Des poids fixes aux réseaux neuronaux : une pratique de transformation de l'apprentissage automatique de la stratégie Pine
 2
2
 641
641
Je suis tombé sur une stratégie intéressante de Pine
Il y a quelques jours, je parcourais les stratégies du forum Inventor et j’ai vu un article intituléPanel Pro+ Quantum SmartPromptAprès avoir examiné le code, j’ai trouvé le concept sous-jacent plutôt intéressant : il utilise 10 indicateurs techniques, attribue une pondération différente à chacun en fonction des conditions de marché et calcule un score pour déterminer les décisions d’achat et de vente. Par exemple, dans un marché haussier, l’indicateur de tendance est pondéré à 2,0 et le RSI à 1,5 ; dans un marché baissier, les pondérations sont différentes. On a l’impression d’imiter la façon de penser des gens : se concentrer sur des éléments différents dans des situations différentes.
Si vous y réfléchissez bien, cette structure ressemble beaucoup à un réseau neuronal :
- 10 indicateurs techniques lors de la saisie
- Classification de l’état du marché comme couche cachée
- La matrice de poids est le poids de la connexion
- Enfin, sortez une partition
Mais le problème est que tous les poids sont codés en dur, par exemple :
if marketType == "Bull"
array.set(weights, 0, 2.0) // 趋势权重固定是2.0
array.set(weights, 1, 1.5) // RSI权重固定是1.5
Ces chiffres sont entièrement fixés par l’auteur sur la base de l’expérience du marché et n’ont été ni étudiés ni optimisés de quelque manière que ce soit.
Idée : rendre les poids faciles à apprendre
Puisque la structure est déjà très similaire à celle d’un réseau neuronal, pourquoi ne pas la rendre réellement capable d’apprendre ?
Mon idée est simple :
- Conservez la méthode de calcul du poids d’origine et obtenez un « score de poids »
- En utilisant ce score pondéré comme entrée, entraînez un petit réseau neuronal
- Laissez le réseau apprendre à prédire les rendements futurs à partir de scores pondérés
- Décider d’ouvrir ou non une position en fonction du taux de rendement prévu
Cela permet non seulement de conserver la stratégie d’origine, mais aussi d’augmenter la capacité d’apprentissage.
Commencez sur la plateforme Inventor
La plateforme Inventor a été choisie principalement parce qu’elle prend en charge Python et contient des données riches.
Étape 1 : Réécrire les indicateurs techniques
J’ai réécrit tous les indicateurs du script Pine en Python, en utilisant la bibliothèque Talib pour garantir des calculs précis. Cela inclut les indicateurs courants tels que l’EMA, le MACD, le RSI et l’ATR, ainsi que l’analyse de volume et la reconnaissance simple des chandeliers.
Étape 2 : Détection de l’état du marché
Suivant la logique de la stratégie d’origine, le type de marché est déterminé en fonction d’une combinaison de divers indicateurs : Bull, Bear, Eagle, Wolf, etc. Cette partie est essentiellement une combinaison de logique if-else.
Étape 3 : Calcul du score de poids
Voici la partie principale. J’ai défini deux jeux de poids :
- Poids de la base :[2.0, 1.5, 2.0, 1.3, 1.2, …]
- Pondération du marché : ajustée en fonction des différentes conditions du marché
Poids final = poids de base × poids du marché
Ce poids est ensuite utilisé pour pondérer les scores originaux des 10 indicateurs et les additionner pour obtenir le « score pondéré ».
Étape 4 : Prédicteur de réseau neuronal
J’ai écrit un réseau très simple :
- Entrée : 1 fonctionnalité (score pondéré)
- Couche cachée : 16 neurones, activation ReLU
- Résultat : taux de rendement prévu, limité à ± 5 % en utilisant tanh
Objectif de formation : Utiliser le score de pondération à l’instant t-1 pour prédire l’évolution des prix à l’instant t.
Étape 5 : Logique de transaction
Au lieu d’acheter ou de vendre directement en fonction de la notation, nous examinons le taux de rendement prévu :
- Taux de rendement prévu > 1,5 % : Ouvrir une position longue ou fermer une position courte
- Taux de rendement prévu < -1,5 % : Ouvrir une position courte ou fermer une position longue
- Autres situations : Maintenir le statu quo
Dans le même temps, conservez le stop-profit et le stop-loss pour garantir que les risques sont contrôlables.
Quelques observations sur le fonctionnement réel
Collecte de données
La stratégie peut collecter des données d’entraînement normalement. À chaque apparition d’un nouveau chandelier, le score de pondération du chandelier précédent est utilisé comme caractéristique, et la hausse ou la baisse du chandelier actuel par rapport au précédent est utilisée comme étiquette.
Les données sont probablement comme ceci :
权重评分=15.6, 收益率=+0.8%
权重评分=-8.2, 收益率=-1.2%
权重评分=22.1, 收益率=+0.3%
Formation sur modèle
Le réseau neuronal peut être entraîné normalement, et la perte MSE diminuera progressivement. Configurez-le pour qu’il se réentraîne toutes les 4 heures afin de garantir que le modèle puisse s’adapter aux évolutions du marché.
Effet de prédiction
Les prédictions du modèle ont une certaine corrélation avec les rendements réels, mais elle n’est pas particulièrement forte.
- Une seule fonctionnalité est trop simple et peut ne pas contenir suffisamment d’informations
- Les fluctuations de prix à court terme sont très aléatoires
- Le marché des contrats est assez bruyant
Performances commerciales
Le risque d’une transaction individuelle est bien maîtrisé grâce aux protections stop-loss et take-profit. Cependant, la rentabilité globale est moyenne, principalement en raison du manque de précision des prévisions.
