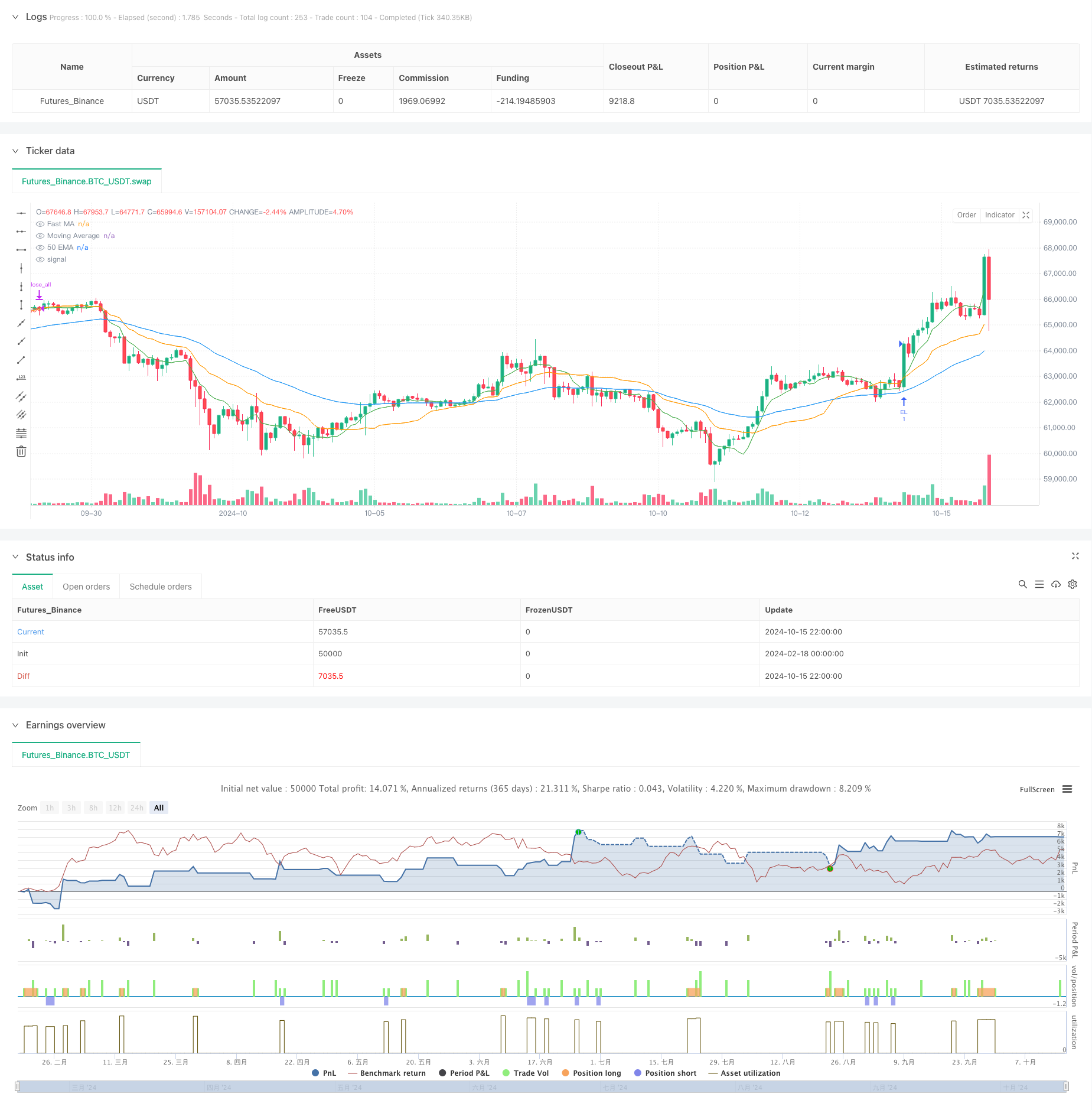
概述
这是一个基于体积加权移动平均线(VWMA)和指数移动平均线(EMA)的趋势跟踪策略,结合了价格角度分析和动态追踪止损机制。该策略主要通过监测VWMA与快速移动平均线的交叉,同时结合价格运动的角度条件来确定入场时机,并使用百分比追踪止损来管理风险。
策略原理
策略的核心逻辑基于以下几个关键组件: 1. 使用25周期的VWMA作为主要趋势指标 2. 通过8周期VWMA作为快速信号线 3. 采用50周期EMA确定更长期趋势 4. 计算50周期EMA的角度(设定为45度阈值) 5. 可选的200周期EMA作为市场偏差过滤器 入场信号在快速移动平均线与主VWMA发生交叉,且价格角度满足条件时触发。策略通过1%的动态追踪止损来保护利润。
策略优势
- 多重时间框架验证 - 策略在H1以上和M1时间框架上表现良好
- 角度过滤 - 通过引入价格运动角度条件,减少假突破
- 风险管理完善 - 采用百分比追踪止损,动态保护利润
- 适应性强 - 可通过参数调整适应不同市场条件
- 趋势确认充分 - 使用多重移动平均线交叉确认趋势
策略风险
- 震荡市场表现欠佳 - 在横盘市场可能产生频繁假信号
- 入场时机滞后 - 由于使用多重确认,可能错过一些趋势初期机会
- M15时间框架效果不理想 - 需要避免在此时间框架使用
- 参数敏感性 - 角度阈值和移动平均线周期的选择对策略性能影响较大
- 追踪止损可能过早出场 - 在波动较大的市场中可能导致过早止损
策略优化方向
- 引入波动率自适应机制 - 根据市场波动率动态调整追踪止损百分比
- 增加成交量过滤器 - 通过成交量确认来提高信号质量
- 优化角度计算方法 - 考虑使用自适应角度阈值
- 加入市场状态识别 - 开发趋势/震荡市场识别机制
- 完善出场机制 - 结合价格形态和动量指标优化出场时机
总结
这是一个结构完善的趋势跟踪策略,通过角度分析和多重移动平均线的配合,能够在主要趋势中获得较好的表现。虽然存在一定的滞后性和参数敏感性问题,但通过建议的优化方向,策略仍有提升空间。特别适合在较长时间周期的趋势交易中应用。
策略源码
/*backtest
start: 2024-02-18 00:00:00
end: 2024-10-16 00:00:00
period: 2h
basePeriod: 2h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=6
strategy("PVSRA Trailing Strategy with Angle Condition (40-50 degrees)", overlay=true)
// === INPUTS ===
priceData = input.source(close, title="Price Data")
maLength = input.int(25, title="Moving Average Length", minval=2)
useBias = input.bool(false, title="Long/Short just above/below 200 EMA")
useTrailing = input.bool(true, title="Use Trailing Stop")
trailPerc = input.float(1.0, title="Trailing Stop Percentage", minval=0.1)
anglePeriod = input.int(14, title="Period for Angle Calculation", minval=1)
// === CÁLCULOS ===
maValue = ta.vwma(priceData, maLength)
maLong = ta.ema(high, 50)
maShort = ta.ema(low, 50)
maFast = ta.vwma(close, 8)
bias = ta.ema(close, 200)
