Thảo luận về Phương pháp kiểm tra chiến lược dựa trên Trình tạo thị trường ngẫu nhiên
 0
0
 880
880
[TOC]

Lời nói đầu
Hệ thống kiểm thử ngược của Inventor Quantitative Trading Platform là hệ thống kiểm thử ngược liên tục lặp lại, cập nhật và nâng cấp. Từ các chức năng kiểm thử ngược cơ bản ban đầu, dần dần bổ sung các chức năng và tối ưu hóa hiệu suất. Khi nền tảng phát triển, hệ thống kiểm thử ngược sẽ tiếp tục được tối ưu hóa và nâng cấp. Hôm nay chúng ta sẽ thảo luận về một chủ đề dựa trên hệ thống kiểm thử ngược: “Kiểm thử chiến lược dựa trên điều kiện thị trường ngẫu nhiên”.
nhu cầu
Trong lĩnh vực giao dịch định lượng, việc phát triển và tối ưu hóa các chiến lược không thể tách rời khỏi việc xác minh dữ liệu thị trường thực tế. Tuy nhiên, trong các ứng dụng thực tế, do môi trường thị trường phức tạp và thay đổi, việc dựa vào dữ liệu lịch sử để kiểm tra ngược có thể có những hạn chế, chẳng hạn như không bao quát được các điều kiện thị trường khắc nghiệt hoặc các kịch bản đặc biệt. Do đó, việc thiết kế một công cụ tạo thị trường ngẫu nhiên hiệu quả trở thành một công cụ hữu hiệu cho các nhà phát triển chiến lược định lượng.
Khi chúng ta cần kiểm tra lại chiến lược trên một sàn giao dịch hoặc loại tiền tệ nhất định bằng dữ liệu lịch sử, chúng ta có thể sử dụng nguồn dữ liệu chính thức của nền tảng FMZ để kiểm tra lại. Đôi khi chúng ta cũng muốn xem chiến lược hoạt động như thế nào trong một thị trường hoàn toàn “không quen thuộc”. Lúc này, chúng ta có thể “chế tạo” một số dữ liệu để kiểm tra chiến lược.
Ý nghĩa của việc sử dụng dữ liệu thị trường ngẫu nhiên là:
- 1. Đánh giá tính vững chắc của chiến lược Công cụ tạo thị trường ngẫu nhiên có thể tạo ra nhiều kịch bản thị trường có thể xảy ra, bao gồm biến động cực độ, biến động thấp, thị trường có xu hướng và thị trường không ổn định. Việc thử nghiệm một chiến lược trong các môi trường mô phỏng này có thể giúp đánh giá liệu hiệu suất của chiến lược đó có ổn định trong các điều kiện thị trường khác nhau hay không. Ví dụ:
Liệu chiến lược có thể thích ứng với xu hướng và sự thay đổi đột ngột không? Liệu chiến lược này có gây ra tổn thất đáng kể trong điều kiện thị trường khắc nghiệt không?
- 2. Xác định điểm yếu tiềm ẩn trong chiến lược của bạn Bằng cách mô phỏng một số tình huống bất thường của thị trường (chẳng hạn như các sự kiện thiên nga đen giả định), những điểm yếu tiềm ẩn trong chiến lược có thể được phát hiện và cải thiện. Ví dụ:
Chiến lược này có phụ thuộc quá nhiều vào cấu trúc thị trường cụ thể không? Có nguy cơ điều chỉnh quá mức các tham số không?
-
- Tối ưu hóa các thông số chiến lược Dữ liệu được tạo ngẫu nhiên cung cấp môi trường thử nghiệm đa dạng hơn để điều chỉnh tham số chiến lược mà không cần phải hoàn toàn dựa vào dữ liệu lịch sử. Điều này cho phép có phạm vi tham số chiến lược toàn diện hơn và tránh bị giới hạn ở các mô hình thị trường cụ thể trong dữ liệu lịch sử.
-
- Lấp đầy khoảng trống trong dữ liệu lịch sử Ở một số thị trường (như thị trường mới nổi hoặc thị trường giao dịch các loại tiền tệ nhỏ), dữ liệu lịch sử có thể không đủ để bao quát mọi điều kiện thị trường có thể xảy ra. Công cụ phân tích ngẫu nhiên có thể cung cấp lượng lớn dữ liệu bổ sung để tạo điều kiện cho việc thử nghiệm toàn diện hơn.
