Học máy: Dự đoán xu hướng giá (1)
 3
3
 1047
1047
 Phân loại trưởng thành: Máy vectơ hỗ trợ (SVM) là một thuật toán phân loại nhị phân (hoặc đa biến) mạnh mẽ và trưởng thành. Dự đoán cổ phiếu sẽ tăng hay giảm là một bài toán phân loại nhị phân điển hình.
Khả năng phi tuyến tính: Bằng cách sử dụng các hàm hạt nhân (như hạt nhân RBF), SVM có thể nắm bắt các mối quan hệ phi tuyến tính phức tạp giữa các tính năng đầu vào, điều này rất quan trọng đối với dữ liệu thị trường tài chính.
Dựa trên tính năng: Hiệu quả của mô hình phụ thuộc phần lớn vào các “tính năng” bạn đưa vào. Hệ số alpha được tính toán hiện tại là một khởi đầu tốt, và chúng ta có thể xây dựng thêm nhiều tính năng tương tự để cải thiện khả năng dự đoán.
Lần này tôi bắt đầu với 3 phác thảo tính năng:
1: Đặc tính dòng chảy tần số cao:
alpha_1min: Hệ số mất cân bằng luồng lệnh được tính toán dựa trên tất cả các tích tắc trong phút trước.
alpha_5min: Hệ số mất cân bằng luồng lệnh được tính toán dựa trên tất cả các biến động trong 5 phút qua.
alpha_15min: Hệ số mất cân bằng luồng lệnh được tính toán dựa trên tất cả các biến động trong 15 phút qua.
ofi_1min (Mất cân bằng dòng lệnh): Tỷ lệ (khối lượng mua / khối lượng bán) trong khoảng thời gian 1 phút. Chỉ số này trực tiếp hơn alpha.
vol_per_trade_1min: Khối lượng giao dịch trung bình trong vòng 1 phút. Dấu hiệu cho thấy các lệnh lớn đang tác động đến thị trường.
Phân loại trưởng thành: Máy vectơ hỗ trợ (SVM) là một thuật toán phân loại nhị phân (hoặc đa biến) mạnh mẽ và trưởng thành. Dự đoán cổ phiếu sẽ tăng hay giảm là một bài toán phân loại nhị phân điển hình.
Khả năng phi tuyến tính: Bằng cách sử dụng các hàm hạt nhân (như hạt nhân RBF), SVM có thể nắm bắt các mối quan hệ phi tuyến tính phức tạp giữa các tính năng đầu vào, điều này rất quan trọng đối với dữ liệu thị trường tài chính.
Dựa trên tính năng: Hiệu quả của mô hình phụ thuộc phần lớn vào các “tính năng” bạn đưa vào. Hệ số alpha được tính toán hiện tại là một khởi đầu tốt, và chúng ta có thể xây dựng thêm nhiều tính năng tương tự để cải thiện khả năng dự đoán.
Lần này tôi bắt đầu với 3 phác thảo tính năng:
1: Đặc tính dòng chảy tần số cao:
alpha_1min: Hệ số mất cân bằng luồng lệnh được tính toán dựa trên tất cả các tích tắc trong phút trước.
alpha_5min: Hệ số mất cân bằng luồng lệnh được tính toán dựa trên tất cả các biến động trong 5 phút qua.
alpha_15min: Hệ số mất cân bằng luồng lệnh được tính toán dựa trên tất cả các biến động trong 15 phút qua.
ofi_1min (Mất cân bằng dòng lệnh): Tỷ lệ (khối lượng mua / khối lượng bán) trong khoảng thời gian 1 phút. Chỉ số này trực tiếp hơn alpha.
vol_per_trade_1min: Khối lượng giao dịch trung bình trong vòng 1 phút. Dấu hiệu cho thấy các lệnh lớn đang tác động đến thị trường.
2: Đặc điểm giá cả và biến động: log_return_5min: Tỷ lệ trả về logarit trong 5 phút qua, log(Pt / P{t-5min}). volatility_15min: Độ lệch chuẩn của lợi nhuận logarit trong 15 phút qua, thước đo mức độ biến động ngắn hạn. atr_14 (Phạm vi trung bình thực): Giá trị ATR dựa trên 14 nến 1 phút trước đó, một chỉ báo biến động cổ điển. rsi_14 (Chỉ số sức mạnh tương đối): Đây là thước đo tình trạng mua quá mức và bán quá mức dựa trên giá trị RSI của 14 nến 1 phút trước đó.
3: Đặc điểm thời gian: hour_of_day: Giờ hiện tại (0-23). Thị trường có diễn biến khác nhau trong các khoảng thời gian khác nhau (ví dụ: phiên giao dịch Châu Á/Châu Âu/Châu Mỹ). day_of_week: Ngày trong tuần (0-6). Cuối tuần và ngày trong tuần có mô hình dao động khác nhau.
def calculate_features_and_labels(klines):
"""
核心函数
"""
features = []
labels = []
# 为了计算RSI等指标,我们需要价格序列
close_prices = [k['close'] for k in klines]
# 从第30根K线开始,因为需要足够的前置数据
for i in range(30, len(klines) - PREDICT_HORIZON):
# 1. 价格与波动率特征
price_change_15m = (klines[i]['close'] - klines[i-15]['close']) / klines[i-15]['close']
volatility_30m = np.std(close_prices[i-30:i])
# 计算RSI
diffs = np.diff(close_prices[i-14:i+1])
gains = np.sum(diffs[diffs > 0]) / 14
losses = -np.sum(diffs[diffs < 0]) / 14
rs = gains / (losses + 1e-10)
rsi_14 = 100 - (100 / (1 + rs))
# 2. 时间特征
dt_object = datetime.fromtimestamp(klines[i]['ts'] / 1000)
hour_of_day = dt_object.hour
day_of_week = dt_object.weekday()
# 组合所有特征
current_features = [price_change_15m, volatility_30m, rsi_14, hour_of_day, day_of_week]
features.append(current_features)
# 3. 数据标注
future_price = klines[i + PREDICT_HORIZON]['close']
current_price = klines[i]['close']
if future_price > current_price * (1 + SPREAD_THRESHOLD):
labels.append(0) # 涨
elif future_price < current_price * (1 - SPREAD_THRESHOLD):
labels.append(1) # 跌
else:
labels.append(2) # 横盘
Sau đó sử dụng ba loại để phân biệt giữa sự tăng lên, giảm xuống và ngang.
