Chiến lược đảo ngược giá trị trung bình dựa trên ATR
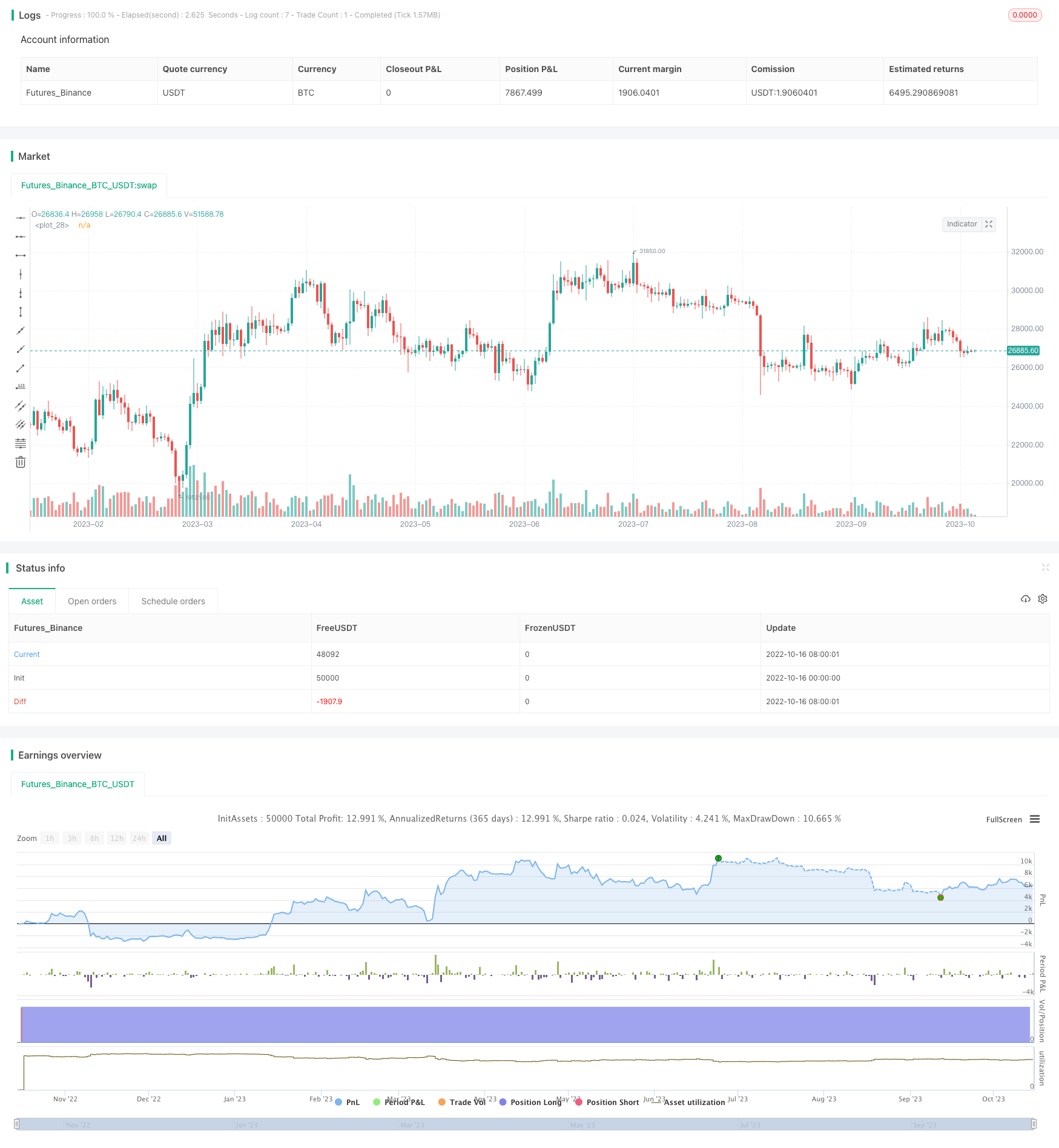
Tổng quan
Chiến lược này sử dụng phương pháp kiểm tra giả định để xác định xem ATR có sai lệch so với giá trị trung bình hay không, kết hợp với dự đoán về biến động giá, thực hiện một chiến lược giao dịch trả lại giá trị trung bình dựa trên ATR. Khi ATR bị sai lệch rõ rệt, cho thấy thị trường có thể có biến động bất thường.
