মাইল্যাঙ্গুয়েজ ডক
লেখক:ছোট্ট স্বপ্ন, সৃষ্টিঃ ২০২২-০৬-৩০ ১৮ঃ২৪ঃ০৬, আপডেটঃ ২০২৪-০২-০৬ ১৭ঃ৩৬ঃ১৯[TOC]
মাইল্যাঙ্গুয়েজ একটি প্রোগ্রাম্যাটিক ট্রেডিং ভাষা যা মাইল্যাঙ্গুয়েজের সাথে সামঞ্জস্যপূর্ণ এবং উন্নত। এফএমজেড কোয়ান্টের মাইল্যাঙ্গুয়েজ কঠোর সিনট্যাক্স চেকিংয়ের মধ্য দিয়ে যাবে। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, জাভাস্ক্রিপ্ট ভাষা কোড এম্বেড করতে ভাষা বর্ধন ব্যবহার করার সময়, অতিরিক্ত স্পেস অক্ষরের পরে%%অপারেটর একটি ত্রুটি রিপোর্ট করতে হবে।
-
প্রাথমিক নির্দেশাবলী
-
চুক্তি
ক্রিপ্টোকারেন্সি চুক্তি
ক্রিপ্টোকারেন্সি চুক্তি
this_week cryptocurrency futures contract this week next_week cryptocurrency futures contract next week month cryptocurrency futures contract month quarter cryptocurrency futures contract quarter next_quarter cryptocurrency futures contract next quarter third_quarter cryptocurrency futures contract third quarter last_quarter contract last quarter XBTUSD BITMEX perpetual contract swap cryptocurrency futures perpetual contracts other than BITMEX exchange For details, please refer to the exchange.SetContractType() function section of the JavaScript/Python/C++ documentation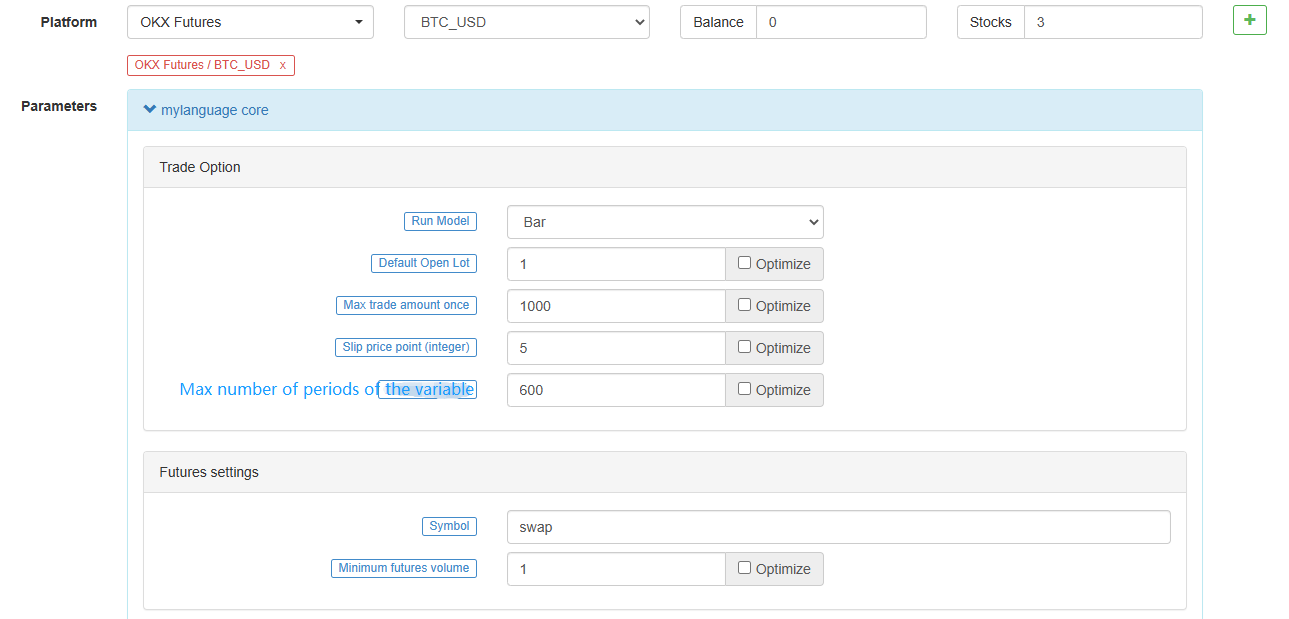
-
ভেরিয়েবল
একটি ভেরিয়েবল হ'ল কম্পিউটারের মেমরিতে ডেটা সঞ্চয় করার জন্য খোলা একটি স্থান। সহজ কথায়, এটি ডেটা সঞ্চয় করতে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
প্রথম ভেরিয়েবল খুলুন
// assign 1 to variable a a:=1;ভিতরে
MyLanguage, এটা সহজ থেকে পার্থক্য করতেdata volume:- একক-মূল্যবান ডেটাঃ কেবলমাত্র একটি মান রয়েছে, যেমনঃ
0,1,'abc'. - সিকোয়েন্স ডেটাঃ একক মানের ডেটাগুলির একটি গ্রুপের সমন্বয়ে গঠিত একটি ডেটা সিকোয়েন্স যেমনঃ
Close(সমাপ্তি মূল্য), যেখানেCloseএর বন্ধের মূল্য রয়েছেnperiods.[ 10.1 , 10.2 , 10.3 , 10.4 , 10.5 ...]
ভেরিয়েবল টাইপ থেকে আলাদা করুন - স্ট্রিং টাইপঃ এটি ``
`' দিয়ে আবৃত হতে হবে, স্ট্রিং টাইপ সরাসরি ব্যবহার করা অনুমোদিত নয়, এবং এটি ফাংশন দিয়ে ভিউতে আউটপুট করা প্রয়োজন।
INFO(CLSOE>OPEN,'OK!');- মানের ধরনঃ পূর্ণসংখ্যা, ভাসমান কমান্ড সংখ্যা (দশমিক সংখ্যা) সহ।
// integer int:=2; // decimal float:=3.1;- বুলিয়ান টাইপ, 1 (সত্য) বা 0 (মিথ্যা) ব্যবহার করেঃ 1, 0, সত্য বা মিথ্যা। উদাহরণস্বরূপঃ
A:=1>0;এই কোডটি চালানোর পর, এর মানAহল ১।
// The closing price of the current period is greater than -999, you will find that the return value of each period is 1, which means true, because the closing price is almost impossible to be negative. is_true:=Close>-999;- গ্লোবাল ভেরিয়েবল
VARIABLE:VALUE1:10; // Declare a global variable, assign the value 10, and execute it only once.ব্যাকটেস্টিং করার সময় লক্ষ্য করুনঃ
VARIABLE:NX:0; // The initial global variable NX is 0 NX..NX+1; // Accumulate 1 each time INFO(1,NX); // Print NX every timeপ্রাথমিকভাবে,
INFOবিবৃতি মুদ্রণ101হয়তো না।0শুরুতে? এর কারণ হল ব্যাকটেস্টে ১০০টি প্রাথমিক কে-লাইন রয়েছে, এবং ১০০টি কে-লাইন ইতিমধ্যে চালানো হয়েছে, যা ১০০ বার জমা হয়েছে। প্রকৃত মূল্য প্রাথমিকভাবে কতগুলি কে-লাইন পাওয়া যায় তার উপর নির্ভর করে।-
নামকরণের নিয়ম
বেশিরভাগ সিস্টেমে, ভেরিয়েবল নামকরণ সিস্টেম
সংরক্ষিত শব্দ (বিল্ট ইন ভেরিয়েবল নাম, ফাংশন নাম) ব্যবহারের অনুমতি দেয় না। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, সুপরিচিত Close,Cএছাড়াও, খাঁটি সংখ্যা বা প্রধান সংখ্যা অনুমোদিত নয়। অবশেষে, এটি খুব দীর্ঘ হতে অনুমোদিত নয়, এবং বিভিন্ন সিস্টেমের বিভিন্ন দৈর্ঘ্যের সীমাবদ্ধতা রয়েছে। প্রকৃতপক্ষে, আপনাকে চীনা ভাষার মূলধারার সিস্টেমের পার্সিংয়ের দক্ষতা সম্পর্কে চিন্তা করতে হবে না। আমি বিশ্বাস করি যেMyLanguage চীনা ভাষার জন্য খুব বন্ধুত্বপূর্ণ। অভিজ্ঞ প্রোগ্রামারদের জন্য এটি সুপারিশ করা হয় যে আপনি নিম্নলিখিত দুটি নামকরণের নিয়ম ব্যবহার করুনঃ - চীনা নাম
// elegant output 5-day moving average:=MA(C,5);- ইংরেজি + আন্ডারলাইন
// Output move_avg_5:=MA(C,5);আপনি যদি ইংরেজি পছন্দ করেন তবে আপনার ভেরিয়েবলগুলির অর্থ যতটা সম্ভব বোধগম্য করার চেষ্টা করুন। নামগুলি ব্যবহার করবেন না যেমনঃ
A1,AAA,BBB...বিশ্বাস করুন, কয়েকদিনের মধ্যে আপনি যখন আবার আপনার সূচক কোডটি পর্যালোচনা করবেন, তখন আপনি স্মৃতিশক্তি হ্রাসের কারণে খুব দুঃখিত হবেন। একইভাবে, যখন আপনি অন্যদের কাছে কোডটি রপ্তানি করবেন, পাঠক অবশ্যই ধ্বংস হয়ে যাবে।তাই এখন থেকে,
MyLanguage কে সম্পূর্ণরূপে গ্রহণ করুন! আমি আশা করি এটি আপনার বিশ্লেষণ এবং সিদ্ধান্ত গ্রহণের জন্য একটি শক্তিশালী হাতিয়ার হয়ে উঠতে পারে।
- একক-মূল্যবান ডেটাঃ কেবলমাত্র একটি মান রয়েছে, যেমনঃ
-
তথ্যের ধরন
ডাটা টাইপ একটি মৌলিক ধারণা। যখন আমরা লিখিতভাবে একটি ভেরিয়েবলের কাছে একটি পরিষ্কার ডেটা বরাদ্দ করি, তখন ভেরিয়েবলটি নিজেই ডাটা টাইপ হয়ে যায়।
-
- মানের ধরনঃ
1.2.3.1.1234.2.23456 ... -
- স্ট্রিং টাইপ ((str):
'1' .'2' .'3' ,String types must be wrapped with '' -
- সিকোয়েন্স ডেটাঃ
A collection of data consisting of a series of single-valued data -
- বুল টাইপ (বুল টাইপ):
ব্যবহার
1প্রতিনিধিত্ব করেtrueএবং0জন্যfalse.উদাহরণ
// declare a variable of value type var_int := 1; // Declare a variable for sequence data var_arr := Close; // The string type cannot be declared alone, it needs to be combined with the function INFO(C>O, 'positive line');
-
-
অপারেটার
সূচক কোড চালানোর জন্য ব্যবহৃত অপারেশন এবং গণনা কেবল অপারেশনে জড়িত চিহ্ন।
-
নিয়োগ অপারেটর
একটি পরিবর্তনশীল একটি মান নির্ধারণ করতে
-
:
:, গ্রাফ (সাবগ্রাফ) এ বরাদ্দ এবং আউটপুট প্রতিনিধিত্ব করে।Close1:Close; // Assign Close to the variable Close1 and output to the figure -
:=
:=, অ্যাসাইনমেন্টের প্রতিনিধিত্ব করে, কিন্তু গ্রাফ (প্রধান গ্রাফ, সাব গ্রাফ...), বা অবস্থা বার টেবিলে প্রদর্শিত হয় না।Close2:=Close; // Assign Close to the variable Close2 -
^^