Ý tưởng cốt lõi của sàng lọc tính năng: Tìm “đồng đội tốt” và loại bỏ “đồng đội xấu”
Mục tiêu của chúng tôi là tìm ra một tập hợp các tính năng:
- Tính liên quan cao: Mỗi tính năng đều có mối tương quan chặt chẽ với những thay đổi về giá trong tương lai (nhãn mục tiêu của chúng tôi).
- Độ dư thừa thấp: Các đặc trưng không nên chứa quá nhiều thông tin trùng lặp. Ví dụ, “động lượng 5 phút” và “động lượng 6 phút” rất giống nhau. Việc bao gồm cả hai sẽ không cải thiện đáng kể mô hình và thậm chí có thể gây nhiễu.
- Tính ổn định: Tính hợp lệ của một tính năng không thể thay đổi quá nhanh theo thời gian. Một tính năng chỉ hợp lệ trong một ngày là rất nguy hiểm.
def run_analysis_report(X, y, clf, scaler):
Log("--- 模型分析报告 ---", "info")
Log("1. 特征重要性 (代理模型: 随机森林):")
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=50, random_state=42); rf.fit(X, y)
importances = sorted(zip(g_feature_names, rf.feature_importances_), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for name, importance in importances: Log(f" - {name}: {importance:.4f}")
Log("2. 特征与标签的互信息:"); mi_scores = mutual_info_classif(X, y)
mi_scores = sorted(zip(g_feature_names, mi_scores), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for name, score in mi_scores: Log(f" - {name}: {score:.4f}")
Log("3. 历史数据回测表现:"); y_pred = clf.predict(scaler.transform(X)); accuracy = accuracy_score(y, y_pred)
Log(f" - **历史回测总胜率: {accuracy * 100:.2f}%**", "success")
Log("4. 混淆矩阵 (行:真实, 列:预测):"); cm = confusion_matrix(y, y_pred)
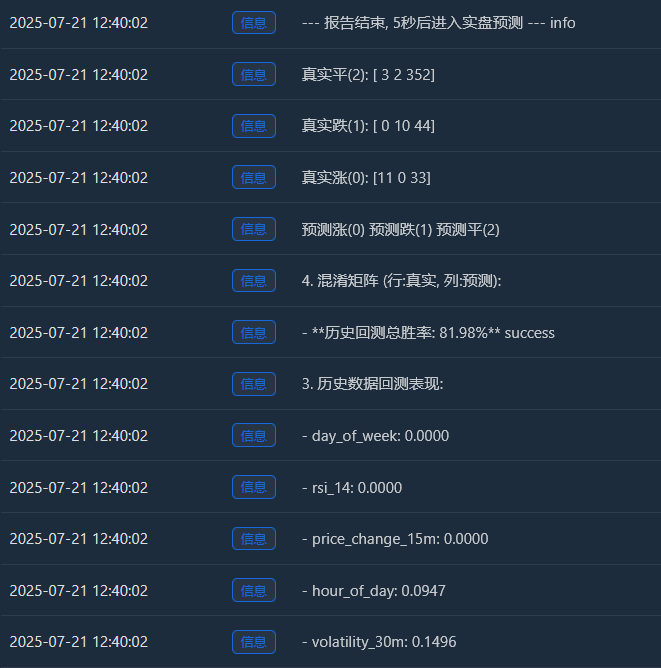
Log(" 预测涨(0) 预测跌(1) 预测平(2)"); Log(f"真实涨(0): {cm[0] if len(cm) > 0 else [0,0,0]}")
Log(f"真实跌(1): {cm[1] if len(cm) > 1 else [0,0,0]}"); Log(f"真实平(2): {cm[2] if len(cm) > 2 else [0,0,0]}")
profit_chart = Chart({'title': {'text': f'历史回测净值曲线 (胜率: {accuracy*100:.2f}%)'}}); profit_chart.reset(); balance = 1
for i in range(len(y)):
if y_pred[i] == y[i] and y[i] != 2: balance *= (1 + 0.01)
elif y_pred[i] != y[i] and y_pred[i] != 2: balance *= (1 - 0.01)
profit_chart.add(i, balance)
Log("--- 报告结束, 5秒后进入实盘预测 ---", "info"); Sleep(5000)
Quá trình này như sau:
Thu thập dữ liệu
 Tính năng quan trọng
Tính năng quan trọng
 Thông tin tương hỗ giữa các tính năng và nhãn và thông tin kiểm tra ngược
Thông tin tương hỗ giữa các tính năng và nhãn và thông tin kiểm tra ngược
Ban đầu tôi nghĩ tỷ lệ thắng 65% là đủ, nhưng không ngờ nó lại đạt tới 81,98%. Phản ứng đầu tiên của tôi lẽ ra phải là: “Tuyệt vời, nhưng tốt quá thì khó tin. Chắc chắn phải có điều gì đó đáng để khám phá ở đây.”
1. Giải thích sâu sắc báo cáo phân tích, giải thích từng nội dung báo cáo:
- Tính năng quan trọng và thông tin tương hỗ: Biến động_30m và thay đổi_giá_15m là những đặc điểm quan trọng nhất. Điều này hợp lý, cho thấy xu hướng thị trường gần đây và biến động là những yếu tố dự báo mạnh nhất cho tương lai. Hour_of_day cũng đóng góp một chút, cho thấy mô hình nắm bắt được các mô hình giao dịch vào các thời điểm khác nhau trong ngày. Đóng góp của rsi_14 và day_of_week gần như bằng 0, điều này cho thấy hai đặc điểm này có thể là “đồng đội lợn” trong tập dữ liệu và tổ hợp đặc điểm hiện tại. Chúng ta có thể cân nhắc loại bỏ chúng trong tương lai để đơn giản hóa mô hình và ngăn ngừa nhiễu.
- Ma trận nhầm lẫn (đây là rất nhiều thông tin!) Tăng thực tế (0):[11 0 33] -> Trong số 44 (11+0+33) đợt tăng giá thực tế, mô hình đã dự đoán đúng 11 lần, nhưng lại dự đoán sai thành “sự hợp nhất” 33 lần. Giảm thực tế (1):[0 10 44] -> Trong số 54 (0+10+44) lần giảm thực tế, mô hình đã dự đoán đúng 10 lần, nhưng lại dự đoán sai thành “xu hướng đi ngang” 44 lần. Ping thực tế (2):[3 2 352] -> Trong số 357 (3+2+352) sự hợp nhất thực tế, mô hình đã dự đoán chính xác 352 trong số đó!