longBias = useBias ? close > bias : true
shortBias = useBias ? close < bias : true
// === CÁLCULO DO ÂNGULO DA MÉDIA MÓVEL DE 50 ===
ma50 = ta.ema(close, 50)
angle = math.atan((ma50 - ma50[anglePeriod]) / anglePeriod) * (180 / math.pi) // Converte radianos para graus
// === CONDIÇÃO DE ÂNGULO ===
validAngleL = angle >= 45
validAngleS = angle <= 45
// === PLOTS ===
plot(maValue, color=color.orange, title="Moving Average")
plot(maFast, color=color.green, title="Fast MA")
plot(ma50, color=color.blue, title="50 EMA")
plotshape(series=(strategy.position_size > 0) ? maValue : na,
color=color.red, style=shape.circle, location=location.absolute,
title="Long Stop")
plotshape(series=(strategy.position_size < 0) ? maValue : na,
color=color.red, style=shape.cross, location=location.absolute,
title="Short Stop")
// === CONDIÇÕES DE ENTRADA ===
enterLong = close > maValue and ta.crossover(maFast, maValue) and close > maLong and longBias and validAngleL
enterShort = close < maValue and ta.crossunder(maFast, maValue) and close < maShort and shortBias and validAngleS
// === CONDIÇÕES DE SAÍDA ===
exitLong = ta.crossunder(maFast, maValue) and strategy.position_size > 0
exitShort = ta.crossover(maFast, maValue) and strategy.position_size < 0
// === EXECUÇÃO DA ESTRATÉGIA ===
if (enterLong)
strategy.entry("EL", strategy.long)
if (enterShort)
strategy.entry("ES", strategy.short)
if (exitLong or exitShort)
strategy.close_all()
// === TRAILING STOP ===
if (useTrailing and strategy.position_size > 0)
trailPrice = close * (1 - trailPerc / 100)
strategy.exit("Trailing Long", from_entry="EL", stop=trailPrice)
if (useTrailing and strategy.position_size < 0)
trailPrice = close * (1 + trailPerc / 100)
strategy.exit("Trailing Short", from_entry="ES", stop=trailPrice)
相关推荐