٹم جدید کوانٹم ٹریڈنگ ٹکنالوجی کی ایک اہم ترقی کی نمائندگی کرتا ہے۔ اس حکمت عملی نے متعدد کلاسیکی تکنیکی تجزیہ ٹولز کو ہوشیار طریقے سے مربوط کرکے ایک مضبوط اور لچکدار تجارتی فریم ورک تشکیل دیا ہے۔ اس کی کثیر فلٹرنگ میکانزم سگنل کے معیار کو یقینی بناتی ہے ، کثیر پرت والے رسک مینجمنٹ سسٹم مؤثر سرمایہ تحفظ فراہم کرتا ہے ، جبکہ ہیجنگ کی خصوصیت حکمت عملی میں اضافی حفاظتی مارجن شامل کرتی ہے۔
حکمت عملی کے کامیاب نفاذ کے لئے اس کے بنیادی اصولوں اور کام کرنے کے طریقہ کار کی مکمل تفہیم کی ضرورت ہوتی ہے ، اور مخصوص تجارتی ماحول کے مطابق مناسب پیرامیٹرز کو ایڈجسٹ اور بہتر بنایا جاتا ہے۔ اگرچہ یہ حکمت عملی نظریاتی طور پر اچھی طرح سے ڈیزائن کی گئی ہے ، لیکن عملی استعمال میں مارکیٹ کے مائیکرو ڈھانچے ، تجارتی اخراجات ، اور اسکیلپنگ جیسے حقیقی عوامل کے اثرات کو مدنظر رکھنا ضروری ہے۔
مصنوعی ذہانت اور مشین لرننگ ٹکنالوجی کی مسلسل ترقی کے ساتھ ، اس حکمت عملی میں بہت زیادہ اصلاح کی گنجائش موجود ہے۔ اس حکمت عملی کی کارکردگی کو مزید بہتر بنانے کے لئے اعداد و شمار کے تجزیہ کی جدید ترین ٹکنالوجیوں اور موافقت کے طریقہ کار کو متعارف کرانے کی توقع کی جارہی ہے۔ اس طرح کی جامع حکمت عملی ایک قیمتی سیکھنے اور بہتری کا پلیٹ فارم مہیا کرتی ہے ، جس سے مارکیٹ کی حرکیات اور خطرے کے انتظام کی اہمیت کو گہرائی سے سمجھنے میں مدد ملتی ہے۔ ||
Overview
The Multi-Level Fibonacci Trend Following and Hedging Trading Strategy System is a comprehensive quantitative trading strategy that integrates multiple technical analysis indicators. This strategy centers on Fibonacci retracement theory, combining Exponential Moving Average (EMA), Average True Range (ATR), Average Directional Index (ADX), and Directional Movement Indicator (DMI) to construct a multi-dimensional market analysis framework. The strategy not only features traditional trend-following capabilities but also integrates bounce trading mechanisms and hedging functionality, aiming to capture profitable opportunities under different market conditions while effectively controlling risk.
The unique aspect of this strategy lies in its multi-layered risk management system and flexible trading modes. By setting multiple take-profit targets (TP1 and TP2) and dynamic stop-loss mechanisms based on ATR, the strategy can maximize profit potential while protecting capital. Additionally, the built-in hedging function adds an extra risk buffer to the strategy, enabling it to maintain relatively stable performance even in highly volatile market environments.
Strategy Principles
The core logic of the strategy is based on the combination of Fibonacci retracement theory and trend analysis. First, the strategy calculates the highest and lowest points within a specified period to determine Fibonacci retracement levels, including key positions at 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, 78.6%, 100%, and 161.8%. These levels serve as important support and resistance zones, providing crucial references for trading signal generation.
For trend identification, the strategy employs a 50-period Exponential Moving Average as the primary trend determination tool. When prices remain above the EMA for three consecutive candlesticks, it’s identified as an uptrend; conversely, it’s considered a downtrend. Simultaneously, the strategy analyzes price structure by identifying higher lows and higher highs to confirm bullish structure, and lower highs and lower lows to confirm bearish structure.