- Tỷ lệ thắng tổng thể trong quá trình kiểm tra ngược lịch sử: 81,98% Nguồn gốc cốt lõi của tỷ lệ thắng cao này là độ chính xác cực cao của mô hình trong việc dự đoán “sự hợp nhất”! Trong tổng số khoảng 455 mẫu, hơn 350 mẫu là thị trường hợp nhất, và mô hình đã nhận diện chúng gần như hoàn hảo. Đây là một khả năng rất có giá trị! Một mô hình có thể cho bạn biết chính xác “tốt nhất là không nên di chuyển lúc này” có thể giúp bạn tiết kiệm rất nhiều phí và giao dịch không hợp lệ.
2Tại sao tỷ lệ chiến thắng thực tế lại thấp hơn 81,98%?
- Định nghĩa về “hợp nhất” quá lỏng lẻo: Ngưỡng SPREAD_THRESHOLD của chúng tôi là 0,5%. Biến động giá không quá 0,5% trong khoảng thời gian 15 phút là khá phổ biến. Do đó, các mẫu “hợp nhất” chiếm phần lớn (khoảng 80%) tập dữ liệu của chúng tôi. Mô hình đã học được một cách thông minh rằng: “Khi tôi không chắc chắn, hãy đoán ‘hợp nhất’ với độ chính xác cao”. Điều này đúng về mặt thống kê, nhưng trong giao dịch, chúng tôi quan tâm nhiều hơn đến việc dự đoán biến động giá.
- Khả năng dự đoán sự tăng và giảm: Tỷ lệ thắng khi dự đoán xu hướng tăng: Mô hình dự đoán 11 + 0 + 3 = 14 xu hướng tăng, trong đó chỉ có 11 xu hướng đúng. Tỷ lệ thắng là 11⁄14 = 78,5%. Tuyệt vời! Tỷ lệ thắng khi dự đoán số lần giảm: Mô hình dự đoán 0 + 10 + 2 = 12 lần giảm và đúng 10 lần. Tỷ lệ thắng là 10⁄12 = 83,3%. Một lần nữa, rất ấn tượng!
- Quá khớp trong mẫu: Bài kiểm tra này được thực hiện trên dữ liệu “đã biết” của mô hình (tức là dữ liệu được sử dụng để huấn luyện và kiểm tra). Điều này giống như yêu cầu một học sinh làm bài kiểm tra mà họ vừa hoàn thành; điểm số thường sẽ cao. Hiệu suất của mô hình trên dữ liệu mới, chưa được biết đến (giao dịch trực tiếp) hầu như luôn thấp hơn điểm số này.
Hiện tại, chúng ta có một “Mô hình Alpha” sơ bộ nhưng có tiềm năng rất lớn. Mặc dù chúng ta không thể trực tiếp diễn giải con số 81,98% là một dự đoán thực tế cho tương lai, nhưng đây là một tín hiệu tích cực mạnh mẽ, chứng minh rằng các mô hình có thể dự đoán được thực sự tồn tại trong dữ liệu và khuôn khổ của chúng ta đã nắm bắt thành công chúng! Giờ đây, chúng tôi cảm thấy như vừa tìm thấy quặng vàng chất lượng cao đầu tiên dưới chân núi. Bước tiếp theo của chúng tôi không phải là bán nó ngay lập tức, mà là sử dụng các công cụ và kỹ thuật chuyên biệt hơn (tối ưu hóa các tính năng và điều chỉnh các thông số) để khai thác toàn bộ ngọn núi một cách hiệu quả và ổn định hơn.
Bây giờ chúng ta hãy giới thiệu sương mù chiến tranh trong “vi mô” — luồng lệnh và đặc điểm của sổ lệnh Bước 1: Nâng cấp việc thu thập dữ liệu - đăng ký kênh sâu hơn Để lấy dữ liệu sổ lệnh, phương thức kết nối WebSocket phải được sửa đổi từ chỉ đăng ký aggTrade (giao dịch) thành đăng ký cả aggTrade và depth (độ sâu). Điều này yêu cầu chúng tôi phải sử dụng URL đăng ký đa luồng tổng quát hơn. Bước 2: Nâng cấp kỹ thuật tính năng - xây dựng ma trận tính năng bộ ba cho “biển, đất liền và không khí” Chúng tôi sẽ thêm các tính năng mới sau vào hàm calculate_features_and_labels:
- Đặc điểm của luồng lệnh (Alpha - Ngắn hạn): alpha_15m: Hệ số mất cân bằng dòng lệnh 15 phút. Đây là chỉ số dòng lệnh cốt lõi mà chúng ta đã thảo luận trước đó.
- Đặc điểm của Sổ lệnh (Sách - Quân đội): wobi_10s: Độ mất cân bằng của sổ lệnh có trọng số trong 10 giây qua. Đây là một chỉ báo tần suất rất cao dùng để đo lường áp lực mua và bán trên thị trường. spread_10s: Chênh lệch giá mua-bán trung bình trong 10 giây qua. Phản ánh thanh khoản ngắn hạn.
- Đặc điểm ban đầu (Giá - Xanh navy): Chúng tôi sẽ giữ lại những tính năng hiệu quả nhất từ phiên bản trước và tối ưu hóa chúng.
