機械学習:価格動向の予測(1)
 3
3
 1047
1047
 成熟した分類器:サポートベクターマシン(SVM)は、強力で成熟した2値(または多変量)分類アルゴリズムです。株価が上昇するか下落するかを予測することは、典型的な2値分類問題です。
非線形機能: カーネル関数 (RBF カーネルなど) を使用することで、SVM は入力機能間の複雑な非線形関係をキャプチャできます。これは金融市場データにとって非常に重要です。
特徴量駆動型:モデルの有効性は、入力する「特徴量」に大きく依存します。現在算出されているアルファ係数は良いスタートであり、今後同様の特徴量をさらに構築することで予測力を向上させることができます。
今回は、3 つの機能の概要から始めました。
1:高頻度注文フローの特性:
alpha_1min: 過去 1 分間のすべてのティックに基づいて計算された注文フローの不均衡係数。
alpha_5min: 過去 5 分間のすべてのティックに基づいて計算された注文フローの不均衡係数。
alpha_15min: 過去 15 分間のすべてのティックに基づいて計算された注文フロー不均衡係数。
ofi_1min(注文フロー不均衡):1分間の(買い数量 / 売り数量)比率。アルファよりも直接的な指標です。
vol_per_trade_1min: 1分間の取引あたりの平均出来高。市場に影響を与える大口注文の兆候です。
成熟した分類器:サポートベクターマシン(SVM)は、強力で成熟した2値(または多変量)分類アルゴリズムです。株価が上昇するか下落するかを予測することは、典型的な2値分類問題です。
非線形機能: カーネル関数 (RBF カーネルなど) を使用することで、SVM は入力機能間の複雑な非線形関係をキャプチャできます。これは金融市場データにとって非常に重要です。
特徴量駆動型:モデルの有効性は、入力する「特徴量」に大きく依存します。現在算出されているアルファ係数は良いスタートであり、今後同様の特徴量をさらに構築することで予測力を向上させることができます。
今回は、3 つの機能の概要から始めました。
1:高頻度注文フローの特性:
alpha_1min: 過去 1 分間のすべてのティックに基づいて計算された注文フローの不均衡係数。
alpha_5min: 過去 5 分間のすべてのティックに基づいて計算された注文フローの不均衡係数。
alpha_15min: 過去 15 分間のすべてのティックに基づいて計算された注文フロー不均衡係数。
ofi_1min(注文フロー不均衡):1分間の(買い数量 / 売り数量)比率。アルファよりも直接的な指標です。
vol_per_trade_1min: 1分間の取引あたりの平均出来高。市場に影響を与える大口注文の兆候です。
2: 価格とボラティリティの特性: log_return_5min: 過去 5 分間の対数リターン率、log(Pt / P{t-5min})。 volatility_15min: 過去 15 分間のログ リターンの標準偏差。短期的なボラティリティの尺度です。 atr_14 (平均真の範囲): 過去 14 本の 1 分間のローソク足に基づく ATR 値。典型的なボラティリティ指標です。 rsi_14 (相対力指数): これは、過去 14 本の 1 分ローソク足の RSI 値に基づいて、買われすぎと売られすぎの状態を測る指標です。
3: 時間特性: hour_of_day: 現在の時間(0~23)。市場の動きは時間帯によって異なります(例:アジア/ヨーロッパ/アメリカ)。 day_of_week: 曜日(0~6)。週末と平日では変動パターンが異なります。
def calculate_features_and_labels(klines):
"""
核心函数
"""
features = []
labels = []
# 为了计算RSI等指标,我们需要价格序列
close_prices = [k['close'] for k in klines]
# 从第30根K线开始,因为需要足够的前置数据
for i in range(30, len(klines) - PREDICT_HORIZON):
# 1. 价格与波动率特征
price_change_15m = (klines[i]['close'] - klines[i-15]['close']) / klines[i-15]['close']
volatility_30m = np.std(close_prices[i-30:i])
# 计算RSI
diffs = np.diff(close_prices[i-14:i+1])
gains = np.sum(diffs[diffs > 0]) / 14
losses = -np.sum(diffs[diffs < 0]) / 14
rs = gains / (losses + 1e-10)
rsi_14 = 100 - (100 / (1 + rs))
# 2. 时间特征
dt_object = datetime.fromtimestamp(klines[i]['ts'] / 1000)
hour_of_day = dt_object.hour
day_of_week = dt_object.weekday()
# 组合所有特征
current_features = [price_change_15m, volatility_30m, rsi_14, hour_of_day, day_of_week]
features.append(current_features)
# 3. 数据标注
future_price = klines[i + PREDICT_HORIZON]['close']
current_price = klines[i]['close']
if future_price > current_price * (1 + SPREAD_THRESHOLD):
labels.append(0) # 涨
elif future_price < current_price * (1 - SPREAD_THRESHOLD):
labels.append(1) # 跌
else:
labels.append(2) # 横盘