^^দুই^প্রতীকগুলি অ্যাসাইনমেন্টের প্রতিনিধিত্ব করে, ভেরিয়েবলগুলির মান নির্ধারণ করে এবং গ্রাফটিতে আউটপুট দেয় (প্রধান গ্রাফ) ।lastPrice^^C; -
..
.., দুই.প্রতীকগুলি অ্যাসাইনমেন্টের প্রতিনিধিত্ব করে, ভেরিয়েবলগুলির মান নির্ধারণ করে এবং চার্টে ভেরিয়েবলের নাম এবং মান প্রদর্শন করে, কিন্তু চার্টে ছবি আঁকে না (প্রধান ছবি, উপ-ছবি...) ।openPrice..O
-
-
সম্পর্কিত অপারেটর
রিলেশনাল অপারেটরগুলি বাইনারি অপারেটর যা দুটি ডেটার মধ্যে সম্পর্ক নির্ধারণের জন্য শর্তাধীন অভিব্যক্তিতে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
রিটার্ন মানঃ বুলিয়ান টাইপ, হয়
true১) অথবাfalse(0).-
- বেশি
>
// Assign the operation result of 2>1 to the rv1 variable, at this time rv1=1 rv1:=2>1; - বেশি
-
- কম
<
// Returns false, which is 0, because 2 is greater than 1 rv3:=2<1; - কম
-
- এর চেয়ে বেশি বা সমান
>=
x:=Close; // Assign the result of the operation that the closing price is more than or equal to 10 to the variable rv2 // Remark that since close is a sequence of data, when close>=10 is performed, the operation is performed in each period, so each period will have a return value of 1 and 0 rv2:=Close>=10; - এর চেয়ে বেশি বা সমান
-
- কম বা সমান
<=
omitted here - কম বা সমান
-
- সমান
=
A:=O=C; // Determine whether the opening price is equal to the closing price. - সমান
-
- সমান নয়
<>
1<>2 // To determine whether 1 is not equal to 2, the return value is 1 (true) - সমান নয়
-
-
লজিক্যাল অপারেটর
রিটার্ন মানঃ বুলিয়ান টাইপ, হয়
true১) অথবাfalse(0).- যৌক্তিক এবং
&&, দ্বারা প্রতিস্থাপিত হতে পারেand, এবং সংযোগের বাম এবং ডান দিক একই সময়ে স্থাপন করা আবশ্যক।
// Determine whether cond_a, cond_b, cond_c are established at the same time cond_a:=2>1; cond_b:=4>3; cond_c:=6>5; cond_a && cond_b and cond_c; // The return value is 1, established- যৌক্তিক বা
||, আপনি ব্যবহার করতে পারেনorবা লিঙ্কের বাম এবং ডান দিকের প্রতিস্থাপনের জন্য, এক দিকটি সত্য (সত্য), পুরোটি সত্য (মূল্য ফেরত সত্য) ।
cond_a:=1>2; cond_b:=4>3; cond_c:=5>6; cond_a || cond_b or cond_c; // The return value is 1, established()অপারেটর, বন্ধনী মধ্যে অভিব্যক্তি প্রথম মূল্যায়ন করা হবে.
1>2 AND (2>3 OR 3<5) // The result of the operation is false 1>2 AND 2>3 OR 3<5 // The result of the operation is true - যৌক্তিক এবং
-
গাণিতিক অপারেটর
Return value: numeric typeগাণিতিক অপারেটর হ'ল গাণিতিক অপারেটর। এটি মৌলিক গাণিতিক ক্রিয়াকলাপগুলি (গাণিতিক অপারেটর) সম্পূর্ণ করার জন্য একটি প্রতীক, যা চারটি গাণিতিক ক্রিয়াকলাপ প্রক্রিয়া করার জন্য ব্যবহৃত একটি প্রতীক।
-
প্লাস +
A:=1+1; // return 2 -
বিয়োগ -
A:=2-1; // return 1 -
*গুণ করুন *
A:=2*2; // return 4 -
বিভক্ত /
A:=4/2; // return 2
-
-
-
কার্যাবলী
-
কার্যাবলী
প্রোগ্রামিং জগতে, একটি
function হল কোডের একটি টুকরা যা একটি নির্দিষ্ট ফাংশন বাস্তবায়ন করে। এবং এটি অন্য কোড দ্বারা কল করা যেতে পারে, সাধারণ ফর্মটি নিম্নরূপঃ function(param1,param2,...)-
রচনাঃ
ফাংশন নাম (প্যারামিটার1, প্যারামিটার2,...), কোন প্যারামিটার থাকতে পারে অথবা একাধিক প্যারামিটার থাকতে পারে। উদাহরণস্বরূপ,
MA(x,n);এর সরল চলমান গড় ফিরে মানেxভিতরেnতাদের মধ্যে,MA()একটি ফাংশন,xএবংnফাংশনের পরামিতি।একটি ফাংশন ব্যবহার করার সময়, আমাদের ফাংশনের মৌলিক সংজ্ঞা বুঝতে হবে, অর্থাৎ ফাংশনটি কল করে কী ডেটা পাওয়া যায়। সাধারণভাবে বলতে গেলে, ফাংশনগুলির পরামিতি রয়েছে। যখন আমরা পরামিতিগুলি পাস করি, তখন আমাদের নিশ্চিত করতে হবে যে ইনকামিং ডেটা টাইপটি ধারাবাহিক। এই পর্যায়ে, বেশিরভাগ আইডিইগুলির কোড ইঙ্গিত ফাংশনটি খুব অসম্পূর্ণ। দেওয়া প্যারামিটারের একটি ডেটা টাইপ রয়েছে, যা আমাদের ব্যবহারে কিছু সমস্যা নিয়ে আসে এবং
MA(x,n);এইভাবে ব্যাখ্যা করা হয়ঃReturn to simple moving average Usage: AVG:=MA(X,N): N-day simple moving average of X, algorithm (X1+X2+X3+...+Xn)/N, N supports variablesএটি নতুনদের জন্য খুবই বিরক্তিকর, কিন্তু পরবর্তী, আমরা ফাংশনটি পুরোপুরি বিশ্লেষণ করব, ফাংশনটি শিখতে এবং ব্যবহার করার দ্রুত উপায় খুঁজে বের করার চেষ্টা করব।
-
-
রিটার্ন মান
দ্রুত ফাংশন শিখতে, আমাদের প্রথমে একটি ধারণা বুঝতে হবে, এটিকে
return value ফিরে যানবলা হয়, , নাম অনুসারে, এর অর্থ return back ; মানটি specific value এর প্রতিনিধিত্ব করে, তাহলে রিটার্ন ভ্যালুর অর্থ হলঃ প্রাপ্ত করা যায় এমন ডেটা। // Because it will be used in the following code, the variable return_value is used to receive and save the return value of function() // retrun_value := function(param1,param2); // For example: AVG:=MA(C,10); // AVG is retrun_value, function is MA function, param1 parameter: C is the closing price sequence data, param2 parameter: 10. -
পরামিতি
দ্বিতীয়ত, ফাংশনের দ্বিতীয় গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ধারণাটি হল প্যারামিটার, এবং বিভিন্ন প্যারামিটারে পাস করে বিভিন্ন রিটার্ন মান পাওয়া যায়।
// The variable ma5 receives the 5-day moving average of closing prices ma5:=MA(C,5); // The variable ma10 receives the 10-day moving average of closing prices ma10:=MA(C,10);প্রথম প্যারামিটার
Xউপরের ভেরিয়েবলগুলির মধ্যেma5,ma10হয়C(বন্ধ মূল্য), আসলে,Cএছাড়াও একটি ফাংশন (খোলার থেকে বর্তমান পর্যন্ত বন্ধ মূল্যের ক্রম ফেরত), কিন্তু এটি কোন পরামিতি আছে। দ্বিতীয় পরামিতি 5 এবং 10 বলতে ব্যবহৃত হয়MA()ফাংশন যা আমরা কয়েক দিনের জন্য বন্ধ মূল্যের চলমান গড় পেতে চান। ফাংশন পরামিতি মাধ্যমে ব্যবহার করার জন্য আরো নমনীয় হয়ে ওঠে। -
কিভাবে শিখবেন
-
- প্রথমত, আমাদের বুঝতে হবে একটি ফাংশন কি করে, অর্থাৎ, এই ফাংশনটি আমাদের কাছে কোন ডেটা ফেরত দিতে পারে।
-
- শেষ জিনিস হল রিটার্ন ভ্যালুর টাইপ বুঝতে হবে। সব পরে, আমরা ফাংশন ব্যবহার রিটার্ন ভ্যালু পেতে।
-
- উপরন্তু, আমরা প্যারামিটার তথ্য টাইপ জানতে হবে
MA(x,n), যদি আপনি প্যারামিটারের ডেটা টাইপ জানেন নাx,n, এটি সঠিকভাবে মান ফেরত পেতে সক্ষম হবে না.
