Oparameter is set tosinalizaçãoorsinalização, theÉ necessário o parâmetro key```.
function main(){
Log(Encode("md5", "raw", "hex", "hello"))
Log(Encode("sha512", "raw", "base64", "hello"))
Log(Encode("keccak256", "raw", "hex", "unwrapWETH9(uint256,address)"))
Log(Encode("raw", "string", "hex", "example")) // 6578616d706c65
Log(Encode("raw", "hex", "string", "6578616d706c65")) // example
}
def main():
Log(Encode("md5", "raw", "hex", "hello", "", ""))
Log(Encode("sha512", "raw", "base64", "hello", "", ""))
Log(Encode("keccak256", "raw", "hex", "unwrapWETH9(uint256,address)", "", ""))
Log(Encode("raw", "string", "hex", "example", "", ""))
Log(Encode("raw", "hex", "string", "6578616d706c65", "", ""))
void main(){
Log(Encode("md5", "raw", "hex", "hello"));
Log(Encode("sha512", "raw", "base64", "hello"));
Log(Encode("keccak256", "raw", "hex", "unwrapWETH9(uint256,address)"));
Log(Encode("raw", "string", "hex", "example")); // 6578616d706c65
Log(Encode("raw", "hex", "string", "6578616d706c65")); // example
}
O parâmetroalgotambém suporta codificação e decodificação de cordas, tais comotext.encoder.utf8, text.decoder.utf8, text.encoder.gbketext.decoder.gbk.
function main(){
var ret1 = Encode("text.encoder.utf8", "raw", "hex", "hello") // e4bda0e5a5bd
Log(ret1)
var ret2 = Encode("text.decoder.utf8", "hex", "string", ret1)
Log(ret2)
var ret3 = Encode("text.encoder.gbk", "raw", "hex", "hello") // c4e3bac3
Log(ret3)
var ret4 = Encode("text.decoder.gbk", "hex", "string", ret3)
Log(ret4)
}
def main():
ret1 = Encode("text.encoder.utf8", "raw", "hex", "hello", "", "") # e4bda0e5a5bd
Log(ret1)
ret2 = Encode("text.decoder.utf8", "hex", "string", ret1, "", "")
Log(ret2)
ret3 = Encode("text.encoder.gbk", "raw", "hex", "hello", "", "") # c4e3bac3
Log(ret3)
ret4 = Encode("text.decoder.gbk", "hex", "string", ret3, "", "")
Log(ret4)
void main(){
auto ret1 = Encode("text.encoder.utf8", "raw", "hex", "hello"); // e4bda0e5a5bd
Log(ret1);
auto ret2 = Encode("text.decoder.utf8", "hex", "string", ret1);
Log(ret2);
auto ret3 = Encode("text.encoder.gbk", "raw", "hex", "hello"); // c4e3bac3
Log(ret3);
auto ret4 = Encode("text.decoder.gbk", "hex", "string", ret3);
Log(ret4);
}
UnixNano ((()
UnixNano()Retorna o carimbo de tempo de nível nanossegundo; se precisar de obter o carimbo de tempo de nível milissegundo, pode utilizar o seguinte código:
function main() {
var time = UnixNano() / 1000000
Log(_N(time, 0))
}
def main():
time = UnixNano()
Log(time)
void main() {
auto time = UnixNano();
Log(time);
}
Unix ((()
Unix()Retorna uma marca de tempo em segundos.
function main() {
var t = Unix()
Log(t)
}
def main():
t = Unix()
Log(t)
void main() {
auto t = Unix();
Log(t);
}
GetOS ((()
GetOS()Retorna informações sobre o sistema onde o docker está localizado.
function main() {
Log("GetOS:", GetOS())
}
def main():
Log("GetOS:", GetOS())
void main() {
Log("GetOS:", GetOS());
}
A saída do log do docker executado porMac OSdo computador Apple:
GetOS:darwin/amd64
darwiné o nome deMac OS system.
