Plataforma de negociación de FMZ Quant Protocolo personalizado Acceso a intercambios personalizados
El autor:- ¿ Por qué?, Creado: 2023-07-12 15:29:54, Actualizado: 2024-01-03 21:01:07
Plataforma de negociación de FMZ Quant Protocolo personalizado Acceso a intercambios personalizados
Documentación de uso del protocolo personalizado
Puede utilizar este protocolo general para acceder a cualquier intercambio que proporciona el comercio de API, el protocolo específico de API no está limitado, ya sea descanso, websocket, fijación... Todo se puede acceder para usar. Ejemplo de protocolo personalizado de Python:https://www.fmz.com/strategy/101399
1. operación del plug-in de protocolo personalizado, configuración del puerto
La configuración para la dirección de escucha y el puerto del complemento de protocolo personalizado puede ser la siguiente:
Por ejemplo:http://127.0.0.1:6666/DigitalAsseto bienhttp://127.0.0.1:6666/exchange.
¿Por qué tenemos que poner estosP.I.ycaminos¿ Qué es eso?
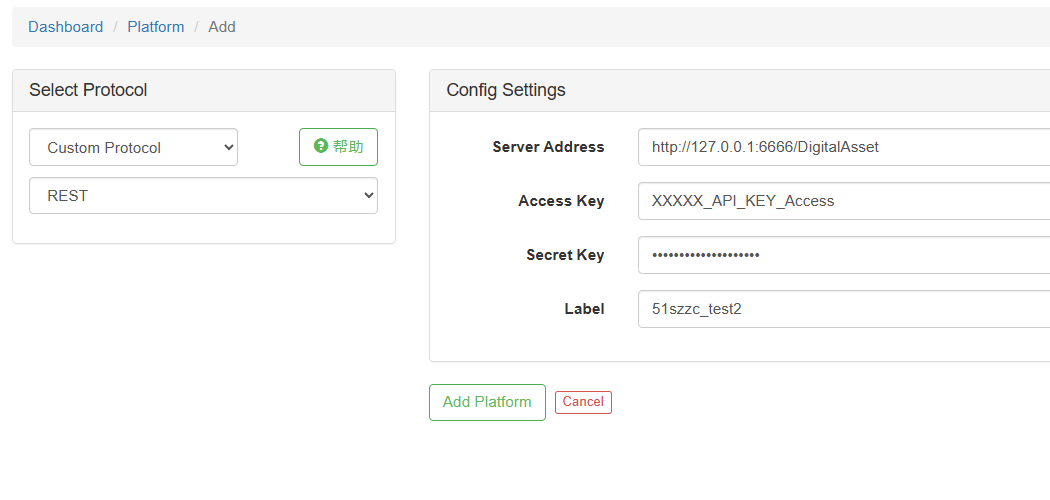
Esto es porque cuandoañadiendo el intercambiopágina en elPanel de control de la plataforma cuántica FMZ, seleccionando la opción API-KEY. Esta dirección de servicio informa al docker dónde acceder a la IP y al puerto (el docker y el programa de complemento de Protocolo Personalizado pueden no estar ejecutándose en el mismo dispositivo).http://127.0.0.1:6666/DigitalAsset. DigitalAssetes sólo un ejemplo y puede ser reemplazado por un nombre de su elección.
En la página access keyysecret keySin embargo, algunas interfaces API de los intercambios requieren que se pase la contraseña de negociación (por ejemplo, la interfaz de colocación de pedidos de ciertos intercambios).secret key(oaccess keyEntonces, en el programa de complemento Custom Protocol, podemos ejecutar una cadenasplitoperación para separar estos datos, como se muestra en la imagen del ejemplo.
Y luego en el complemento, procesarlo para obtenerXXX_PassWord¿ Qué pasa?
Por ejemplo, en el ejemplo completo al final de este post, en la función newBitgo:
func newBitgo(accessKey, secretKey string) *iBitgo {
s := new(iBitgo)
s.accessKey = accessKey
s.secretKey = secretKey
// Additional configuration information in the secretKey can be separated here and can be written as in the following comment
/*
arr := strings.SplitN(secretKey, ",", 2)
if len(arr) != 2 {
panic("Configuration error!")
}
s.secretKey = arr[0] // secret key
s.passWord = arr[1] // XXX_PassWord
*/
s.apiBase = "https://www.bitgo.cn"
s.timeout = 20 * time.Second
s.timeLocation = time.FixedZone("Asia/Shanghai", 8*60*60)
return s
}
Al analizar los parámetros en los datos de solicitud de nuevo, el docker envía los datos de solicitud como:
"secret_key" : "XXX",
El complemento recibe los datos entrantes que contienen este tipo de información y separa la XXX_PassWord de ella basándose en el separador de comas, para que obtenga los datos adicionales pasados.