次に、3 つのカテゴリを使用して、上昇、下降、横ばいを区別します。
機能スクリーニングの核となる考え方:「良いチームメイト」を見つけ、「悪いチームメイト」を排除する
私たちの目標は、次のような一連の機能を見つけることです。
- 高い関連性: 各機能は、将来の価格変動 (ターゲット ラベル) と強い相関関係があります。
- 冗長性が低い:特徴量には重複する情報が多すぎないようにしてください。例えば、「5分モメンタム」と「6分モメンタム」は非常に類似しています。両方を含めてもモデルの改善にはつながりにくく、ノイズが生じる可能性があります。
- 安定性:機能の有効性は、時間の経過とともに急速に変化してはなりません。1日だけ有効な機能は危険です。
def run_analysis_report(X, y, clf, scaler):
Log("--- 模型分析报告 ---", "info")
Log("1. 特征重要性 (代理模型: 随机森林):")
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=50, random_state=42); rf.fit(X, y)
importances = sorted(zip(g_feature_names, rf.feature_importances_), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for name, importance in importances: Log(f" - {name}: {importance:.4f}")
Log("2. 特征与标签的互信息:"); mi_scores = mutual_info_classif(X, y)
mi_scores = sorted(zip(g_feature_names, mi_scores), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for name, score in mi_scores: Log(f" - {name}: {score:.4f}")
Log("3. 历史数据回测表现:"); y_pred = clf.predict(scaler.transform(X)); accuracy = accuracy_score(y, y_pred)
Log(f" - **历史回测总胜率: {accuracy * 100:.2f}%**", "success")
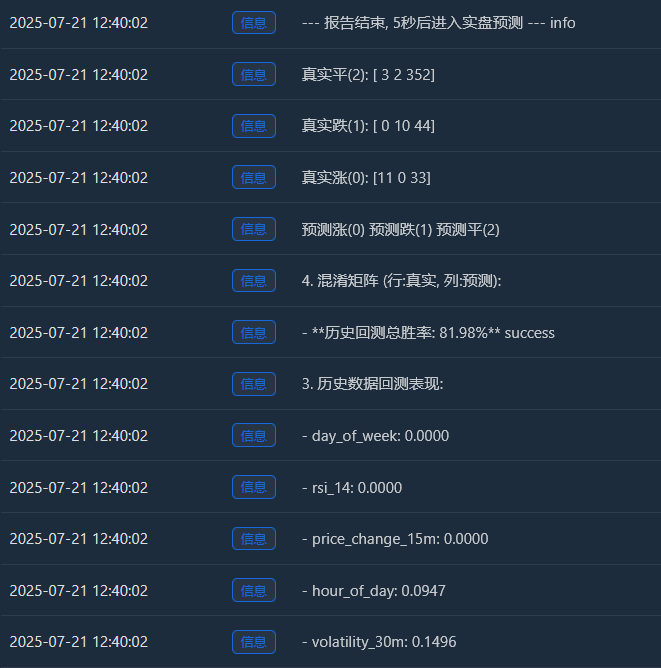
Log("4. 混淆矩阵 (行:真实, 列:预测):"); cm = confusion_matrix(y, y_pred)
Log(" 预测涨(0) 预测跌(1) 预测平(2)"); Log(f"真实涨(0): {cm[0] if len(cm) > 0 else [0,0,0]}")
Log(f"真实跌(1): {cm[1] if len(cm) > 1 else [0,0,0]}"); Log(f"真实平(2): {cm[2] if len(cm) > 2 else [0,0,0]}")
profit_chart = Chart({'title': {'text': f'历史回测净值曲线 (胜率: {accuracy*100:.2f}%)'}}); profit_chart.reset(); balance = 1
for i in range(len(y)):
if y_pred[i] == y[i] and y[i] != 2: balance *= (1 + 0.01)
elif y_pred[i] != y[i] and y_pred[i] != 2: balance *= (1 - 0.01)
profit_chart.add(i, balance)
Log("--- 报告结束, 5秒后进入实盘预测 ---", "info"); Sleep(5000)
プロセスは次のとおりです。
データの収集
 機能の重要度
機能の重要度
 特徴とラベル間の相互情報量とバックテスト情報
特徴とラベル間の相互情報量とバックテスト情報
当初は勝率65%で十分だと思っていましたが、まさか81.98%に達するとは思いませんでした。最初の反応は「素晴らしいけど、話が良すぎる。何か掘り下げる価値があるはずだ」だったはずです。
1分析レポートの詳細な解釈、レポートの内容を一つ一つ解釈します。
- 特徴量の重要度と相互情報量: Volatility_30mとprice_change_15mが最も重要な特徴です。これは論理的であり、最近の市場動向とボラティリティが将来の最も強力な予測因子であることを示しています。 hour_of_day も少し貢献しており、モデルが一日のさまざまな時間帯の取引パターンを捉えていることを示しています。 rsi_14とday_of_weekの寄与はほぼ0であるため、現在のデータセットと特徴量の組み合わせでは、これら2つの特徴量は「豚のチームメイト」である可能性があります。将来的には、モデルを簡素化し、ノイズを防ぐために、これらを削除することも検討できます。
- 混同マトリックス (これは大量の情報です!) 実質増加額(0):[11 0 33] -> 44回(11+0+33)の実際の上昇のうち、モデルは11回を正しく予測しましたが、33回は「統合」と誤って予測しました。 実質ドロップ(1):[0 10 44] -> 54 回 (0+10+44) の実際の下落のうち、モデルは 10 回を正しく予測しましたが、44 回は「統合」と誤って予測しました。 リアルピン(2)[3 2 352] -> 357 (3+2+352) 件の実際の統合のうち、モデルは 352 件を正しく予測しました。
- 過去のバックテストの総勝率: 81.98% この高い勝率の根幹は、モデルが「統合」を予測する極めて高い精度にあります。合計約455のサンプルのうち、350以上が統合市場であり、モデルはそれらをほぼ完璧に特定しました。 これ自体が非常に貴重な能力です!「今は動かない方が良い」と正確に判断できるモデルがあれば、多くの手数料や無効な取引を節約できます。
2実際の勝率が 81.98% より低くなるのはなぜでしょうか?