Nguyên tắc chiến lược
Kiểm tra giả định
Chu kỳ ATR nhanh (( tham sốatr_fast) và chu kỳ ATR chậm (( tham sốatr_slow) thực hiện hai mẫu t kiểm tra. Giả sử kiểm tra giả định 0 H0 là trung bình của hai mẫu không có sự khác biệt đáng kể.
Nếu số liệu kiểm tra cao hơn ngưỡng ((trong phạm vi tin cậy được xác định bởi tham số reliability_factor), thì giả định ban đầu được từ chối, tức là cho rằng ATR nhanh đã bị lệch rõ ràng khỏi ATR chậm.
Dự báo giá cả
Tính trung bình di chuyển của lợi nhuận đối số được tính như là tỷ lệ trôi dự kiến (drift tham số).
Nếu tỷ lệ trôi dạt tăng lên, thì đó là xu hướng lạc quan.
Nhập và rút lỗ
Khi ATR khác biệt rõ rệt và xu hướng đi lên, hãy tham gia nhiều hơn.
Sau đó, sử dụng tính toán ATR để điều chỉnh liên tục đường dừng.
Phân tích lợi thế
Sử dụng thử nghiệm giả định để xác định ATR bất thường từ khoa học hơn, tham số tự điều chỉnh.
Kết hợp với dự báo xu hướng giá, tránh giao dịch sai chỉ vì ATR sai lệch.
Điều chỉnh liên tục để giảm rủi ro lỗ.
Phân tích rủi ro
Trong khi đó, các nhà đầu tư khác cũng có xu hướng giảm giá.
Có một số người cho rằng đây là một dấu hiệu của xu hướng và có thể là một điểm cao nhất.
Thiết lập tham số không đúng sẽ bỏ lỡ thời điểm giao dịch chính xác hoặc thêm giao dịch không cần thiết.
Lời khuyên tối ưu hóa
Có thể xem xét việc xác nhận đa yếu tố với các chỉ số khác để tránh các giao dịch sai lầm do chỉ số đơn lẻ.
Có thể thử nghiệm các kết hợp khác nhau của tham số ATR để tìm tham số ổn định hơn.
Tăng khả năng đánh giá phá vỡ các ngưỡng giá quan trọng, tránh mua các lỗ hổng giả mạo.
Tóm tắt
Chiến lược này có ý tưởng tổng thể rõ ràng, có thể sử dụng giả định kiểm tra để đánh giá biến động bất thường. Tuy nhiên, ATR không thể đánh giá hoàn toàn xu hướng, cần phải tăng cơ sở đánh giá để tăng độ chính xác. Quy tắc dừng lỗ là đáng tin cậy, nhưng không thể đối phó với sự sụt giảm theo kiểu vách đá. Có thể cải thiện trong tương lai từ điều kiện nhập cảnh, lựa chọn tham số, tối ưu hóa dừng lỗ.