-
- Phát triển lặp lại nhanh chóng Việc sử dụng dữ liệu ngẫu nhiên để thử nghiệm nhanh có thể tăng tốc quá trình lặp lại quá trình phát triển chiến lược mà không cần dựa vào điều kiện thị trường theo thời gian thực hoặc việc dọn dẹp và tổ chức dữ liệu tốn nhiều thời gian.
Tuy nhiên, cũng cần phải đánh giá chiến lược một cách hợp lý. Đối với dữ liệu thị trường được tạo ngẫu nhiên, vui lòng lưu ý:
- 1. Mặc dù các công cụ tạo thị trường ngẫu nhiên rất hữu ích, nhưng ý nghĩa của chúng phụ thuộc vào chất lượng dữ liệu được tạo ra và thiết kế của kịch bản mục tiêu:
- 2. Logic tạo ra dữ liệu cần gần với thị trường thực tế: Nếu các điều kiện thị trường được tạo ngẫu nhiên hoàn toàn không phù hợp với thực tế, kết quả thử nghiệm có thể thiếu giá trị tham chiếu. Ví dụ, máy phát điện có thể được thiết kế kết hợp với các đặc điểm thống kê thực tế của thị trường (như phân phối biến động, tỷ lệ xu hướng).
- 3. Không thể thay thế hoàn toàn việc kiểm tra dữ liệu thực tế: dữ liệu ngẫu nhiên chỉ có thể bổ sung cho việc phát triển và tối ưu hóa các chiến lược. Chiến lược cuối cùng vẫn cần được xác minh về hiệu quả của nó trong dữ liệu thị trường thực tế.
Nói như vậy, làm sao chúng ta có thể “chế tạo” được dữ liệu? Làm thế nào chúng ta có thể “chế tạo” dữ liệu để sử dụng trong hệ thống kiểm thử ngược một cách thuận tiện, nhanh chóng và dễ dàng?
Ý tưởng thiết kế
Bài viết này được thiết kế để cung cấp điểm khởi đầu cho thảo luận và cung cấp một phép tính tạo thị trường ngẫu nhiên tương đối đơn giản. Trên thực tế, có nhiều thuật toán mô phỏng, mô hình dữ liệu và các công nghệ khác có thể được áp dụng. Do không gian thảo luận có hạn , chúng tôi sẽ không sử dụng các phương pháp mô phỏng dữ liệu đặc biệt phức tạp.
Kết hợp chức năng nguồn dữ liệu tùy chỉnh của hệ thống kiểm thử nền tảng, chúng tôi đã viết một chương trình bằng Python.
- 1. Tạo ngẫu nhiên một tập dữ liệu dòng K và ghi chúng vào tệp CSV để ghi liên tục, để dữ liệu được tạo ra có thể được lưu lại.
- 2. Sau đó tạo một dịch vụ để cung cấp hỗ trợ nguồn dữ liệu cho hệ thống kiểm thử ngược.
- 3. Hiển thị dữ liệu đường K được tạo trong biểu đồ.
