आप बाजार कलेक्टर बैकटेस्ट कस्टम डेटा स्रोत का उन्नयन करने के लिए सिखाएँ
लेखक:अच्छाई, बनाया गयाः 2020-06-06 08:53:02, अद्यतन किया गयाः 2023-11-01 20:28:58
पिछला लेखबाजार उद्धरण कलेक्टर को लागू करने के लिए आप सिखाओहमने एक रोबोट प्रोग्राम लागू किया है जो बाजार के उद्धरणों को एक साथ एकत्र करता है।
बाजार डेटा का उपयोग कैसे करें जब हम इसे एकत्र करते हैं? यह बैकटेस्ट सिस्टम के लिए उपयोग करेगा। एफएमजेड प्लेटफॉर्म बैकटेस्ट सिस्टम के कस्टम डेटा स्रोत फ़ंक्शन पर निर्भर करते हुए, हम सीधे एकत्र किए गए डेटा का उपयोग बैकटेस्ट सिस्टम के डेटा स्रोत के रूप में कर सकते हैं, ताकि हम बैकटेस्ट सिस्टम को किसी भी बाजार में उपयोग कर सकें जहां हम ऐतिहासिक डेटा का बैकटेस्ट करना चाहते हैं।
इसलिए, हम
तैयार हो जाओ
यह पिछले लेख में तैयारी के काम से अलग है. पिछली बार एक डॉकर कार्यक्रम मेरे स्थानीय मैक कंप्यूटर पर चल रहा था, डेटाबेस सेवा शुरू करने के लिए mongodb डेटाबेस स्थापित कर रहा था. इस बार हमने ऑपरेटिंग वातावरण को VPS में बदल दिया और हमारे कार्यक्रमों के सेट को चलाने के लिए अलीबाबा क्लाउड लिनक्स सर्वर का उपयोग किया।
- Mongodb डेटाबेस
पिछले लेख में की तरह, हम डिवाइस पर mongodb डेटाबेस स्थापित करने की जरूरत है जहां बाजार कलेक्टर कार्यक्रम चल रहा है और सेवा शुरू. यह मूल रूप से एक मैक कंप्यूटर पर mongodb स्थापित करने के समान है. इंटरनेट पर ट्यूटोरियल का एक बहुत कुछ है, आप इसे गूगल कर सकते हैं, यह बहुत सरल है.
- पायथन 3 स्थापित करें
कार्यक्रम python3 का उपयोग करता है, कुछ पायथन पुस्तकालयों के उपयोग पर ध्यान दें, यदि वे स्थापित नहीं हैं, तो आपको उन्हें पहले स्थापित करने की आवश्यकता है।
पिमोंगो http उर्लिब
- डॉकर
एक FMZ डॉकर चलाने के लिए पर्याप्त हो जाएगा.
मार्केट कोट्स कलेक्टर को बदल दें
बाजार उद्धरण संग्रहकर्ता यह हैःhttps://www.fmz.com/strategy/199120(RecordsCollector) रणनीति।
आइए इसमें कुछ संशोधन करें:
डेटा इकट्ठा करने के लिए प्रोग्राम के लूप में प्रवेश करने से पहले, एक बहु-थ्रेडेड लाइब्रेरी का उपयोग किया जाता है, और समवर्ती निष्पादन FMZ प्लेटफॉर्म बैकटेस्ट सिस्टम के डेटा अनुरोध की निगरानी के लिए एक सेवा शुरू करता है। (अन्य विवरणों को अनदेखा किया जा सकता है)
RecordsCollector (अनुकूलित डेटा स्रोत फ़ंक्शन प्रदान करने के लिए उन्नयन)
import _thread
import pymongo
import json
import math
from http.server import HTTPServer, BaseHTTPRequestHandler
from urllib.parse import parse_qs, urlparse
def url2Dict(url):
query = urlparse(url).query
params = parse_qs(query)
result = {key: params[key][0] for key in params}
return result
class Provider(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def do_GET(self):
try:
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header("Content-type", "application/json")
self.end_headers()
dictParam = url2Dict(self.path)
Log("The custom data source service receives the request, self.path:", self.path, "query parameter:", dictParam)
# At present, the backtesting system can only select the exchange name from the list. When adding a custom data source, set it to Binance, that is: Binance
exName = exchange.GetName()
# Note that period is the bottom K-line period
tabName = "%s_%s" % ("records", int(int(dictParam["period"]) / 1000))
priceRatio = math.pow(10, int(dictParam["round"]))