Ma trận tính năng mới này giống như một bộ chỉ huy tác chiến chung, đồng thời nắm bắt thông tin tình báo thời gian thực từ “biển (xu hướng giá)”, “đất liền (vị thế thị trường)” và “không khí (tác động giao dịch)”, và khả năng ra quyết định của nó sẽ vượt trội hơn nhiều so với trước đây. Mã như sau:
import json
import math
import time
import websocket
import threading
from datetime import datetime
import numpy as np
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score
from sklearn.feature_selection import mutual_info_classif
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# ========== 全局配置 ==========
TRAIN_BARS = 100
PREDICT_HORIZON = 15
SPREAD_THRESHOLD = 0.005
SYMBOL_FMZ = "ETH_USDT"
SYMBOL_API = SYMBOL_FMZ.replace('_', '').lower()
WEBSOCKET_URL = f"wss://fstream.binance.com/stream?streams={SYMBOL_API}@aggTrade/{SYMBOL_API}@depth20@100ms"
# ========== 全局状态变量 ==========
g_model, g_scaler = None, None
g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history = [], [], []
g_last_kline_ts = 0
g_feature_names = ['price_change_15m', 'volatility_30m', 'rsi_14', 'hour_of_day',
'alpha_15m', 'wobi_10s', 'spread_10s']
# ========== 特征工程与模型训练 ==========
def calculate_features_and_labels(klines, ticks, order_books_history, is_realtime=False):
features, labels = [], []
close_prices = [k['close'] for k in klines]
# 根据是训练还是实时预测,决定循环范围
start_index = 30
end_index = len(klines) - PREDICT_HORIZON if not is_realtime else len(klines)
for i in range(start_index, end_index):
kline_start_ts = klines[i]['ts']
# --- 特征计算部分 ---
price_change_15m = (klines[i]['close'] - klines[i-15]['close']) / klines[i-15]['close']
volatility_30m = np.std(close_prices[i-30:i])
diffs = np.diff(close_prices[i-14:i+1]); gains = np.sum(diffs[diffs > 0]) / 14; losses = -np.sum(diffs[diffs < 0]) / 14
rsi_14 = 100 - (100 / (1 + gains / (losses + 1e-10)))
dt_object = datetime.fromtimestamp(kline_start_ts / 1000)
ticks_in_15m = [t for t in ticks if t['ts'] >= klines[i-15]['ts'] and t['ts'] < kline_start_ts]
buy_vol = sum(t['qty'] for t in ticks_in_15m if t['side'] == 'buy'); sell_vol = sum(t['qty'] for t in ticks_in_15m if t['side'] == 'sell')
alpha_15m = (buy_vol - sell_vol) / (buy_vol + sell_vol + 1e-10)
books_in_10s = [b for b in order_books_history if b['ts'] >= kline_start_ts - 10000 and b['ts'] < kline_start_ts]
if not books_in_10s: wobi_10s, spread_10s = 0, 0.0
else:
wobis, spreads = [], []
for book in books_in_10s:
if not book['bids'] or not book['asks']: continue
bid_vol = sum(float(p[1]) for p in book['bids']); ask_vol = sum(float(p[1]) for p in book['asks'])
wobis.append(bid_vol / (bid_vol + ask_vol + 1e-10))
spreads.append(float(book['asks'][0][0]) - float(book['bids'][0][0]))
wobi_10s = np.mean(wobis) if wobis else 0; spread_10s = np.mean(spreads) if spreads else 0
current_features = [price_change_15m, volatility_30m, rsi_14, dt_object.hour, alpha_15m, wobi_10s, spread_10s]
features.append(current_features)
# --- 标签计算部分 ---
if not is_realtime:
future_price = klines[i + PREDICT_HORIZON]['close']; current_price = klines[i]['close']
if future_price > current_price * (1 + SPREAD_THRESHOLD): labels.append(0)
elif future_price < current_price * (1 - SPREAD_THRESHOLD): labels.append(1)
else: labels.append(2)
return np.array(features), np.array(labels)
def run_analysis_report(X, y, clf, scaler):
Log("--- 模型分析报告 ---", "info")
Log("1. 特征重要性 (代理模型: 随机森林):")
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=50, random_state=42); rf.fit(X, y)
importances = sorted(zip(g_feature_names, rf.feature_importances_), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for name, importance in importances: Log(f" - {name}: {importance:.4f}")
Log("2. 特征与标签的互信息:"); mi_scores = mutual_info_classif(X, y)
mi_scores = sorted(zip(g_feature_names, mi_scores), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for name, score in mi_scores: Log(f" - {name}: {score:.4f}")
Log("3. 历史数据回测表现:"); y_pred = clf.predict(scaler.transform(X)); accuracy = accuracy_score(y, y_pred)
Log(f" - **历史回测总胜率: {accuracy * 100:.2f}%**", "success")
Log("4. 混淆矩阵 (行:真实, 列:预测):"); cm = confusion_matrix(y, y_pred)
Log(" 预测涨(0) 预测跌(1) 预测平(2)"); Log(f"真实涨(0): {cm[0] if len(cm) > 0 else [0,0,0]}")
Log(f"真实跌(1): {cm[1] if len(cm) > 1 else [0,0,0]}"); Log(f"真实平(2): {cm[2] if len(cm) > 2 else [0,0,0]}")
profit_chart = Chart({'title': {'text': f'历史回测净值曲线 (胜率: {accuracy*100:.2f}%)'}}); profit_chart.reset(); balance = 1
for i in range(len(y)):
if y_pred[i] == y[i] and y[i] != 2: balance *= (1 + 0.01)
elif y_pred[i] != y[i] and y_pred[i] != 2: balance *= (1 - 0.01)
profit_chart.add(i, balance)
Log("--- 报告结束, 5秒后进入实盘预测 ---", "info"); Sleep(5000)
def train_and_analyze():
global g_model, g_scaler, g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history
MIN_REQUIRED_BARS = 30 + PREDICT_HORIZON
if len(g_klines_1min) < MIN_REQUIRED_BARS:
Log(f"K线数量({len(g_klines_1min)})不足以进行特征工程,需要至少 {MIN_REQUIRED_BARS} 根。", "warning"); return False
Log("开始训练模型 (V2.2)...")
X, y = calculate_features_and_labels(g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history)
if len(X) < 50 or len(set(y)) < 3:
Log(f"有效训练样本不足(X: {len(X)}, 类别: {len(set(y))}),无法训练。", "warning"); return False
scaler = StandardScaler(); X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
clf = svm.SVC(kernel='rbf', C=1.0, gamma='scale'); clf.fit(X_scaled, y)
g_model, g_scaler = clf, scaler
Log("模型训练完成!", "success")
run_analysis_report(X, y, g_model, g_scaler)
return True
def aggregate_ticks_to_kline(ticks):
if not ticks: return None
return {'ts': ticks[0]['ts'] // 60000 * 60000, 'open': ticks[0]['price'], 'high': max(t['price'] for t in ticks), 'low': min(t['price'] for t in ticks), 'close': ticks[-1]['price'], 'volume': sum(t['qty'] for t in ticks)}
def on_message(ws, message):
global g_ticks, g_klines_1min, g_last_kline_ts, g_order_book_history
try:
payload = json.loads(message)
data = payload.get('data', {}); stream = payload.get('stream', '')
if 'aggTrade' in stream:
trade_data = {'ts': int(data['T']), 'price': float(data['p']), 'qty': float(data['q']), 'side': 'sell' if data['m'] else 'buy'}
g_ticks.append(trade_data)
current_minute_ts = trade_data['ts'] // 60000 * 60000
if g_last_kline_ts == 0: g_last_kline_ts = current_minute_ts
if current_minute_ts > g_last_kline_ts:
last_minute_ticks = [t for t in g_ticks if t['ts'] >= g_last_kline_ts and t['ts'] < current_minute_ts]
if last_minute_ticks:
kline = aggregate_ticks_to_kline(last_minute_ticks); g_klines_1min.append(kline)
g_ticks = [t for t in g_ticks if t['ts'] >= current_minute_ts]
g_last_kline_ts = current_minute_ts
elif 'depth' in stream:
book_snapshot = {'ts': int(data['E']), 'bids': data['b'], 'asks': data['a']}
g_order_book_history.append(book_snapshot)
if len(g_order_book_history) > 5000: g_order_book_history.pop(0)
except Exception as e: Log(f"OnMessage Error: {e}")
def start_websocket():
ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(WEBSOCKET_URL, on_message=on_message)
wst = threading.Thread(target=ws.run_forever); wst.daemon = True; wst.start()
Log("WebSocket多流订阅已启动...")