The introduction of ADX and DMI indicators enhances the precision of trend strength assessment. An ADX value greater than 20 is considered the standard for a strong trend, while the relative strength of +DI and -DI is used to determine trend direction. Volume analysis is also an important component of the strategy, where volume exceeding 1.2 times the 20-period average is considered effective volume confirmation.
Trade signal generation requires multiple conditions to be met simultaneously: clear trend direction, price proximity to key Fibonacci levels, sufficient trend strength, directional indicator confirmation, and volume expansion. This multi-filter mechanism significantly improves signal reliability and reduces the probability of false signals.
Strategy Advantages
This strategy possesses multiple significant advantages, first manifested in its comprehensive technical analysis framework. By integrating Fibonacci theory, trend analysis, momentum indicators, and volume analysis, the strategy can evaluate market conditions from multiple dimensions, providing more comprehensive and accurate trading signals. This multi-indicator fusion approach effectively reduces misleading signals that might be generated by single indicators, improving the overall stability and reliability of the strategy.
The strategy’s risk management system represents another major advantage. The dual take-profit mechanism allows traders to lock in partial profits upon reaching the first target while maintaining remaining positions to pursue greater returns. ATR-based dynamic stop-loss settings can automatically adjust risk control levels according to market volatility, tightening stops during low volatility to protect profits and relaxing stops during high volatility to avoid being stopped out by normal fluctuations.
The bounce trading functionality adds additional profit opportunities to the strategy. When prices bounce at key support or resistance levels, the strategy can quickly identify and participate in such short-term reversal movements, thereby adding more trading opportunities beyond trend trading. This flexibility enables the strategy to adapt to different market conditions, finding suitable trading opportunities whether in strong trending markets or range-bound markets.
The integration of hedging functionality is an innovative feature of this strategy. When holding long positions and a short signal appears, the strategy will open a hedge short position; vice versa. This mechanism can provide additional protection during rapid market reversals, reducing potential losses and possibly converting them into new profit opportunities.
The time filter setting prevents overtrading issues. By requiring at least 5 candlesticks between consecutive signals, the strategy avoids frequent position opening within short periods, reducing trading costs and improving signal quality.
Strategy Risks
Despite the strategy’s multiple advantages, several risk factors require attention. First is parameter dependency risk. The strategy involves multiple parameter settings, including Fibonacci period, tolerance, ATR multipliers, etc. The selection of these parameters significantly impacts strategy performance. Inappropriate parameter settings may lead to overfitting historical data or poor performance in actual markets. Therefore, sufficient backtesting and parameter optimization are needed to find the most suitable parameter combinations for specific markets and timeframes.
Market environment adaptability represents another potential risk. The strategy is primarily based on technical analysis and may underperform in certain market conditions, such as during fundamental-driven strong unidirectional moves where technical indicators might fail. Additionally, in extremely low or high volatility market environments, both signal generation frequency and accuracy may be affected.
Slippage and execution risks also need consideration. In actual trading, particularly during high volatility market conditions, there may be differences between order execution prices and expected prices. This slippage cost could erode the strategy’s theoretical returns, especially for frequently trading strategies.
While the hedging function provides additional protection, it also increases strategy complexity. In certain situations, hedging operations might result in simultaneous losses on both long and short positions, or generate additional costs in terms of commissions. Therefore, careful evaluation of the hedging function’s actual effectiveness is needed, along with consideration of whether to enable this function under specific market conditions.
Strategy Optimization Directions
To further enhance strategy performance, optimization can be pursued in multiple directions. First is the introduction of dynamic parameter adjustment mechanisms. Key parameters such as Fibonacci period and ATR multipliers can be dynamically adjusted based on market volatility, trend strength, and other factors. For example, increasing ATR multipliers in high volatility markets to provide larger stop-loss space, and decreasing ATR multipliers in low volatility markets to tighten risk control.
Integration of machine learning technology represents another important optimization direction. Machine learning algorithms can be used to identify optimal entry timing or learn optimal parameter combination configurations based on historical data. Additionally, natural language processing technology can be utilized to analyze market sentiment and news event impacts on prices, adding fundamental analysis dimensions to the strategy.
