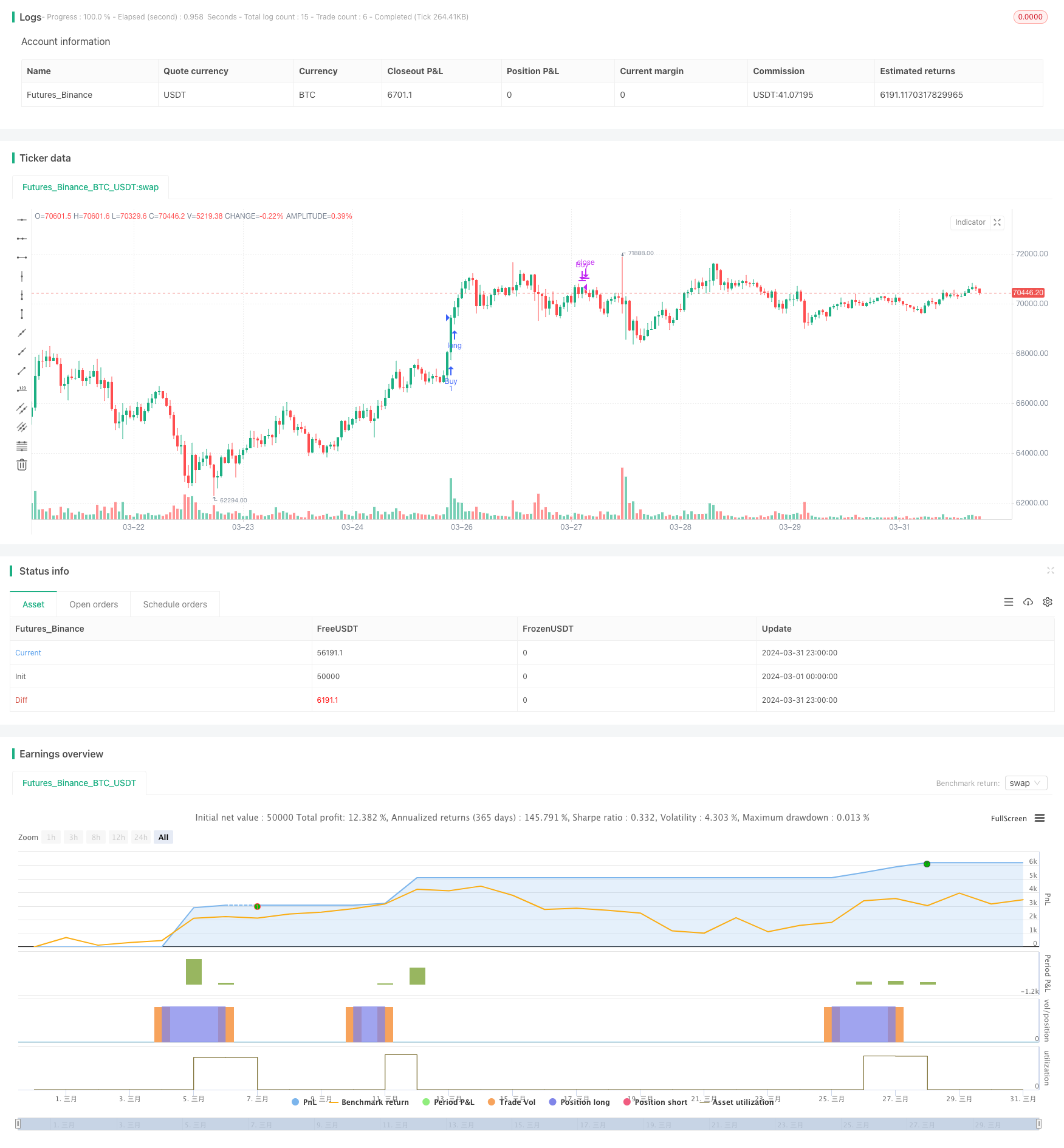
[trans]
Tổng quan
Chiến lược này là một chiến lược giao dịch biến động có thể mở rộng dựa trên giao dịch trong ngày. Nó tìm kiếm các cơ hội giao dịch đa đầu và trống tiềm năng bằng cách kết hợp nhiều chỉ số kỹ thuật và điều kiện thị trường, bao gồm biến động, khối lượng giao dịch, phạm vi giá, chỉ số kỹ thuật và chất xúc tác mới.