Ejemplo de un complemento de protocolo personalizado generalmainFunción:GoDescripción del idioma:
func main(){
var addr = flag.String("b", "127.0.0.1:6666", "bing addr") // Set command line parameters, default value description, port setting 6666
flag.Parse() // Parsing the command line
if *addr == "" {
flag.Usage() // Display the command line description
return
}
basePath := "/DigitalAsset"
log.Println("Running ", fmt.Sprintf("http://%s%s", *addr, basePath), "...") // Print listening port information
http.HandleFunc(basePath, OnPost)
http.ListenAndServe(*addr, nil)
}
2. Función de respuesta
El programa requestUna vez que se recibe una solicitud, se invoca la función de respuesta para ejecutar y luego analiza los parámetros de los datos de la solicitud. Los datos de solicitud enviados por el docker son:
/* JSON structure of request, FMZ Quant call GetTicker, docker sent to the custom protocol plugin case example (the value of params may be different for each API call, here the method is ticker):
{
"access_key" : "XXX", // `json:"access_key"`
"secret_key" : "XXX", // `json:"secret_key"`
"nonce" : "1502345965295519602", // `json:"nonce"`
"method" : "ticker", // `json:"method"`
"params" : { // `json:"params"`
"symbol" : "btc",
...
}, // The parameters are slightly different for each request. That is, different FMZ Quant APIs are called in the strategy with different parameters, which are described in the following sections for each API.
}
*/
Así que, basado en elMethodel campo en elrequestestructura obtenida por JSON deserializando la solicitud de los datos del cuerpo recibidos en el programa Universal Protocol Plugin, podemos utilizar unswitchDeclaración para clasificar y manejar diferentes API de FMZ Quant que se están llamando en el docker (es decir, identificar qué FMZ QuantAPIla estrategia que se ejecuta en el docker está invocando):
Ejemplo enGoLenguaje:
switch request.Method { // M of request.Method is capitalized here, the body of the request received by the custom protocol program for the JSON data, in the Go language, the anti-JSON serialization (Unmarshal) is a structure, the first letter of the field must be capitalized
case "accounts" : // When the exchange.GetAccount() function is called in the bot strategy on the docker, the docker sends in a request where the Body carries data with a method attribute value of accounts
data, err = e.GetAccount(symbol)
case "ticker" :
data, err = e.GetTicker(symbol)
case "depth" :
data, err = e.GetDepth(symbol)
case "trades" :
data, err = e.GetTrades(symbol)
case "trade" :
...
default:
...
Después de ejecutar estas ramas, los datos devueltos deben escribirse en la estructura que el programa Custom Protocol Plugin usará para responder a la solicitud del docker.
Ejemplo en el lenguaje Go:
defer func(){ // Handling of closing work
if e := recover(); e != nil { // The recover() function is used to catch panic, e ! = nil, i.e. an error has occurred
if ee, ok := e.(error); ok { // Type derivation, successful derivation assigns ee.Error() to e
e = ee.Error() // Call the Error method to get the returned error string
}
ret = map[string]string{"error": fmt.Sprintf("%v", e)}
}
b, _ := json.Marshal(ret) // Encode the result obtained from this call, ret, assign it to b, and write it into the response pointer
w.Write(b)
//fmt.Println("after w.Write the b is", string(b)) // test
}()
3. Tipos de llamadas de API
Aproximadamente dividido en dos categorías:
- las interfaces públicas que no requieren una firma, por ejemplo:
GetTicker()
GetDepth()
GetTrades()
GetRecords(period)
…
- las interfaces de usuario que necesitan firmar, como:
Buy, Sell
GetOrder(id)
GetOrders()
GetAccount()
CancelOrder(id)- ¿ Qué?
Los métodos de firma pueden variar de un intercambio a otro y deben escribirse específicamente de acuerdo con las necesidades.
4. El formato de datos para la interacción entre el complemento de protocolo personalizado y el docker al llamar a varias interfaces de la API FMZ Quant:
Algunas interfaces de la API FMZ Quant, como
GetName(),GetLabel(), etc., no envíe solicitudes a laPlugin de protocolo personalizadocuando lo llamen. Cuando llamasexchange.GetName(), el intercambio configurado en el complemento universal devolveráExchange .
-
- GetTicker: Se utiliza para obtener los datos actuales del ticker.
ElmethodEn elrequestenviado por elel buque de embarquea la función de respuesta de escucha esticker.
El docker envía el parámetro:request.Params.symbol, que es enviado por el docker basado en la moneda establecida en la página del robot.
El formato de datos (JSON) llevado en el cuerpo de la solicitud cuando el docker solicita el complemento de protocolo personalizado
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // millisecond timestamp
"method" : "ticker",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC"}, // Take the ETH_BTC trading pair for example
}
Estructura del valor de retorno final enviado al docker: (es decir, el formato en el que los datos se devuelven al docker después de que el plug-in de protocolo común solicite la interfaz de intercambio)
Estructura de JSON
{
"data": {
"time": 1500793319499, // Millisecond timestamp, integer
"buy": 1000, // floating-point type as follows
"sell": 1001,
"last": 1005,
"high": 1100,
"low": 980,
"vol": 523,
}
}
-
- GetRecords: Se utiliza para recuperar los datos de línea K proporcionados por el intercambio. (Basado en los parámetros solicitados por el docker)
ElmethodEn elrequestenviado por el docker a la función de respuesta de escucha esrecords.
El docker envía los parámetros:request.Params.period, que está asociado con el primer parámetro delexchange.GetRecordsLa función realrequest.Params.periodPor ejemplo, el período diario es60*24, que es1440. request.Params.symbolse envía por el docker basado en la moneda establecida.
El formato de datos llevado en el cuerpo de la solicitud cuando el docker solicita el complemento de protocolo personalizado.