Đối với một số tiêu chuẩn tạo và lưu trữ tệp dữ liệu K-line, có thể xác định các điều khiển tham số sau:
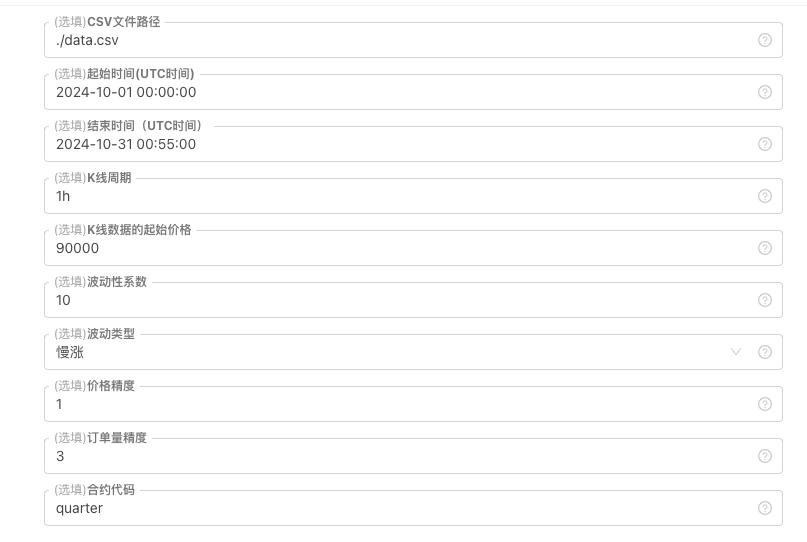
Mẫu dữ liệu được tạo ngẫu nhiên Để mô phỏng loại biến động của dữ liệu K-line, một thiết kế đơn giản được thực hiện đơn giản bằng cách sử dụng các xác suất khác nhau của số ngẫu nhiên dương và âm. Khi dữ liệu được tạo ra không lớn, mô hình thị trường cần thiết có thể không được phản ánh. Nếu có cách tốt hơn, bạn có thể thay thế phần mã này. Dựa trên thiết kế đơn giản này, việc điều chỉnh phạm vi tạo số ngẫu nhiên và một số hệ số trong mã có thể ảnh hưởng đến hiệu ứng dữ liệu được tạo ra.
Xác minh dữ liệu Dữ liệu K-line được tạo ra cũng cần được kiểm tra tính hợp lý, để kiểm tra xem giá mở cửa cao và giá đóng cửa thấp có vi phạm định nghĩa hay không, để kiểm tra tính liên tục của dữ liệu K-line, v.v.
Hệ thống kiểm tra ngược Máy phát báo giá ngẫu nhiên
import _thread
import json
import math
import csv
import random
import os
import datetime as dt
from http.server import HTTPServer, BaseHTTPRequestHandler
from urllib.parse import parse_qs, urlparse
arrTrendType = ["down", "slow_up", "sharp_down", "sharp_up", "narrow_range", "wide_range", "neutral_random"]
def url2Dict(url):
query = urlparse(url).query
params = parse_qs(query)
result = {key: params[key][0] for key in params}
return result
class Provider(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def do_GET(self):
global filePathForCSV, pround, vround, ct
try:
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header("Content-type", "application/json")
self.end_headers()
dictParam = url2Dict(self.path)
Log("自定义数据源服务接收到请求,self.path:", self.path, "query 参数:", dictParam)
eid = dictParam["eid"]
symbol = dictParam["symbol"]
arrCurrency = symbol.split(".")[0].split("_")
baseCurrency = arrCurrency[0]
quoteCurrency = arrCurrency[1]
fromTS = int(dictParam["from"]) * int(1000)
toTS = int(dictParam["to"]) * int(1000)
priceRatio = math.pow(10, int(pround))
amountRatio = math.pow(10, int(vround))
data = {
"detail": {
"eid": eid,
"symbol": symbol,
"alias": symbol,
"baseCurrency": baseCurrency,
"quoteCurrency": quoteCurrency,
"marginCurrency": quoteCurrency,
"basePrecision": vround,
"quotePrecision": pround,
"minQty": 0.00001,
"maxQty": 9000,
"minNotional": 5,
"maxNotional": 9000000,
"priceTick": 10 ** -pround,
"volumeTick": 10 ** -vround,
"marginLevel": 10,
"contractType": ct
},
"schema" : ["time", "open", "high", "low", "close", "vol"],
"data" : []
}
listDataSequence = []
with open(filePathForCSV, "r") as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
header = next(reader)
headerIsNoneCount = 0
if len(header) != len(data["schema"]):
Log("CSV文件格式有误,列数不同,请检查!", "#FF0000")
return
for ele in header:
for i in range(len(data["schema"])):
if data["schema"][i] == ele or ele == "":
if ele == "":
headerIsNoneCount += 1
if headerIsNoneCount > 1:
Log("CSV文件格式有误,请检查!", "#FF0000")
return
listDataSequence.append(i)
break
while True:
record = next(reader, -1)
if record == -1:
break
index = 0
arr = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
for ele in record:
arr[listDataSequence[index]] = int(ele) if listDataSequence[index] == 0 else (int(float(ele) * amountRatio) if listDataSequence[index] == 5 else int(float(ele) * priceRatio))
index += 1
data["data"].append(arr)
Log("数据data.detail:", data["detail"], "响应回测系统请求。")
self.wfile.write(json.dumps(data).encode())
except BaseException as e:
Log("Provider do_GET error, e:", e)
return
def createServer(host):
try:
server = HTTPServer(host, Provider)
Log("Starting server, listen at: %s:%s" % host)
server.serve_forever()
except BaseException as e:
Log("createServer error, e:", e)
raise Exception("stop")
class KlineGenerator:
def __init__(self, start_time, end_time, interval):
self.start_time = dt.datetime.strptime(start_time, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
self.end_time = dt.datetime.strptime(end_time, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
self.interval = self._parse_interval(interval)
self.timestamps = self._generate_time_series()
def _parse_interval(self, interval):
unit = interval[-1]
value = int(interval[:-1])
if unit == "m":
return value * 60
elif unit == "h":
return value * 3600
elif unit == "d":
return value * 86400
else:
raise ValueError("不支持的K线周期,请使用 'm', 'h', 或 'd'.")