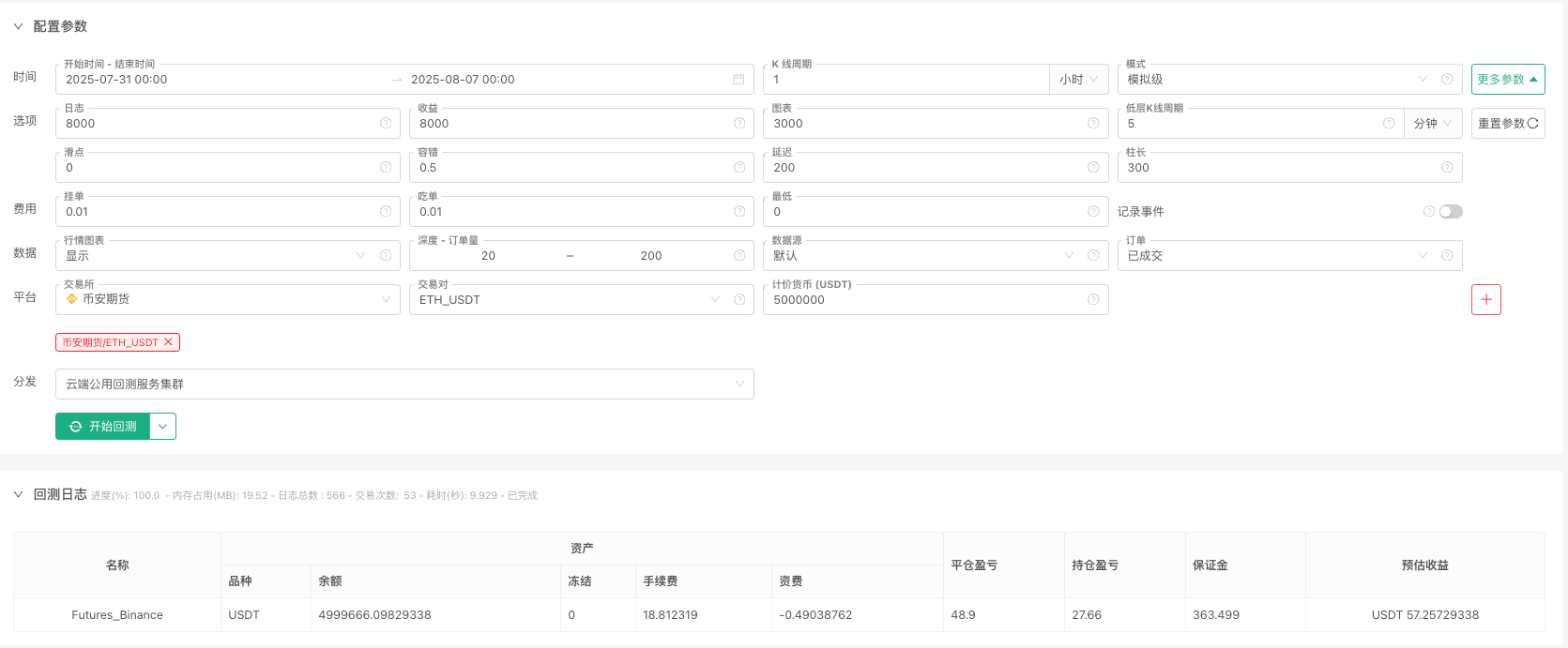
Quelques problèmes rencontrés
Les fonctionnalités sont trop simples:Se limiter à la pondération pour évaluer une seule caractéristique est en effet un peu simpliste. Le marché est si complexe qu’il est difficile de le résumer entièrement avec un seul chiffre.
Qualité d’échantillon instable:Les prix des contrats fluctuent considérablement à court terme et, dans de nombreux cas, la hausse et la baisse sont en fait aléatoires, ce qui rend la qualité des échantillons de formation instable.
Le risque d’une suradaptation:Bien que le réseau soit simple, il peut néanmoins être surajusté lorsque la taille de l’échantillon est limitée.
Exigences en temps réel:L’apprentissage en ligne nécessite un équilibre entre le temps de formation et les performances en temps réel.
Temps limité et optimisation insuffisante
Il existe encore de nombreux domaines dans lesquels cette stratégie peut être améliorée, mais le temps et l’énergie sont limités, nous ne pouvons donc pas l’optimiser en profondeur :
Caractéristiques:Vous pouvez ajouter d’autres indicateurs techniques ou utiliser les caractéristiques statistiques de la série de prix.
Modèle:Vous pouvez essayer un modèle de séquence tel que LSTM, ou intégrer plusieurs modèles.
Données:Améliorez la qualité des échantillons et augmentez le nettoyage des données.
Le contrôle du vent: Améliorez le stop loss dynamique et optimisez la gestion des positions.
Gains et réflexions
Cette exploration m’a appris une leçon : la clé des bonnes idées réside dans leur mise en œuvre rapide ! Lorsque j’ai vu la matrice de pondération conçue dans le script Pine, j’ai immédiatement pensé à la possibilité de l’améliorer grâce à un réseau neuronal. Si je m’étais contenté d’y réfléchir ou que j’avais remis à plus tard, l’idée aurait probablement été oubliée. Heureusement, la plateforme Inventor proposait un environnement Python et une interface de données, ce qui m’a permis de transformer rapidement mon idée en code exécutable. De la génération de l’idée à sa mise en œuvre, il n’a fallu qu’une journée. Si les performances de la stratégie finale ont été médiocres, la mise en œuvre concrète a au moins permis de vérifier la faisabilité de l’idée. Plus important encore, le processus de mise en œuvre a généré de nouvelles idées et des améliorations. Sans une action rapide, ces découvertes et perspectives ultérieures auraient été impossibles. Discuter d’idées sur papier ne peut jamais se comparer à l’expérience concrète d’écriture de code, d’exécution de données et d’observation des résultats. C’est la nature du trading quantitatif. Les idées sont nombreuses, mais les plus précieuses sont celles qui sont rapidement mises en œuvre et vérifiées.