Nguyên tắc chiến lược
Nguyên tắc cốt lõi của chiến lược này là sử dụng nhiều yếu tố như biến động thị trường, khối lượng giao dịch, phạm vi giá, chỉ số kỹ thuật và chất xúc tác mới để đánh giá tổng hợp xu hướng thị trường và cơ hội giao dịch tiềm năng. Cụ thể, chiến lược này sử dụng các bước sau để tạo tín hiệu giao dịch:
Tính toán chỉ số ATR để đo lường mức độ biến động của thị trường. ATR hiện tại lớn hơn 1,2 lần so với ATR trước đó, cho thấy thị trường đang trong trạng thái biến động cao.
Điều kiện này được sử dụng để đảm bảo giao dịch khi có khối lượng giao dịch lớn hơn để tăng độ tin cậy của giao dịch.
Tính toán phạm vi giá ((giá cao nhất - giá thấp nhất) trong ngày giao dịch hiện tại và đánh giá xem nó có lớn hơn 0,005 không. Điều kiện này được sử dụng để đảm bảo giao dịch trong trường hợp giá biến động lớn để có được nhiều lợi nhuận tiềm năng hơn.
Sử dụng hai đường trung bình di chuyển đơn giản ((ngày 5 và 20) để đánh giá xu hướng thị trường. Khi đường trung bình 5 ngày nằm trên đường trung bình 20 ngày, thị trường có xu hướng đa đầu; ngược lại, thị trường có xu hướng không đầu.
Xác định liệu có sự xuất hiện của chất xúc tác mới hay không, tức là giá đóng cửa hiện tại có cao hơn giá mở cửa hay không. Điều kiện này được sử dụng để đảm bảo giao dịch khi có các yếu tố thuận lợi mới để tăng tỷ lệ thành công của giao dịch.
Khi tất cả các điều kiện trên được đáp ứng, theo xu hướng thị trường (((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((
Đối với giao dịch đa đầu, khi đường trung bình nhanh vượt qua đường trung bình chậm dưới đường trung bình nhanh, vị trí yên thoát; đối với giao dịch đầu trống, khi đường trung bình nhanh vượt qua đường trung bình chậm, vị trí yên thoát.
Lợi thế chiến lược
Phân tích đa yếu tố: Chiến lược này tính đến nhiều yếu tố như biến động thị trường, khối lượng giao dịch, phạm vi giá cả, chỉ số kỹ thuật và chất xúc tác mới, cho phép đánh giá toàn diện tình trạng thị trường và cơ hội giao dịch tiềm năng, nâng cao độ tin cậy của tín hiệu giao dịch.
Khả năng thích ứng: Bằng cách sử dụng chỉ số ATR để đo lường sự biến động của thị trường, chiến lược này có thể thích ứng với các môi trường thị trường khác nhau. Khi có sự biến động cao, chiến lược sẽ tự động điều chỉnh điều kiện giao dịch để đối phó với sự thay đổi của thị trường.
Kiểm soát rủi ro: Chiến lược này đặt ra các điều kiện nhập cảnh và xuất cảnh rõ ràng, giúp kiểm soát rủi ro giao dịch. Đồng thời, bằng cách xem xét các yếu tố như khối lượng giao dịch và phạm vi giá, chiến lược này có thể tránh giao dịch khi thị trường thiếu thanh khoản hoặc biến động quá nhỏ, làm giảm rủi ro hơn nữa.
Theo dõi xu hướng: Bằng cách sử dụng trung bình di chuyển đơn giản để đánh giá xu hướng thị trường, chiến lược này có thể theo dõi các hướng chính của thị trường và điều chỉnh chiến lược giao dịch kịp thời theo xu hướng thay đổi, tăng độ chính xác của giao dịch.
Giao dịch tự động: Chiến lược này có thể thực hiện giao dịch tự động, giảm sự can thiệp của con người và ảnh hưởng của cảm xúc, tăng hiệu quả giao dịch và tính nhất quán.
Rủi ro chiến lược
Rủi ro tối ưu hóa tham số: Chiến lược này liên quan đến nhiều tham số, chẳng hạn như chu kỳ ATR, yếu tố tỷ lệ dao động, chu kỳ trung bình di chuyển đơn giản của khối lượng giao dịch. Việc lựa chọn các tham số này có ảnh hưởng quan trọng đến hiệu suất của chiến lược và cài đặt tham số không đúng cách có thể dẫn đến thất bại hoặc hiệu suất kém của chiến lược. Do đó, cần tối ưu hóa và thử nghiệm các tham số để tìm ra sự kết hợp tham số tốt nhất.