- 「統合」の定義が緩すぎます。SPREAD_THRESHOLDは0.5%です。15分以内の価格変動が0.5%以下というのはよくあることです。その結果、「統合」サンプルがデータセットの大部分(約80%)を占めています。モデルは「確信が持てないときは、『統合』を高い精度で推測する」と巧みに学習しました。これは統計的には正しいのですが、取引においては価格変動の予測の方が重要です。
- 上昇と下降を予測する能力: 上昇トレンド予測の勝率:モデルは11 + 0 + 3 = 14個の上昇トレンドを予測しましたが、そのうち正しく予測できたのは11個だけでした。勝率は11 / 14 = 78.5%です。素晴らしい! 下落予測の勝率:モデルは0 + 10 + 2 = 12回の下落を予測し、そのうち10回は正しかった。勝率は10 / 12 = 83.3%。これもまた、非常に印象的です!
- インサンプル・オーバーフィッティング:このテストは、モデルにとって「既知」のデータ(つまり、トレーニングとテストに使用されたデータ)に対して実行されます。これは、生徒に直前に完了したテストを解かせるようなものです。通常、スコアは高くなります。一方、新しい未知のデータ(実際の取引データ)に対するモデルのパフォーマンスは、ほぼ常にこのスコアよりも低くなります。
予備的ではあるものの、潜在的に巨大な「アルファモデル」が完成しました。81.98%という数字を将来の現実的な予測として直接解釈することはできませんが、これはデータの中に予測可能なパターンが存在し、私たちのフレームワークがそれをうまく捉えていることを示す、非常に前向きなシグナルです。 まるで山の麓で初めて良質の金鉱石を見つけたかのような気分です。次のステップは、すぐに販売するのではなく、より専門的なツールと技術(機能の最適化とパラメータの調整)を用いて、山全体をより効率的かつ安定的に採掘することです。
それでは、「縮図」における戦場の霧、つまり注文フローと注文帳の特徴を紹介しましょう。 ステップ1: データ収集をアップグレードする - より深いチャネルを購読する 注文簿データを取得するには、WebSocket 接続方法を、aggTrade (取引) のみをサブスクライブする方法から、aggTrade と depth (深さ) の両方をサブスクライブする方法に変更する必要があります。 これには、より一般的なマルチストリーム サブスクリプション URL を使用する必要があります。 ステップ2: 特徴エンジニアリングのアップグレード - 「海、陸、空」の3つの特徴マトリックスを構築する calculate_features_and_labels 関数に次の新しい機能を追加します。
- 注文フロー特性(アルファ - ショート): alpha_15m: 15分間の注文フロー不均衡係数。これは、先ほど説明した注文フローのコア指標です。
- 注文書の特性 (注文書 - 陸軍): wobi_10s: 過去10秒間の加重注文板不均衡。これは市場における売買圧力を測定する非常に高頻度の指標です。 spread_10s: 過去10秒間の平均ビッド・アスク・スプレッド。短期的な流動性を反映しています。
- オリジナル特性(価格 - ネイビー): 以前のバージョンから最もパフォーマンスが良かった機能をそのまま維持し、最適化していきます。
この新しい機能マトリックスは、統合戦闘司令部のようなもので、「海(価格動向)」「陸(市場ポジション)」「空(取引影響)」からのリアルタイム情報を同時に把握し、その意思決定能力は従来よりもはるかに優れています。 コードは次のとおりです。
import json
import math
import time
import websocket
import threading
from datetime import datetime
import numpy as np
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score
from sklearn.feature_selection import mutual_info_classif
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# ========== 全局配置 ==========
TRAIN_BARS = 100
PREDICT_HORIZON = 15
SPREAD_THRESHOLD = 0.005
SYMBOL_FMZ = "ETH_USDT"
SYMBOL_API = SYMBOL_FMZ.replace('_', '').lower()
WEBSOCKET_URL = f"wss://fstream.binance.com/stream?streams={SYMBOL_API}@aggTrade/{SYMBOL_API}@depth20@100ms"
# ========== 全局状态变量 ==========
g_model, g_scaler = None, None
g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history = [], [], []
g_last_kline_ts = 0
g_feature_names = ['price_change_15m', 'volatility_30m', 'rsi_14', 'hour_of_day',
'alpha_15m', 'wobi_10s', 'spread_10s']
# ========== 特征工程与模型训练 ==========
def calculate_features_and_labels(klines, ticks, order_books_history, is_realtime=False):
features, labels = [], []
close_prices = [k['close'] for k in klines]
# 根据是训练还是实时预测,决定循环范围
start_index = 30
end_index = len(klines) - PREDICT_HORIZON if not is_realtime else len(klines)
for i in range(start_index, end_index):
kline_start_ts = klines[i]['ts']
# --- 特征计算部分 ---
price_change_15m = (klines[i]['close'] - klines[i-15]['close']) / klines[i-15]['close']
volatility_30m = np.std(close_prices[i-30:i])
diffs = np.diff(close_prices[i-14:i+1]); gains = np.sum(diffs[diffs > 0]) / 14; losses = -np.sum(diffs[diffs < 0]) / 14
rsi_14 = 100 - (100 / (1 + gains / (losses + 1e-10)))
dt_object = datetime.fromtimestamp(kline_start_ts / 1000)
ticks_in_15m = [t for t in ticks if t['ts'] >= klines[i-15]['ts'] and t['ts'] < kline_start_ts]
buy_vol = sum(t['qty'] for t in ticks_in_15m if t['side'] == 'buy'); sell_vol = sum(t['qty'] for t in ticks_in_15m if t['side'] == 'sell')
alpha_15m = (buy_vol - sell_vol) / (buy_vol + sell_vol + 1e-10)
books_in_10s = [b for b in order_books_history if b['ts'] >= kline_start_ts - 10000 and b['ts'] < kline_start_ts]
if not books_in_10s: wobi_10s, spread_10s = 0, 0.0
else:
wobis, spreads = [], []
for book in books_in_10s:
if not book['bids'] or not book['asks']: continue
bid_vol = sum(float(p[1]) for p in book['bids']); ask_vol = sum(float(p[1]) for p in book['asks'])
wobis.append(bid_vol / (bid_vol + ask_vol + 1e-10))
spreads.append(float(book['asks'][0][0]) - float(book['bids'][0][0]))
wobi_10s = np.mean(wobis) if wobis else 0; spread_10s = np.mean(spreads) if spreads else 0
current_features = [price_change_15m, volatility_30m, rsi_14, dt_object.hour, alpha_15m, wobi_10s, spread_10s]