”`py “‘backtest start: 2025-07-31 00:00:00 end: 2025-08-07 00:00:00 period: 1h basePeriod: 5m exchanges: [{“eid”:“Futures_Binance”,“currency”:“ETH_USDT”,“balance”:5000000,“fee”:[0.01,0.01]}] “’
import numpy as np from collections import deque import talib as TA
========== 异常类 ==========
class Error_noSupport(BaseException): def init(self): Log(“只支持期货交易!#FF0000”)
class Error_AtBeginHasPosition(BaseException): def init(self): Log(“启动时有期货持仓! #FF0000”)
========== 收益率预测神经网络 ==========
class ReturnPredictor: def init(self, input_size=10, hidden_size=20, output_size=1): “”“收益率预测网络: X[t] -> yt+1”“” self.W1 = np.random.randn(input_size, hidden_size) * 0.1 self.b1 = np.zeros((1, hidden_size)) self.W2 = np.random.randn(hidden_size, output_size) * 0.1 self.b2 = np.zeros((1, output_size)) self.learning_rate = 0.001
def sigmoid(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-np.clip(x, -250, 250)))
def tanh(self, x):
return np.tanh(x)
def forward(self, X):
self.z1 = np.dot(X, self.W1) + self.b1
self.a1 = self.sigmoid(self.z1)
self.z2 = np.dot(self.a1, self.W2) + self.b2
# 输出预测收益率,使用tanh限制在合理范围
self.a2 = self.tanh(self.z2) * 0.1 # 限制在±10%范围内
return self.a2
def backward(self, X, y, output):
m = X.shape[0]
# MSE损失的梯度
dZ2 = (output - y) / m
# tanh的导数
tanh_derivative = 1 - (output / 0.1) ** 2
dZ2 = dZ2 * 0.1 * tanh_derivative
dW2 = np.dot(self.a1.T, dZ2)
db2 = np.sum(dZ2, axis=0, keepdims=True)
dA1 = np.dot(dZ2, self.W2.T)
dZ1 = dA1 * self.a1 * (1 - self.a1) # sigmoid导数
dW1 = np.dot(X.T, dZ1)
db1 = np.sum(dZ1, axis=0, keepdims=True)
# 更新权重
self.W2 -= self.learning_rate * dW2
self.b2 -= self.learning_rate * db2
self.W1 -= self.learning_rate * dW1
self.b1 -= self.learning_rate * db1
def train(self, X, y, epochs=100):
for i in range(epochs):
output = self.forward(X)
self.backward(X, y, output)
if i % 20 == 0:
loss = np.mean((output - y) ** 2)
Log(f"收益率预测训练轮次 {i}, MSE损失: {loss:.6f}")
def predict(self, X):
return self.forward(X)
========== 技术指标计算类 ==========
class TechnicalIndicators: @staticmethod def calculate_indicators(records, use_completed_only=True): “”“计算技术指标和特征”“” if len(records) < 55: return None, None
# 只使用已完成的K线数据
if use_completed_only and len(records) > 1:
working_records = records[:-1]
else:
working_records = records
if len(working_records) < 55:
return None, None
closes = np.array([r['Close'] for r in working_records])
highs = np.array([r['High'] for r in working_records])
lows = np.array([r['Low'] for r in working_records])
volumes = np.array([r['Volume'] for r in working_records])
opens = np.array([r['Open'] for r in working_records])
try:
# 基础指标
ema_55 = TA.EMA(closes, timeperiod=55)
sma_vol20 = TA.SMA(volumes, timeperiod=20)
macd, signal_line, _ = TA.MACD(closes)
rsi_val = TA.RSI(closes, timeperiod=14)
atr14 = TA.ATR(highs, lows, closes, timeperiod=14)
range20 = TA.STDDEV(closes, timeperiod=20)
# 计算派生指标
sma_atr20 = TA.SMA(atr14, timeperiod=20)
sma_range20 = TA.SMA(range20, timeperiod=20)
rvol = volumes / sma_vol20 if sma_vol20[-1] > 0 else np.ones_like(volumes)
delta = closes - opens
# 计算量能阈值
vol_abs_thresh = sma_vol20 * 1.2
sniper_thresh = np.percentile(volumes[-40:], 80) if len(volumes) >= 40 else sma_vol20[-1]
# 趋势
trend = np.where(closes > ema_55, 1, np.where(closes < ema_55, -1, 0))
# 简化K线形态
body_size = np.abs(closes - opens)
total_range = highs - lows
# 锤子线
is_hammer = ((total_range > 3 * body_size) &
((closes - lows) / (total_range + 0.001) > 0.6) &
((opens - lows) / (total_range + 0.001) > 0.6))
# 吞噬形态
is_engulfing = np.zeros_like(closes, dtype=bool)
if len(closes) >= 2:
is_engulfing[1:] = ((closes[1:] > opens[:-1]) &
(opens[1:] < closes[:-1]) &
(closes[1:] > opens[1:]) &
(opens[1:] < closes[1:]))
pattern = np.where(is_hammer, 1, np.where(is_engulfing, 2, 0))
# 🔥 计算标准化特征向量(用于神经网络输入)
features = []
# 1. 趋势特征
if len(ema_55) > 0 and not np.isnan(ema_55[-1]):
trend_feature = (closes[-1] - ema_55[-1]) / ema_55[-1]
features.append(np.tanh(trend_feature * 100))
else:
features.append(0)
# 2. RSI特征
if len(rsi_val) > 0 and not np.isnan(rsi_val[-1]):
rsi_feature = (rsi_val[-1] - 50) / 50
features.append(rsi_feature)
else:
features.append(0)
# 3. MACD特征
if len(macd) > 0 and not np.isnan(macd[-1]) and not np.isnan(signal_line[-1]):
macd_feature = (macd[-1] - signal_line[-1]) / closes[-1] if closes[-1] > 0 else 0
features.append(np.tanh(macd_feature * 1000))
else:
features.append(0)
# 4. 成交量特征
if len(vol_abs_thresh) > 0 and vol_abs_thresh[-1] > 0:
vol_feature = volumes[-1] / vol_abs_thresh[-1] - 1
features.append(np.tanh(vol_feature))
else:
features.append(0)
# 5. 相对成交量特征
if len(rvol) > 0 and not np.isnan(rvol[-1]):