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // millisecond timestamp
"method" : "records",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC", "period" : "1440"}, // Example of an ETH_BTC pair with a daily K-period
}
Estructura del valor de retorno final enviado al docker:
Estructura de JSON
{
"data": [
[1500793319, 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5], // "Time":1500793319000,"Open":1.1,"High":2.2,"Low":3.3,"Close":4.4,"Volume":5.5
[1500793259, 1.01, 2.02, 3.03, 4.04, 5.05],
...
]
}
Datos de la prueba de idiomas:
ret_records = []interface{}{
[6]interface{}{1500793319, 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5},
[6]interface{}{1500793259, 1.01, 2.02, 3.03, 4.04, 5.05}
}
Plataforma cuántica FMZLogLas pantallasrecordsLos datos:
[
{"Time":1500793319000,"Open":1.1,"High":2.2,"Low":3.3,"Close":4.4,"Volume":5.5},
{"Time":1500793259000,"Open":1.01,"High":2.02,"Low":3.03,"Close":4.04,"Volume":5.05}
]
Nota: 1. El primer elemento de la matriz bidimensional es de tipointEl docker multiplicará automáticamente la marca de tiempo por 1000, como se mencionó anteriormente.
-
- GetDepth: Recupera la información de profundidad (libro de pedidos, ask1, ask2... bid1, bid2...) del intercambio.
ElmethodEn elrequestenviado por el docker a la función de respuesta de escucha esdepth.
El docker envía el parámetro:request.Params.symbol, que es enviado por el docker basado en la moneda establecida en la estrategia.
El formato de datos llevado en el cuerpo de la solicitud cuando el docker solicita el complemento de protocolo personalizado
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // millisecond timestamp
"method" : "depth",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC"}, // Take the ETH_BTC trading pair for example
}
Estructura del valor de retorno final enviado al docker:
Estructura de JSON
{
"data" : {
"time" : 1500793319499,
"asks" : [ [1000, 0.5], [1001, 0.23], [1004, 2.1], ... ],
"bids" : [ [999, 0.25], [998, 0.8], [995, 1.4], ... ],
}
}
-
- GetTrades: Obtener los registros de operaciones de toda la bolsa dentro de un cierto período de tiempo (excluyendo las propias operaciones)
ElmethodEn elrequestenviado por el docker a la función de respuesta de escucha es:trades.
Parámetros enviados por el docker: el valor derequest.Params.symboles la moneda de negociación, por ejemplo:btc, que es enviado por el docker basado en la configuración de la estrategia.
El formato de datos llevado por el docker al solicitar el complemento de protocolo personalizado es el siguiente
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // millisecond timestamp
"method" : "trades",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC"}, // Take the ETH_BTC trading pair for example
}
Estructura del valor de retorno final enviado al docker:
Estructura de JSON
{
"data": [
{
"id": 12232153,
"time" : 1529919412968,
"price": 1000,
"amount": 0.5,
"type": "buy", // "buy"、"sell"
},{
"id": 12545664,
"time" : 1529919412900,
"price": 1001,
"amount": 1,
"type": "sell",
},{
...
}
]
}
-
- Obtener información de los activos de la cuenta.
ElmethodEn elrequestenviado por el docker a la función de respuesta de escucha es:accounts.
Parámetros enviados por el docker: (Nota: Generalmente, es para obtener todos los activos de la cuenta! Consulte la interfaz de intercambio para ver si es para obtener los activos individuales o la información total de los activos)
El formato de datos llevado por el docker al solicitar el complemento de protocolo personalizado es el siguiente
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // millisecond timestamp
"method" : "accounts",
"params" : {},
}
Estructura del valor de retorno final enviado al docker:
Estructura de JSON
{
"data": [
{"currency": "btc", "free": 1.2, "frozen": 0.1},
{"currency": "ltc", "free": 25, "frozen": 2.1},
{"currency": "ltc", "free": 25, "frozen": 2.1},
...
],
"raw" : {...} // It is possible to write the raw message (response) returned by the exchange when the plugin accesses the exchange
}
-
- Comprar, vender: Poner una orden para la negociación (orden de mercado o orden de límite).
ElmethodEn elrequestenviado por el docker a la función de respuesta de escucha es:trade.
Parámetros enviados por el docker:request.Params.type: enviado por el docker basado en si está llamandoexchange.Buyo bienexchange.Sell, request.Params.price: el primer parámetro delAPIfunción llamada en la estrategia,request.Params.amount: el segundo parámetro delAPIfunción llamada en la estrategia,request.Params.symbol: enviado por el muelle basado en la moneda de negociación establecida.
El formato de datos llevado por el docker al solicitar el complemento de protocolo personalizado es el siguiente
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // millisecond timestamp
"method" : "trade",
"params" : {
"symbol" : "ETH_BTC",
"type" : "buy",
"price" : "1000",
"amount" : "1"
}, // Example of an ETH_BTC trading pair, "type": "buy" buy request, price 1000, quantity 1
}
Estructura del valor de retorno final enviado al docker:
Estructura de JSON
{
"data": {
"id": 125456, // Order id returned after placing an order
// If the order id is in the form of a string like "asdf346sfasf532"
// Here the id can also be a string type
}
}
-
- GetOrder: Obtener información de un pedido específico por orden ID
ElmethodEn elrequestenviado por el docker a la función de respuesta de escucha es:order.