features.append(current_features)
# --- 标签计算部分 ---
if not is_realtime:
future_price = klines[i + PREDICT_HORIZON]['close']; current_price = klines[i]['close']
if future_price > current_price * (1 + SPREAD_THRESHOLD): labels.append(0)
elif future_price < current_price * (1 - SPREAD_THRESHOLD): labels.append(1)
else: labels.append(2)
return np.array(features), np.array(labels)
def run_analysis_report(X, y, clf, scaler):
Log("--- 模型分析报告 ---", "info")
Log("1. 特征重要性 (代理模型: 随机森林):")
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=50, random_state=42); rf.fit(X, y)
importances = sorted(zip(g_feature_names, rf.feature_importances_), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for name, importance in importances: Log(f" - {name}: {importance:.4f}")
Log("2. 特征与标签的互信息:"); mi_scores = mutual_info_classif(X, y)
mi_scores = sorted(zip(g_feature_names, mi_scores), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for name, score in mi_scores: Log(f" - {name}: {score:.4f}")
Log("3. 历史数据回测表现:"); y_pred = clf.predict(scaler.transform(X)); accuracy = accuracy_score(y, y_pred)
Log(f" - **历史回测总胜率: {accuracy * 100:.2f}%**", "success")
Log("4. 混淆矩阵 (行:真实, 列:预测):"); cm = confusion_matrix(y, y_pred)
Log(" 预测涨(0) 预测跌(1) 预测平(2)"); Log(f"真实涨(0): {cm[0] if len(cm) > 0 else [0,0,0]}")
Log(f"真实跌(1): {cm[1] if len(cm) > 1 else [0,0,0]}"); Log(f"真实平(2): {cm[2] if len(cm) > 2 else [0,0,0]}")
profit_chart = Chart({'title': {'text': f'历史回测净值曲线 (胜率: {accuracy*100:.2f}%)'}}); profit_chart.reset(); balance = 1
for i in range(len(y)):
if y_pred[i] == y[i] and y[i] != 2: balance *= (1 + 0.01)
elif y_pred[i] != y[i] and y_pred[i] != 2: balance *= (1 - 0.01)
profit_chart.add(i, balance)
Log("--- 报告结束, 5秒后进入实盘预测 ---", "info"); Sleep(5000)
def train_and_analyze():
global g_model, g_scaler, g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history
MIN_REQUIRED_BARS = 30 + PREDICT_HORIZON
if len(g_klines_1min) < MIN_REQUIRED_BARS:
Log(f"K线数量({len(g_klines_1min)})不足以进行特征工程,需要至少 {MIN_REQUIRED_BARS} 根。", "warning"); return False
Log("开始训练模型 (V2.2)...")
X, y = calculate_features_and_labels(g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history)
if len(X) < 50 or len(set(y)) < 3:
Log(f"有效训练样本不足(X: {len(X)}, 类别: {len(set(y))}),无法训练。", "warning"); return False
scaler = StandardScaler(); X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
clf = svm.SVC(kernel='rbf', C=1.0, gamma='scale'); clf.fit(X_scaled, y)
g_model, g_scaler = clf, scaler
Log("模型训练完成!", "success")
run_analysis_report(X, y, g_model, g_scaler)
return True
def aggregate_ticks_to_kline(ticks):
if not ticks: return None
return {'ts': ticks[0]['ts'] // 60000 * 60000, 'open': ticks[0]['price'], 'high': max(t['price'] for t in ticks), 'low': min(t['price'] for t in ticks), 'close': ticks[-1]['price'], 'volume': sum(t['qty'] for t in ticks)}
def on_message(ws, message):
global g_ticks, g_klines_1min, g_last_kline_ts, g_order_book_history
try:
payload = json.loads(message)
data = payload.get('data', {}); stream = payload.get('stream', '')
if 'aggTrade' in stream:
trade_data = {'ts': int(data['T']), 'price': float(data['p']), 'qty': float(data['q']), 'side': 'sell' if data['m'] else 'buy'}
g_ticks.append(trade_data)
current_minute_ts = trade_data['ts'] // 60000 * 60000
if g_last_kline_ts == 0: g_last_kline_ts = current_minute_ts
if current_minute_ts > g_last_kline_ts:
last_minute_ticks = [t for t in g_ticks if t['ts'] >= g_last_kline_ts and t['ts'] < current_minute_ts]
if last_minute_ticks:
kline = aggregate_ticks_to_kline(last_minute_ticks); g_klines_1min.append(kline)
g_ticks = [t for t in g_ticks if t['ts'] >= current_minute_ts]
g_last_kline_ts = current_minute_ts
elif 'depth' in stream:
book_snapshot = {'ts': int(data['E']), 'bids': data['b'], 'asks': data['a']}
g_order_book_history.append(book_snapshot)
if len(g_order_book_history) > 5000: g_order_book_history.pop(0)
except Exception as e: Log(f"OnMessage Error: {e}")
def start_websocket():
ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(WEBSOCKET_URL, on_message=on_message)
wst = threading.Thread(target=ws.run_forever); wst.daemon = True; wst.start()
Log("WebSocket多流订阅已启动...")