rvol_feature = rvol[-1] - 1
features.append(np.tanh(rvol_feature))
else:
features.append(0)
# 6. Delta特征
if len(delta) > 0 and not np.isnan(delta[-1]) and closes[-1] > 0:
delta_feature = delta[-1] / closes[-1]
features.append(np.tanh(delta_feature * 100))
else:
features.append(0)
# 7. ATR特征
if len(atr14) > 0 and len(sma_atr20) > 0 and sma_atr20[-1] > 0:
atr_feature = atr14[-1] / sma_atr20[-1] - 1
features.append(np.tanh(atr_feature))
else:
features.append(0)
# 8. Blocks特征
if len(volumes) >= 10:
highest_vol = np.max(volumes[-10:])
blocks_feature = volumes[-1] / highest_vol - 0.8 if highest_vol > 0 else 0
features.append(np.tanh(blocks_feature * 5))
else:
features.append(0)
# 9. Tick特征
if len(sma_vol20) > 0 and sma_vol20[-1] > 0:
tick_feature = volumes[-1] / sma_vol20[-1] - 1
features.append(np.tanh(tick_feature))
else:
features.append(0)
# 10. 形态特征
pattern_feature = pattern[-1] / 2.0 if len(pattern) > 0 else 0
features.append(pattern_feature)
# 确保特征数量正确
while len(features) < 10:
features.append(0)
features = np.array(features[:10]).reshape(1, -1)
indicators = {
'ema_55': ema_55,
'sma_vol20': sma_vol20,
'macd': macd,
'signal_line': signal_line,
'rsi_val': rsi_val,
'atr14': atr14,
'range20': range20,
'sma_atr20': sma_atr20,
'sma_range20': sma_range20,
'rvol': rvol,
'delta': delta,
'vol_abs_thresh': vol_abs_thresh,
'sniper_thresh': sniper_thresh,
'trend': trend,
'pattern': pattern,
'volumes': volumes,
'closes': closes,
'highs': highs,
'lows': lows
}
return indicators, features
except Exception as e:
Log(f"计算技术指标异常: {str(e)}")
return None, None
========== 市场状态检测类 ==========
class MarketStateDetector: @staticmethod def detect_market_type(indicators): “”“检测市场状态”“” if indicators is None: return “Unknown”
try:
# 获取最新值
close = indicators['closes'][-1]
ema_55 = indicators['ema_55'][-1]
macd = indicators['macd'][-1]
signal_line = indicators['signal_line'][-1]
rsi_val = indicators['rsi_val'][-1]
atr14 = indicators['atr14'][-1]
volume = indicators['volumes'][-1]
sma_vol20 = indicators['sma_vol20'][-1]
sma_atr20 = indicators['sma_atr20'][-1]
range20 = indicators['range20'][-1]
sma_range20 = indicators['sma_range20'][-1]
rvol = indicators['rvol'][-1]
delta = indicators['delta'][-1]
# 检查有效性
if (np.isnan(ema_55) or np.isnan(macd) or np.isnan(signal_line) or
np.isnan(rsi_val) or np.isnan(atr14) or np.isnan(sma_atr20)):
return "Unknown"
# 市场类型判断
is_bull = (close > ema_55 and macd > signal_line and rsi_val > 50 and rvol > 1)
is_bear = (close < ema_55 and macd < signal_line and rsi_val < 50 and volume > sma_vol20)
is_sideways = (abs(close - ema_55) < atr14 * 0.5 and atr14 < sma_atr20)
is_volatile = (atr14 > sma_atr20 * 1.2)
# 需要历史数据的判断
if len(indicators['closes']) >= 2:
price_change = indicators['closes'][-1] - indicators['closes'][-2]
is_momentum = (price_change > atr14 * 1.5 and volume > sma_vol20 * 1.5)
is_wolf = (price_change < -atr14 and close < ema_55)
else:
is_momentum = False
is_wolf = False
is_mean_rev = (rsi_val > 70 or rsi_val < 30)
is_box = (is_sideways and range20 < sma_range20 * 0.8)
is_macro = (abs(delta) > atr14 * 2) if not np.isnan(delta) else False
is_eagle = (is_bull and atr14 < sma_atr20 * 0.8)
# 优先级判断
if is_eagle:
return "Eagle"
elif is_bull:
return "Bull"
elif is_wolf:
return "Wolf"
elif is_bear:
return "Bear"
elif is_box:
return "Box"
elif is_sideways:
return "Sideways"
elif is_volatile:
return "Volatile"
elif is_momentum:
return "Momentum"
elif is_mean_rev:
return "MeanRev"
elif is_macro:
return "Macro"
else:
return "Unknown"
except Exception as e:
Log(f"市场状态检测异常: {str(e)}")
return "Unknown"
========== 动态权重生成器 ==========
class DynamicWeightGenerator: @staticmethod def generate_weights_from_predicted_return(predicted_return, market_type): “”“根据预测收益率和市场状态生成动态权重”“”
# 基础权重矩阵(不同市场类型)
base_weights_matrix = {
"Bull": [2.0, 1.5, 2.0, 1.3, 1.2, 1.0, 1.2, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
"Bear": [2.0, 1.5, 2.0, 1.5, 1.3, 1.1, 1.2, 1.1, 1.0, 1.0],
"Eagle": [2.2, 1.4, 2.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.1, 1.1, 1.0, 1.0, 1.1],
"Wolf": [1.8, 1.6, 1.8, 1.6, 1.2, 1.0, 1.3, 1.2, 1.0, 0.9],
"Momentum": [1.5, 1.2, 1.8, 2.0, 2.0, 1.5, 1.5, 1.3, 1.2, 1.0],
"Sideways": [1.0, 1.4, 1.0, 0.8, 0.7, 1.0, 0.9, 0.8, 1.0, 1.3],
"Volatile": [1.2, 1.5, 1.3, 1.6, 1.8, 1.2, 1.4, 1.3, 1.4, 1.0],
}
base_weights = base_weights_matrix.get(market_type, [1.0] * 10)
# 🔥 根据预测收益率动态调整权重
adjustment_factors = [1.0] * 10
# 预测收益率的强度
return_strength = abs(predicted_return)
return_direction = 1 if predicted_return > 0 else -1
if return_strength > 0.02: # 强预测信号 > 2%