- উপরন্তু, আমরা প্যারামিটার তথ্য টাইপ জানতে হবে
নিম্নলিখিত ফাংশন প্রবর্তন এবং ব্যবহারে, উপরের তিনটি নীতি অনুসরণ করুন।
-
-
-
ভাষার উন্নতি
-
MyLanguageএবংJavaScriptমিশ্র ভাষার প্রোগ্রামিং%% // This can call any API quantified of FMZ scope.TEST = function(obj) { return obj.val * 100; } %% Closing price: C; Closing price magnified 100 times: TEST(C); The last closing price is magnified by 100 times: TEST(REF(C, 1)); // When the mouse moves to the K-line of the backtest, the variable value will be prompted-
scopeবস্তুদ্য
scopeobject অ্যাট্রিবিউট যোগ করতে পারে এবং অ্যাট্রিবিউটগুলিতে অ্যানোনিম ফাংশন বরাদ্দ করতে পারে, এবং এই অ্যাট্রিবিউট দ্বারা উল্লেখিত অ্যানোনিম ফাংশনটি MyLanguage এর কোড অংশে কল করা যেতে পারে। -
scope.getRefs(obj)ফাংশনভিতরে
JavaScriptকোড ব্লক, কল করুনscope.getRefs(obj)ফাংশন পাস ইন তথ্য ফেরতobjobject.দ্য
JavaScriptনিম্নলিখিত কোড দিয়ে আবৃত%% %%পেয়ে যাবেCপাস করা হয় যখনTEST(C)MyLanguage কোডের ফাংশনটিকে Close price বলা হয়। দ্যscope.getRefsফাংশন এই K-লাইন তথ্য সব বন্ধ মূল্য ফেরত দেবে.throw "stop"প্রোগ্রাম বিরতি দিতে, পরিবর্তনশীলarrআপনি মুছে ফেলার চেষ্টা করতে পারেনthrow "stop", এটি বাস্তবায়ন করবেreturnশেষেJavaScriptকোড, এবং সব বন্ধ মূল্য তথ্য ফেরত।%% scope.TEST = function(obj){ var arr = scope.getRefs(obj) Log("arr:", arr) throw "stop" return } %% TEST(C); -
scope.bars
অ্যাক্সেস সব K-লাইন বার
JavaScriptকোড ব্লক।দ্য
TESTফাংশন একটি মান প্রদান করে। 1 একটি নেতিবাচক রেখা এবং 0 একটি ধনাত্মক রেখা।%% scope.TEST = function(){ var bars = scope.bars return bars[bars.length - 1].Open > bars[bars.length - 1].Close ? 1 : 0 // Only numeric values can be returned } %% arr:TEST;# Attention: # An anonymous function received by TEST, the return value must be a numeric value. # If the anonymous function has no parameters, it will result in an error when calling TEST, writing VAR:=TEST; and writing VAR:=TEST(); directly. # TEST in scope.TEST must be uppercase. -
এ বিষয়ে
JavaScriptকোড ব্লক, বর্তমান বার অ্যাক্সেস.উচ্চ উদ্বোধনী মূল্য এবং নিম্ন বন্ধ মূল্যের গড় গণনা করুন।
%% scope.TEST = function(){ var bar = scope.bar var ret = (bar.Open + bar.Close + bar.High + bar.Low) / 4 return ret } %% avg^^TEST; -
scope.depth
বাজারের গভীরতার তথ্যের অ্যাক্সেস (অর্ডার বুক)
%% scope.TEST = function(){ Log(scope.depth) throw "stop" // After printing the depth data once, throw an exception and pause } %% TEST; -
scope.symbol
বর্তমান ট্রেডিং জোড়ার নাম স্ট্রিং পান।
%% scope.TEST = function(){ Log(scope.symbol) throw "stop" } %% TEST; -
scope.barPos
K-লাইন এর Bar অবস্থান নিন.
%% scope.TEST = function(){ Log(scope.barPos) throw "stop" } %% TEST; -
scope.get_locals ((
name ) এই ফাংশনটি MyLanguage এর কোড বিভাগে ভেরিয়েবল পেতে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
V:10; %% scope.TEST = function(obj){ return scope.get_locals('V') } %% GET_V:TEST(C);# Attention: # If a variable cannot calculate the data due to insufficient periods, call the scope.get_locals function in the JavaScript code at this time # When getting this variable, an error will be reported: line:XX - undefined locals A variable name is undefined -
scope.canTrade
দ্য
canTradeবর্তমান বারটি ট্রেড করা যায় কিনা তা চিহ্নিত করে (বর্তমান বারটি শেষ কিনা)উদাহরণস্বরূপ, বাজারের তথ্য মুদ্রণ করা হয় যখন কৌশলটি এমন অবস্থায় থাকে যেখানে অর্ডারটি ট্রেড করা যায়
%% scope.LOGTICKER = function() { if(exchange.IO("status") && scope.canTrade){ var ticker = exchange.GetTicker(); if(ticker){ Log("ticker:", ticker); return ticker.Last; } } } %% LASTPRICE..LOGTICKER;
-
-
অ্যাপ্লিকেশন উদাহরণঃ
%% scope.TEST = function(a){ if (a.val) { throw "stop" } } %% O>C,BK; C>O,SP; TEST(ISLASTSP);একবার পজিশন খোলার এবং বন্ধ করার পর কৌশল বন্ধ করুন।
-
-
মাল্টি-পিরিয়ড রেফারেন্স
সিস্টেমটি স্বয়ংক্রিয়ভাবে একটি উপযুক্ত অন্তর্নিহিত কে-লাইন সময়কাল নির্বাচন করবে এবং ডেটাগুলির নির্ভুলতা নিশ্চিত করার জন্য সমস্ত রেফারেন্সযুক্ত কে-লাইন ডেটা সংশ্লেষণ করতে এই অন্তর্নিহিত কে-লাইন সময়কালের ডেটা ব্যবহার করবে।
-
ব্যবহারঃ
#EXPORT formula_name ... #ENDযদি সূত্রটি শুধুমাত্র বিভিন্ন সময়ের তথ্য পাওয়ার জন্য গণনা করা না হয়, তাহলে আপনি একটি খালি সূত্রও লিখতে পারেন।একটি খালি সূত্র হলঃ
#EXPORT TEST NOP; #END // end -
ব্যবহারঃ
#IMPORT [MIN,period,formula name] AS variable valueএকটি সূত্র উল্লেখ করতে। সেট সময়ের বিভিন্ন তথ্য (বন্ধ মূল্য, খোলার মূল্য, ইত্যাদি, পরিবর্তনশীল মান দ্বারা প্রাপ্ত) পান।দ্য
MINমধ্যেIMPORTকমান্ড মানেমিনিট স্তর.MyLanguage এর FMZ Quant প্ল্যাটফর্ম, এবং শুধুমাত্রMINস্তর সমর্থন করা হয়IMPORTcommand. অ-মানক সময়কাল এখন সমর্থিত. উদাহরণস্বরূপ, আপনি ব্যবহার করতে পারেন#IMPORT [MIN, 240, TEST] AS VAR240যেমন 240-মিনিট সময়কাল (4 ঘন্টা) কে-লাইন ডেটা আমদানি করতে।কোডের উদাহরণঃ