amountRatio = math.pow(10, int(dictParam["vround"]))
fromTS = int(dictParam["from"]) * int(1000)
toTS = int(dictParam["to"]) * int(1000)
# Connect to the database
Log("Connect to the database service to obtain data, the database:", exName, "table:", tabName)
myDBClient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017")
ex_DB = myDBClient[exName]
exRecords = ex_DB[tabName]
# Request data
data = {
"schema" : ["time", "open", "high", "low", "close", "vol"],
"data" : []
}
# Construct query condition: greater than a certain value{'age': {'$gt': 20}} Less than a certain value{'age': {'$lt': 20}}
dbQuery = {"$and":[{'Time': {'$gt': fromTS}}, {'Time': {'$lt': toTS}}]}
Log("Query conditions:", dbQuery, "Number of inquiries:", exRecords.find(dbQuery).count(), "Total number of databases:", exRecords.find().count())
for x in exRecords.find(dbQuery).sort("Time"):
# Need to process data accuracy according to request parameters round and vround
bar = [x["Time"], int(x["Open"] * priceRatio), int(x["High"] * priceRatio), int(x["Low"] * priceRatio), int(x["Close"] * priceRatio), int(x["Volume"] * amountRatio)]
data["data"].append(bar)
Log("data:", data, "Respond to backtest system requests.")
# Write data reply
self.wfile.write(json.dumps(data).encode())
except BaseException as e:
Log("Provider do_GET error, e:", e)
def createServer(host):
try:
server = HTTPServer(host, Provider)
Log("Starting server, listen at: %s:%s" % host)
server.serve_forever()
except BaseException as e:
Log("createServer error, e:", e)
raise Exception("stop")
def main():
LogReset(1)
exName = exchange.GetName()
period = exchange.GetPeriod()
Log("collect", exName, "Exchange K-line data,", "K line cycle:", period, "second")
# Connect to the database service, service address mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017 See the settings of mongodb installed on the server
Log("Connect to the mongodb service of the hosting device, mongodb://localhost:27017")
myDBClient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017")
# Create a database
ex_DB = myDBClient[exName]
# Print the current database table
collist = ex_DB.list_collection_names()
Log("mongodb ", exName, " collist:", collist)
# Check if the table is deleted
arrDropNames = json.loads(dropNames)
if isinstance(arrDropNames, list):
for i in range(len(arrDropNames)):
dropName = arrDropNames[i]
if isinstance(dropName, str):
if not dropName in collist:
continue
tab = ex_DB[dropName]
Log("dropName:", dropName, "delete:", dropName)
ret = tab.drop()
collist = ex_DB.list_collection_names()
if dropName in collist:
Log(dropName, "failed to delete")
else :
Log(dropName, "successfully deleted")
# Start a thread to provide a custom data source service
try:
# _thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("localhost", 9090), )) # local computer test
_thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("0.0.0.0", 9090), )) # Test on VPS server
Log("Open the custom data source service thread", "#FF0000")
except BaseException as e:
Log("Failed to start the custom data source service!")