if return_direction > 0: # 预测上涨
adjustment_factors[0] *= 1.3 # 增强趋势权重
adjustment_factors[2] *= 1.2 # 增强MACD权重
adjustment_factors[4] *= 1.15 # 增强相对成交量权重
adjustment_factors[1] *= 0.9 # 降低RSI权重
else: # 预测下跌
adjustment_factors[1] *= 1.3 # 增强RSI权重
adjustment_factors[3] *= 1.2 # 增强成交量权重
adjustment_factors[0] *= 0.9 # 降低趋势权重
elif return_strength > 0.01: # 中等预测信号 1%-2%
if return_direction > 0:
adjustment_factors[0] *= 1.15
adjustment_factors[2] *= 1.1
else:
adjustment_factors[1] *= 1.15
adjustment_factors[3] *= 1.1
# 波动性调整
if return_strength > 0.03: # 高波动预期 > 3%
adjustment_factors[4] *= 1.2 # 增强相对成交量权重
adjustment_factors[6] *= 1.15 # 增强sniper权重
adjustment_factors[7] *= 1.1 # 增强blocks权重
# 生成最终动态权重
dynamic_weights = [base_weights[i] * adjustment_factors[i] for i in range(10)]
# 权重标准化(可选)
# total_weight = sum(dynamic_weights)
# dynamic_weights = [w / total_weight * 10 for w in dynamic_weights]
return dynamic_weights
========== 智能得分计算系统 ==========
class SmartScoringSystem: def init(self): self.return_predictor = ReturnPredictor() self.weight_generator = DynamicWeightGenerator() self.is_model_trained = False
def calculate_score(self, indicators, market_type, features=None):
"""计算交易得分(使用预测收益率的动态权重)"""
if indicators is None:
return 50.0
try:
# 🔥 核心逻辑:使用当前指标预测下期收益率
if self.is_model_trained and features is not None:
predicted_return = self.return_predictor.predict(features)[0, 0]
else:
predicted_return = 0.0
Log(f"📊 使用基础权重计算")
# 根据预测收益率生成动态权重
dynamic_weights = self.weight_generator.generate_weights_from_predicted_return(
predicted_return, market_type)
# 获取最新指标值
trend = indicators['trend'][-1]
rsi_val = indicators['rsi_val'][-1]
macd = indicators['macd'][-1]
signal_line = indicators['signal_line'][-1]
volume = indicators['volumes'][-1]
vol_abs_thresh = indicators['vol_abs_thresh'][-1]
sma_vol20 = indicators['sma_vol20'][-1]
rvol = indicators['rvol'][-1]
delta = indicators['delta'][-1]
sniper_thresh = indicators['sniper_thresh']
pattern = indicators['pattern'][-1]
# 计算各项得分
base_score = 0.0
# 1. 趋势得分
trend_score = 20 if trend == 1 else (-20 if trend == -1 else 0)
base_score += trend_score * dynamic_weights[0]
# 2. RSI得分
rsi_score = -10 if rsi_val > 70 else (10 if rsi_val < 30 else 0)
base_score += rsi_score * dynamic_weights[1]
# 3. MACD得分
macd_score = 10 if macd > signal_line else -10
base_score += macd_score * dynamic_weights[2]
# 4. 成交量得分
vol_score = 8 if volume > vol_abs_thresh else (-8 if volume < sma_vol20 else 0)
base_score += vol_score * dynamic_weights[3]
# 5. 相对成交量得分
rvol_score = 7 if rvol > 1.5 else (-7 if rvol < 0.8 else 0)
base_score += rvol_score * dynamic_weights[4]
# 6. Delta得分
delta_score = 6 if delta > 0 else -6
base_score += delta_score * dynamic_weights[5]
# 7. Sniper得分
sniper_score = 8 if volume > sniper_thresh else (-8 if volume < sma_vol20 else 0)
base_score += sniper_score * dynamic_weights[6]
# 8. Blocks得分
if len(indicators['volumes']) >= 10:
highest_vol = np.max(indicators['volumes'][-10:])
blocks_score = 5 if volume > highest_vol * 0.8 else (-5 if volume < sma_vol20 else 0)
else:
blocks_score = 0
base_score += blocks_score * dynamic_weights[7]
# 9. Tick得分
tick_score = 5 if volume > sma_vol20 else -5
base_score += tick_score * dynamic_weights[8]
# 10. 形态得分
pattern_score = 7 if pattern == 1 else (5 if pattern == 2 else 0)
base_score += pattern_score * dynamic_weights[9]
# 转换为百分比得分
score_pct = max(0, min(100, 50 + base_score))
return score_pct
except Exception as e:
Log(f"得分计算异常: {str(e)}")
return 50.0
def train_return_predictor(self, X, y):
"""训练收益率预测器"""
if len(X) < 20:
Log("训练数据不足,跳过收益率预测器训练")
return False
X_array = np.array(X)
y_array = np.array(y).reshape(-1, 1)
Log(f"🧠 开始训练收益率预测器,样本数: {len(X_array)}")
Log(f"📊 收益率范围: [{np.min(y_array)*100:.3f}%, {np.max(y_array)*100:.3f}%]")
self.return_predictor.train(X_array, y_array, epochs=100)
self.is_model_trained = True
# 验证模型预测效果
predictions = self.return_predictor.predict(X_array)
mse = np.mean((predictions - y_array) ** 2)
correlation = np.corrcoef(predictions.flatten(), y_array.flatten())[0, 1]
Log(f"✅ 收益率预测器训练完成")
Log(f"📈 MSE: {mse:.6f}, 相关系数: {correlation:.4f}")
return True
========== 动态参数管理器 ==========
class DynamicParameterManager: def init(self): self.market_params = { “Bull”: {“stop_loss”: 0.02, “take_profit”: 0.05}, “Bear”: {“stop_loss”: 0.02, “take_profit”: 0.05}, “Eagle”: {“stop_loss”: 0.015, “take_profit”: 0.06}, “Wolf”: {“stop_loss”: 0.025, “take_profit”: 0.04}, “Momentum”: {“stop_loss”: 0.025, “take_profit”: 0.06}, “Sideways”: {“stop_loss”: 0.01, “take_profit”: 0.02}, “Volatile”: {“stop_loss”: 0.03, “take_profit”: 0.07}, “Unknown”: {“stop_loss”: 0.02, “take_profit”: 0.03} }