MD5 ((String)
MD5(String); valor do parâmetro: tipo de cadeia.
function main() {
Log("MD5", MD5("hello world"))
}
def main():
Log("MD5", MD5("hello world"))
void main() {
Log("MD5", MD5("hello world"));
}
Saída de log:
MD5 5eb63bbbe01eeed093cb22bb8f5acdc3
DBExec ((...)
DBExec(), seu valor de parâmetro pode ser string, número ou booleano, nulo e outros tipos; retornar valor: o objeto com os resultados de execução na linguagem SQLite.DBExec(), a função de interface do banco de dados, através de passagem de parâmetros, pode executar o banco de dados do bot (base de dados SQLite).SQLiteO sistema no banco de dados de bots salva tabelas incluindo:kvdb, cfg, log, profitechartNota: a funçãoDBExec()Só suporta o robô real.
-
Suporta banco de dados de memória Para os parâmetros da função
DBExec, se oQuadradoA declaração começa com:, as operações na base de dados de memória serão mais rápidas sem a gravação de arquivos.function main() { var strSql = [ ":CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(", "TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,", "HIGH REAL NOT NULL,", "OPEN REAL NOT NULL,", "LOW REAL NOT NULL,", "CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,", "VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)" ].join("") var ret = DBExec(strSql) Log(ret) // Add a piece of data Log(DBExec(":INSERT INTO TEST_TABLE (TS, HIGH, OPEN, LOW, CLOSE, VOLUME) VALUES (1518970320000, 100, 99.1, 90, 100, 12345.6);")) // Query the data Log(DBExec(":SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;")) }def main(): arr = [ ":CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(", "TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,", "HIGH REAL NOT NULL,", "OPEN REAL NOT NULL,", "LOW REAL NOT NULL,", "CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,", "VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)" ] strSql = "" for i in range(len(arr)): strSql += arr[i] ret = DBExec(strSql) Log(ret) # Add a piece of data Log(DBExec(":INSERT INTO TEST_TABLE (TS, HIGH, OPEN, LOW, CLOSE, VOLUME) VALUES (1518970320000, 100, 99.1, 90, 100, 12345.6);")) # Query the data Log(DBExec(":SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;"))void main() { string strSql = ":CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(\ TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,\ HIGH REAL NOT NULL,\ OPEN REAL NOT NULL,\ LOW REAL NOT NULL,\ CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,\ VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)"; auto ret = DBExec(strSql); Log(ret); // Add a piece of data Log(DBExec(":INSERT INTO TEST_TABLE (TS, HIGH, OPEN, LOW, CLOSE, VOLUME) VALUES (1518970320000, 100, 99.1, 90, 100, 12345.6);")); // Query the data Log(DBExec(":SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;")); } -
Criar uma tabela
function main() {
var strSql = [
"CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(",
"TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,",
"HIGH REAL NOT NULL,",
"OPEN REAL NOT NULL,",
"LOW REAL NOT NULL,",
"CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,",
"VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)"
].join("")
var ret = DBExec(strSql)
Log(ret)
}
def main():
arr = [
"CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(",
"TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,",
"HIGH REAL NOT NULL,",
"OPEN REAL NOT NULL,",
"LOW REAL NOT NULL,",
"CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,",
"VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)"
]
strSql = ""
for i in range(len(arr)):
strSql += arr[i]
ret = DBExec(strSql)
Log(ret)
void main() {
string strSql = "CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(\
TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,\
HIGH REAL NOT NULL,\
OPEN REAL NOT NULL,\
LOW REAL NOT NULL,\
CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,\
VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)";
auto ret = DBExec(strSql);