Log("Error message:", e)
raise Exception("stop")
# Create the records table
ex_DB_Records = ex_DB["%s_%d" % ("records", period)]
Log("Start collecting", exName, "K-line data", "cycle:", period, "Open (create) the database table:", "%s_%d" % ("records", period), "#FF0000")
preBarTime = 0
index = 1
while True:
r = _C(exchange.GetRecords)
if len(r) < 2:
Sleep(1000)
continue
if preBarTime == 0:
# Write all BAR data for the first time
for i in range(len(r) - 1):
bar = r[i]
# Write line by line, you need to determine whether the data already exists in the current database table, based on timestamp detection, if there is the data, then skip, if not write in
retQuery = ex_DB_Records.find({"Time": bar["Time"]})
if retQuery.count() > 0:
continue
# Write bar to the database table
ex_DB_Records.insert_one({"High": bar["High"], "Low": bar["Low"], "Open": bar["Open"], "Close": bar["Close"], "Time": bar["Time"], "Volume": bar["Volume"]})
index += 1
preBarTime = r[-1]["Time"]
elif preBarTime != r[-1]["Time"]:
bar = r[-2]
# Check before writing data, whether the data already exists, based on time stamp detection
retQuery = ex_DB_Records.find({"Time": bar["Time"]})
if retQuery.count() > 0:
continue
ex_DB_Records.insert_one({"High": bar["High"], "Low": bar["Low"], "Open": bar["Open"], "Close": bar["Close"], "Time": bar["Time"], "Volume": bar["Volume"]})
index += 1
preBarTime = r[-1]["Time"]
LogStatus(_D(), "preBarTime:", preBarTime, "_D(preBarTime):", _D(preBarTime/1000), "index:", index)
# adding drawing display
ext.PlotRecords(r, "%s_%d" % ("records", period))