// This code demonstrates how to reference formulas of different periods in the same code // #EXPORT extended grammar, ending with #END marked as a formula, you can declare multiple #EXPORT TEST Mean value 1: EMA(C, 20); Mean value 2: EMA(C, 10); #END // end #IMPORT [MIN,15,TEST] AS VAR15 // Quoting the formula, the K-line period takes 15 minutes #IMPORT [MIN,30,TEST] AS VAR30 // Quoting the formula, the K-line period takes 30 minutes CROSSUP(VAR15.Mean value is 1, VAR30.Mean value is 1),BPK; CROSSDOWN(VAR15.Mean value is 2, VAR30.Mean value is 2),SPK; The highest price in fifteen minutes:VAR15.HIGH; The highest price in thirty minutes:VAR30.HIGH; AUTOFILTER; -
ব্যবহারের সময় সতর্কতা অবলম্বন করা প্রয়োজন।
REF,LLV,HHVএকাধিক সময়কালের ডেটা রেফারেন্স করার সময় ডেটা রেফারেন্স করার জন্য অন্যান্য নির্দেশাবলী।(*backtest start: 2021-08-05 00:00:00 end: 2021-08-05 00:15:00 period: 1m basePeriod: 1m exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_OKCoin","currency":"ETH_USD"}] args: [["TradeAmount",100,126961],["ContractType","swap",126961]] *) %% scope.PRINTTIME = function() { var bars = scope.bars; return _D(bars[bars.length - 1].Time); } %% BARTIME:PRINTTIME; #EXPORT TEST REF1C:REF(C,1); REF1L:REF(L,1); #END // end #IMPORT [MIN,5,TEST] AS MIN5 INFO(1, 'C:', C, 'MIN5.REF1C:', MIN5.REF1C, 'REF(MIN5.C, 1):', REF(MIN5.C, 1), 'Trigger BAR time:', BARTIME, '#FF0000'); INFO(1, 'L:', L, 'MIN5.REF1L:', MIN5.REF1L, 'REF(MIN5.L, 1):', REF(MIN5.L, 1), 'Trigger BAR time:', BARTIME, '#32CD32'); AUTOFILTER;এর মধ্যে পার্থক্যের তুলনা
MIN5.REF1CএবংREF(MIN5.C, 1)আমরা খুঁজে পেতে পারিঃMIN5.REF1C৫ মিনিটের কে-লাইন ডেটার বর্তমান মুহুর্তে পূর্ববর্তী BAR-এর বন্ধের মূল্য।REF(MIN5.C, 1)বর্তমান মডেলের K-লাইন সময়কাল (উপরের কোড ব্যাকটেস্ট সময়কাল 1 মিনিটে সেট করা হয়েছে, অর্থাৎ ```period: 1m``), 5 মিনিটের সময়ের বন্ধের মূল্য যেখানে বর্তমান মুহুর্তে penultimate BAR অবস্থিত। এই দুটি সংজ্ঞা পৃথক, এবং তারা প্রয়োজন হিসাবে ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে।
-
-
মোড বর্ণনা
-
এক খোলার এবং এক স্তরায়নের সিগন্যাল ফিল্টারিং মডেল
মডেলের মধ্যে,
AUTOFILTERফাংশনটি একটি খোলার এবং এক বন্ধের সংকেত ফিল্টারিং নিয়ন্ত্রণ এবং উপলব্ধি করার জন্য লেখা হয়েছে। যখন শর্ত পূরণ করে এমন একাধিক খোলার সংকেত থাকে, প্রথম সংকেতটি বৈধ সংকেত হিসাবে নেওয়া হয়, এবং একই সংকেতটি কে-লাইনে ফিল্টার করা হবে।ফিল্টারিং মডেল দ্বারা সমর্থিত নির্দেশাবলীঃ BK, BP, BPK, SK, SP, SPK, CLOSEOUT ইত্যাদি। লট নম্বর সহ নির্দেশাবলী যেমন BK ((5) সমর্থিত নয়।
উদাহরণস্বরূপ
MA1:MA(CLOSE,5); MA2:MA(CLOSE,10); CROSSUP(C,MA1),BK; CROSSUP(MA1,MA2),BK; C>BKPRICE+10||C<BKPRICE-5,SP; AUTOFILTER;Comprehension: As in the above example, when AUTOFILTER is not set, the third row BK, the fourth row BK and the fifth row SP are triggered in sequence, and each K-line triggers a signal once. After opening the position, and closing the position, the model state is reset. If AUTOFILTER is set, after triggering BK, only SP is triggered, other BK signals are ignored, and each K-line triggers a signal once. -
ক্রমবর্ধমান এবং হ্রাস অবস্থান মডেল
দ্য
AUTOFILTERফাংশনটি মডেলটিতে লিখিত নয়, যা ধারাবাহিক খোলার সংকেত বা ধারাবাহিক বন্ধের সংকেত দেয়, যা অবস্থান বাড়াতে এবং হ্রাস করতে পারে।সমর্থিত নির্দেশাবলীঃ BK ((N), BP ((N), SK ((N), SP ((N), CLOSEOUT, BPK ((N), SPK ((N), লটের আকার ছাড়া খোলা এবং বন্ধ আদেশগুলি সমর্থিত নয়। (১) নির্দেশাবলীর গোষ্ঠীভুক্তকরণ সমর্থিত। (২) যখন একই সময়ে একাধিক নির্দেশের শর্ত পূরণ করা হয়, তখন সিগন্যালগুলি শর্তাধীন বিবৃতিগুলি লেখার ক্রম অনুসারে কার্যকর করা হয়। উদাহরণস্বরূপঃ
MA1:MA(CLOSE,5); MA2:MA(CLOSE,10); CROSSUP(C,MA1),BK(1); CROSSUP(MA1,MA2),BK(1); C>BKPRICE+10||C<BKPRICE-5,SP(BKVOL);ব্যবহার
TRADE\_AGAINএকই কমান্ড লাইন, একাধিক সিগন্যাল পরপর করা সম্ভব।Comprehension: The above example is executed one by one, and the signal after execution is no longer triggered. Reset the model status after closing the position. A K -line triggers a signal once. -
এক K-লাইন এবং এক সংকেত সহ মডেল
K-লাইন শেষ হয়েছে কিনা তা নির্বিশেষে, সিগন্যালটি রিয়েল-টাইম অর্ডারে গণনা করা হয়, অর্থাৎ, অর্ডারটি শেষ হওয়ার আগে K-লাইন স্থাপন করা হয়; K-লাইনটি শেষে পর্যালোচনা করা হয়। যদি অবস্থান দিকটি K-লাইনের শেষে সংকেতের দিকের সাথে মেলে না, তবে অবস্থানটি স্বয়ংক্রিয়ভাবে সিঙ্ক্রোনাইজ হবে।
উদাহরণস্বরূপঃ
MA1:MA(CLOSE,5); MA2:MA(CLOSE,10); CROSSUP(MA1,MA2),BPK; //The 5-period moving average crosses up, and the 10-period moving average goes long. CROSSDOWN(MA1,MA2),SPK; //The 5-period moving average crosses down, and the 10-period moving average goes short. AUTOFILTER; -
এক কে-লাইনে একাধিক সংকেতের একটি মডেল
মডেল ব্যবহার করে
multsigএকটি K-লাইন থেকে একাধিক সংকেত নিয়ন্ত্রণ এবং বাস্তবায়ন করতে।K-লাইন শেষ হয়েছে কিনা তা নির্বিশেষে, সিগন্যালটি রিয়েল টাইমে গণনা করা হয়।
সিগন্যালটি পর্যালোচনা করা হয় না, কোন সিগন্যাল অদৃশ্য হয় না, এবং সিগন্যালের দিকটি সর্বদা অবস্থানের দিকের সাথে সামঞ্জস্যপূর্ণ।
যদি একাধিক সিগন্যাল শর্ত এক কে-লাইনে পূরণ করা হয়, এটি বারবার চালানো যেতে পারে।