def _generate_time_series(self):
timestamps = []
current_time = self.start_time
while current_time <= self.end_time:
timestamps.append(int(current_time.timestamp() * 1000))
current_time += dt.timedelta(seconds=self.interval)
return timestamps
def generate(self, initPrice, trend_type="neutral", volatility=1):
data = []
current_price = initPrice
angle = 0
for timestamp in self.timestamps:
angle_radians = math.radians(angle % 360)
cos_value = math.cos(angle_radians)
if trend_type == "down":
upFactor = random.uniform(0, 0.5)
change = random.uniform(-0.5, 0.5 * upFactor) * volatility * random.uniform(1, 3)
elif trend_type == "slow_up":
downFactor = random.uniform(0, 0.5)
change = random.uniform(-0.5 * downFactor, 0.5) * volatility * random.uniform(1, 3)
elif trend_type == "sharp_down":
upFactor = random.uniform(0, 0.5)
change = random.uniform(-10, 0.5 * upFactor) * volatility * random.uniform(1, 3)
elif trend_type == "sharp_up":
downFactor = random.uniform(0, 0.5)
change = random.uniform(-0.5 * downFactor, 10) * volatility * random.uniform(1, 3)
elif trend_type == "narrow_range":
change = random.uniform(-0.2, 0.2) * volatility * random.uniform(1, 3)
elif trend_type == "wide_range":
change = random.uniform(-3, 3) * volatility * random.uniform(1, 3)
else:
change = random.uniform(-0.5, 0.5) * volatility * random.uniform(1, 3)
change = change + cos_value * random.uniform(-0.2, 0.2) * volatility
open_price = current_price
high_price = open_price + random.uniform(0, abs(change))
low_price = max(open_price - random.uniform(0, abs(change)), random.uniform(0, open_price))
close_price = open_price + change if open_price + change < high_price and open_price + change > low_price else random.uniform(low_price, high_price)
if (high_price >= open_price and open_price >= close_price and close_price >= low_price) or (high_price >= close_price and close_price >= open_price and open_price >= low_price):
pass
else:
Log("异常数据:", high_price, open_price, low_price, close_price, "#FF0000")
high_price = max(high_price, open_price, close_price)
low_price = min(low_price, open_price, close_price)
base_volume = random.uniform(1000, 5000)
volume = base_volume * (1 + abs(change) * 0.2)
kline = {
"Time": timestamp,
"Open": round(open_price, 2),
"High": round(high_price, 2),
"Low": round(low_price, 2),
"Close": round(close_price, 2),
"Volume": round(volume, 2),
}
data.append(kline)
current_price = close_price
angle += 1
return data
def save_to_csv(self, filename, data):
with open(filename, mode="w", newline="") as csvfile:
writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
writer.writerow(["", "open", "high", "low", "close", "vol"])
for idx, kline in enumerate(data):
writer.writerow(
[kline["Time"], kline["Open"], kline["High"], kline["Low"], kline["Close"], kline["Volume"]]
)
Log("当前路径:", os.getcwd())
with open("data.csv", "r") as file:
lines = file.readlines()
if len(lines) > 1:
Log("文件写入成功,以下是文件内容的一部分:")
Log("".join(lines[:5]))
else:
Log("文件写入失败,文件为空!")
def main():
Chart({})
LogReset(1)
try:
# _thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("localhost", 9090), ))
_thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("0.0.0.0", 9090), ))
Log("开启自定义数据源服务线程,数据由CSV文件提供。", ", 地址/端口:0.0.0.0:9090", "#FF0000")
except BaseException as e:
Log("启动自定义数据源服务失败!")