Sleep(10000)
परीक्षण
रोबोट को कॉन्फ़िगर करें
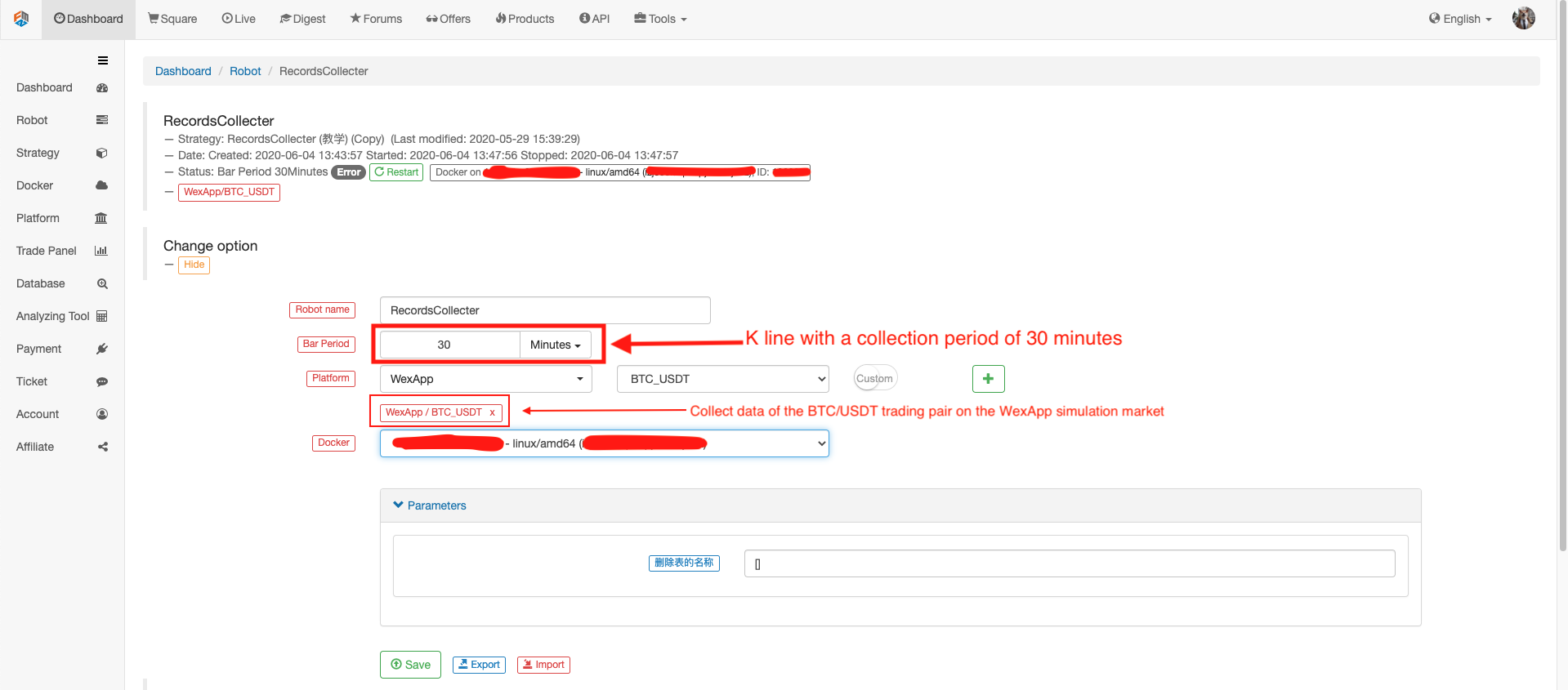
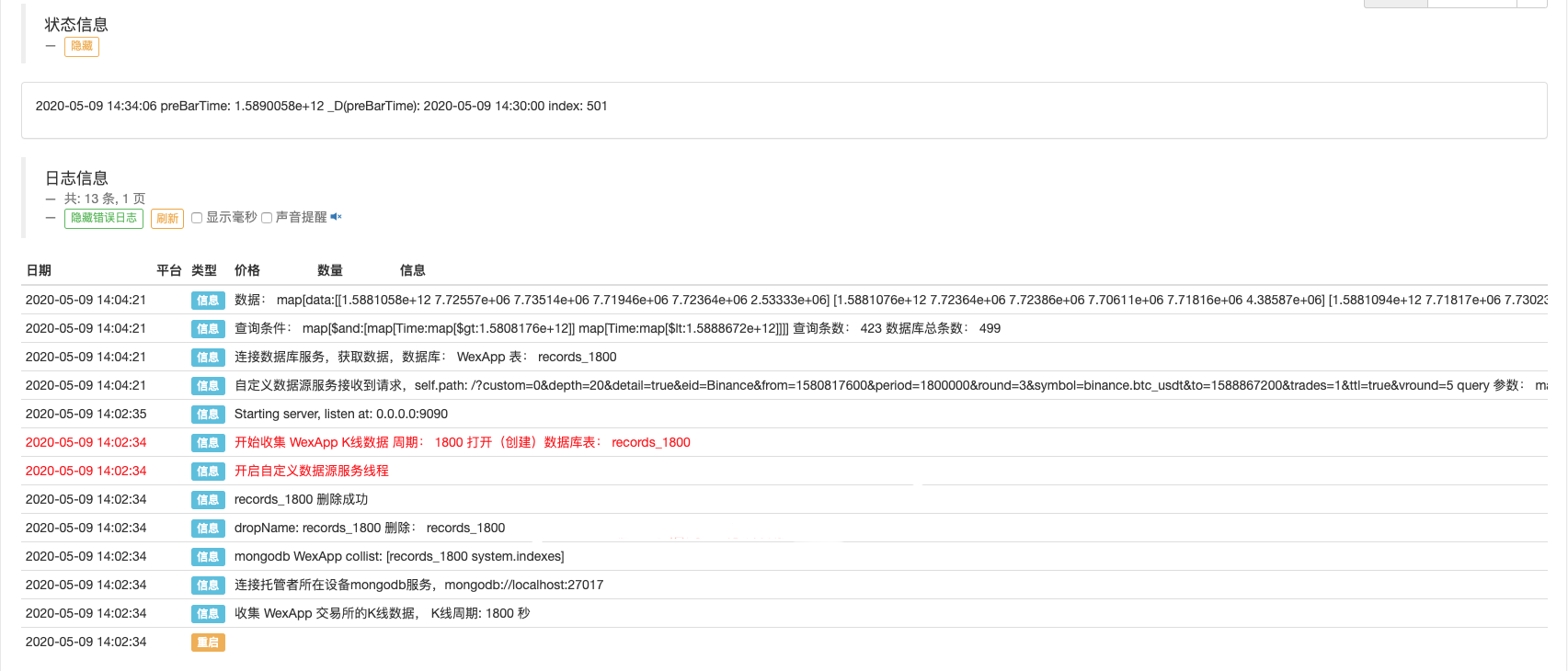
रोबोट चलाओ, बाजार उद्धरण कलेक्टर चलाओ।
बैकटेस्ट के लिए एक परीक्षण रणनीति खोलें. उदाहरण के लिएः
function main() {
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords().length)
}
बैकटेस्ट विकल्प को कॉन्फ़िगर करें, एक्सचेंज को बिनेंस पर सेट करें क्योंकि अस्थायी कस्टम डेटा स्रोत अभी तक खुद से एक्सचेंज नाम तैयार नहीं कर सकता है, आप केवल सूची में एक्सचेंज कॉन्फ़िगरेशन में से एक उधार ले सकते हैं, बैकटेस्ट से पता चलता है कि बिनेंस, वास्तविक यह WexApp के अनुकरण बाजार का डेटा है।
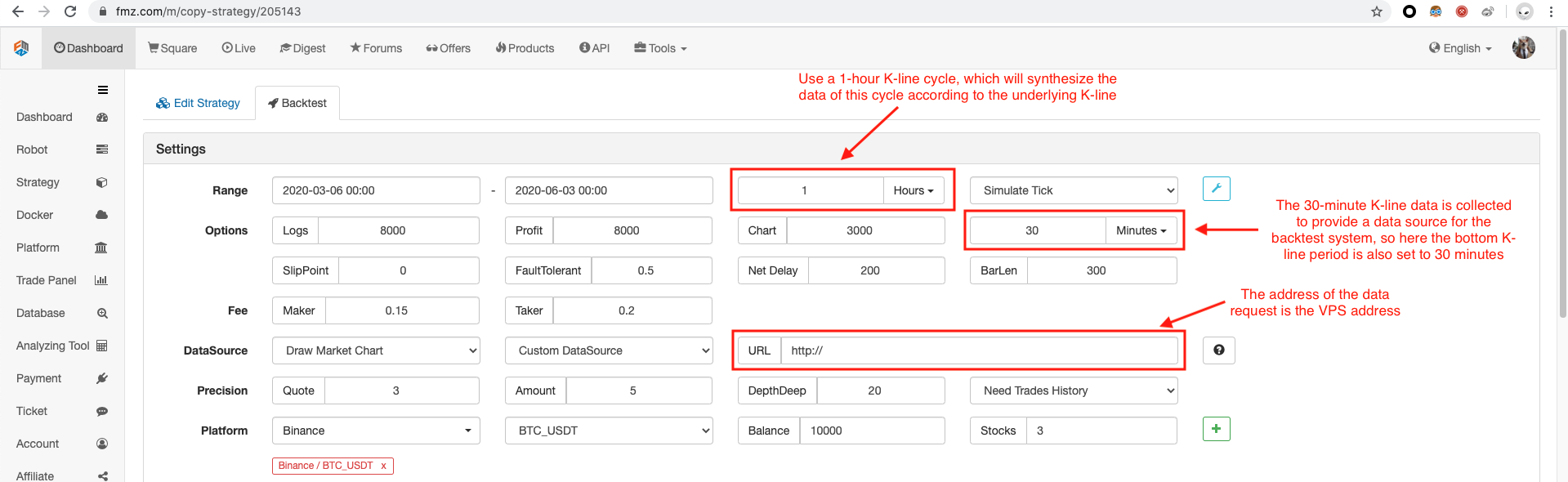
तुलना करें कि क्या बाजार उद्धरण कलेक्टर के आधार पर बैकटेस्ट प्रणाली द्वारा उत्पन्न चार्ट एक कस्टम डेटा स्रोत के रूप में wexApp एक्सचेंज पृष्ठ पर 1-घंटे के-लाइन चार्ट के समान है।