def get_params(self, market_type):
return self.market_params.get(market_type, self.market_params["Unknown"])
========== 主策略类 ==========
class PredictiveNeuralTradingStrategy: def init(self): self.data_buffer = deque(maxlen=200) self.feature_buffer = deque(maxlen=100) self.label_buffer = deque(maxlen=100) # 存储收益率标签 self.scoring_system = SmartScoringSystem() self.param_manager = DynamicParameterManager()
# 训练控制
self.last_retrain_time = 0
self.retrain_interval = 3600 * 6 # 6小时重新训练
self.min_train_samples = 30
# 交易状态
self.POSITION_NONE = 0
self.POSITION_LONG = 1
self.POSITION_SHORT = 2
self.position_state = self.POSITION_NONE
# 交易记录
self.open_price = 0
self.counter = {'win': 0, 'loss': 0}
# K线数据管理
self.last_processed_time = 0
def get_current_position(self):
"""获取当前期货持仓状态"""
try:
positions = exchange.GetPosition()
if not positions:
return self.POSITION_NONE, 0
long_amount = 0
short_amount = 0
for pos in positions:
amount = pos.get('Amount', 0)
pos_type = pos.get('Type', -1)
if amount > 0:
if pos_type == 0: # 多仓
long_amount += amount
elif pos_type == 1: # 空仓
short_amount += amount
net_position = long_amount - short_amount
if net_position > 0:
return self.POSITION_LONG, net_position
elif net_position < 0:
return self.POSITION_SHORT, abs(net_position)
else:
return self.POSITION_NONE, 0
except Exception as e:
Log(f"获取持仓异常: {str(e)}")
return self.POSITION_NONE, 0
def collect_data(self, records):
"""收集数据并生成训练样本"""
if not records or len(records) < 55:
return False
# 检查是否有新的已完成K线
if len(records) > 1:
latest_completed = records[-2]
current_time = latest_completed['Time']
# 如果这根K线已经处理过,跳过
if current_time <= self.last_processed_time:
return False
self.last_processed_time = current_time
# 添加已完成的K线到缓冲区
completed_records = records[:-1] if len(records) > 1 else []
if completed_records:
self.data_buffer.extend(completed_records[-5:])
# 🔥 生成训练样本:X[t] -> y[t+1]
if len(self.data_buffer) >= 2:
# 使用倒数第二条记录作为特征,最后一条记录计算收益率标签
buffer_list = list(self.data_buffer)
# 计算t-1时刻的指标作为特征
feature_records = buffer_list[:-1] if len(buffer_list) > 1 else buffer_list
indicators, features = TechnicalIndicators.calculate_indicators(
feature_records, use_completed_only=False)
if indicators is not None and features is not None:
# 计算t时刻相对于t-1时刻的收益率作为标签
if len(buffer_list) >= 2:
current_close = buffer_list[-1]['Close']
previous_close = buffer_list[-2]['Close']
if previous_close > 0:
return_rate = (current_close - previous_close) / previous_close
# 添加到训练集
self.feature_buffer.append(features[0])
self.label_buffer.append(return_rate)
Log(f"📈 新样本: 收益率={return_rate*100:.3f}%, 特征维度={features.shape}")
return True
def should_retrain(self):
"""判断是否需要重新训练"""
import time
current_time = time.time()
return (current_time - self.last_retrain_time > self.retrain_interval and
len(self.feature_buffer) >= self.min_train_samples)
def train_model(self):
"""训练收益率预测器"""
if len(self.feature_buffer) < self.min_train_samples:
Log("训练数据不足,跳过训练")
return False
X = list(self.feature_buffer)
y = list(self.label_buffer)
success = self.scoring_system.train_return_predictor(X, y)
if success:
import time
self.last_retrain_time = time.time()
return success
def get_trading_signals(self, records):
"""获取交易信号"""
# 计算当前时刻的技术指标
indicators, features = TechnicalIndicators.calculate_indicators(
list(self.data_buffer), use_completed_only=False)
if indicators is None:
return 50.0, "Unknown"
# 检测市场类型
market_type = MarketStateDetector.detect_market_type(indicators)
# 🔥 使用预测收益率的动态权重计算得分
score = self.scoring_system.calculate_score(indicators, market_type, features)
return score, market_type
def check_entry_conditions(self, score, market_type):
"""检查开仓条件"""
# 多头条件
long_condition = ((market_type in ["Bull", "Eagle", "Momentum"]) and score > 65)
# 空头条件
short_condition = ((market_type in ["Bear", "Wolf"]) and score < 35)
return long_condition, short_condition
def open_long(self):
"""开多仓"""
try:
ticker = exchange.GetTicker()
if not ticker:
return False
buy_price = ticker['Last'] + 20
order_id = exchange.CreateOrder("", "buy", buy_price, AmountOP)
if order_id:
Sleep(2000)
order_info = exchange.GetOrder(order_id)
if order_info and order_info.get('Status') == 1:
self.open_price = order_info.get('AvgPrice', buy_price)
self.position_state = self.POSITION_LONG
Log(f"🚀 开多仓成功: 价格={self.open_price}, 数量={AmountOP}")
return True
else:
exchange.CancelOrder(order_id)
Log("开多仓订单未完全成交,已取消")
return False
except Exception as e:
Log(f"开多仓异常: {str(e)}")
return False
def open_short(self):
"""开空仓"""
try:
ticker = exchange.GetTicker()
if not ticker:
return False
sell_price = ticker['Last'] - 20
order_id = exchange.CreateOrder("", "sell", sell_price, AmountOP)
if order_id:
Sleep(2000)
order_info = exchange.GetOrder(order_id)
if order_info and order_info.get('Status') == 1:
self.open_price = order_info.get('AvgPrice', sell_price)
self.position_state = self.POSITION_SHORT
Log(f"🎯 开空仓成功: 价格={self.open_price}, 数量={AmountOP}")
return True
else:
exchange.CancelOrder(order_id)
Log("开空仓订单未完全成交,已取消")
return False
except Exception as e:
Log(f"开空仓异常: {str(e)}")
return False
def close_position(self):
"""平仓"""
try:
positions = exchange.GetPosition()
if not positions:
Log("没有持仓需要平仓")
self.position_state = self.POSITION_NONE
self.open_price = 0
return True
ticker = exchange.GetTicker()
if not ticker:
return False
close_success = True
for pos in positions:
if pos['Amount'] == 0:
continue
amount = pos['Amount']
pos_type = pos['Type']
if pos_type == 0: # 平多仓
close_price = ticker['Last'] - 20
order_id = exchange.CreateOrder("", "closebuy", close_price, amount)
Log(f"📤 平多仓: 价格={close_price}, 数量={amount}")
elif pos_type == 1: # 平空仓
close_price = ticker['Last'] + 20
order_id = exchange.CreateOrder("", "closesell", close_price, amount)
Log(f"📤 平空仓: 价格={close_price}, 数量={amount}")
if order_id:
Sleep(2000)
order_info = exchange.GetOrder(order_id)
if order_info and order_info.get('Status') == 1:
close_price = order_info.get('AvgPrice', close_price)
Log(f"✅ 平仓成功: 成交价格={close_price}")
self.update_profit_stats(close_price)
else:
exchange.CancelOrder(order_id)
close_success = False
Log(f"平仓订单未完全成交,已取消")
else:
close_success = False
Log("平仓订单创建失败")
if close_success:
self.position_state = self.POSITION_NONE
self.open_price = 0
return close_success
except Exception as e:
Log(f"平仓异常: {str(e)}")
return False
def update_profit_stats(self, close_price):
"""更新盈亏统计"""
if self.open_price == 0:
return
if self.position_state == self.POSITION_LONG:
if close_price > self.open_price:
self.counter['win'] += 1
Log("💰 多仓盈利")
else:
self.counter['loss'] += 1
Log("💸 多仓亏损")
elif self.position_state == self.POSITION_SHORT:
if close_price < self.open_price:
self.counter['win'] += 1
Log("💰 空仓盈利")
else:
self.counter['loss'] += 1
Log("💸 空仓亏损")
def check_stop_loss_take_profit(self, current_price, params):
"""检查止损止盈并执行平仓"""
if self.open_price == 0 or self.position_state == self.POSITION_NONE:
return False
stop_loss_pct = params["stop_loss"]
take_profit_pct = params["take_profit"]
if self.position_state == self.POSITION_LONG:
profit_pct = (current_price - self.open_price) / self.open_price
if profit_pct <= -stop_loss_pct:
Log(f"🔴 多仓止损触发: 开仓价={self.open_price:.2f}, 当前价={current_price:.2f}, 亏损={profit_pct:.4f}")
return self.execute_close_position("止损")
elif profit_pct >= take_profit_pct:
Log(f"🟢 多仓止盈触发: 开仓价={self.open_price:.2f}, 当前价={current_price:.2f}, 盈利={profit_pct:.4f}")
return self.execute_close_position("止盈")
elif self.position_state == self.POSITION_SHORT:
profit_pct = (self.open_price - current_price) / self.open_price
if profit_pct <= -stop_loss_pct:
Log(f"🔴 空仓止损触发: 开仓价={self.open_price:.2f}, 当前价={current_price:.2f}, 亏损={profit_pct:.4f}")
return self.execute_close_position("止损")
elif profit_pct >= take_profit_pct:
Log(f"🟢 空仓止盈触发: 开仓价={self.open_price:.2f}, 当前价={current_price:.2f}, 盈利={profit_pct:.4f}")
return self.execute_close_position("止盈")
return False
def execute_close_position(self, reason):
"""执行平仓操作(专门用于止盈止损)"""
try:
positions = exchange.GetPosition()
if not positions:
Log(f"{reason}平仓: 没有持仓")
self.position_state = self.POSITION_NONE
self.open_price = 0
return True
ticker = exchange.GetTicker()
if not ticker:
Log(f"{reason}平仓失败: 无法获取ticker")
return False
Log(f"🚨 执行{reason}平仓操作...")
close_success = True
for pos in positions:
if pos['Amount'] == 0:
continue
amount = pos['Amount']
pos_type = pos['Type']
order_id = None
if pos_type == 0: # 平多仓
close_price = ticker['Last'] - 50
order_id = exchange.CreateOrder("", "closebuy", close_price, amount)
Log(f"📤 {reason}平多仓订单: 价格={close_price}, 数量={amount}")
elif pos_type == 1: # 平空仓
close_price = ticker['Last'] + 50
order_id = exchange.CreateOrder("", "closesell", close_price, amount)
Log(f"📤 {reason}平空仓订单: 价格={close_price}, 数量={amount}")
if order_id:
Log(f"📋 {reason}平仓订单ID: {order_id}")
Sleep(1500)
for retry in range(2):
order_info = exchange.GetOrder(order_id)
if order_info:
status = order_info.get('Status', -1)
if status == 1:
close_price = order_info.get('AvgPrice', close_price)
Log(f"✅ {reason}平仓成功: 成交价格={close_price}")
self.update_profit_stats(close_price)
break
elif status == 0:
if retry == 0:
Log(f"⏳ {reason}平仓订单执行中,等待...")