Rủi ro quá phù hợp: Chiến lược sử dụng nhiều điều kiện để tạo tín hiệu giao dịch, có thể có nguy cơ quá phù hợp. Quá phù hợp có thể dẫn đến chiến lược hoạt động tốt trên dữ liệu lịch sử, nhưng hoạt động kém trong giao dịch thực tế. Để giảm nguy cơ quá phù hợp, có thể sử dụng dữ liệu ngoài mẫu để thử nghiệm và kiểm tra sức mạnh của chiến lược.
Rủi ro thị trường: Chiến lược này được sử dụng chủ yếu trong môi trường thị trường có xu hướng rõ ràng, có tỷ lệ biến động cao. Hiệu suất của chiến lược có thể bị ảnh hưởng khi xu hướng thị trường không rõ ràng hoặc có tỷ lệ biến động thấp. Ngoài ra, chiến lược cũng bị ảnh hưởng bởi các yếu tố bên ngoài như sự kiện thiên bạch đen, thay đổi chính sách, những yếu tố này có thể dẫn đến thất bại của chiến lược.
Rủi ro chi phí giao dịch: Chiến lược này là chiến lược giao dịch trong ngày, tần suất giao dịch cao, có thể tạo ra chi phí giao dịch cao hơn, chẳng hạn như điểm trượt, phí xử lý, v.v. Những chi phí này sẽ làm xói mòn lợi nhuận của chiến lược và làm giảm hiệu suất tổng thể của chiến lược. Do đó, trong ứng dụng thực tế, cần xem xét tác động của chi phí giao dịch và tối ưu hóa chiến lược cho phù hợp.
Rủi ro về thanh khoản: tín hiệu giao dịch của chiến lược này phụ thuộc vào nhiều điều kiện, chẳng hạn như khối lượng giao dịch, phạm vi giá, v.v. Trong trường hợp thị trường thiếu thanh khoản, các điều kiện này có thể không được đáp ứng, dẫn đến việc chiến lược không thể tạo ra tín hiệu giao dịch hiệu quả. Do đó, khi áp dụng chiến lược này, cần phải chọn thị trường có thanh khoản tốt hơn và giao dịch.
Hướng tối ưu hóa
Các tham số điều chỉnh động: xem xét sử dụng các thuật toán thích ứng hoặc phương pháp học máy để tự động điều chỉnh các tham số chiến lược theo tình hình thị trường thay đổi để thích ứng với các môi trường thị trường khác nhau, tăng cường sự ổn định và thích ứng của chiến lược.
Nhập các biện pháp quản lý rủi ro: Nhập các biện pháp quản lý rủi ro trong chiến lược, chẳng hạn như dừng lỗ, quản lý vị trí, v.v., để kiểm soát tổn thất tiềm ẩn. Đồng thời, bạn có thể xem xét sử dụng phương pháp quản lý vị trí điều chỉnh tỷ lệ dao động, điều chỉnh kích thước vị trí theo biến động của thị trường để kiểm soát rủi ro.
Tối ưu hóa tín hiệu giao dịch: Bạn có thể xem xét việc đưa ra các chỉ số kỹ thuật hoặc các yếu tố thị trường khác, chẳng hạn như chỉ số tương đối mạnh (RSI), chỉ số cảm xúc thị trường, để tối ưu hóa việc tạo tín hiệu giao dịch. Ngoài ra, bạn cũng có thể sử dụng thuật toán học máy, chẳng hạn như hỗ trợ máy vector (SVM), rừng ngẫu nhiên, để đào tạo và tối ưu hóa tín hiệu giao dịch.
Cải thiện chiến lược dừng lỗ: Hiện tại, chiến lược này sử dụng một đường trung bình di chuyển đơn giản để đánh giá điều kiện ra sân, có thể xem xét việc giới thiệu các chiến lược dừng lỗ phức tạp hơn, chẳng hạn như theo dõi dừng lỗ, dừng biến động, v.v., để bảo vệ lợi nhuận và kiểm soát rủi ro tốt hơn.