Integration of multi-timeframe analysis can provide a more comprehensive market perspective. Larger timeframes can be used to confirm major trend direction, while shorter timeframes can be used to find precise entry points. This coordinated multi-timeframe analysis can improve signal quality and reduce counter-trend trading risks.
Money management optimization is also an important avenue for enhancing strategy performance. Position sizes can be dynamically adjusted based on market conditions, strategy confidence levels, and other factors. For example, increasing positions during high-confidence signals and reducing positions during low-confidence signals. Additionally, maximum drawdown control mechanisms can be introduced to automatically reduce positions or pause trading when the strategy experiences significant losses.
Further refinement of take-profit and stop-loss logic is also worth considering. Trailing stop mechanisms can be introduced to dynamically adjust stop-loss positions based on price movements to lock in more profits. Simultaneously, more intelligent take-profit targets can be set based on market structure characteristics, such as taking profits early near key resistance levels.
Conclusion
The Multi-Level Fibonacci Trend Following and Hedging Trading Strategy System represents an important development direction in modern quantitative trading technology. This strategy cleverly integrates multiple classic technical analysis tools to construct a trading framework that is both robust and flexible. Its multi-filter mechanism ensures signal quality, the multi-layered risk management system provides effective capital protection, and the hedging function adds an additional safety margin to the strategy.
Successful implementation of this strategy requires thorough understanding of its fundamental principles and operational mechanisms, along with appropriate parameter adjustments and optimizations based on specific trading environments. While the strategy has excellent theoretical design, practical application still requires consideration of real-world factors such as market microstructure, trading costs, and slippage.
With the continuous development of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, this strategy still has enormous optimization potential. Through the introduction of more advanced data analysis techniques and adaptive mechanisms, strategy performance is expected to be further enhanced. For quantitative traders, such comprehensive strategies provide a valuable learning and improvement platform, helping to deepen understanding of market dynamics and the importance of risk management.[/trans]
/*backtest
start: 2024-05-26 00:00:00
end: 2025-05-25 00:00:00
period: 2d
basePeriod: 2d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"SOL_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("Fibonacci Trend v6.4 - TP/SL Labels", overlay=true, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value=100)
// === Parameters ===
fibLen = input.int(50, "Fibonacci Range")
fibTol = input.float(0.01, "Fib Proximity Tolerance (%)", step=0.001)
slMult = input.float(1.5, "SL - ATR", step=0.1)
tp2Mult = input.float(2.0, "TP2 - ATR", step=0.1)
srLookback = input.int(20, "Support/Resistance Lookback Bars")
useBounce = input.bool(true, "Enable Bounce Entry")
// === Indicators ===
ema50 = ta.ema(close, 50)
atr = ta.atr(14)
volAvg = ta.sma(volume, 20)
volHigh = volume > volAvg * 1.2
// === Fibonacci Levels ===
lowWick = ta.lowest(low, fibLen)
highWick = ta.highest(high, fibLen)
rangeWick = highWick - lowWick
fib236 = lowWick + 0.236 * rangeWick
fib382 = lowWick + 0.382 * rangeWick
fib5 = lowWick + 0.5 * rangeWick
fib618 = lowWick + 0.618 * rangeWick
fib786 = lowWick + 0.786 * rangeWick
fib1 = highWick
fib1618 = lowWick + 1.618 * rangeWick
nearSupport = math.abs(low - fib382)/close < fibTol or math.abs(low - fib5)/close < fibTol
nearResist = math.abs(high - fib618)/close < fibTol
// === Trend Structure ===
higherLow = low > low[1] and low[1] > low[2]
higherHigh = high > high[1]
lowerHigh = high < high[1] and high[1] < high[2]
lowerLow = low < low[1]
longStruct = higherLow and higherHigh
shortStruct = lowerHigh and lowerLow