Parámetros enviados por el docker:request.Params.id, request.Params.symbol.
El formato de datos llevado por el docker al solicitar el complemento de protocolo personalizado es el siguiente
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // millisecond timestamp
"method" : "order",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC", "id" : "XXX"}, // Take the ETH_BTC trading pair and order ID XXX as an example. Please note that some exchanges use numerical order IDs, such as 123456, while others use string order IDs, such as poimd55sdfheqxv. The specific format of the order ID depends on the exchange.
}
Estructura del valor de retorno final enviado al docker:
Estructura de JSON
{
"data": {
"id": 2565244,
"amount": 0.15,
"price": 1002,
"status": "open", // "open": pending, "closed": closed, "canceled": canceled
"deal_amount": 0,
"type": "buy", // "buy"、"sell"
"avg_price": 0, // If not provided by the exchange, it can be assigned a value of 0 during processing
}
}
-
- GetOrders: Obtener información para todos los pedidos no cumplidos
ElmethodEn elrequestenviado por el docker a la función de respuesta de escucha esorders.
Parámetros enviados por el docker:request.Params.symbol
El formato de datos llevado por el docker al solicitar el complemento de protocolo personalizado es el siguiente
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // millisecond timestamp
"method" : "orders",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC"}, // Take the ETH_BTC trading pair for example
}
Estructura del valor de retorno final enviado al docker:
Estructura de JSON
{
"data": [{
"id": 542156,
"amount": 0.25,
"price": 1005,
"deal_amount": 0,
"type": "buy", // "buy"、"sell"
"status": "open", // "open"
},{
...
}]
}
-
- CancelOrder: cancelar una orden con el ID de orden especificado
ElmethodEn elrequestenviado por el docker a la función de respuesta de escucha escancel.
Parámetros enviados por el docker:request.Params.id(tipo de cadena, el primer parámetro de la función API llamada por la estrategia),request.Params.symbol(por ejemplo, btc, enviado por el docker basado en la moneda establecida por la estrategia)
El formato de datos llevado por el docker al solicitar el complemento de protocolo personalizado es el siguiente
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // millisecond timestamp
"method" : "cancel",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC", "id" : "XXX"}, // Take an ETH_BTC trading pair with an id of "XXX" (same as the GetOrder function's parameter id) for example
}
Estructura del valor de retorno final enviado al docker:
Estructura de JSON
{
"data": true, // true or false
}
-
- Llama a laexchange.IOFunción de la plataforma cuántica FMZ
ElmethodEn elrequestenviado por el docker a la función de respuesta de escucha comienza con_api_.
El formato de datos llevado por el docker al solicitar el complemento de protocolo personalizado es el siguiente
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // millisecond timestamp
"method" : "__api_XXX", // XXX is the API interface for the specific exchange (base address not included)
"params" : {"borrow_id" : "123", "symbol" : "cny"}, // Specifically, the parameters passed into the IO function
}
Estructura del valor de retorno final enviado al docker:
{
"data": {...} // The return value of a specific interface call
}
A modo de ejemplo, la convocatoria de estrategia:
var io_str = exchange.IO("api", "POST", "cancel_borrow", "symbol=cny&borrow_id=123")
Código de prueba en el complemento (idioma de acceso):
fmt.Println("request.Method:", request.Method, "request.Params:", request.Params)
Línea de comandos del plugin: 2017/08/31 10:19:59 Corriendohttp://127.0.0.1:6666/DigitalAsset …
Impresión de la línea de comandos del complemento: request.Method, request.ParamsEn el cuerpo de la solicitud enviada por el docker, los datos analizados en la solicitud son los siguientes:request.Methodes__api_cancel_borrow
request.Paramses{"borrow_id" : "123", "symbol" : "cny"}
Puede personalizar el manejo de estosexchange.IOllamadas que acceden directamente al intercambioAPI.
# Attention:
# When calling exchange.IO("api", "POST", "/api/v1/getAccount", "symbol=BTC_USDT"),
# If the second parameter is not POST but: exchange.IO("api", "GET", "/api/v1/getAccount", "symbol=BTC_USDT")
# is the GET method, which is then stored in the header Http-Method in the http request accepted by the custom protocol plugin.
# So you need to refer to the following sample code for the custom protocol handling IO function implementation:
// tapiCall function definition
func (p *iStocksExchange) tapiCall(method string, params map[string]string, httpType string) (js *Json, err error) {
...
}
// In the OnPost function
if strings.HasPrefix(request.Method, "__api_") {
var js *Json
js, err = e.tapiCall(request.Method[6:], request.Params, r.Header.Get("Http-Method"))
...
}
- Apoyo para el intercambio.GetRawJSON:
El sistema subyacente maneja automáticamente las llamadas aexchange.GetRawJSON, por lo que no hay necesidad de implementarlo en el complemento.
- Apoyo para el intercambio.