# ========== 主程序入口 ==========
def main():
global TRAIN_BARS
exchange.SetContractType("swap")
start_websocket()
Log("策略启动,进入数据收集中...")
main.last_predict_ts = 0
while True:
if g_model is None:
# --- 训练模式 ---
if len(g_klines_1min) >= TRAIN_BARS:
if not train_and_analyze():
Log("模型训练或分析失败,将增加50根K线后重试...", "error")
TRAIN_BARS += 50
else:
LogStatus(f"正在收集K线数据: {len(g_klines_1min)} / {TRAIN_BARS}")
else:
# --- **新功能:实时预测模式** ---
if len(g_klines_1min) > 0 and g_klines_1min[-1]['ts'] > main.last_predict_ts:
# 1. 标记已处理,防止重复预测
main.last_predict_ts = g_klines_1min[-1]['ts']
kline_time_str = datetime.fromtimestamp(main.last_predict_ts / 1000).strftime('%H:%M:%S')
Log(f"检测到新K线 ({kline_time_str}),准备进行实时预测...")
# 2. 检查是否有足够历史数据来为这根新K线计算特征
if len(g_klines_1min) < 30: # 至少需要30根历史K线
Log("历史K线不足,无法为当前新K线计算特征。", "warning")
continue
# 3. 计算最新K线的特征
# 我们只计算最后一条数据,所以传入 is_realtime=True
latest_features, _ = calculate_features_and_labels(g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history, is_realtime=True)
if latest_features.shape[0] == 0:
Log("无法为最新K线生成有效特征。", "warning")
continue
# 4. 标准化并预测
last_feature_vector = latest_features[-1].reshape(1, -1)
last_feature_scaled = g_scaler.transform(last_feature_vector)
prediction = g_model.predict(last_feature_scaled)[0]
# 5. 展示预测结果
prediction_text = ['**上涨**', '**下跌**', '盘整'][prediction]
Log(f"==> 实时预测结果 ({kline_time_str}): 未来 {PREDICT_HORIZON} 分钟可能 {prediction_text}", "success" if prediction != 2 else "info")
# 在这里,您可以根据 prediction 的结果,添加您的开平仓交易逻辑
# 例如: if prediction == 0: exchange.Buy(...)
else:
LogStatus(f"模型已就绪,等待新K线... 当前K线数: {len(g_klines_1min)}")
Sleep(1000) # 每秒检查一次是否有新K线
Mã này yêu cầu rất nhiều phép tính dòng K Báo cáo này rất có giá trị vì nó cho chúng ta biết “suy nghĩ” và “tính cách” của mô hình.
- Tỷ lệ thắng tổng thể trong quá trình kiểm tra ngược lịch sử: 93,33% Đây là một con số cực kỳ ấn tượng! Mặc dù chúng ta cần xem xét nó một cách khách quan (đây là một bài kiểm tra mẫu), nhưng nó cho thấy rõ sức mạnh dự đoán to lớn của các tính năng luồng lệnh và sổ lệnh mới được bổ sung! Mô hình đã tìm thấy những mô hình rất mạnh trong dữ liệu lịch sử.
- Tính năng quan trọng & Thông tin tương hỗ Vua đã ra đời: volatility_15m (biến động) và price_change_5m (thay đổi giá) vẫn là cốt lõi tuyệt đối, đúng như mong đợi. Rising Star: rsi_14 đã chứng kiến sự gia tăng đáng kể về tầm quan trọng! Điều này cho thấy trên khung thời gian ngắn hơn 5 phút, chỉ báo tâm lý “quá mua/quá bán” của RSI đã trở nên có ý nghĩa hơn. Có khả năng, wobi_10s (mất cân bằng sổ lệnh) và spread_10s (spread) cũng cho thấy một số đóng góp. Điều này rất đáng khích lệ và cho thấy các đặc điểm cấu trúc vi mô của chúng tôi đang bắt đầu hoạt động! Suy ngẫm: Đóng góp của alpha_5m (luồng lệnh) gần như bằng không. Điều này có thể là do phương pháp tính toán alpha của chúng tôi quá đơn giản, hoặc bản thân alpha 5 phút và biến động giá 5 phút chứa quá nhiều thông tin chồng chéo. Đây là một điểm tối ưu hóa quan trọng cho chúng tôi trong tương lai.
- Ma trận nhầm lẫn (bằng chứng quan trọng của thành công!) Tăng thực tế (0):[22 0] -> Trong tất cả 22 cuộc biểu tình thực tế, mô hình đã dự đoán chính xác 100%, không có bất kỳ sai sót nào! Giảm thực tế (1):[2 6] -> Trong số 8 lần giảm thực tế, mô hình đã dự đoán đúng 6 lần và bỏ lỡ 2 lần (nhầm lẫn chúng với mức tăng). Diễn giải: Mô hình này thể hiện một đặc điểm rất thú vị: nó là một công cụ phát hiện xu hướng tăng cực kỳ mạnh mẽ, nắm bắt các tín hiệu tăng gần như hoàn hảo. Nó cũng hoạt động tốt trong việc xác định xu hướng giảm (độ chính xác 6⁄8 = 75%), nhưng đôi khi mắc lỗi nhầm lẫn xu hướng giảm thành xu hướng tăng.