# ========== 主程序入口 ==========
def main():
global TRAIN_BARS
exchange.SetContractType("swap")
start_websocket()
Log("策略启动,进入数据收集中...")
main.last_predict_ts = 0
while True:
if g_model is None:
# --- 训练模式 ---
if len(g_klines_1min) >= TRAIN_BARS:
if not train_and_analyze():
Log("模型训练或分析失败,将增加50根K线后重试...", "error")
TRAIN_BARS += 50
else:
LogStatus(f"正在收集K线数据: {len(g_klines_1min)} / {TRAIN_BARS}")
else:
# --- **新功能:实时预测模式** ---
if len(g_klines_1min) > 0 and g_klines_1min[-1]['ts'] > main.last_predict_ts:
# 1. 标记已处理,防止重复预测
main.last_predict_ts = g_klines_1min[-1]['ts']
kline_time_str = datetime.fromtimestamp(main.last_predict_ts / 1000).strftime('%H:%M:%S')
Log(f"检测到新K线 ({kline_time_str}),准备进行实时预测...")
# 2. 检查是否有足够历史数据来为这根新K线计算特征
if len(g_klines_1min) < 30: # 至少需要30根历史K线
Log("历史K线不足,无法为当前新K线计算特征。", "warning")
continue
# 3. 计算最新K线的特征
# 我们只计算最后一条数据,所以传入 is_realtime=True
latest_features, _ = calculate_features_and_labels(g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history, is_realtime=True)
if latest_features.shape[0] == 0:
Log("无法为最新K线生成有效特征。", "warning")
continue
# 4. 标准化并预测
last_feature_vector = latest_features[-1].reshape(1, -1)
last_feature_scaled = g_scaler.transform(last_feature_vector)
prediction = g_model.predict(last_feature_scaled)[0]
# 5. 展示预测结果
prediction_text = ['**上涨**', '**下跌**', '盘整'][prediction]
Log(f"==> 实时预测结果 ({kline_time_str}): 未来 {PREDICT_HORIZON} 分钟可能 {prediction_text}", "success" if prediction != 2 else "info")
# 在这里,您可以根据 prediction 的结果,添加您的开平仓交易逻辑
# 例如: if prediction == 0: exchange.Buy(...)
else:
LogStatus(f"模型已就绪,等待新K线... 当前K线数: {len(g_klines_1min)}")
Sleep(1000) # 每秒检查一次是否有新K线
このコードは多くのKライン計算を必要とする このレポートは、モデルの「思想」や「性格」を伝えてくれるので、非常に価値があります。
- 過去のバックテストの総勝率:93.33% これは非常に印象的な数字です!客観的に見る必要がありますが(これはサンプル内テストです)、新たに追加された注文フローと注文帳機能の驚異的な予測力を明確に示しています。モデルは過去のデータに非常に強いパターンを発見しました。
- 特徴重要度と相互情報量 王の誕生: volatility_15m (ボラティリティ) と price_change_5m (価格変動) は依然として絶対的に中核であり、これは予想どおりです。 ライジングスター:rsi_14の重要性が大幅に増加しました!これは、より短い5分足の時間枠において、RSIの「買われ過ぎ/売られ過ぎ」感情指標がより重要になっていることを示しています。 wobi_10s(オーダーブックの不均衡)とspread_10s(スプレッド)も、潜在的に何らかの寄与を示している可能性があります。これは非常に心強い兆候であり、ミクロ構造の機能が機能し始めていることを示唆しています。 考察:alpha_5m(注文フロー)の寄与はほぼゼロです。これは、アルファ計算方法が過度に単純化されていること、あるいは5分アルファと5分価格変動自体に重複する情報が多すぎることが原因である可能性があります。これは、今後の最適化において重要なポイントとなります。
- 混同マトリックス(成功の重要な証拠!) 実質増加額(0):[22 0] -> 実際の 22 回のラリーをすべて、モデルは間違いなく 100% 正確に予測しました。 実質ドロップ(1):[2 6] -> 実際の 8 件の減少のうち、モデルは 6 件を正しく予測し、2 件を見逃しました (増加と間違えました)。 解釈:このモデルは非常に興味深い特性を示します。非常に強力な強気シグナル検出能力を持ち、強気シグナルをほぼ完璧に捉えます。また、弱気トレンドの識別能力も優れています(6/8 = 75%の精度)。しかし、弱気トレンドを上昇トレンドと誤認する誤りが時折見られます。
では次に何が起こるのか 「トレーディングシグナルステートマシン」の紹介 これが今回のアップグレードの核心であり、最も独創的な部分です。戦略の現在の「ポジション」ステータスを管理するために、g_active_signalなどのグローバル状態変数を導入します(これは仮想的なポジションステータスであり、実際の取引には関係しないことに注意してください)。 このステートマシンの動作ロジックは次のとおりです。
- 初期状態: アイドル
- 戦略がこの状態にあるときは、現在と同じように、新しい K ラインごとに予測が行われます。
- レジーム移行: モデルが明確なシグナル(例:「上昇」)を予測すると、戦略は次のようになります。
- 目を引く単一のエントリ シグナルをジャーナルに出力します。例: 🎯 新しい取引シグナル: 予測がアップ! 観測期間 15 分。
- 戦略ステータスをアイドルからインシグナルに切り替えます。 現在の信号のトリガー時間と方向を記録します。
- ポジションステータス: 信号中
- この状態になると、戦略は新たなKラインの予測を完全に停止します。毎分ごとの変動を気にしなくなり、「弾丸を飛ばす」モードに移行します。
- 唯一の処理は時間をチェックすることです。つまり、シグナルがトリガーされてから 15 分 (PREDICT_HORIZON の長さ) が経過したかどうかをチェックします。
- 状態遷移: 15 分間の観察期間後、ポリシーは次のようになります。
- 🏁シグナル期間の終了など、明確な終了シグナルをログに出力します。戦略をリセットし、新たな機会を探します。
- 戦略ステータスを保留からアイドルに切り替えます。
- この時点で、この戦略は再び新しい K ラインの予測を開始し、次の取引機会を探します。
このシンプルなステート マシンにより、1 つの信号、1 つの完全な観測サイクル、期間中の干渉情報なしという要件が完全に達成されました。
import json
import math
import time
import websocket
import threading
from datetime import datetime
import numpy as np
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score
from sklearn.feature_selection import mutual_info_classif
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# ========== 全局配置 ==========
TRAIN_BARS = 200 #需要更多初始数据
PREDICT_HORIZON = 15 # 回归15分钟预测周期
SPREAD_THRESHOLD = 0.005 # 适配15分钟周期的涨跌阈值
SYMBOL_FMZ = "ETH_USDT"
SYMBOL_API = SYMBOL_FMZ.replace('_', '').lower()
WEBSOCKET_URL = f"wss://fstream.binance.com/stream?streams={SYMBOL_API}@aggTrade/{SYMBOL_API}@depth20@100ms"
# ========== 全局状态变量 ==========
g_model, g_scaler = None, None