Tham gia phân tích cấu trúc vi mô thị trường: Xem xét việc tích hợp phân tích cấu trúc vi mô thị trường vào các chiến lược, chẳng hạn như phân tích dòng lệnh, độ sâu của kho mua bán, để có được nhiều thông tin hơn về thị trường và tăng độ chính xác của quyết định giao dịch.
Kết hợp phân tích cơ bản: Kết hợp phân tích cơ bản với phân tích kỹ thuật, xem xét các yếu tố như chỉ số kinh tế vĩ mô, xu hướng ngành, dữ liệu tài chính của công ty để có được thông tin thị trường toàn diện hơn, tăng độ tin cậy và sức mạnh của chiến lược.
Tóm tắt
Chiến lược này là một chiến lược giao dịch biến động trong ngày có thể mở rộng dựa trên phân tích nhiều yếu tố, tạo ra tín hiệu giao dịch đa đầu và vô đầu bằng cách tính đến các yếu tố như biến động của thị trường, khối lượng giao dịch, phạm vi giá, chỉ số kỹ thuật và chất xúc tác mới. Ưu điểm của chiến lược này là khả năng thích ứng mạnh, các biện pháp kiểm soát rủi ro rõ ràng, khả năng theo dõi xu hướng mạnh mẽ, đồng thời có các rủi ro về tối ưu hóa tham số, quá phù hợp, rủi ro thị trường, chi phí giao dịch và tính thanh khoản.
||
Overview
This strategy is an intraday scalable volatility trading strategy based on day trading. It combines multiple technical indicators and market conditions, including volatility, volume, price range, technical indicators, and new catalysts, to identify potential long and short trading opportunities. The strategy uses the ATR indicator to measure market volatility and determines whether to trade based on the level of volatility. At the same time, the strategy also considers factors such as trading volume, price range, technical indicators, and new catalysts to improve the reliability of trading signals.
Strategy Principle
The core principle of this strategy is to use multiple factors such as market volatility, trading volume, price range, technical indicators, and new catalysts to comprehensively judge market trends and potential trading opportunities. Specifically, the strategy uses the following steps to generate trading signals:
Calculate the ATR indicator to measure market volatility. When the current ATR value is greater than 1.2 times the previous ATR value, it indicates that the market is in a high volatility state.
Determine whether the current trading volume is greater than the simple moving average of the trading volume over 50 periods. This condition is used to ensure that trading is carried out when the trading volume is relatively large, to improve the reliability of trading.
Calculate the price range (highest price - lowest price) of the current trading day and determine whether it is greater than 0.005. This condition is used to ensure that trading is carried out when the price fluctuation is relatively large, to obtain more potential profits.
Use two simple moving averages (5-day and 20-day) to judge the market trend. When the 5-day average is above the 20-day average, it indicates that the market is in a bullish trend; otherwise, it indicates that the market is in a bearish trend.
Determine whether a new catalyst has appeared, that is, whether the current closing price is higher than the opening price. This condition is used to ensure that trading is carried out when there are new favorable factors, to increase the success rate of trading.
When all of the above conditions are met, generate corresponding trading signals (buy or sell) according to the market trend (bullish or bearish).
For long trades, when the fast moving average crosses below the slow moving average, close the position and exit; for short trades, when the fast moving average crosses above the slow moving average, close the position and exit.
Strategy Advantages
Comprehensive multi-factor judgment: The strategy comprehensively considers multiple factors such as market volatility, trading volume, price range, technical indicators, and new catalysts, which can comprehensively evaluate market conditions and potential trading opportunities, and improve the reliability of trading signals.
Strong adaptability: By using the ATR indicator to measure market volatility, the strategy can adapt to different market environments. When volatility is high, the strategy automatically adjusts trading conditions to cope with market changes.
Risk control: The strategy sets clear entry and exit conditions, which helps to control trading risks. At the same time, by considering factors such as trading volume and price range, the strategy can avoid trading when market liquidity is insufficient or volatility is too small, further reducing risks.
Trend tracking: By using simple moving averages to judge market trends, the strategy can track the main direction of the market and adjust trading strategies in a timely manner according to changes in trends, improving the accuracy of trading.
Automated trading: The strategy can achieve automated trading, reducing human intervention and emotional impact, and improving trading efficiency and consistency.
Strategy Risks
Parameter optimization risk: The strategy involves multiple parameters, such as the ATR period, volatility factor, simple moving average period of trading volume, etc. The selection of these parameters has an important impact on strategy performance, and improper parameter settings may lead to strategy failure or poor performance. Therefore, it is necessary to optimize and test the parameters to find the best parameter combination.