Sleep(1500)
else:
Log(f"⚠️ {reason}平仓订单未完全成交,强制取消")
exchange.CancelOrder(order_id)
close_success = False
else:
Log(f"❌ {reason}平仓订单状态异常: {status}")
exchange.CancelOrder(order_id)
close_success = False
break
else:
Log(f"⚠️ 无法获取{reason}平仓订单信息,重试 {retry+1}/2")
if retry == 1:
close_success = False
else:
Log(f"❌ {reason}平仓订单创建失败")
close_success = False
if close_success:
Sleep(1000)
new_positions = exchange.GetPosition()
total_amount = sum(pos['Amount'] for pos in new_positions) if new_positions else 0
if total_amount == 0:
Log(f"✅ {reason}平仓完成,持仓已清零")
self.position_state = self.POSITION_NONE
self.open_price = 0
return True
else:
Log(f"⚠️ {reason}平仓不完全,剩余持仓: {total_amount}")
return False
else:
Log(f"❌ {reason}平仓失败")
return False
except Exception as e:
Log(f"❌ {reason}平仓异常: {str(e)}")
return False
def execute_trade_logic(self, score, market_type, current_price):
"""执行交易逻辑"""
params = self.param_manager.get_params(market_type)
# 获取当前实际持仓状态
actual_position, position_amount = self.get_current_position()
# 同步内部状态
self.position_state = actual_position
# 先检查止损止盈(最高优先级)
if self.position_state != self.POSITION_NONE:
if self.check_stop_loss_take_profit(current_price, params):
Log("🚨 触发止盈止损,已执行平仓,跳过其他交易信号")
return
# 获取开仓条件
long_condition, short_condition = self.check_entry_conditions(score, market_type)
# 执行交易逻辑
if long_condition and self.position_state <= self.POSITION_NONE:
Log(f"📈 开多仓信号: 市场={market_type}, 预测得分={score:.1f} > 65")
self.open_long()
if short_condition and self.position_state >= self.POSITION_NONE:
Log(f"📉 开空仓信号: 市场={market_type}, 预测得分={score:.1f} < 35")
self.open_short()
if not long_condition and self.position_state > self.POSITION_NONE:
Log(f"📤 平多仓信号: 市场={market_type}, 预测得分={score:.1f}")
self.close_position()
if not short_condition and self.position_state < self.POSITION_NONE:
Log(f"📤 平空仓信号: 市场={market_type}, 预测得分={score:.1f}")
self.close_position()
def CancelPendingOrders(): “”“取消所有挂单”“” while True: orders = exchange.GetOrders() if not orders: break for order in orders: exchange.CancelOrder(order[‘Id’]) Sleep(500)
def main(): global AmountOP, LoopInterval
# 检查初始持仓
initial_positions = exchange.GetPosition()
if initial_positions and any(pos['Amount'] > 0 for pos in initial_positions):
raise Error_AtBeginHasPosition()
# 取消所有挂单
CancelPendingOrders()
# 初始化策略
strategy = PredictiveNeuralTradingStrategy()
Log("🔮 预测型神经网络期货交易策略启动")
LogProfitReset()
# 数据预热期
Log("进入数据预热期...")
warmup_count = 0
warmup_target = 60
while warmup_count < warmup_target:
records = exchange.GetRecords()
if records and len(records) >= 55:
if strategy.collect_data(records):
warmup_count += 1
if warmup_count % 10 == 0:
Log(f"预热进度: {warmup_count}/{warmup_target}")
Sleep(5000)
Log("数据预热完成,开始首次收益率预测器训练...")
strategy.train_model()
# 主交易循环
loop_count = 0
while True:
loop_count += 1
# 获取K线数据
records = exchange.GetRecords()
if not records or len(records) < 55:
Sleep(LoopInterval * 1000)
continue
# 数据处理
data_updated = strategy.collect_data(records)
# 检查是否需要重新训练
if strategy.should_retrain():
Log("🔄 重新训练收益率预测器...")
strategy.train_model()
# 获取交易信号
score, market_type = strategy.get_trading_signals(records)
# 获取当前实时价格
ticker = exchange.GetTicker()
if ticker:
current_price = ticker['Last']
else:
current_price = records[-1]['Close']
# 获取当前参数
params = strategy.param_manager.get_params(market_type)
# 优先检查止损止盈(使用实时价格)
if strategy.position_state != strategy.POSITION_NONE:
if strategy.check_stop_loss_take_profit(current_price, params):
Log("⚡ 触发止盈止损,已执行平仓")
Sleep(LoopInterval * 1000)
continue
# 执行交易逻辑(只在有新数据时执行)
if data_updated:
strategy.execute_trade_logic(score, market_type, current_price)
# 状态显示
pos_state_name = {
strategy.POSITION_NONE: "无仓",
strategy.POSITION_LONG: "多仓",
strategy.POSITION_SHORT: "空仓"
}.get(strategy.position_state, "未知")
data_status = "📊新数据" if data_updated else "⏸️等待"
model_status = "🔮预测" if stra