g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history = [], [], []
g_last_kline_ts = 0
g_feature_names = ['price_change_15m', 'volatility_30m', 'rsi_14', 'hour_of_day',
'alpha_15m', 'wobi_10s', 'spread_10s']
# 新功能: 信号状态机
g_active_signal = {'active': False, 'start_ts': 0, 'prediction': -1}
# ========== 特征工程与模型训练 ==========
def calculate_features_and_labels(klines, ticks, order_books_history, is_realtime=False):
features, labels = [], []
close_prices = [k['close'] for k in klines]
start_index = 30
end_index = len(klines) - PREDICT_HORIZON if not is_realtime else len(klines)
for i in range(start_index, end_index):
kline_start_ts = klines[i]['ts']
price_change_15m = (klines[i]['close'] - klines[i-15]['close']) / klines[i-15]['close']
volatility_30m = np.std(close_prices[i-30:i])
diffs = np.diff(close_prices[i-14:i+1]); gains = np.sum(diffs[diffs > 0]) / 14; losses = -np.sum(diffs[diffs < 0]) / 14
rsi_14 = 100 - (100 / (1 + gains / (losses + 1e-10)))
dt_object = datetime.fromtimestamp(kline_start_ts / 1000)
ticks_in_15m = [t for t in ticks if t['ts'] >= klines[i-15]['ts'] and t['ts'] < kline_start_ts]
buy_vol = sum(t['qty'] for t in ticks_in_15m if t['side'] == 'buy'); sell_vol = sum(t['qty'] for t in ticks_in_15m if t['side'] == 'sell')
alpha_15m = (buy_vol - sell_vol) / (buy_vol + sell_vol + 1e-10)
books_in_10s = [b for b in order_books_history if b['ts'] >= kline_start_ts - 10000 and b['ts'] < kline_start_ts]
if not books_in_10s: wobi_10s, spread_10s = 0, 0.0
else:
wobis, spreads = [], []
for book in books_in_10s:
if not book['bids'] or not book['asks']: continue
bid_vol = sum(float(p[1]) for p in book['bids']); ask_vol = sum(float(p[1]) for p in book['asks'])
wobis.append(bid_vol / (bid_vol + ask_vol + 1e-10))
spreads.append(float(book['asks'][0][0]) - float(book['bids'][0][0]))
wobi_10s = np.mean(wobis) if wobis else 0; spread_10s = np.mean(spreads) if spreads else 0
current_features = [price_change_15m, volatility_30m, rsi_14, dt_object.hour, alpha_15m, wobi_10s, spread_10s]
if not is_realtime:
future_price = klines[i + PREDICT_HORIZON]['close']; current_price = klines[i]['close']
if future_price > current_price * (1 + SPREAD_THRESHOLD):
labels.append(0); features.append(current_features)
elif future_price < current_price * (1 - SPREAD_THRESHOLD):
labels.append(1); features.append(current_features)
else:
features.append(current_features)
return np.array(features), np.array(labels)
def run_analysis_report(X, y, clf, scaler):
Log("--- 模型分析报告 V2.5 (15分钟预测) ---", "info")
Log("1. 特征重要性 (代理模型: 随机森林):")
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=50, random_state=42); rf.fit(X, y)
importances = sorted(zip(g_feature_names, rf.feature_importances_), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for name, importance in importances: Log(f" - {name}: {importance:.4f}")
Log("2. 特征与标签的互信息:"); mi_scores = mutual_info_classif(X, y)
mi_scores = sorted(zip(g_feature_names, mi_scores), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for name, score in mi_scores: Log(f" - {name}: {score:.4f}")
Log("3. 历史数据回测表现:"); y_pred = clf.predict(scaler.transform(X)); accuracy = accuracy_score(y, y_pred)
Log(f" - **历史回测总胜率: {accuracy * 100:.2f}%**", "success")
Log("4. 混淆矩阵 (行:真实, 列:预测):"); cm = confusion_matrix(y, y_pred)
Log(" 预测涨(0) 预测跌(1)"); Log(f"真实涨(0): {cm[0] if len(cm) > 0 else [0,0]}")
Log(f"真实跌(1): {cm[1] if len(cm) > 1 else [0,0]}")
profit_chart = Chart({'title': {'text': f'历史回测净值曲线 (胜率: {accuracy*100:.2f}%)'}}); profit_chart.reset(); balance = 1
for i in range(len(y)):
if y_pred[i] == y[i]: balance *= (1 + 0.01)
else: balance *= (1 - 0.01)
profit_chart.add(i, balance)
Log("--- 报告结束, 5秒后进入实盘预测 ---", "info"); Sleep(5000)
def train_and_analyze():
global g_model, g_scaler, g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history
MIN_REQUIRED_BARS = 30 + PREDICT_HORIZON
if len(g_klines_1min) < MIN_REQUIRED_BARS:
Log(f"K线数量({len(g_klines_1min)})不足以进行特征工程,需要至少 {MIN_REQUIRED_BARS} 根。", "warning"); return False
Log("开始训练模型 (V2.5)...")