El sistema subyacente maneja automáticamente las llamadas aexchange.Go, así que no hay necesidad de manejarlo en el plugin.
var beginTime = new Date().getTime()
var ret = exchange.Go("GetDepth")
var endTime = new Date().getTime()
Log(endTime - beginTime, "#FF0000")
// Sleep(2000)
beginTime = new Date().getTime()
Log(exchange.GetTicker())
endTime = new Date().getTime()
Log(endTime - beginTime, "#FF0000")
var depth = ret.wait()
Log("depth:", depth)
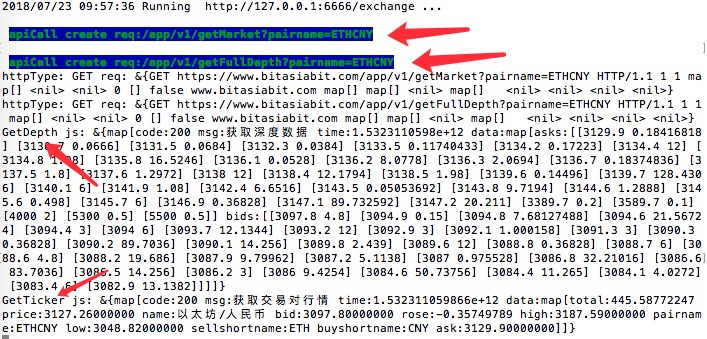
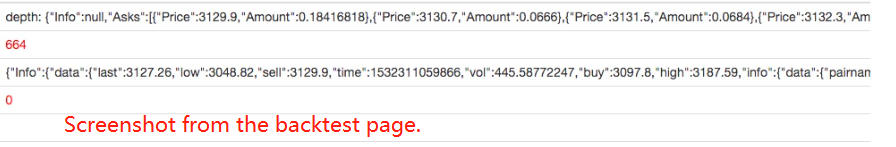
# Note: If you specify a timeout when waiting using exchange.
# Always make sure to obtain the final data so that the concurrent threads of the application can be reclaimed.
- Apoyo a las funciones de futuros:
Es necesario implementar un manejo específico en el programa de complemento para las funciones de futuros. Por ejemplo, establecer apalancamiento, código de contrato y dirección de orden. Puede establecer una variable local para registrar esta información. Para recuperar posiciones, deberá acceder a la API de intercambio para obtener datos en bruto y procesarlos en la estructura de posición definida en la plataforma FMZ, y luego devolverlos.
Cuando las siguientes funciones son llamadas en la estrategia, el formato de laRpcLa solicitud recibida por el programa de complemento es ligeramente diferente de otras interfaces.RpcRequestLa principal diferencia es que el valor de params es una estructura compuesta.
Tipo de contrato establecido Establezca el código del contrato.
{"access_key":"123","method":"io","nonce":1623307269528738000,"params":{"args":["quarter"],"code":2},"secret_key":"123"}
Establecer la dirección Establece la dirección para colocar órdenes de futuros.
{"access_key":"123","method":"io","nonce":1623308734966484000,"params":{"args":["closesell"],"code":1},"secret_key":"123"}
Establecer el nivel de margen Establece el apalancamiento de los futuros.
{"access_key":"123","method":"io","nonce":1623308734966939000,"params":{"args":[12],"code":0},"secret_key":"123"}
ObtenerPosición Obtener la posición de futuros. ¿Cuándo?
exchange.GetPosition()se llama:
{"access_key":"123","method":"io","nonce":1623308734967442000,"params":{"args":[],"code":3},"secret_key":"123"}
¿Cuándo?exchange.GetPosition("swap")se llama:
{"access_key":"123","method":"io","nonce":1623308734967442000,"params":{"args":["swap"],"code":3},"secret_key":"123"}
- Lenguaje Go completo Ejemplo de complemento de protocolo personalizado (acceso a Bitgo Exchange)
/*
GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -ldflags '-s -w -extldflags -static' rest_bitgo.go
*/
package main
import (
"bytes"
"crypto/md5"
"encoding/hex"
"encoding/json"
"errors"
"flag"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
"net/url"
"sort"
"strconv"
"strings"
"time"
)
func toFloat(s interface{}) float64 {
var ret float64
switch v := s.(type) {
case float64:
ret = v
case float32:
ret = float64(v)
case int64:
ret = float64(v)
case int:
ret = float64(v)
case int32:
ret = float64(v)
case string:
ret, _ = strconv.ParseFloat(strings.TrimSpace(v), 64)
}
return ret
}
func float2str(i float64) string {
return strconv.FormatFloat(i, 'f', -1, 64)
}
func toInt64(s interface{}) int64 {
var ret int64
switch v := s.(type) {
case int:
ret = int64(v)
case float64:
ret = int64(v)
case bool:
if v {
ret = 1
} else {
ret = 0
}
case int64:
ret = v
case string:
ret, _ = strconv.ParseInt(strings.TrimSpace(v), 10, 64)
}
return ret
}
func toString(s interface{}) string {
var ret string
switch v := s.(type) {
case string:
ret = v
case int64:
ret = strconv.FormatInt(v, 10)
case float64:
ret = strconv.FormatFloat(v, 'f', -1, 64)
case bool:
ret = strconv.FormatBool(v)
default:
ret = fmt.Sprintf("%v", s)
}
return ret
}
type Json struct {
data interface{}
}
func NewJson(body []byte) (*Json, error) {
j := new(Json)
err := j.UnmarshalJSON(body)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return j, nil
}
func (j *Json) UnmarshalJSON(p []byte) error {
return json.Unmarshal(p, &j.data)
}
func (j *Json) Get(key string) *Json {
m, err := j.Map()
if err == nil {
if val, ok := m[key]; ok {
return &Json{val}
}
}
return &Json{nil}
}
func (j *Json) CheckGet(key string) (*Json, bool) {
m, err := j.Map()
if err == nil {
if val, ok := m[key]; ok {
return &Json{val}, true
}
}
return nil, false
}
func (j *Json) Map() (map[string]interface{}, error) {
if m, ok := (j.data).(map[string]interface{}); ok {
return m, nil
}
return nil, errors.New("type assertion to map[string]interface{} failed")
}
func (j *Json) Array() ([]interface{}, error) {
if a, ok := (j.data).([]interface{}); ok {
return a, nil
}
return nil, errors.New("type assertion to []interface{} failed")
}
func (j *Json) Bool() (bool, error) {
if s, ok := (j.data).(bool); ok {
return s, nil
}
return false, errors.New("type assertion to bool failed")
}
func (j *Json) String() (string, error) {
if s, ok := (j.data).(string); ok {
return s, nil
}
return "", errors.New("type assertion to string failed")
}
func (j *Json) Bytes() ([]byte, error) {
if s, ok := (j.data).(string); ok {
return []byte(s), nil
}
return nil, errors.New("type assertion to []byte failed")
}
func (j *Json) Int() (int, error) {
if f, ok := (j.data).(float64); ok {