Overfitting risk: The strategy uses multiple conditions to generate trading signals, which may have the risk of overfitting. Overfitting may cause the strategy to perform well on historical data but perform poorly in actual trading. To reduce the risk of overfitting, out-of-sample data can be used for testing and robustness testing of the strategy.
Market risk: The strategy is mainly applicable to market environments with obvious trends and high volatility. When market trends are not obvious or volatility is low, the performance of the strategy may be affected. In addition, the strategy is also affected by external factors such as black swan events and policy changes, which may cause the strategy to fail.
Transaction cost risk: The strategy is an intraday trading strategy with a high trading frequency, which may generate high transaction costs, such as slippage and commission. These costs will erode the profits of the strategy and reduce the overall performance of the strategy. Therefore, in practical applications, it is necessary to consider the impact of transaction costs and optimize the strategy accordingly.
Liquidity risk: The trading signals of the strategy depend on multiple conditions, such as trading volume, price range, etc. In the case of insufficient market liquidity, these conditions may not be met, resulting in the strategy not being able to generate effective trading signals. Therefore, when applying the strategy, it is necessary to select markets and trading targets with good liquidity.
Optimization Direction
Dynamic parameter adjustment: Consider using adaptive algorithms or machine learning methods to automatically adjust strategy parameters according to changes in market conditions, to adapt to different market environments and improve the robustness and adaptability of the strategy.
Introduce risk management measures: Introduce risk management measures in the strategy, such as stop loss and position management, to control potential losses. At the same time, consider using volatility-adjusted position management methods to dynamically adjust position size according to the level of market volatility to control risk.
Optimize trading signals: Consider introducing other technical indicators or market factors, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI), market sentiment indicators, etc., to optimize the generation of trading signals. In addition, machine learning algorithms such as support vector machines (SVM) and random forests can be used to train and optimize trading signals.
Improve stop-profit and stop-loss strategies: At present, the strategy uses simple moving average crossover to determine exit conditions. More complex stop-profit and stop-loss strategies, such as trailing stop loss and volatility stop loss, can be considered to better protect profits and control risks.
Incorporate market microstructure analysis: Consider incorporating market microstructure analysis into the strategy, such as analyzing order flow, order book depth, etc., to obtain more market information and improve the accuracy of trading decisions.
Combine fundamental analysis: Combine fundamental analysis with technical analysis, considering factors such as macroeconomic indicators, industry trends, company financial data, etc., to obtain more comprehensive market information and improve the reliability and robustness of the strategy.
Summary
This strategy is an intraday scalable volatility trading strategy based on multi-factor analysis, which generates long and short trading signals by comprehensively considering factors such as market volatility, trading volume, price range, technical indicators, and new catalysts. The advantages of the strategy are strong adaptability, clear risk control measures, and strong trend tracking ability. At the same time, there are
/*backtest
start: 2024-03-01 00:00:00
end: 2024-03-31 23:59:59
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=4
strategy("Intraday Scalping Strategy with Exit Conditions", shorttitle="ISS", overlay=true)
// Define Volatility based on ATR for intraday
atrPeriod = 10
atrValue = atr(atrPeriod)
volatilityFactor = 1.2
highVolatility = atrValue > volatilityFactor * atrValue[1]
// Define Volume conditions for intraday
volumeCondition = volume > sma(volume, 50)
// Define Price Range for intraday
range = high - low
// Define Technical Indicator (SMA example) for intraday
smaFast = sma(close, 5)
smaSlow = sma(close, 20)
isBullish = smaFast > smaSlow
// Define New Catalyst condition for intraday (example)
newCatalyst = close > open
// Combine all conditions for entry in intraday
enterLong = highVolatility and volumeCondition and range > 0.005 and isBullish and newCatalyst
enterShort = highVolatility and volumeCondition and range > 0.005 and not isBullish and newCatalyst
// Submit entry orders based on conditions
strategy.entry("Buy", strategy.long, when=enterLong)
strategy.entry("Sell", strategy.short, when=enterShort)
// Define exit conditions
exitLong = crossover(smaFast, smaSlow) // Example exit condition for long position
exitShort = crossunder(smaFast, smaSlow) // Example exit condition for short position
// Submit exit orders based on conditions
strategy.close("Buy", when=exitLong)
strategy.close("Sell", when=exitShort)