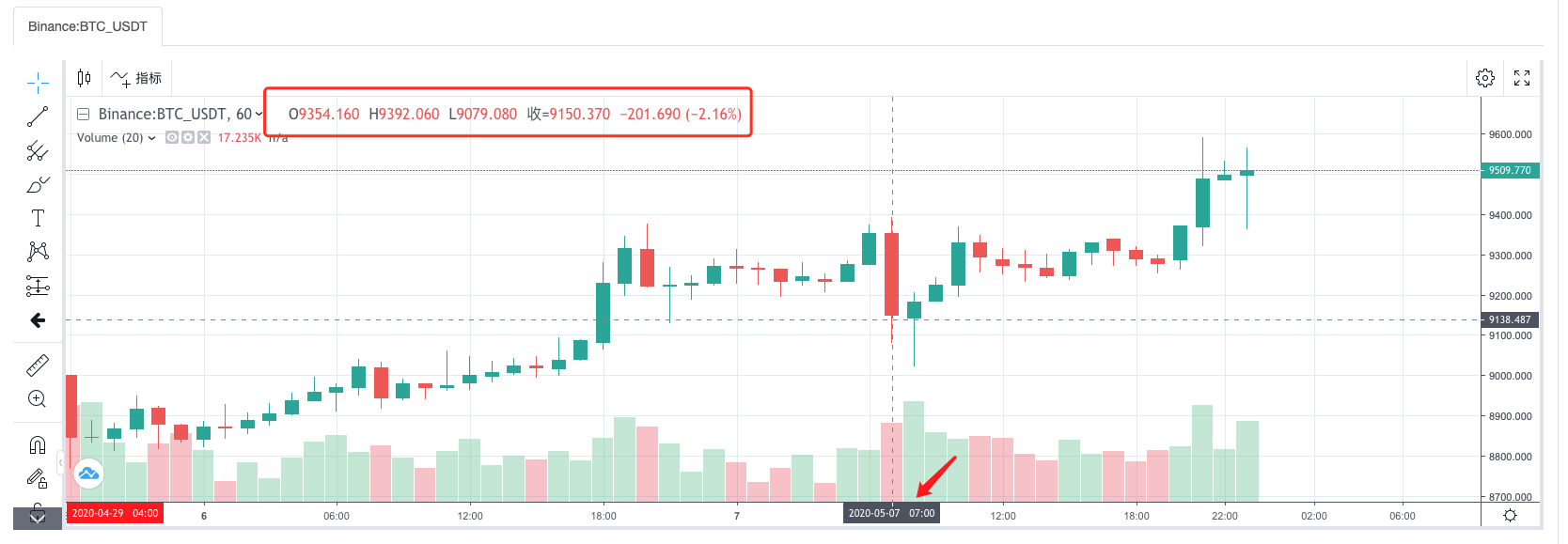
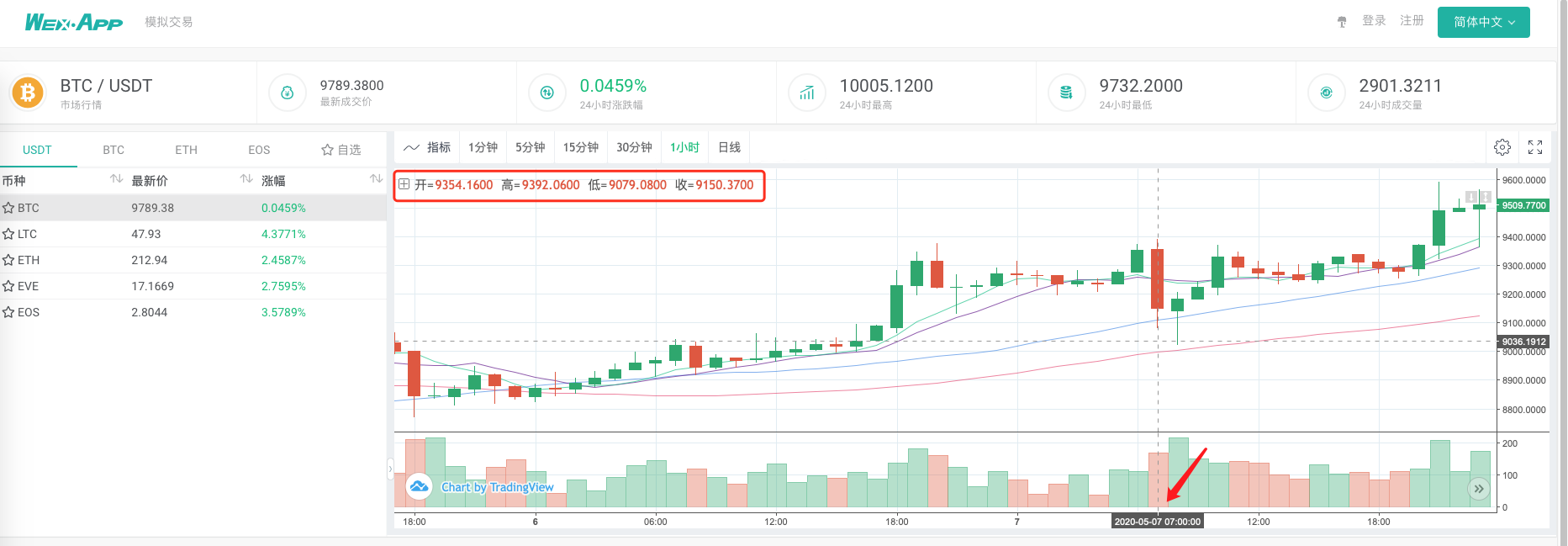
इस तरह, वीपीएस पर रोबोट अपने आप से के-लाइन डेटा एकत्र कर सकता है, और हम किसी भी समय एकत्रित डेटा प्राप्त कर सकते हैं और सीधे बैकटेस्ट सिस्टम में बैकटेस्ट कर सकते हैं।
आप विस्तार करना जारी रख सकते हैं, उदाहरण के लिए, वास्तविक स्तर के बैकटेस्ट कस्टम डेटा स्रोतों, और बहु-विविधता, बहु-बाजार डेटा संग्रह और अन्य कार्यों का प्रयास करें।
- क्रिप्टोक्यूरेंसी बाजार में मौलिक विश्लेषण की मात्राः डेटा को खुद के लिए बोलने दें!
- मौद्रिक सर्कल के मूलभूत मात्रात्मक अनुसंधान - अब हर तरह के जादूगरों पर भरोसा न करें, डेटा निष्पक्ष रूप से बोलते हैं!
- क्वांटिफाइड ट्रेडिंग के लिए आवश्यक उपकरण - आविष्कारक क्वांटिफाइड डेटा एक्सप्लोरर मॉड्यूल