Vậy thì điều gì sẽ xảy ra tiếp theo Giới thiệu “Máy trạng thái tín hiệu giao dịch” Đây là phần cốt lõi và khéo léo nhất của bản nâng cấp này. Chúng tôi sẽ giới thiệu một biến trạng thái toàn cục, chẳng hạn như g_active_signal, để quản lý trạng thái “vị thế” hiện tại của chiến lược (lưu ý rằng đây chỉ là trạng thái vị thế ảo và không liên quan đến giao dịch thực tế). Logic hoạt động của máy trạng thái này như sau:
- Trạng thái ban đầu: Nhàn rỗi
- Khi chiến lược ở trạng thái này, nó sẽ đưa ra dự đoán cho mỗi dòng K mới, giống như hiện tại.
- Chuyển đổi chế độ: Khi mô hình dự đoán tín hiệu rõ ràng (ví dụ: “Lên”), chiến lược sẽ:
- In một tín hiệu vào sổ nhật ký đơn giản, dễ nhìn, ví dụ: 🎯 Tín hiệu giao dịch mới: Dự báo tăng! Thời gian quan sát 15 phút.
- Chuyển trạng thái chiến lược từ Nhàn rỗi sang Có tín hiệu. Ghi lại thời điểm kích hoạt và hướng của tín hiệu hiện tại.
- Trạng thái vị trí: Trong tín hiệu
- Khi chiến lược ở trạng thái này, nó sẽ hoàn toàn ngừng dự đoán các dòng K mới. Nó không còn quan tâm đến biến động của từng phút nữa và chuyển sang chế độ “để đạn bay”.
- Việc duy nhất nó làm là kiểm tra thời gian: liệu 15 phút (độ dài của PREDICT_HORIZON) đã trôi qua kể từ khi tín hiệu được kích hoạt hay chưa.
- Chuyển đổi trạng thái: Sau thời gian quan sát 15 phút, chính sách sẽ:
- In tín hiệu thoát rõ ràng vào nhật ký, chẳng hạn như kết thúc chu kỳ tín hiệu 🏁. Đặt lại chiến lược và tìm kiếm cơ hội mới…
- Chuyển trạng thái chiến lược từ giữ sang nhàn rỗi.
- Tại thời điểm này, chiến lược sẽ bắt đầu dự đoán lại đường K mới và tìm kiếm cơ hội giao dịch tiếp theo.
Với máy trạng thái đơn giản này, chúng tôi đã đáp ứng hoàn hảo các yêu cầu: một tín hiệu, một chu kỳ quan sát hoàn chỉnh và không có thông tin nhiễu trong suốt thời gian đó.
import json
import math
import time
import websocket
import threading
from datetime import datetime
import numpy as np
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score
from sklearn.feature_selection import mutual_info_classif
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# ========== 全局配置 ==========
TRAIN_BARS = 200 #需要更多初始数据
PREDICT_HORIZON = 15 # 回归15分钟预测周期
SPREAD_THRESHOLD = 0.005 # 适配15分钟周期的涨跌阈值
SYMBOL_FMZ = "ETH_USDT"
SYMBOL_API = SYMBOL_FMZ.replace('_', '').lower()
WEBSOCKET_URL = f"wss://fstream.binance.com/stream?streams={SYMBOL_API}@aggTrade/{SYMBOL_API}@depth20@100ms"
# ========== 全局状态变量 ==========
g_model, g_scaler = None, None
g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history = [], [], []
g_last_kline_ts = 0
g_feature_names = ['price_change_15m', 'volatility_30m', 'rsi_14', 'hour_of_day',
'alpha_15m', 'wobi_10s', 'spread_10s']
# 新功能: 信号状态机
g_active_signal = {'active': False, 'start_ts': 0, 'prediction': -1}
# ========== 特征工程与模型训练 ==========
def calculate_features_and_labels(klines, ticks, order_books_history, is_realtime=False):
features, labels = [], []
close_prices = [k['close'] for k in klines]
start_index = 30
end_index = len(klines) - PREDICT_HORIZON if not is_realtime else len(klines)
for i in range(start_index, end_index):
kline_start_ts = klines[i]['ts']
price_change_15m = (klines[i]['close'] - klines[i-15]['close']) / klines[i-15]['close']
volatility_30m = np.std(close_prices[i-30:i])
diffs = np.diff(close_prices[i-14:i+1]); gains = np.sum(diffs[diffs > 0]) / 14; losses = -np.sum(diffs[diffs < 0]) / 14
rsi_14 = 100 - (100 / (1 + gains / (losses + 1e-10)))
dt_object = datetime.fromtimestamp(kline_start_ts / 1000)
ticks_in_15m = [t for t in ticks if t['ts'] >= klines[i-15]['ts'] and t['ts'] < kline_start_ts]
buy_vol = sum(t['qty'] for t in ticks_in_15m if t['side'] == 'buy'); sell_vol = sum(t['qty'] for t in ticks_in_15m if t['side'] == 'sell')
alpha_15m = (buy_vol - sell_vol) / (buy_vol + sell_vol + 1e-10)
books_in_10s = [b for b in order_books_history if b['ts'] >= kline_start_ts - 10000 and b['ts'] < kline_start_ts]
if not books_in_10s: wobi_10s, spread_10s = 0, 0.0
else:
wobis, spreads = [], []
for book in books_in_10s:
if not book['bids'] or not book['asks']: continue
bid_vol = sum(float(p[1]) for p in book['bids']); ask_vol = sum(float(p[1]) for p in book['asks'])
wobis.append(bid_vol / (bid_vol + ask_vol + 1e-10))
spreads.append(float(book['asks'][0][0]) - float(book['bids'][0][0]))
wobi_10s = np.mean(wobis) if wobis else 0; spread_10s = np.mean(spreads) if spreads else 0
current_features = [price_change_15m, volatility_30m, rsi_14, dt_object.hour, alpha_15m, wobi_10s, spread_10s]
if not is_realtime:
future_price = klines[i + PREDICT_HORIZON]['close']; current_price = klines[i]['close']
if future_price > current_price * (1 + SPREAD_THRESHOLD):
labels.append(0); features.append(current_features)
elif future_price < current_price * (1 - SPREAD_THRESHOLD):
labels.append(1); features.append(current_features)
else:
features.append(current_features)
return np.array(features), np.array(labels)
def run_analysis_report(X, y, clf, scaler):
Log("--- 模型分析报告 V2.5 (15分钟预测) ---", "info")
Log("1. 特征重要性 (代理模型: 随机森林):")
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=50, random_state=42); rf.fit(X, y)
importances = sorted(zip(g_feature_names, rf.feature_importances_), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for name, importance in importances: Log(f" - {name}: {importance:.4f}")
Log("2. 特征与标签的互信息:"); mi_scores = mutual_info_classif(X, y)
mi_scores = sorted(zip(g_feature_names, mi_scores), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for name, score in mi_scores: Log(f" - {name}: {score:.4f}")
Log("3. 历史数据回测表现:"); y_pred = clf.predict(scaler.transform(X)); accuracy = accuracy_score(y, y_pred)
Log(f" - **历史回测总胜率: {accuracy * 100:.2f}%**", "success")
Log("4. 混淆矩阵 (行:真实, 列:预测):"); cm = confusion_matrix(y, y_pred)
Log(" 预测涨(0) 预测跌(1)"); Log(f"真实涨(0): {cm[0] if len(cm) > 0 else [0,0]}")
Log(f"真实跌(1): {cm[1] if len(cm) > 1 else [0,0]}")
profit_chart = Chart({'title': {'text': f'历史回测净值曲线 (胜率: {accuracy*100:.2f}%)'}}); profit_chart.reset(); balance = 1
for i in range(len(y)):
if y_pred[i] == y[i]: balance *= (1 + 0.01)
else: balance *= (1 - 0.01)
profit_chart.add(i, balance)
Log("--- 报告结束, 5秒后进入实盘预测 ---", "info"); Sleep(5000)
def train_and_analyze():
global g_model, g_scaler, g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history
MIN_REQUIRED_BARS = 30 + PREDICT_HORIZON
if len(g_klines_1min) < MIN_REQUIRED_BARS:
Log(f"K线数量({len(g_klines_1min)})不足以进行特征工程,需要至少 {MIN_REQUIRED_BARS} 根。", "warning"); return False
Log("开始训练模型 (V2.5)...")