/*backtest
start: 2022-10-16 00:00:00
end: 2023-10-16 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © DojiEmoji
//@version=5
strategy("Mean Reversion (ATR) Strategy v2 [KL] ", overlay=true, pyramiding=1)
var string ENUM_LONG = "Long"
var string GROUP_TEST = "Hypothesis testing"
var string GROUP_TSL = "Stop loss"
var string GROUP_TREND = "Trend prediction"
backtest_timeframe_start = input(defval=timestamp("01 Apr 2000 13:30 +0000"), title="Backtest Start Time")
within_timeframe = true
// TSL: calculate the stop loss price. {
ATR_TSL = ta.atr(input(14, title="Length of ATR for trailing stop loss", group=GROUP_TSL)) * input(2.0, title="ATR Multiplier for trailing stop loss", group=GROUP_TSL)
TSL_source = low
TSL_line_color = color.green
TSL_transp = 100
var stop_loss_price = float(0)
if strategy.position_size == 0 or not within_timeframe
TSL_line_color := color.black
stop_loss_price := TSL_source - ATR_TSL
else if strategy.position_size > 0
stop_loss_price := math.max(stop_loss_price, TSL_source - ATR_TSL)
TSL_transp := 0
plot(stop_loss_price, color=color.new(TSL_line_color, TSL_transp))
// } end of "TSL" block
// Entry variables {
// ATR diversion test via Hypothesis testing (2-tailed):
// H0 : atr_fast equals atr_slow
// Ha : reject H0 if z_stat is above critical value, say reliability factor of 1.96 for a 95% confidence interval
len_fast = input(14,title="Length of ATR (fast) for diversion test", group=GROUP_TEST)
atr_fast = ta.atr(len_fast)
std_error = ta.stdev(ta.tr, len_fast) / math.pow(len_fast, 0.5) // Standard Error (SE) = std / sq root(sample size)
atr_slow = ta.atr(input(28,title="Length of ATR (slow) for diversion test", group=GROUP_TEST))
test_stat = (atr_fast - atr_slow) / std_error
reject_H0 = math.abs(test_stat) > input.float(1.645,title="Reliability factor", tooltip="Strategy uses 2-tailed test; Confidence Interval = Point Estimate (avg ATR) +/- Reliability Factor x Standard Error; i.e use 1.645 for a 90% confidence interval", group=GROUP_TEST)
// main entry signal, subject to confirmation(s), gets passed onto the next bar
var _signal_diverted_ATR = false
if not _signal_diverted_ATR
_signal_diverted_ATR := reject_H0
// confirmation: trend prediction; based on expected lognormal returns
_prcntge_chng = math.log(close / close[1])
// Expected return (drift) = average percentage change + half variance over the lookback period
len_drift = input(14, title="Length of drift", group=GROUP_TREND)
_drift = ta.sma(_prcntge_chng, len_drift) - math.pow(ta.stdev(_prcntge_chng, len_drift), 2) * 0.5
_signal_uptrend = _drift > _drift[1]
entry_signal_all = _signal_diverted_ATR and _signal_uptrend // main signal + confirmations
// } end of "Entry variables" block
// MAIN {
// Update the stop limit if strategy holds a position
if strategy.position_size > 0 and ta.change(stop_loss_price)
strategy.exit(ENUM_LONG, comment="sl", stop=stop_loss_price)
// Entry
if within_timeframe and entry_signal_all
strategy.entry(ENUM_LONG, strategy.long, comment=strategy.position_size > 0 ? "adding" : "initial")
// Alerts
_atr = ta.atr(14)
alert_helper(msg) =>
prefix = "[" + syminfo.root + "] "
suffix = "(P=" + str.tostring(close, "#.##") + "; atr=" + str.tostring(_atr, "#.##") + ")"
alert(str.tostring(prefix) + str.tostring(msg) + str.tostring(suffix), alert.freq_once_per_bar)
if strategy.position_size > 0 and ta.change(strategy.position_size)
if strategy.position_size > strategy.position_size[1]
alert_helper("BUY")
else if strategy.position_size < strategy.position_size[1]
alert_helper("SELL")
// Clean up - set the variables back to default values once no longer in use
if strategy.position_size == 0
stop_loss_price := float(0)
if ta.change(strategy.position_size)
_signal_diverted_ATR := false
// } end of MAIN block