X, y = calculate_features_and_labels(g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history)
if len(X) < 20 or len(set(y)) < 2:
Log(f"有效涨跌样本不足(X: {len(X)}, 类别: {len(set(y))}),无法训练。", "warning"); return False
scaler = StandardScaler(); X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
clf = svm.SVC(kernel='rbf', C=1.0, gamma='scale'); clf.fit(X_scaled, y)
g_model, g_scaler = clf, scaler
Log("模型训练完成!", "success")
run_analysis_report(X, y, g_model, g_scaler)
return True
# ========== WebSocket实时数据处理 ==========
def aggregate_ticks_to_kline(ticks):
if not ticks: return None
return {'ts': ticks[0]['ts'] // 60000 * 60000, 'open': ticks[0]['price'], 'high': max(t['price'] for t in ticks), 'low': min(t['price'] for t in ticks), 'close': ticks[-1]['price'], 'volume': sum(t['qty'] for t in ticks)}
def on_message(ws, message):
global g_ticks, g_klines_1min, g_last_kline_ts, g_order_book_history
try:
payload = json.loads(message)
data = payload.get('data', {}); stream = payload.get('stream', '')
if 'aggTrade' in stream:
trade_data = {'ts': int(data['T']), 'price': float(data['p']), 'qty': float(data['q']), 'side': 'sell' if data['m'] else 'buy'}
g_ticks.append(trade_data)
current_minute_ts = trade_data['ts'] // 60000 * 60000
if g_last_kline_ts == 0: g_last_kline_ts = current_minute_ts
if current_minute_ts > g_last_kline_ts:
last_minute_ticks = [t for t in g_ticks if t['ts'] >= g_last_kline_ts and t['ts'] < current_minute_ts]
if last_minute_ticks:
kline = aggregate_ticks_to_kline(last_minute_ticks); g_klines_1min.append(kline)
g_ticks = [t for t in g_ticks if t['ts'] >= current_minute_ts]
g_last_kline_ts = current_minute_ts
elif 'depth' in stream:
book_snapshot = {'ts': int(data['E']), 'bids': data['b'], 'asks': data['a']}
g_order_book_history.append(book_snapshot)
if len(g_order_book_history) > 5000: g_order_book_history.pop(0)
except Exception as e: Log(f"OnMessage Error: {e}")
def start_websocket():
ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(WEBSOCKET_URL, on_message=on_message)
wst = threading.Thread(target=ws.run_forever); wst.daemon = True; wst.start()
Log("WebSocket多流订阅已启动...")
# ========== 主程序入口 ==========
def main():
global TRAIN_BARS, g_active_signal
exchange.SetContractType("swap")
start_websocket()
Log("策略启动 ,进入数据收集中...")
main.last_predict_ts = 0
while True:
if g_model is None:
if len(g_klines_1min) >= TRAIN_BARS:
if not train_and_analyze():
Log(f"模型训练失败,当前目标 {TRAIN_BARS} 根K线。将增加50根后重试...", "error")
TRAIN_BARS += 50
else:
LogStatus(f"正在收集K线数据: {len(g_klines_1min)} / {TRAIN_BARS}")
else:
if not g_active_signal['active']:
if len(g_klines_1min) > 0 and g_klines_1min[-1]['ts'] > main.last_predict_ts:
main.last_predict_ts = g_klines_1min[-1]['ts']
kline_time_str = datetime.fromtimestamp(main.last_predict_ts / 1000).strftime('%H:%M:%S')
if len(g_klines_1min) < 30:
LogStatus("历史K线不足,无法预测。等待更多数据..."); continue
latest_features, _ = calculate_features_and_labels(g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history, is_realtime=True)
if latest_features.shape[0] == 0:
LogStatus(f"({kline_time_str}) 无法生成特征,跳过..."); continue
last_feature_vector = latest_features[-1].reshape(1, -1)
last_feature_scaled = g_scaler.transform(last_feature_vector)
prediction = g_model.predict(last_feature_scaled)[0]
if prediction == 0 or prediction == 1:
g_active_signal['active'] = True
g_active_signal['start_ts'] = main.last_predict_ts
g_active_signal['prediction'] = prediction
prediction_text = ['**上涨**', '**下跌**'][prediction]
Log(f"🎯 新的交易信号 ({kline_time_str}): 预测 {prediction_text}!观察周期 {PREDICT_HORIZON} 分钟。", "success" if prediction == 0 else "error")
else:
LogStatus(f"({kline_time_str}) 无明确信号,继续观察...")