X, y = calculate_features_and_labels(g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history)
if len(X) < 20 or len(set(y)) < 2:
Log(f"有效涨跌样本不足(X: {len(X)}, 类别: {len(set(y))}),无法训练。", "warning"); return False
scaler = StandardScaler(); X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
clf = svm.SVC(kernel='rbf', C=1.0, gamma='scale'); clf.fit(X_scaled, y)
g_model, g_scaler = clf, scaler
Log("模型训练完成!", "success")
run_analysis_report(X, y, g_model, g_scaler)
return True
# ========== WebSocket实时数据处理 ==========
def aggregate_ticks_to_kline(ticks):
if not ticks: return None
return {'ts': ticks[0]['ts'] // 60000 * 60000, 'open': ticks[0]['price'], 'high': max(t['price'] for t in ticks), 'low': min(t['price'] for t in ticks), 'close': ticks[-1]['price'], 'volume': sum(t['qty'] for t in ticks)}
def on_message(ws, message):
global g_ticks, g_klines_1min, g_last_kline_ts, g_order_book_history
try:
payload = json.loads(message)
data = payload.get('data', {}); stream = payload.get('stream', '')
if 'aggTrade' in stream:
trade_data = {'ts': int(data['T']), 'price': float(data['p']), 'qty': float(data['q']), 'side': 'sell' if data['m'] else 'buy'}
g_ticks.append(trade_data)
current_minute_ts = trade_data['ts'] // 60000 * 60000
if g_last_kline_ts == 0: g_last_kline_ts = current_minute_ts
if current_minute_ts > g_last_kline_ts:
last_minute_ticks = [t for t in g_ticks if t['ts'] >= g_last_kline_ts and t['ts'] < current_minute_ts]
if last_minute_ticks:
kline = aggregate_ticks_to_kline(last_minute_ticks); g_klines_1min.append(kline)
g_ticks = [t for t in g_ticks if t['ts'] >= current_minute_ts]
g_last_kline_ts = current_minute_ts
elif 'depth' in stream:
book_snapshot = {'ts': int(data['E']), 'bids': data['b'], 'asks': data['a']}
g_order_book_history.append(book_snapshot)
if len(g_order_book_history) > 5000: g_order_book_history.pop(0)
except Exception as e: Log(f"OnMessage Error: {e}")
def start_websocket():
ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(WEBSOCKET_URL, on_message=on_message)
wst = threading.Thread(target=ws.run_forever); wst.daemon = True; wst.start()
Log("WebSocket多流订阅已启动...")
# ========== 主程序入口 ==========
def main():
global TRAIN_BARS, g_active_signal
exchange.SetContractType("swap")
start_websocket()
Log("策略启动 ,进入数据收集中...")
main.last_predict_ts = 0
while True:
if g_model is None:
if len(g_klines_1min) >= TRAIN_BARS:
if not train_and_analyze():
Log(f"模型训练失败,当前目标 {TRAIN_BARS} 根K线。将增加50根后重试...", "error")
TRAIN_BARS += 50
else:
LogStatus(f"正在收集K线数据: {len(g_klines_1min)} / {TRAIN_BARS}")
else:
if not g_active_signal['active']:
if len(g_klines_1min) > 0 and g_klines_1min[-1]['ts'] > main.last_predict_ts:
main.last_predict_ts = g_klines_1min[-1]['ts']
kline_time_str = datetime.fromtimestamp(main.last_predict_ts / 1000).strftime('%H:%M:%S')
if len(g_klines_1min) < 30:
LogStatus("历史K线不足,无法预测。等待更多数据..."); continue
latest_features, _ = calculate_features_and_labels(g_klines_1min, g_ticks, g_order_book_history, is_realtime=True)
if latest_features.shape[0] == 0:
LogStatus(f"({kline_time_str}) 无法生成特征,跳过..."); continue
last_feature_vector = latest_features[-1].reshape(1, -1)
last_feature_scaled = g_scaler.transform(last_feature_vector)
prediction = g_model.predict(last_feature_scaled)[0]
if prediction == 0 or prediction == 1:
g_active_signal['active'] = True
g_active_signal['start_ts'] = main.last_predict_ts
g_active_signal['prediction'] = prediction
prediction_text = ['**上涨**', '**下跌**'][prediction]
Log(f"🎯 新的交易信号 ({kline_time_str}): 预测 {prediction_text}!观察周期 {PREDICT_HORIZON} 分钟。", "success" if prediction == 0 else "error")
else:
LogStatus(f"({kline_time_str}) 无明确信号,继续观察...")
else:
current_ts = time.time() * 1000
elapsed_minutes = (current_ts - g_active_signal['start_ts']) / (1000 * 60)
if elapsed_minutes >= PREDICT_HORIZON:
Log(f"🏁 信号周期结束。重置策略,寻找新机会...", "info")
g_active_signal['active'] = False
else:
prediction_text = ['**上涨**', '**下跌**'][g_active_signal['prediction']]
LogStatus(f"信号生效中: {prediction_text}。剩余观察时间: {PREDICT_HORIZON - elapsed_minutes:.1f} 分钟。")
Sleep(5000)
Sau đó tôi chạy mã này
 Phân tích chuyên sâu: Tại sao lại tồn tại tỷ lệ chiến thắng “hoàn hảo” 100%?