return int(f), nil
}
return -1, errors.New("type assertion to float64 failed")
}
func (j *Json) MustArray(args ...[]interface{}) []interface{} {
var def []interface{}
switch len(args) {
case 0:
case 1:
def = args[0]
default:
log.Panicf("MustArray() received too many arguments %d", len(args))
}
a, err := j.Array()
if err == nil {
return a
}
return def
}
func (j *Json) MustMap(args ...map[string]interface{}) map[string]interface{} {
var def map[string]interface{}
switch len(args) {
case 0:
case 1:
def = args[0]
default:
log.Panicf("MustMap() received too many arguments %d", len(args))
}
a, err := j.Map()
if err == nil {
return a
}
return def
}
func (j *Json) MustString(args ...string) string {
var def string
switch len(args) {
case 0:
case 1:
def = args[0]
default:
log.Panicf("MustString() received too many arguments %d", len(args))
}
s, err := j.String()
if err == nil {
return s
}
return def
}
func (j *Json) MustInt64() int64 {
var ret int64
var err error
switch v := j.data.(type) {
case int:
ret = int64(v)
case int64:
ret = v
case float64:
ret = int64(v)
case string:
if ret, err = strconv.ParseInt(v, 10, 64); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
default:
ret = 0
//panic("type assertion to int64 failed")
}
return ret
}
func (j *Json) MustFloat64() float64 {
var ret float64
var err error
switch v := j.data.(type) {
case int:
ret = float64(v)
case int64:
ret = float64(v)
case float64:
ret = v
case string:
v = strings.Replace(v, ",", "", -1)
if ret, err = strconv.ParseFloat(v, 64); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
default:
ret = 0
//panic("type assertion to float64 failed")
}
return ret
}
type iBitgo struct {
accessKey string
secretKey string
currency string
opCurrency string
baseCurrency string
secret string
secretExpires int64
apiBase string
step int64
newRate float64
timeout time.Duration
timeLocation *time.Location
}
type MapSorter []Item
type Item struct {
Key string
Val string
}
func NewMapSorter(m map[string]string) MapSorter {
ms := make(MapSorter, 0, len(m))
for k, v := range m {
if strings.HasPrefix(k, "!") {
k = strings.Replace(k, "!", "", -1)
}
ms = append(ms, Item{k, v})
}
return ms
}
func (ms MapSorter) Len() int {
return len(ms)
}
func (ms MapSorter) Less(i, j int) bool {
//return ms[i].Val < ms[j].Val // Sort by value
return ms[i].Key < ms[j].Key // Sort by key
}
func (ms MapSorter) Swap(i, j int) {
ms[i], ms[j] = ms[j], ms[i]
}
func encodeParams(params map[string]string, escape bool) string {
ms := NewMapSorter(params)
sort.Sort(ms)
v := url.Values{}
for _, item := range ms {
v.Add(item.Key, item.Val)
}
if escape {
return v.Encode()
}
var buf bytes.Buffer
keys := make([]string, 0, len(v))
for k := range v {
keys = append(keys, k)
}
sort.Strings(keys)
for _, k := range keys {
vs := v[k]
prefix := k + "="
for _, v := range vs {
if buf.Len() > 0 {
buf.WriteByte('&')
}
buf.WriteString(prefix)
buf.WriteString(v)
}
}
return buf.String()
}
func newBitgo(accessKey, secretKey string) *iBitgo {
s := new(iBitgo)
s.accessKey = accessKey
s.secretKey = secretKey
s.apiBase = "https://www.bitgo.cn"
s.timeout = 20 * time.Second
s.timeLocation = time.FixedZone("Asia/Shanghai", 8*60*60)
return s
}
func (p *iBitgo) apiCall(method string) (*Json, error) {
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", fmt.Sprintf("%s/appApi.html?%s", p.apiBase, method), nil)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
resp, err := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
b, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return NewJson(b)
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetTicker(symbol string) (ticker interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.apiCall("action=market&symbol=" + symbol)
if err != nil {
return
}
dic := js.Get("data")
ticker = map[string]interface{}{
"time": js.Get("time").MustInt64(),
"buy": dic.Get("buy").MustFloat64(),
"sell": dic.Get("sell").MustFloat64(),
"last": dic.Get("last").MustFloat64(),
"high": dic.Get("high").MustFloat64(),
"low": dic.Get("low").MustFloat64(),
"vol": dic.Get("vol").MustFloat64(),
}
return
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetDepth(symbol string) (depth interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.apiCall("action=depth&symbol=" + symbol)
if err != nil {
return
}
dic := js.Get("data")
asks := [][2]float64{}
bids := [][2]float64{}
for _, pair := range dic.Get("asks").MustArray() {
arr := pair.([]interface{})
asks = append(asks, [2]float64{toFloat(arr[0]), toFloat(arr[1])})
}
for _, pair := range dic.Get("bids").MustArray() {
arr := pair.([]interface{})
bids = append(bids, [2]float64{toFloat(arr[0]), toFloat(arr[1])})
}
depth = map[string]interface{}{
"time": js.Get("time").MustInt64(),
"asks": asks,
"bids": bids,
}
return
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetTrades(symbol string) (trades interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.apiCall("action=trades&symbol=" + symbol)
if err != nil {
return
}
dic := js.Get("data")
items := []map[string]interface{}{}
for _, pair := range dic.MustArray() {
item := map[string]interface{}{}
arr := pair.(map[string]interface{})
item["id"] = toInt64(arr["id"])
item["price"] = toFloat(arr["price"])