- सब कुछ में महारत हासिल करना - एफएमजेड ट्रेडिंग टर्मिनल का नया संस्करण (टीआरबी आर्बिट्रेज स्रोत कोड के साथ)
- सब कुछ जानने के लिए FMZ के नए संस्करण के लिए ट्रेडिंग टर्मिनल का परिचय (अनुदानित TRB सूट स्रोत कोड)
- एफएमजेड क्वांटः क्रिप्टोकरेंसी बाजार में सामान्य आवश्यकताओं के डिजाइन उदाहरणों का विश्लेषण (II)
- 80 पंक्तियों के कोड में उच्च आवृत्ति रणनीति के साथ मस्तिष्क रहित बिक्री बॉट्स का शोषण कैसे करें
- एफएमजेड क्वांटिकेशनः क्रिप्टोक्यूरेंसी बाजार में आम जरूरतों के डिजाइन उदाहरण का विश्लेषण
- 80 लाइनों के कोड के साथ उच्च आवृत्ति रणनीतियों का उपयोग करके बेचने के लिए मस्तिष्क रहित रोबोट का शोषण कैसे करें
- एफएमजेड क्वांटः क्रिप्टोकरेंसी बाजार में सामान्य आवश्यकताओं के डिजाइन उदाहरणों का विश्लेषण (I)
- एफएमजेड क्वांटिकेशनः क्रिप्टोक्यूरेंसी बाजार में आम जरूरतों के डिजाइन उदाहरण का विश्लेषण (1)