For example: MA1:MA(CLOSE,5); MA2:MA(CLOSE,10); CROSSUP(MA1,MA2),BK; C>BKPRICE+10||C<BKPRICE-5,SP; AUTOFILTER; MULTSIG(0,0,2,0);MULTSIGএক কমান্ড লাইনের মধ্যে একাধিক কমান্ড লাইন চালাতে পারে। একটি কমান্ড লাইন শুধুমাত্র একবার সিগন্যাল করা হয়.O<C,BK; // These conditions may all be executed in a K-line Bar, but only one signal per line 10+O<C,BK; // Strategy plus TRADE_AGAIN(10);it can make multiple signals per line 20+O<C,BK; 40+O<C,BK; MULTSIG(1,1,10);পরিপূরকঃ ১.পজিশন যোগ ও হ্রাসের মডেল, একটি সংকেত এবং একটি কে-লাইন দুটি উপায়েঃ ক্লোজিং মূল্যে অর্ডার স্থাপন এবং অর্ডার মূল্যে অর্ডার স্থাপন, উভয়ই সমর্থিত। ২.পজিশন যোগ ও হ্রাসের মডেলটি একটি কে-লাইন থেকে একাধিক সংকেত অর্ডার করারও সমর্থন করে। যোগ এবং পজিশন হ্রাস মডেল, লিখুন
multsigএকটি K-লাইন একাধিক সংযোজন বা একাধিক হ্রাস উপলব্ধি করার জন্য ফাংশন।
-
-
কার্যকর মোড
-
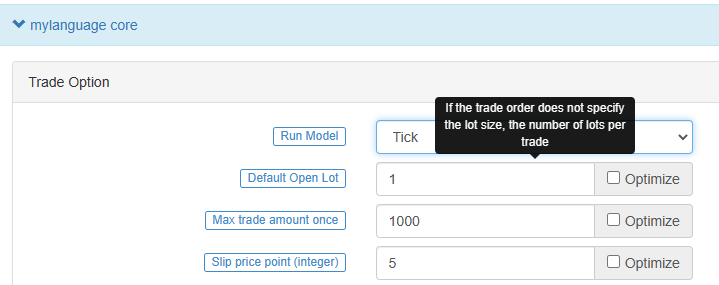
বার মডেল
বার মডেলটি এমন মডেলকে বোঝায় যা বর্তমান বারটি সম্পন্ন হওয়ার পরে কার্যকর হয় এবং পরবর্তী বারটি শুরু হলে ট্রেডিং কার্যকর হয়।
-
টিক মডেল
টিক মডেলের অর্থ হল যে মডেলটি প্রতিটি মূল্য আন্দোলনের জন্য একবার কার্যকর করা হয় এবং যখনই কোনও সংকেত থাকে তখনই ট্রেড করা হয়। টিক মডেল পূর্ববর্তী দিনের সংকেতকে উপেক্ষা করে (পূর্ববর্তী দিনের সংকেতটি একই দিনে অবিলম্বে কার্যকর করা হয়), এবং টিক মডেলটি কেবলমাত্র বর্তমান বাজারের ডেটাতে ফোকাস করে সংকেতটি ট্রিগার হয় কিনা তা নির্ধারণ করতে।
-
-
চার্ট প্রদর্শন
-
প্রধান চার্টের জন্য অতিরিক্ত সূচক
অপারেটর ব্যবহার করুন
^^, সেট সূচকগুলি মূল চার্টে প্রদর্শিত হয় যখন ভেরিয়েবলগুলির মান নির্ধারণ করা হয়।MA60^^MA(C, 60); // Calculate the average indicator with the parameter of 60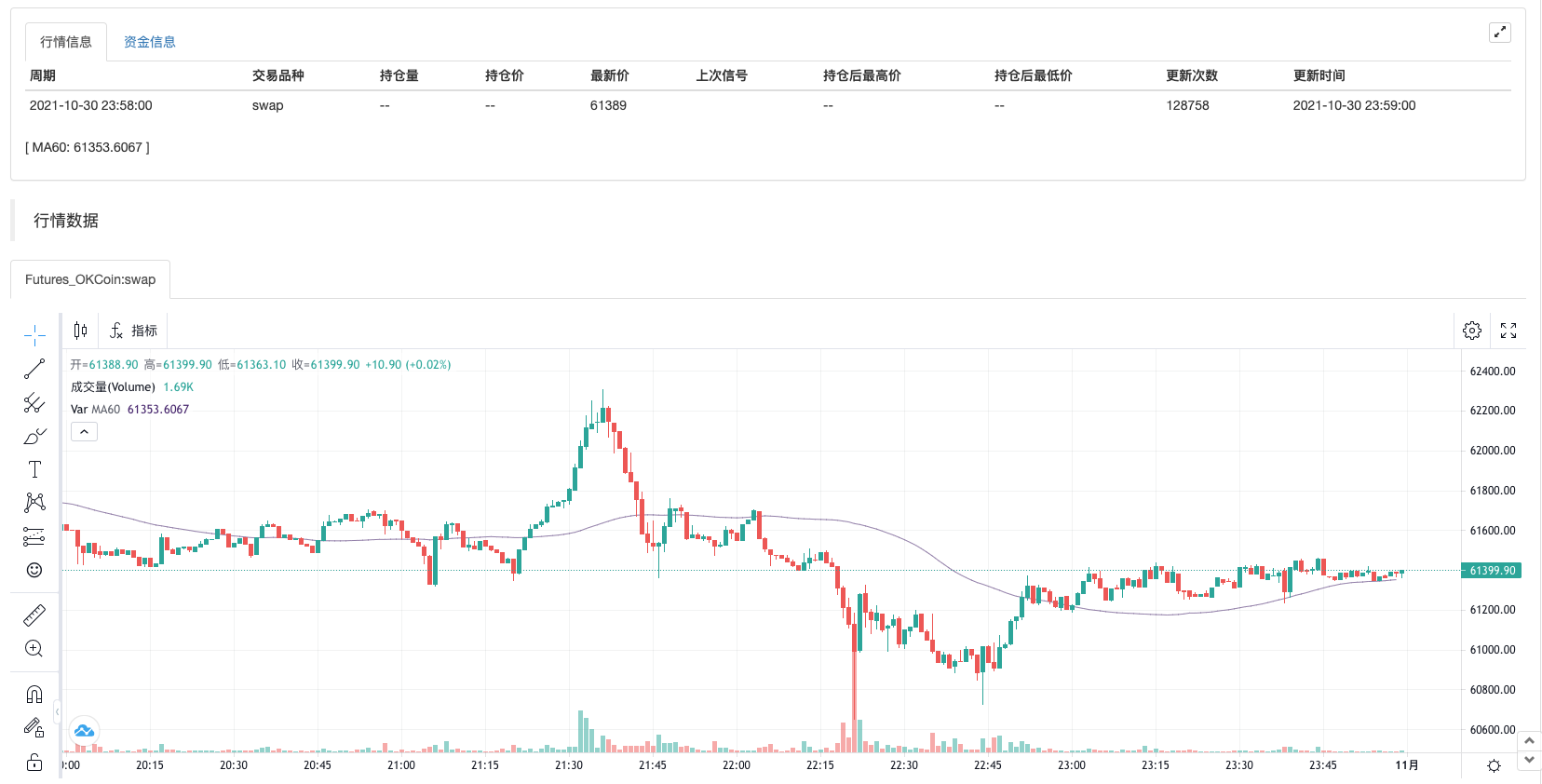
-
উপ-গ্রাফের জন্য অতিরিক্ত সূচক
অপারেটর ব্যবহার করুন
:, ভেরিয়েবলের মান নির্ধারণ করার সময় উপ-চার্টটিতে সেট সূচক প্রদর্শিত হয়।ATR:MA(MAX(MAX((HIGH-LOW),ABS(REF(CLOSE,1)-HIGH)),ABS(REF(CLOSE,1)-LOW)),26); // Assign a value to the ATR variable, the ":" symbol is followed by the formula for calculating the ATR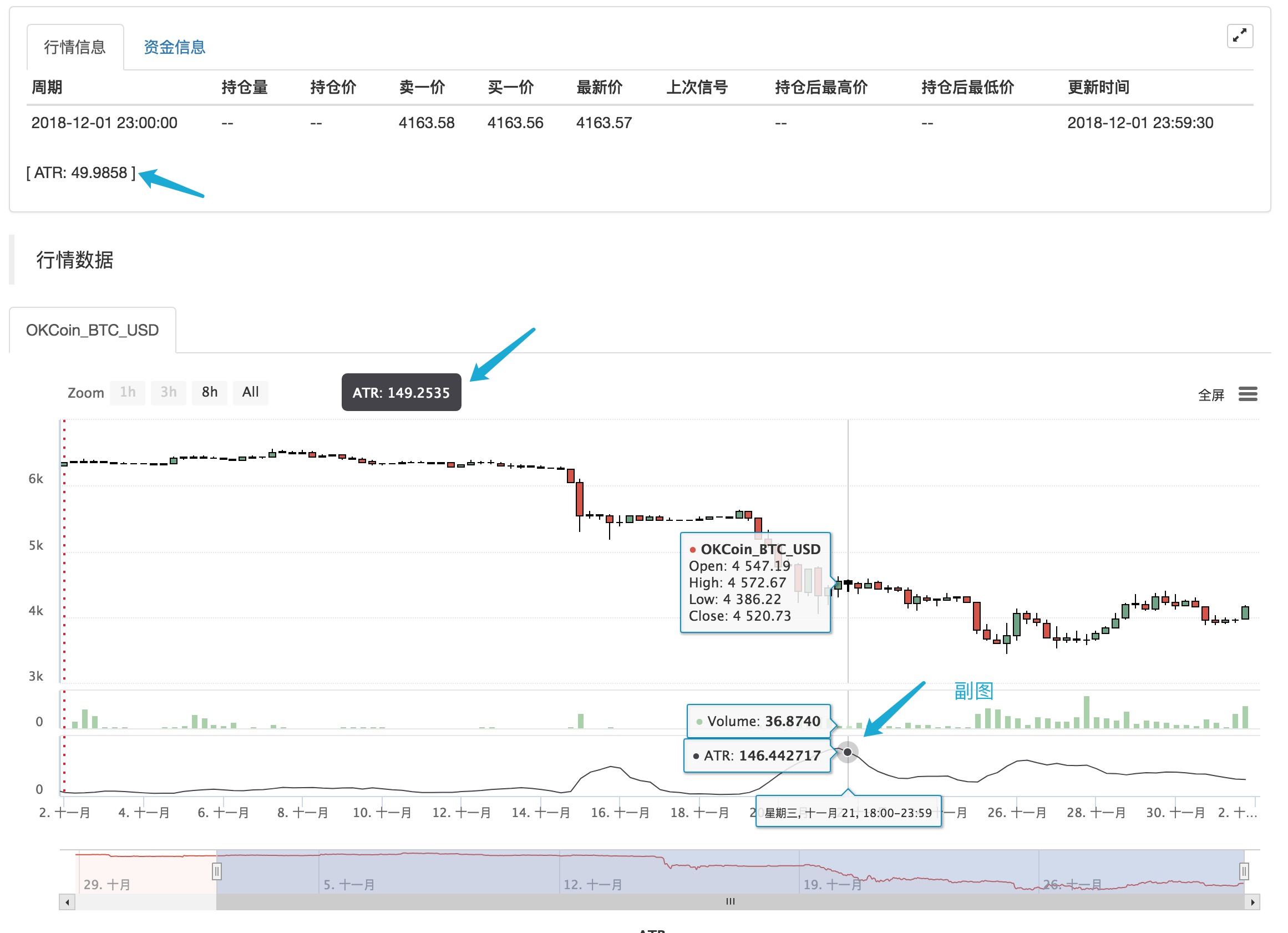
যদি আপনি চান না যে এটি প্রধান বা উপচার্টে প্রদর্শিত হবে, তাহলে
... অপারেটর ব্যবহার করুন। MA60..MA(C, 60); // Calculate the average indicator with the parameter of 60আপনি ব্যবহার করতে পারেন
DOTএবংCOLORREDলাইন টাইপ এবং লাইন রঙ, ইত্যাদি সেট করতে, মাইল্যাঙ্গুয়েজের সাথে পরিচিত ব্যবহারকারীদের অভ্যাস অনুসারে।
-
-
সাধারণ সমস্যা
উপস্থাপন করুনসমস্যাসাধারণভাবে নির্দেশক লেখার প্রক্রিয়ায় দেখা যায়, সাধারণত লেখার সময় যে বিষয়গুলির প্রতি মনোযোগ দিতে হবে (ধারাবাহিকভাবে যুক্ত) ।
-
সেমিকোলনটি লক্ষ্য করুন
;শেষের দিকে। -
মনে রাখবেন যে সিস্টেম কীওয়ার্ডগুলি ভেরিয়েবল হিসাবে ঘোষণা করা যাবে না।
-
লক্ষ্য করুন যে স্ট্রিং ব্যবহার করেএকক উদ্ধৃতি, উদাহরণস্বরূপঃ স্ট্রিং
'Open position'. -
মন্তব্য
সংক্ষিপ্তসার
-
// The Remark content(ইনপুট পদ্ধতি উভয় চীনা এবং ইংরেজি টাইপ করা যেতে পারে) মানে যে কোড কার্যকর প্রক্রিয়া চলাকালীন কম্পাইল করা হয় না, অর্থাৎ বিষয়বস্তু পরে//সাধারণত আমরা কোডের অর্থ চিহ্নিত করতে এটি ব্যবহার করি, যখন এটি কোড পর্যালোচনা করার জন্য সুবিধাজনক হয়, এটি দ্রুত বোঝা যায় এবং স্মরণ করা যায়। -
{ Remark content }ব্লক মন্তব্য।A:=MA(C,10); {The previous line of code is to calculate the moving average.} -
(* Remark content *)ব্লক মন্তব্য।A:=MA(C,10); (*The previous line of code is to calculate the moving average.*)
-
-
ইনপুট
কোড লেখার সময়, কারণ ইনপুট পদ্ধতিটি প্রায়শই চীনা এবং ইংরেজি মধ্যে স্যুইচ করা হয়, যার ফলে প্রতীক ত্রুটি হয়। সাধারণ ত্রুটিগুলি নিম্নরূপঃ
:টার্মিনেটর;কমা,, কোষাগার(), ইত্যাদি। চীনা এবং ইংরেজি ভাষার এই অক্ষরগুলোতে মনোযোগ প্রয়োজন।আপনি Sogou, Baidu, বা Bing ইনপুট পদ্ধতি ব্যবহার করেন, আপনি দ্রুত চীনা এবং ইংরেজি মধ্যে সুইচ করতে পারেন
shiftচাবি একবার. -
ত্রুটি-প্রবণতা যুক্তিবিজ্ঞান
- কমপক্ষে, কমপক্ষে, কমপক্ষেঃ সংশ্লিষ্ট রিলেশনাল অপারেটর
>=. - সর্বাধিকঃ সংশ্লিষ্ট রিলেশনাল অপারেটর
<=.
- কমপক্ষে, কমপক্ষে, কমপক্ষেঃ সংশ্লিষ্ট রিলেশনাল অপারেটর
-
কৌশল প্রবর্তন সিঙ্ক্রোনাইজেশন
ফিউচার স্ট্র্যাটেজিতে, যদি স্ট্র্যাটেজি রোবট শুরু হওয়ার আগে একটি ম্যানুয়ালি খোলা অবস্থান থাকে, যখন রোবট শুরু হয়, তখন এটি অবস্থান তথ্য সনাক্ত করবে এবং এটি প্রকৃত অবস্থানের স্থিতিতে সিঙ্ক্রোনাইজ করবে। কৌশলতে, আপনি ব্যবহার করতে পারেন
SP,BP,CLOSEOUTঅবস্থান বন্ধ করার নির্দেশ দেয়।%% if (!scope.init) { var ticker = exchange.GetTicker(); exchange.Buy(ticker.Sell+10, 1); scope.init = true; } %% C>0, CLOSEOUT; -
দ্বি-মুখী অবস্থান সমর্থিত নয়
মাইল্যাঙ্গুয়েজ একই চুক্তিকে লং এবং শর্ট পজিশনে সমর্থন করে না।
-
-
-
কে-লাইন ডেটা উদ্ধৃতি
-
খোলা
কে-লাইন চার্টের উদ্বোধনী মূল্য পান।
প্রারম্ভিক মূল্য
ফাংশনঃ ওপেন, O এর সংক্ষিপ্ত রূপ
প্যারামিটারঃ কোনটিই নয়
ব্যাখ্যাঃ
এই সময়ের প্রারম্ভিক মূল্য প্রদান করে সিকোয়েন্স ডেটা
OPEN gets the opening price of the K-line chart. Remark: 1.It can be abbreviated as O. Example 1: OO:=O; //Define OO as the opening price; Remark that the difference between O and 0. Example 2: NN:=BARSLAST(DATE<>REF(DATE,1)); OO:=REF(O,NN); //Take the opening price of the day Example 3: MA5:=MA(O,5); //Define the 5-period moving average of the opening price (O is short for OPEN). -