item["amount"] = toFloat(arr["amount"])
// trade.Time = toInt64(arr["time"]) * 1000
if toString(arr["en_type"]) == "bid" {
item["type"] = "buy"
} else {
item["type"] = "sell"
}
items = append(items, item)
}
trades = items
return
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetRecords(step int64, symbol string) (records interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.apiCall(fmt.Sprintf("action=kline&symbol=%s&step=%d", symbol, step*60))
if err != nil {
return
}
items := []interface{}{}
for _, pair := range js.Get("data").MustArray() {
arr := pair.([]interface{})
if len(arr) < 6 {
err = errors.New("response format error")
return
}
item := [6]interface{}{}
item[0] = toInt64(arr[0])
item[1] = toFloat(arr[1])
item[2] = toFloat(arr[2])
item[3] = toFloat(arr[3])
item[4] = toFloat(arr[4])
item[5] = toFloat(arr[5])
items = append(items, item)
}
records = items
return
}
func (p *iBitgo) tapiCall(method string, params map[string]string) (js *Json, err error) {
if params == nil {
params = map[string]string{}
}
params["api_key"] = p.accessKey
h := md5.New()
h.Write([]byte(encodeParams(params, false) + "&secret_key=" + p.secretKey))
params["sign"] = strings.ToUpper(hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil)))
params["action"] = method
qs := encodeParams(params, false)
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", fmt.Sprintf("%s/appApi.html?%s", p.apiBase, qs), nil)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
resp, err := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
b, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
js, err = NewJson(b)
if js != nil {
if code := js.Get("code").MustInt64(); code != 200 {
s := js.Get("msg").MustString()
if s == "" {
s = fmt.Sprintf("%v", toString(js.data))
}
return nil, errors.New(s)
}
}
return js, err
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetAccount(symbol string) (account interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.tapiCall("userinfo", nil)
if err != nil {
return
}
mp := js.Get("data")
assets := map[string]map[string]interface{}{}
for k := range mp.MustMap() {
dic := mp.Get(k)
if k == "free" {
for c := range dic.MustMap() {
if _, ok := assets[c]; !ok {
assets[c] = map[string]interface{}{}
}
assets[c]["currency"] = c
assets[c]["free"] = dic.Get(c).MustFloat64()
}
} else if k == "frozen" {
for c := range dic.MustMap() {
if _, ok := assets[c]; !ok {
assets[c] = map[string]interface{}{}
}
assets[c]["currency"] = c
assets[c]["frozen"] = dic.Get(c).MustFloat64()
}
}
}
accounts := []map[string]interface{}{}
for _, pair := range assets {
accounts = append(accounts, pair)
}
account = accounts
return
}
func (p *iBitgo) Trade(side string, price, amount float64, symbol string) (orderId interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.tapiCall("trade", map[string]string{
"symbol": symbol,
"type": side,
"price": float2str(price),
"amount": float2str(amount),
})
if err != nil {
return
}
orderId = map[string]int64{"id": js.Get("orderId").MustInt64()}
return
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetOrders(symbol string) (orders interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.tapiCall("entrust", map[string]string{"symbol": symbol})
if err != nil {
return
}
items := []map[string]interface{}{}
for _, ele := range js.Get("data").MustArray() {
mp := ele.(map[string]interface{})
item := map[string]interface{}{}
item["id"] = toInt64(mp["id"])
item["amount"] = toFloat(mp["count"])
if _, ok := mp["prize"]; ok {
item["price"] = toFloat(mp["prize"])
} else {
item["price"] = toFloat(mp["price"])
}
item["deal_amount"] = toFloat(mp["success_count"])
if toInt64(mp["type"]) == 0 {
item["type"] = "buy"
} else {
item["type"] = "sell"
}
item["status"] = "open"
items = append(items, item)
}
return items, nil
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetOrder(orderId int64, symbol string) (order interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.tapiCall("order", map[string]string{"id": toString(orderId)})
if err != nil {
return
}
found := false
item := map[string]interface{}{}
for _, ele := range js.Get("data").MustArray() {
mp := ele.(map[string]interface{})
if toInt64(mp["id"]) != orderId {
continue
}
item["id"] = toInt64(mp["id"])
item["amount"] = toFloat(mp["count"])
if _, ok := mp["prize"]; ok {
item["price"] = toFloat(mp["prize"])
} else {
item["price"] = toFloat(mp["price"])
}
item["deal_amount"] = toFloat(mp["success_count"])
if toInt64(mp["type"]) == 0 {
item["type"] = "buy"
} else {
item["type"] = "sell"
}
switch toInt64(mp["status"]) {
case 1, 2:
item["status"] = "open"
case 3:
item["status"] = "closed"
case 4:
item["status"] = "cancelled"
}
found = true
break
}
if !found {
return nil, errors.New("order not found")
}
return item, nil
}
func (p *iBitgo) CancelOrder(orderId int64, symbol string) (ret bool, err error) {
_, err = p.tapiCall("cancel_entrust", map[string]string{"id": strconv.FormatInt(orderId, 10)})
if err != nil {
return
}
ret = true
return
}
type RpcRequest struct { // The fields in a struct must start with an uppercase letter, otherwise they cannot be parsed correctly. Structs can have exported and unexported fields, where fields starting with an uppercase letter are considered exported.