else:
current_ts = time.time() * 1000
elapsed_minutes = (current_ts - g_active_signal['start_ts']) / (1000 * 60)
if elapsed_minutes >= PREDICT_HORIZON:
Log(f"🏁 信号周期结束。重置策略,寻找新机会...", "info")
g_active_signal['active'] = False
else:
prediction_text = ['**上涨**', '**下跌**'][g_active_signal['prediction']]
LogStatus(f"信号生效中: {prediction_text}。剩余观察时间: {PREDICT_HORIZON - elapsed_minutes:.1f} 分钟。")
Sleep(5000)
次にこのコードを実行します
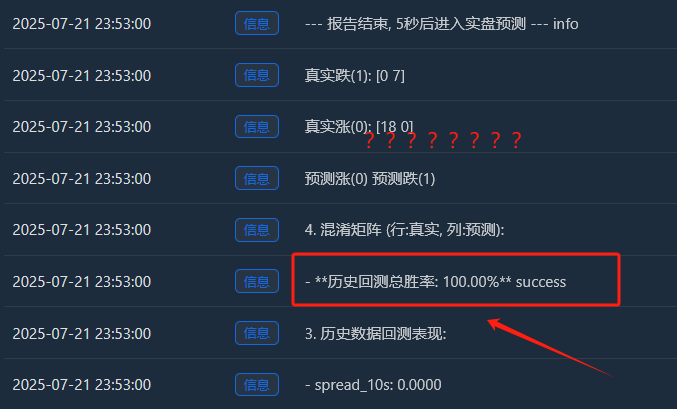 徹底分析:「完璧な」100% の勝率が存在するのはなぜでしょうか?
この「完璧な」結果は、機械学習と金融市場に関するいくつかの重要かつ深遠な洞察を明らかにしています。これはバグではなく、「過剰適合」と呼ばれる典型的な現象であり、特定の条件下で発生する可能性があります。
「過剰適合」とはどういう意味ですか?
徹底分析:「完璧な」100% の勝率が存在するのはなぜでしょうか?
この「完璧な」結果は、機械学習と金融市場に関するいくつかの重要かつ深遠な洞察を明らかにしています。これはバグではなく、「過剰適合」と呼ばれる典型的な現象であり、特定の条件下で発生する可能性があります。
「過剰適合」とはどういう意味ですか?
分かりやすい例え話をしましょう。ある学生(SVMモデル)に、非常に短く簡単な演習(収集した200個のローソク足データポイント)を解かせたとします。この学生は非常に頭が良く、一般的な問題解決法を学ぶ代わりに、これらの問題の答えをただ暗記するだけです。
結果: 同じ練習問題セットでテストすると (これは「過去のバックテスト」です)、彼は確かに 100 点満点を取ることができます。しかし、彼が今まで見たことのないまったく新しい問題セット (実際の先物市場) を与えると、彼はどの問題にも答えられなくなる可能性があります。
- なぜモデルは「過剰適合」するのでしょうか?
トレーニング サンプルが「少なすぎる」かつ「特殊すぎる」:
ログによると、200 本の K ライン (約 3.3 時間) を収集しましたが、定義を満たす「有効な上昇と下降」サンプルの最終的な数は 18 + 7 = 25 のみでした。
複雑な SVM モデルの場合、25 個のサンプルは海の波のようなもので、少なすぎます。
さらに重要なのは、これら25のサンプルはすべて、同じ午後の非常に相関性の高い市場状況から得られたものであることです。これらは非常に類似した「ルーティン」を持っている可能性が高いです。
- モデルの能力が「強すぎる」:
- SVMは非常に強力な非線形分類器です。その能力は、スーパーメモリを備えた脳のようなものです。
- 強力なモデルが単純すぎて反復的なデータセットから学習する場合、そのモデルの背後にあるより普遍的なマクロ法則を学習するのではなく、データのすべての詳細とノイズを「記憶」する傾向があります。
- 混同行列からの証拠:
- 実質増加額(0):[18 0] -> 18 個の上昇サンプル、すべて完璧に記憶されています。
- 実質ドロップ(1):[0 7] -> 7 つの落下サンプル、すべて完璧に記憶されました。
- この完璧な[ [18, 0], [[0, 7]行列は、モデルの過剰適合の明白な証拠です。このモデルはほぼ間違いを犯さず、これはランダム性に満ちた金融市場においては本質的に異常なことです。
したがって、この 100% の勝率は次のように解釈する必要があります。
このモデルは過去3時間で、特定の市場状況におけるあらゆるパターンを驚くほど巧みに学習し、記憶しました。これは、当社の特徴量エンジニアリングとモデルフレームワークの有効性を示しています。しかし、将来的にも現実の市場でこれほど高い勝率を維持できるとは到底期待できません。これは「大学入試」の最終結果というより、むしろ完璧な「抜き打ちテスト」のようなものです。
機械学習も最近私が研究している分野です。次号でそれについてお話します。 この「偏見を持つ生徒」に対しては、徹底的な「思考転換」を行う必要があります。私たちの目標は、彼または彼女の偏見を打ち破り、「良い点と悪い点」を公平かつ客観的に捉えられるようにすることです。