উচ্চ
কে-লাইন চার্টে সর্বোচ্চ মূল্য পান।
সর্বোচ্চ মূল্য
ফাংশনঃ HIGH, সংক্ষিপ্ত H
প্যারামিটারঃ কোনটিই নয়
ব্যাখ্যাঃ
এই সময়ের সর্বোচ্চ মূল্য প্রদান করুন সিকোয়েন্স ডেটা
HIGH achieved the highest price on the K-line chart. Remark: 1.It can be abbreviated as H. Example 1: HH:=H; // Define HH as the highest price Example 2: HH:=HHV(H,5); // Take the maximum value of the highest price in 5 periods Example 3: REF(H,1); // Take the highest price of the previous K-line -
কম
কে-লাইন চার্টে সর্বনিম্ন মূল্য পান।
সর্বনিম্ন মূল্য
ফাংশনঃ LOW, সংক্ষিপ্ত L
প্যারামিটারঃ কোনটিই নয়
ব্যাখ্যাঃ
এই সময়ের সর্বনিম্ন মূল্য প্রদান করুন সিকোয়েন্স ডেটা
LOW gets the lowest price on the K-line chart. Remark: 1.It can be abbreviated as L. Example 1: LL:=L; // Define LL as the lowest price Example 2: LL:=LLV(L,5); // Get the minimum value of the lowest price in 5 periods Example 3: REF(L,1); // Get the lowest price of the previous K-line -
বন্ধ
কে-লাইন চার্টের ক্লোজিং প্রাইস নিন।
বন্ধের মূল্য
ফাংশনঃ CLOSE, সংক্ষিপ্ত হিসাবে C
প্যারামিটারঃ কোনটিই নয়
ব্যাখ্যাঃ
এই সময়ের বন্ধের মূল্য প্রদান করে সিকোয়েন্স ডেটা
CLOSE Get the closing price of the K-line chart Remarks: 1.Obtain the latest price when the intraday K-line has not finished. 2.It can be abbreviated as C. Example 1: A:=CLOSE; //Define the variable A as the closing price (A is the latest price when the intraday K-line has not finished) Example 2: MA5:=MA(C,5); //Define the 5-period moving average of the closing price (C is short for CLOSE) Example 3: A:=REF(C,1); //Get the closing price of the previous K-line -
ভিওএল
কে-লাইন চার্টের ট্রেডিং ভলিউম পান।
লেনদেনের পরিমাণ
ফাংশনঃ ভিওএল, সংক্ষিপ্তভাবে ভি
প্যারামিটারঃ কোনটিই নয়
ব্যাখ্যাঃ
এই সময়ের ট্রেডিং ভলিউম প্রদান করে সিকোয়েন্স ডেটা
VOL obtains the trading volume of the K-line chart. Remarks: It can be abbreviated as V. The return value of this function on the current TICK is the cumulative value of all TICK trading volume on that day. Example 1: VV:=V; // Define VV as the trading volume Example 2: REF(V,1); // Indicates the trading volume of the previous period Example 3: V>=REF(V,1); // The trading volume is greater than the trading volume of the previous period, indicating that the trading volume has increased (V is the abbreviation of VOL) -
ওপিআই
ফিউচার (চুক্তি) বাজারে বর্তমান মোট অবস্থান নিন।
OpenInterest:OPI; -
রিফ
ফরওয়ার্ড সিটিশন।
Reference the value of X before N periods. Remarks: 1.When N is a valid value, but the current number of K-lines is less than N, returns null; 2.Return the current X value when N is 0; 3.Return a null value when N is null. 4.N can be a variable. Example 1: REF(CLOSE,5);Indicate the closing price of the 5th period before the current period is referenced Example 2: AA:=IFELSE(BARSBK>=1,REF(C,BARSBK),C);//Take the closing price of the K-line of the latest position opening signal // 1)When the BK signal is sent, the bar BARSBK returns null, then the current K-line REF(C, BARSBK) that sends out the BK signal returns null; // 2)When the BK signal is sent out, the K-line BARSBK returns null, and if BARSBK>=1 is not satisfied, it is the closing price of the K-line. // 3)The K-line BARSBK after the BK signal is sent, returns the number of periods from the current K-line between the K-line for purchasing and opening a position, REF(C,BARSBK) Return the closing price of the opening K-line. // 4)Example: three K-lines: 1, 2, and 3, 1 K-line is the current K-line of the position opening signal, then returns the closing price of the current K-line, 2, 3 The K-line returns the closing price of the 1 K-line. -
ইউনিট
ডাটা কন্ট্রাক্টের ট্রেডিং ইউনিটটা নিয়ে নাও।
Get the trading unit of the data contract. Usage: UNIT takes the trading unit of the loaded data contract.ক্রিপ্টোকারেন্সি স্পট
ইউনিট মান হল ১।
ক্রিপ্টোকারেন্সি ফিউচার
UNIT মানটি চুক্তির মুদ্রার সাথে সম্পর্কিত।
OKEX futures currency standard contracts: 1 contract for BTC represents $100, 1 contract for other currencies represents $10 -
MINPRICE
ডাটা চুক্তির সর্বনিম্ন বৈচিত্র্য মূল্য।
Take the minimum variation price of the data contract. Usage: MINPRICE; Take the minimum variation price of the loaded data contract. -
MINPRICE1
একটি ট্রেডিং চুক্তির সর্বনিম্ন পরিবর্তন মূল্য।
Take the minimum variation price of a trading contract. Usage: MINPRICE1; Take the minimum variation price of a trading contract.
-
-
সময় ফাংশন
-
বারপোস
কে-লাইনের অবস্থান নিন।
BARPOS, Returns the number of periods from the first K-line to the current one. Remarks: 1.BARPOS returns the number of locally available K-line, counting from the data that exists on the local machine. 2.The return value of the first K-line existing in this machine is 1. Example 1:LLV(L,BARPOS); // Find the minimum value of locally available data. Example 2:IFELSE(BARPOS=1,H,0); // The current K-line is the first K-line that already exists in this machine, and it takes the highest value, otherwise it takes 0. -