// During unmarshaling, the JSON tag of a struct is used to match and find the corresponding field. Therefore, modifiers are required in this case.
AccessKey string `json:"access_key"`
SecretKey string `json:"secret_key"`
Nonce int64 `json:"nonce"`
Method string `json:"method"`
Params map[string]string `json:"params"`
}
func OnPost(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
var ret interface{}
defer func() {
if e := recover(); e != nil {
if ee, ok := e.(error); ok {
e = ee.Error()
}
ret = map[string]string{"error": fmt.Sprintf("%v", e)}
}
b, _ := json.Marshal(ret)
w.Write(b)
}()
b, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
var request RpcRequest
err = json.Unmarshal(b, &request)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
e := newBitgo(request.AccessKey, request.SecretKey)
symbol := request.Params["symbol"]
if s := request.Params["access_key"]; len(s) > 0 {
e.accessKey = s
}
if s := request.Params["secret_key"]; len(s) > 0 {
e.secretKey = s
}
if symbolIdx, ok := map[string]int{
"btc": 1,
"ltc": 2,
"etp": 3,
"eth": 4,
"etc": 5,
"doge": 6,
"bec": 7,
}[strings.Replace(strings.ToLower(symbol), "_cny", "", -1)]; ok {
symbol = toString(symbolIdx)
}
var data interface{}
switch request.Method {
case "ticker":
data, err = e.GetTicker(symbol)
case "depth":
data, err = e.GetDepth(symbol)
case "trades":
data, err = e.GetTrades(symbol)
case "records":
data, err = e.GetRecords(toInt64(request.Params["period"]), symbol)
case "accounts":
data, err = e.GetAccount(symbol)
case "trade":
side := request.Params["type"]
if side == "buy" {
side = "0"
} else {
side = "1"
}
price := toFloat(request.Params["price"])
amount := toFloat(request.Params["amount"])
data, err = e.Trade(side, price, amount, symbol)
case "orders":
data, err = e.GetOrders(symbol)
case "order":
data, err = e.GetOrder(toInt64(request.Params["id"]), symbol)
case "cancel":
data, err = e.CancelOrder(toInt64(request.Params["id"]), symbol)
default:
if strings.HasPrefix(request.Method, "__api_") {
data, err = e.tapiCall(request.Method[6:], request.Params)
} else {
panic(errors.New(request.Method + " not support"))
}
}
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
ret = map[string]interface{}{
"data": data,
}
return
}
func main() {
var addr = flag.String("b", "127.0.0.1:6666", "bind addr")
flag.Parse()
if *addr == "" {
flag.Usage()
return
}
basePath := "/exchange"
log.Println("Running ", fmt.Sprintf("http://%s%s", *addr, basePath), "...")
http.HandleFunc(basePath, OnPost)
http.ListenAndServe(*addr, nil)
}
- FMZ Uniswap V3 Cuantificación de la movilidad de las piscinas de intercambio (I)
- Construcción de funciones de botón interactivo en la barra de estado de la estrategia
- Configuración de parámetros de la interfaz de estrategia
- FMZ Plataforma cuantitativa de criptomonedas Guía de uso de WebSocket (explicación detallada de la función de marcado mejorada)
- Curso de Python en X minutos
- Curso rápido en JavaScript en X minutos
- Con respecto a cómo colocar órdenes de límite de BitMEX y órdenes por lotes utilizando IO (un ejemplo)
- Biblioteca de código abierto FMZ Quant TA, aprender a usar (con versiones Javascript / Python / C ++)
- FMZ ha lanzado el motor local de pruebas de Python
- Tutoriales avanzados para escribir estrategias de la plataforma FMZ Quant
- Aplicación de la función "__Thread" en el diseño de estrategias JavaScript