Log("错误信息:", e)
raise Exception("stop")
while True:
cmd = GetCommand()
if cmd:
if cmd == "createRecords":
Log("生成器参数:", "起始时间:", startTime, "结束时间:", endTime, "K线周期:", KLinePeriod, "初始价格:", firstPrice, "波动类型:", arrTrendType[trendType], "波动性系数:", ratio)
generator = KlineGenerator(
start_time=startTime,
end_time=endTime,
interval=KLinePeriod,
)
kline_data = generator.generate(firstPrice, trend_type=arrTrendType[trendType], volatility=ratio)
generator.save_to_csv("data.csv", kline_data)
ext.PlotRecords(kline_data, "%s_%s" % ("records", KLinePeriod))
LogStatus(_D())
Sleep(2000)
Thực hành trong hệ thống kiểm thử ngược
- Tạo phiên bản chính sách ở trên, cấu hình các tham số và chạy nó.
- Thị trường thực (trường hợp chiến lược) cần phải được chạy trên máy chủ được triển khai trên máy chủ, vì hệ thống kiểm tra ngược cần có IP công khai để truy cập và lấy dữ liệu.
- Nhấp vào nút tương tác và chiến lược sẽ tự động bắt đầu tạo dữ liệu thị trường ngẫu nhiên.

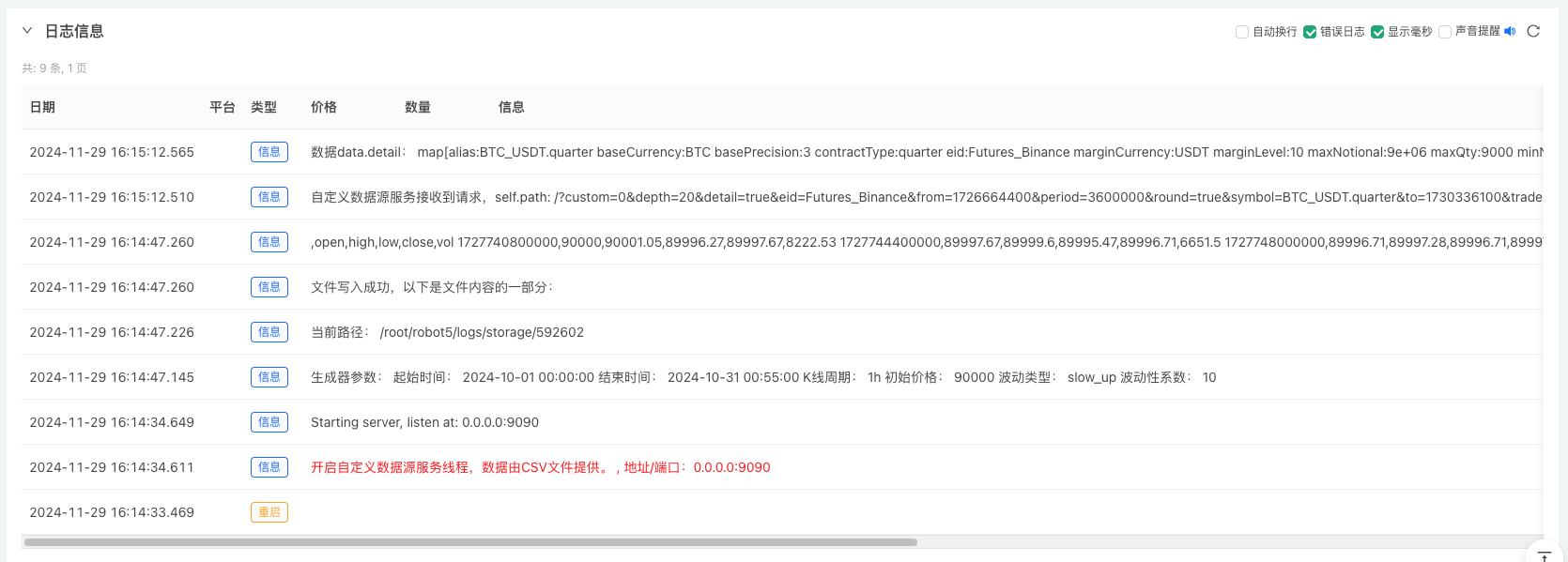
- Dữ liệu được tạo ra sẽ được hiển thị trên biểu đồ để dễ quan sát và dữ liệu sẽ được ghi vào tệp data.csv cục bộ
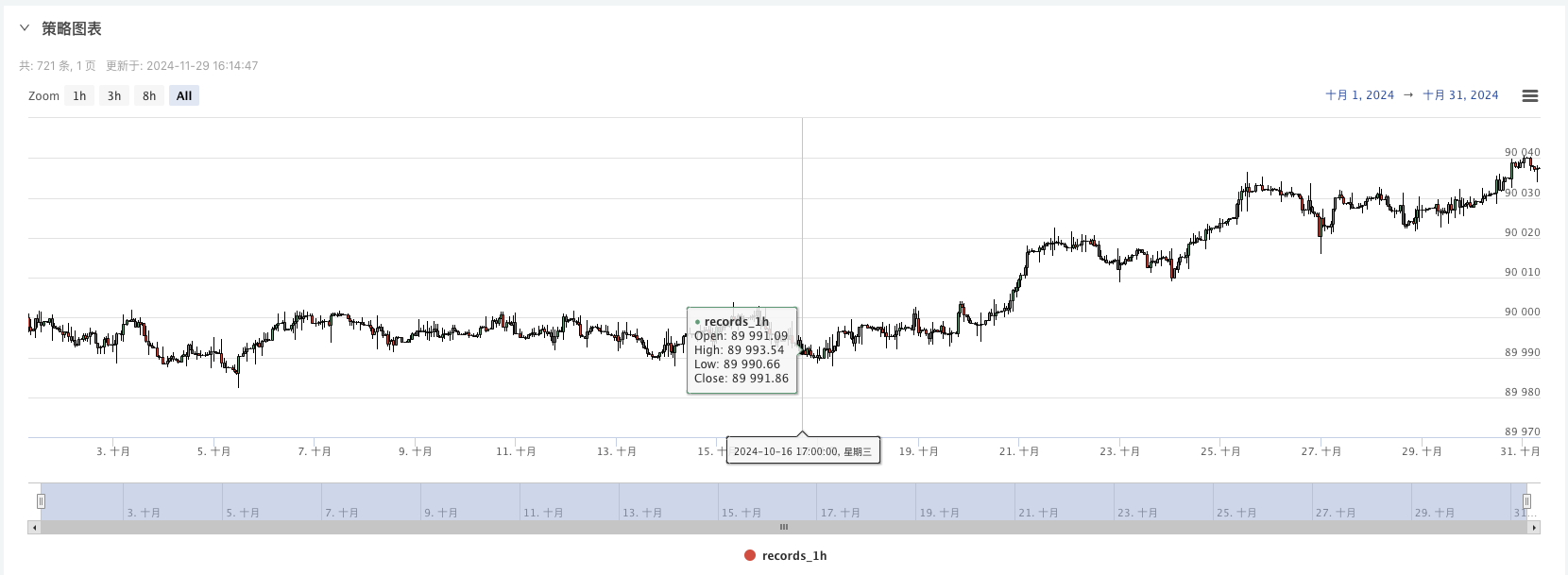
- Bây giờ chúng ta có thể sử dụng dữ liệu được tạo ngẫu nhiên này và sử dụng bất kỳ chiến lược nào để kiểm tra ngược
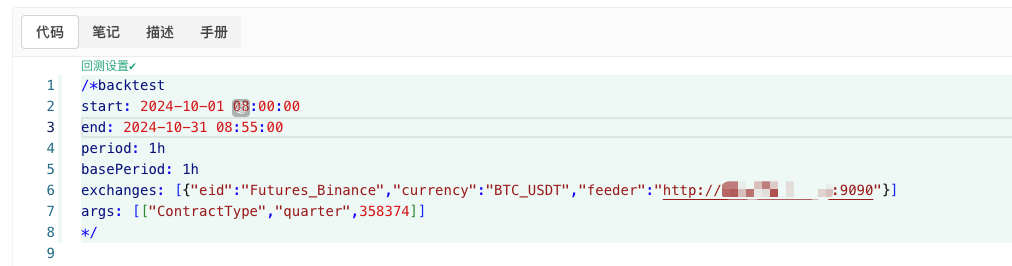
/*backtest
start: 2024-10-01 08:00:00
end: 2024-10-31 08:55:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT","feeder":"http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:9090"}]
args: [["ContractType","quarter",358374]]
*/
Cấu hình theo thông tin trên và thực hiện các điều chỉnh cụ thể.http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:9090Đây là địa chỉ IP của máy chủ và cổng mở của chiến lược tạo thị trường ngẫu nhiên trên đĩa thực.