ডেইবারপোস
DAYBARPOS বর্তমান K-লাইন BAR হল দিনের K-লাইন BAR।
-
সময়কাল
সময়ের মান হল মিনিটের সংখ্যা।
1, 3, 5, 15, 30, 60, 1440 -
তারিখ
তারিখফাংশন DATE, 1900 সাল থেকে সময়ের বছর, মাস এবং দিন পান.
Example 1: AA..DATE; // The value of AA at the time of testing is 220218, which means February 18, 2022 -
সময়
কে-লাইন নেওয়ার সময়।
TIME, the time of taking the K-line. Remarks: 1.The function returns in real time in the intraday, and returns the starting time of the K-line after the K-line is completed. 2.This function returns the exchange data reception time, which is the exchange time. 3.The TIME function returns a six-digit form when used on a second period, namely: HHMMSS, and displays a four-digit form on other periods, namely: HHMM. 4.The TIME function can only be loaded in periods less than the daily period, and the return value of the function is always 1500 in the daily period and periods above the daily period. 5. It requires attention when use the TIME function to close a position at the end of the day (1).It is recommended to set the time for closing positions at the end of the market to the time that can actually be obtained from the return value of the K-line (for example: the return time of the last K-line in the 5-minute period of the thread index is 1455, and the closing time at the end of the market is set to TIME>=1458, CLOSEOUT; the signal of closing the position at the end of the market cannot appear in the effect test) (2).If the TIME function is used as the condition for closing the position at the end of the day, it is recommended that the opening conditions should also have a corresponding time limit (for example, if the condition for closing the position at the end of the day is set to TIME>=1458, CLOSEOUT; then the condition TIME needs to be added to the corresponding opening conditions. <1458; avoid re-opening after closing) Example 1: C>O&&TIME<1450,BK; C<O&&TIME<1450,SK; TIME>=1450,SP; TIME>=1450,BP; AUTOFILTER; // Close the position after 14:50. Example 2: ISLASTSK=0&&C>O&&TIME>=0915,SK; -
বছর
Year.
YEAR, year of acquisition. Remark: The value range of YEAR is 1970-2033. Example 1: N:=BARSLAST(YEAR<>REF(YEAR,1))+1; HH:=REF(HHV(H,N),N); LL:=REF(LLV(L,N),N); OO:=REF(VALUEWHEN(N=1,O),N); CC:=REF(C,N); // Take the highest price, lowest price, opening price, and closing price of the previous year Example 2: NN:=IFELSE(YEAR>=2000 AND MONTH>=1,0,1); -
মাস
এই মাসটা নাও।
MONTH, returns the month of a period. Remark: The value range of MONTH is 1-12. Example 1: VALUEWHEN(MONTH=3&&DAY=1,C); // Take its closing price when the K-line date is March 1 Example 2: C>=VALUEWHEN(MONTH<REF(MONTH,1),O),SP; -
দিন
একটি সময়ের মধ্যে দিন সংখ্যা পান
DAY, returns the number of days in a period. Remark: The value range of DAY is 1-31. Example 1: DAY=3&&TIME=0915,BK; // 3 days from the same day, at 9:15, buy it Example 2: N:=BARSLAST(DATE<>REF(DATE,1))+1; CC:=IFELSE(DAY=1,VALUEWHEN(N=1,O),0); // When the date is 1, the opening price is taken, otherwise the value is 0 -
ঘন্টা
Hour.
HOUR, returns the number of hours in a period. Remark: The value range of HOUR is 0-23 Example 1: HOUR=10; // The return value is 1 on the K-line at 10:00, and the return value on the remaining K-lines is 0 -
মিনিট
Minute.
MINUTE, returns the number of minutes in a period. Remarks: 1: The value range of MINUTE is 0-59 2: This function can only be loaded in the minute period, and returns the number of minutes when the K-line starts. Example 1: MINUTE=0; // The return value of the minute K-line at the hour is 1, and the return value of the other K-lines is 0 Example 2: TIME>1400&&MINUTE=50,SP; // Sell and close the position at 14:50 -
সপ্তাহের দিন
সপ্তাহের নম্বরটা নিয়ে নাও।
WEEKDAY, get the number of the week. Remark: 1: The value range of WEEKDAY is 0-6. (Sunday ~ Saturday) Example 1: N:=BARSLAST(MONTH<>REF(MONTH,1))+1; COUNT(WEEKDAY=5,N)=3&&TIME>=1450,BP; COUNT(WEEKDAY=5,N)=3&&TIME>=1450,SP; AUTOFILTER; // Automatically close positions at the end of the monthly delivery day Example 2: C>VALUEWHEN(WEEKDAY<REF(WEEKDAY,1),O)+10,BK; AUTOFILTER;
-
-
যৌক্তিক বিচার ফাংশন
-
বারস্ট্যাটাস
বর্তমান সময়ের অবস্থানের অবস্থা প্রদান করুন।
BARSTATUS returns the position status for the current period. Remark: The function returns 1 to indicate that the current period is the first period, returns 2 to indicate that it is the last period, and returns 0 to indicate that the current period is in the middle. Example: A:=IFELSE(BARSTATUS=1,H,0); // If the current K-line is the first period, variable A returns the highest value of the K-line, otherwise it takes 0 -
মাঝখানে
Between.