// === ADX / DMI ===
dmiLen = 14
upMove = high - high[1]
downMove = low[1] - low
plusDM = (upMove > downMove and upMove > 0) ? upMove : 0
minusDM = (downMove > upMove and downMove > 0) ? downMove : 0
tr = ta.tr(true)
tr14 = ta.rma(tr, dmiLen)
plusDI = 100 * ta.rma(plusDM, dmiLen) / tr14
minusDI = 100 * ta.rma(minusDM, dmiLen) / tr14
dx = 100 * math.abs(plusDI - minusDI) / (plusDI + minusDI)
adx = ta.rma(dx, dmiLen)
trendStrong = adx > 20
// === EMA Momentum Break ===
emaBreakLong = close > ema50 and close[1] < ema50 and volume > volAvg
emaBreakShort = close < ema50 and close[1] > ema50 and volume > volAvg
// === Time Filter ===
var int lastLongBar = na
var int lastShortBar = na
canLong = na(lastLongBar) or (bar_index - lastLongBar > 5)
canShort = na(lastShortBar) or (bar_index - lastShortBar > 5)
priceAboveEMA = close > ema50 and close[1] > ema50 and close[2] > ema50
priceBelowEMA = close < ema50 and close[1] < ema50 and close[2] < ema50
// === Support / Resistance ===
support = ta.lowest(low, srLookback)
resist = ta.highest(high, srLookback)
// === Entry Conditions ===
longTrend = priceAboveEMA and nearSupport and trendStrong and plusDI > minusDI and longStruct and (volHigh or emaBreakLong) and canLong
shortTrend = priceBelowEMA and nearResist and trendStrong and minusDI > plusDI and shortStruct and (volHigh or emaBreakShort) and canShort
bounceLong = useBounce and math.abs(low - support)/close < fibTol and close > open and close > close[1]
bounceShort = useBounce and math.abs(high - resist)/close < fibTol and close < open and close < close[1]
longSignal = longTrend or bounceLong
shortSignal = shortTrend or bounceShort
// === TP/SL Calculations ===
tp1Long = resist
tp2Long = close + atr * tp2Mult
slLong = close - atr * slMult
tp1Short = support
tp2Short = close - atr * tp2Mult
slShort = close + atr * slMult
tp1ColorLong = bounceLong ? color.blue : color.yellow
tp1ColorShort = bounceShort ? color.blue : color.yellow
// === Long Entry ===
if (longSignal and strategy.position_size <= 0)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
strategy.exit("TP1", from_entry="Long", limit=tp1Long, stop=slLong, qty_percent=50)
strategy.exit("TP2", from_entry="Long", limit=tp2Long, stop=slLong)
lastLongBar := bar_index
label.new(bar_index, close, text="ENTRY: " + str.tostring(close, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=color.green, textcolor=color.white)
label.new(bar_index, tp1Long, text="TP1: " + str.tostring(tp1Long, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=tp1ColorLong)
label.new(bar_index, tp2Long, text="TP2: " + str.tostring(tp2Long, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=color.green)
label.new(bar_index, slLong, text="SL: " + str.tostring(slLong, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=color.red)
// === Short Entry ===
if (shortSignal and strategy.position_size >= 0)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
strategy.exit("TP1", from_entry="Short", limit=tp1Short, stop=slShort, qty_percent=50)
strategy.exit("TP2", from_entry="Short", limit=tp2Short, stop=slShort)
lastShortBar := bar_index
label.new(bar_index, close, text="ENTRY: " + str.tostring(close, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=color.red, textcolor=color.white)
label.new(bar_index, tp1Short, text="TP1: " + str.tostring(tp1Short, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=tp1ColorShort)
label.new(bar_index, tp2Short, text="TP2: " + str.tostring(tp2Short, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=color.green)
label.new(bar_index, slShort, text="SL: " + str.tostring(slShort, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=color.red)
// === Hedge Orders ===
if (strategy.position_size > 0 and shortSignal)
strategy.entry("HedgeShort", strategy.short)
if (strategy.position_size < 0 and longSignal)
strategy.entry("HedgeLong", strategy.long)
// === Fibonacci Plotting ===
plot(fib236, "Fib 0.236", color=color.gray)
plot(fib382, "Fib 0.382", color=color.green)
plot(fib5, "Fib 0.5", color=color.orange)
plot(fib618, "Fib 0.618", color=color.red)
plot(fib786, "Fib 0.786", color=color.fuchsia)
plot(fib1, "Fib 1.0", color=color.white)
plot(fib1618, "Fib 1.618", color=color.blue)