Đây là nguồn dữ liệu tùy chỉnh. Bạn có thể tham khảo phần nguồn dữ liệu tùy chỉnh trong tài liệu API nền tảng để biết thêm thông tin.
- Sau khi hệ thống kiểm tra ngược thiết lập nguồn dữ liệu, bạn có thể kiểm tra dữ liệu thị trường ngẫu nhiên
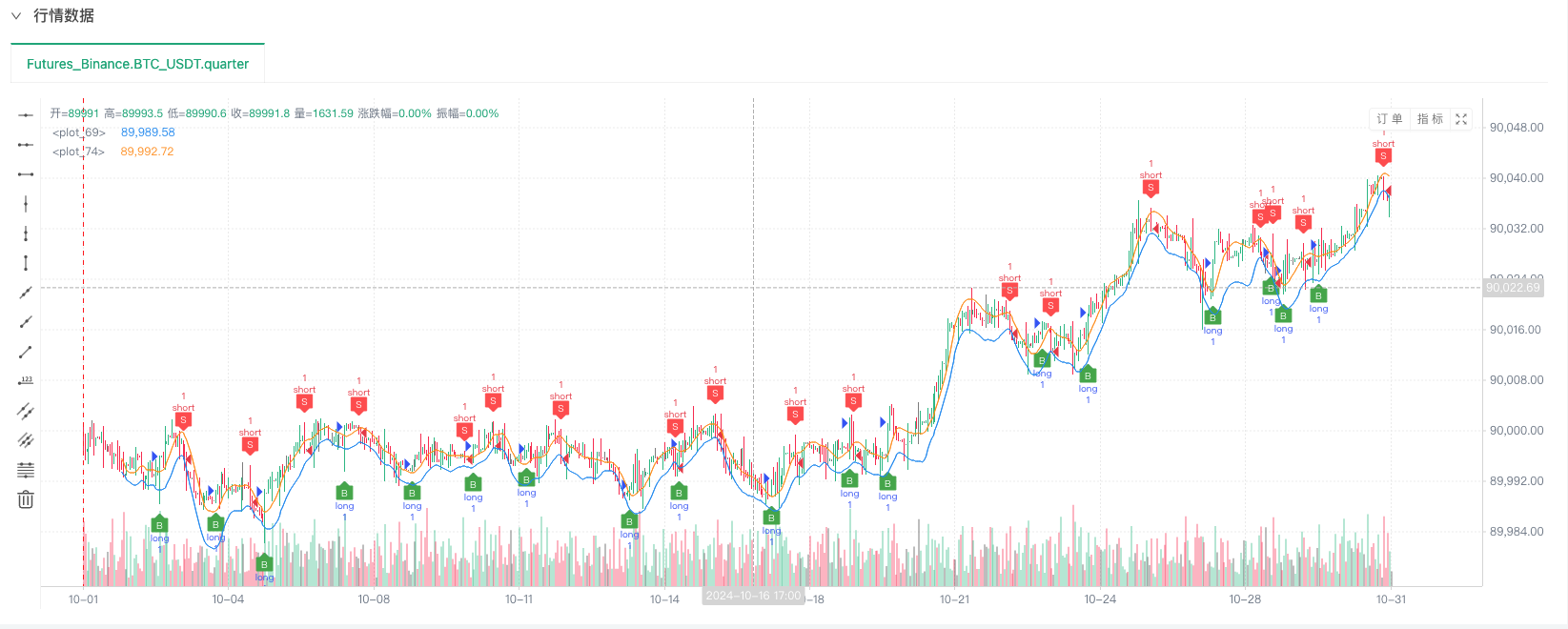
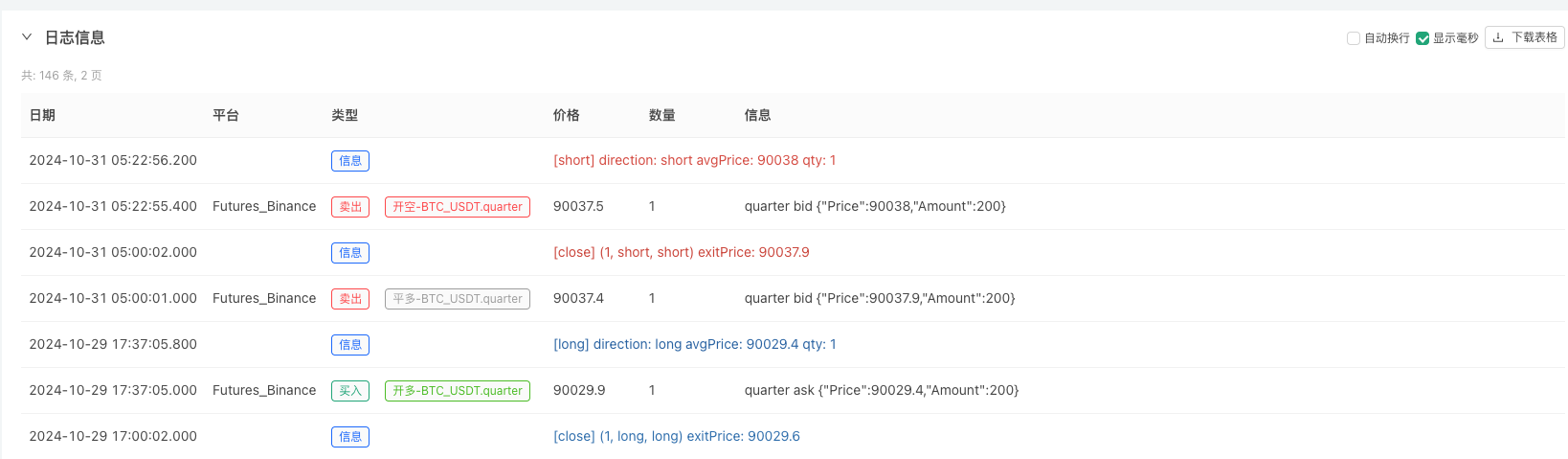
Tại thời điểm này, hệ thống kiểm tra ngược được thử nghiệm bằng cách sử dụng dữ liệu mô phỏng “giả tạo” của chúng tôi. Theo dữ liệu trong biểu đồ thị trường trong quá trình kiểm tra ngược, hãy so sánh dữ liệu trong biểu đồ thời gian thực được tạo ra bởi các điều kiện thị trường ngẫu nhiên. Thời gian là 17:00 ngày 16 tháng 10 năm 2024. Dữ liệu giống nhau.
- Ồ đúng rồi, tôi gần như quên mất không nói điều đó! Lý do chương trình Python tạo thị trường ngẫu nhiên này tạo ra một thị trường thực sự là để tạo điều kiện thuận lợi cho việc trình diễn, vận hành và hiển thị dữ liệu K-line được tạo ra. Trong ứng dụng thực tế, bạn có thể viết một tập lệnh python độc lập, do đó bạn không cần phải chạy đĩa thực tế.
Mã nguồn chiến lược:Hệ thống kiểm tra ngược Máy phát báo giá ngẫu nhiên
Cảm ơn các bạn đã ủng hộ và đọc bài viết.