Kết quả “hoàn hảo” này hé lộ nhiều hiểu biết quan trọng và sâu sắc về học máy và thị trường tài chính. Đây không phải là lỗi, mà là một hiện tượng điển hình được gọi là “quá khớp”, có thể xảy ra trong một số điều kiện nhất định.
“Overfitting” có nghĩa là gì?
Phân tích chuyên sâu: Tại sao lại tồn tại tỷ lệ chiến thắng “hoàn hảo” 100%?
Kết quả “hoàn hảo” này hé lộ nhiều hiểu biết quan trọng và sâu sắc về học máy và thị trường tài chính. Đây không phải là lỗi, mà là một hiện tượng điển hình được gọi là “quá khớp”, có thể xảy ra trong một số điều kiện nhất định.
“Overfitting” có nghĩa là gì?
Đây là một phép so sánh sinh động: Hãy tưởng tượng chúng ta có một học sinh (mô hình SVM của chúng ta) làm một bộ bài tập rất ngắn và rất đơn giản (200 điểm dữ liệu nến mà chúng ta đã thu thập). Học sinh này rất thông minh, và thay vì học các phương pháp giải quyết vấn đề chung chung, em chỉ cần ghi nhớ câu trả lời cho một vài bài toán này.
Kết quả: Khi chúng tôi kiểm tra anh ấy bằng cùng một bộ câu hỏi thực hành (đây là “kiểm tra ngược lịch sử” của chúng tôi), anh ấy chắc chắn có thể đạt điểm tuyệt đối là 100. Tuy nhiên, khi chúng tôi đưa cho anh ấy một bộ câu hỏi hoàn toàn mới mà anh ấy chưa từng thấy trước đây (thị trường tương lai thực tế), anh ấy có thể sẽ không trả lời được bất kỳ câu hỏi nào.
- Tại sao mô hình của chúng tôi lại “quá phù hợp”?
Các mẫu đào tạo “quá ít” và “quá đặc biệt”:
Mặc dù chúng tôi đã thu thập được 200 dòng K (khoảng 3,3 giờ), theo nhật ký, số lượng mẫu “tăng và giảm hiệu quả” cuối cùng đáp ứng định nghĩa của chúng tôi chỉ là 18 + 7 = 25.
Đối với một mô hình SVM phức tạp, 25 mẫu giống như một vài con sóng trên đại dương, quá nhỏ.
Quan trọng hơn, 25 mẫu này đều đến từ một thị trường có mối tương quan cao vào cùng một buổi chiều. Chúng có thể có những “thói quen” rất giống nhau.
- Khả năng của mô hình “quá mạnh”:
- SVM là một bộ phân loại phi tuyến tính rất mạnh mẽ. Khả năng của nó giống như một bộ não có trí nhớ siêu việt.
- Khi một mô hình mạnh học từ một tập dữ liệu quá đơn giản và lặp đi lặp lại, nó có xu hướng “ghi nhớ” tất cả các chi tiết và nhiễu của dữ liệu thay vì học các quy luật vĩ mô phổ quát hơn đằng sau nó.
- Bằng chứng từ ma trận nhầm lẫn:
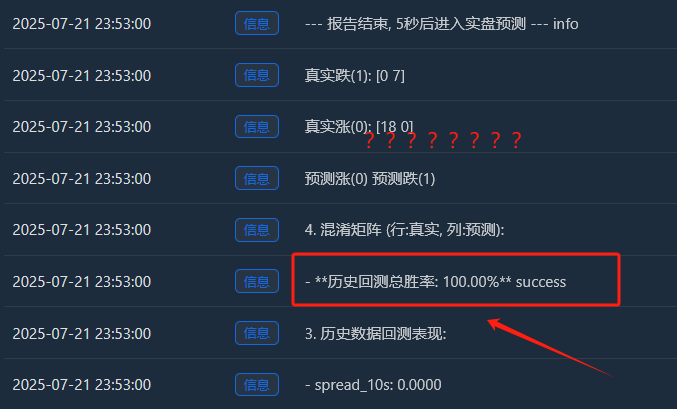
- Tăng thực tế (0):[18 0] -> 18 mẫu đang tăng, tất cả đều được ghi nhớ hoàn hảo.
- Giảm thực tế (1):[0 7] -> 7 mẫu rơi, tất cả đều được ghi nhớ hoàn hảo.
- Sự hoàn hảo này[ [18, 0], [Ma trận [0, 7] là bằng chứng không thể chối cãi về việc mô hình bị quá khớp. Nó hầu như không mắc lỗi, điều này vốn bất thường trong một thị trường tài chính đầy rẫy sự ngẫu nhiên.
Do đó, chúng ta nên hiểu tỷ lệ chiến thắng 100% này như sau:
“Mô hình đã học và ghi nhớ đáng kể tất cả các mô hình của các điều kiện thị trường cụ thể trong ba giờ qua. Điều này chứng minh tính hiệu quả của kỹ thuật tính năng và khuôn khổ mô hình của chúng tôi. Tuy nhiên, chúng tôi hoàn toàn không thể kỳ vọng nó sẽ duy trì tỷ lệ thắng cao như vậy trên thị trường thực trong tương lai. Điều này giống như một ‘bài kiểm tra bất ngờ’ hoàn hảo hơn là kết quả cuối cùng của ‘kỳ thi tuyển sinh đại học’.”
Học máy cũng là một chủ đề mà tôi đang khám phá gần đây, chúng ta sẽ nói về nó trong số tiếp theo! Chúng ta cần phải thực hiện một “cuộc chuyển đổi tư duy” toàn diện đối với “học sinh có thành kiến” này. Mục tiêu của chúng ta là phá vỡ thành kiến của em ấy và cho phép em ấy nhìn nhận “những thăng trầm” một cách công bằng và khách quan.