BETWEEN(X,Y,Z) indicates whether X is between Y and Z, returns 1 (Yes) if established, otherwise returns 0 (No). Remark: 1.The function returns 1(Yse) if X=Y, X=Z, or X=Y and Y=Z. Example 1: BETWEEN(CLOSE,MA5,MA10); // It indicates that the closing price is between the 5-day moving average and the 10-day moving average -
বারসলস্টকাউন্ট
BARSLASTCOUNT(COND) বর্তমান সময়ের থেকে এগিয়ে গণনা করে, ধারাবাহিক সময়ের সংখ্যা গণনা করে যা শর্তটি পূরণ করে।
Remark: 1. The return value is the number of consecutive non zero periods calculated from the current period 2. the first time the condition is established when the return value of the current K-line BARSLASTCOUNT(COND) is 1 Example: BARSLASTCOUNT(CLOSE>OPEN); //Calculate the number of consecutive positive periods within the current K-line -
ক্রস
ক্রস ফাংশন।
CROSS(A,B) means that A crosses B from bottom to top, and returns 1 (Yes) if established, otherwise returns 0 (No) Remark: 1.To meet the conditions for crossing, the previous k-line must satisfy A<=B, and when the current K-line satisfies A>B, it is considered to be crossing. Example 1: CROSS(CLOSE,MA(CLOSE,5)); // Indicates that the closing line crosses the 5-period moving average from below -
ক্রসডাউন
ক্রসডাউন
CROSSDOWN(A,B): indicates that when A passes through B from top to bottom, it returns 1 (Yes) if it is established, otherwise it returns 0 (No) Remark: 1.CROSSDOWN(A,B) is equivalent to CROSS(B,A), and CROSSDOWN(A,B) is easier to understand Example 1: MA5:=MA(C,5); MA10:=MA(C,10); CROSSDOWN(MA5,MA10),SK; // MA5 crosses down MA10 to sell and open a position // CROSSDOWN(MA5,MA10),SK; Same meaning as CROSSDOWN(MA5,MA10)=1,SK; -
ক্রসপ
Crossup.
CROSSUP(A,B) means that when A crosses B from the bottom up, it returns 1 (Yes) if it is established, otherwise it returns 0 (No) Remark: 1.CROSSUP(A,B) is equivalent to CROSS(A,B), and CROSSUP(A,B) is easier to understand. Example 1: MA5:=MA(C,5); MA10:=MA(C,10); CROSSUP(MA5,MA10),BK; // MA5 crosses MA10, buy open positions // CROSSUP(MA5,MA10),BK;与CROSSUP(MA5,MA10)=1,BK; express the same meaning -
সবাই
এটি ক্রমাগত সন্তুষ্ট কিনা তা নির্ধারণ করুন।
EVERY(COND,N), Determine whether the COND condition is always satisfied within N periods. The return value of the function is 1 if it is satisfied, and 0 if it is not satisfied. Remarks: 1.N contains the current K-line. 2.If N is a valid value, but there are not so many K-lines in front, or N is a null value, it means that the condition is not satisfied, and the function returns a value of 0. 3.N can be a variable. Example 1: EVERY(CLOSE>OPEN,5); // Indicates that it has been a positive line for 5 periods Example 2: MA5:=MA(C,5); // Define a 5-period moving average MA10:=MA(C,10); // Define a 10-period moving average EVERY(MA5>MA10,4),BK; // If MA5 is greater than MA10 within 4 periods, then buy the open position // EVERY(MA5>MA10,4),BK; has the same meaning as EVERY(MA5>MA10,4)=1,BK; -
বিদ্যমান
সন্তুষ্টি আছে কিনা তা নির্ধারণ করুন।
EXIST(COND, N) judges whether there is a condition that satisfies COND within N periods. Remarks: 1.N contains the current K-line. 2.N can be a variable. 3.If N is a valid value, but there are not so many K-lines in front, it is calculated according to the actual number of periods. Example 1: EXIST(CLOSE>REF(HIGH,1),10); // Indicates whether there is a closing price greater than the highest price of the previous period in 10 periods, returns 1 if it exists, and returns 0 if it does not exist Example 2: N:=BARSLAST(DATE<>REF(DATE,1))+1; EXIST(C>MA(C,5),N); // Indicates whether there is a K-line that satisfies the closing price greater than the 5-period moving average on the day, returns 1 if it exists, returns 0 if it does not exist -
যদি
শর্ত ফাংশন।
IF(COND,A,B)Returns A if the COND condition is true, otherwise returns B. Remarks: 1.COND is a judgment condition; A and B can be conditions or values. 2.This function supports the variable circular reference to the previous period's own variable, that is, supports the following writing Y: IF(CON,X,REF(Y,1)). Example 1: IF(ISUP,H,L); // The K-line is the positive line, the highest price is taken, otherwise the lowest price is taken Example 2: A:=IF(MA5>MA10,CROSS(DIFF,DEA),IF(CROSS(D,K),2,0)); // When MA5>MA10, check whether it satisfies the DIFF and pass through DEA, otherwise (MA5 is not greater than MA10), when K and D are dead fork, let A be assigned a value of 2, if none of the above conditions are met, A is assigned a value of 0 A=1,BPK; // When MA5>MA10, the condition for opening a long position is to cross DEA above the DIFF A=2,SPK; // When MA5 is not greater than MA10, use K and D dead forks as the conditions for opening short positions -
আইফেলস
শর্ত ফাংশন।
IFELSE(COND,A,B) Returns A if the COND condition is true, otherwise returns B. Remarks: 1.COND is a judgment condition; A and B can be conditions or values. 2.This function supports variable circular reference to the previous period's own variable, that is, supports the following writing Y: IFELSE(CON,X,REF(Y,1)); Example 1: IFELSE(ISUP,H,L); // The K-line is the positive line, the highest price is taken, otherwise the lowest price is taken Example 2: A:=IFELSE(MA5>MA10,CROSS(DIFF,DEA),IFELSE(CROSS(D,K),2,0)); // When MA5>MA10, check whether it satisfies the DIFF and pass through DEA, otherwise (MA5 is not greater than MA10), when K and D are dead fork, let A be assigned a value of 2, if none of the above conditions are met, A is assigned a value of 0 A=1,BPK; // When MA5>MA10, the condition for opening a long position is to cross DEA above the DIFF A=2,SPK; // When MA5 is not greater than MA10, use K and D dead forks as the conditio
-
- ema ঢাল গণনা
- উচ্চ-ফ্রিকোয়েন্সি লেনদেন সমস্যা
- নতুন আবিষ্কারঃ চেইন ডেটা + ইন-ফিল্ড লেনদেনের ডেটা = প্রধান ইনপুট এবং আউটপুট পয়েন্ট
- পদ্ধতিগত কাঠামো এবং বহু-কৌশলগত সংমিশ্রণের সমস্যাগুলির জন্য সাহায্যের জন্য জিজ্ঞাসা করুন
- পাইন স্ক্রিপ্ট কি সরাসরি মার্কেট ডেটা স্যুইচ করে?
- ওয়েব পেজ রিচার্জ সমস্যা
- আপনি কি মনে করেন যে, একটি রিসেট গ্রাফ মাত্র কয়েক হাজার তথ্য দেখায়?
- সূচকগুলির রাজা ম্যাকড, একটি নিবন্ধে বৃহত্তর পরিবারের সমমানের সূচকগুলি ধরে রাখে
- এফএমজেড-এর মাধ্যমে কীভাবে অর্ডার করা যায়
- নতুন সংস্করণে টিভি রিসোর্স আইকনটি খুব সুবিধাজনক নয়।
- সবচেয়ে উন্নত লেনদেনের পদ্ধতিঃ অর্ডার ওয়াল!
- ভলিউমের একক কি?
- সাম্প্রতিক বছরগুলিতে কোনটি উচ্চতর হয়েছে, প্রত্যক্ষ বা বিপরীত মূলধন সুইচ?
- ট্রেডিংভিউ সংক্রান্ত সমস্যাঃ সিগন্যাল থেকে এফএমজেড পর্যন্ত সর্বদা 1 থেকে 2 সেকেন্ডের বিলম্ব হয়
- কিভাবে একটি ভার্চুয়াল ডিস্কে একাধিক অ্যাকাউন্ট পরিচালনা করবেন
- উইকিমিডিয়া কি কোনও নীতিমালার সতর্কতা গ্রহণ করতে পারেনি?
- পরিমাণ মূল্য বিতরণ চার্ট চামচ দেখতে, গড় খরচ বুঝতে
- ডিস্ক ত্রুটি রিপোর্ট সমস্যা
- কেন ক্ষুদ্র মুদ্রা পুনরায় মূল্যায়ন করা যায় না?
- গ্রিড কৌশল