Log(ret);
}
- As operações de adição, exclusão, consulta e modificação registadas no quadro
function main() {
var strSql = [
"CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(",
"TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,",
"HIGH REAL NOT NULL,",
"OPEN REAL NOT NULL,",
"LOW REAL NOT NULL,",
"CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,",
"VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)"
].join("")
Log(DBExec(strSql))
// Add a piece of data
Log(DBExec("INSERT INTO TEST_TABLE (TS, HIGH, OPEN, LOW, CLOSE, VOLUME) VALUES (1518970320000, 100, 99.1, 90, 100, 12345.6);"))
// Query the data
Log(DBExec("SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;"))
// Modify the data
Log(DBExec("UPDATE TEST_TABLE SET HIGH=? WHERE TS=?", 110, 1518970320000))
// Delete the data
Log(DBExec("DELETE FROM TEST_TABLE WHERE HIGH=?", 110))
}
def main():
arr = [
"CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(",
"TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,",
"HIGH REAL NOT NULL,",
"OPEN REAL NOT NULL,",
"LOW REAL NOT NULL,",
"CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,",
"VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)"
]
strSql = ""
for i in range(len(arr)):
strSql += arr[i]
Log(DBExec(strSql))
# Add a piece of data
Log(DBExec("INSERT INTO TEST_TABLE (TS, HIGH, OPEN, LOW, CLOSE, VOLUME) VALUES (1518970320000, 100, 99.1, 90, 100, 12345.6);"))
# Query the data
Log(DBExec("SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;"))
# Modify the data
Log(DBExec("UPDATE TEST_TABLE SET HIGH=? WHERE TS=?", 110, 1518970320000))
# Delete the data
Log(DBExec("DELETE FROM TEST_TABLE WHERE HIGH=?", 110))
void main() {
string strSql = "CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(\
TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,\
HIGH REAL NOT NULL,\
OPEN REAL NOT NULL,\
LOW REAL NOT NULL,\
CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,\
VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)";
Log(DBExec(strSql));
// Add a piece of data
Log(DBExec("INSERT INTO TEST_TABLE (TS, HIGH, OPEN, LOW, CLOSE, VOLUME) VALUES (1518970320000, 100, 99.1, 90, 100, 12345.6);"));
// Query the data
Log(DBExec("SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;"));
// Modify the data
Log(DBExec("UPDATE TEST_TABLE SET HIGH=? WHERE TS=?", 110, 1518970320000));
// Delete the data
Log(DBExec("DELETE FROM TEST_TABLE WHERE HIGH=?", 110));
}
UUID (()
UUID(), retorna um UUID único de 32 bits, esta função está disponível apenas para bots reais.
function main() {
var uuid1 = UUID()
var uuid2 = UUID()
Log(uuid1, uuid2)
}
def main():
uuid1 = UUID()
uuid2 = UUID()
Log(uuid1, uuid2)
void main() {
auto uuid1 = UUID();
auto uuid2 = UUID();
Log(uuid1, uuid2);
}
EventLoop (Timeout)
EventLoop(timeout), retorna depois de haver qualquerwebsocketlegível ouexchange.Go, HttpQuery_Goe outras tarefas simultâneas são concluídas.timeoutSe for definido em 0, espere que um evento ocorra antes de retornar. Se for maior que 0, defina o tempo de espera do evento. Se for menor que 0, retorne o último evento imediatamente. Se o objeto retornado não fornull, oEventEsta função está disponível apenas para negociação de bots reais.
A primeira chamada deEventLoopNo código irá inicializar o mecanismo de escuta do evento.EventLoopA estrutura de fila encapsulada pelo sistema subjacente armazenará em cache até 500 chamadas de evento.EventLoopse não for chamado a tempo para remoção durante a execução do programa, as chamadas posteriores de eventos além do cache 500 serão perdidas.EventLoopfunção não afetará a fila de cache dowebsocketO sistema subjacente, nem o cache deexchange.GoPara esses caches, você ainda precisa usar seus próprios métodos para recuperar dados. para os dados que foram retirados antes doEventLoopfunção retorna, nenhum evento de retorno será gerado noEventLoop function.
O objectivo principal doEventLoopA função é notificar a camada de estratégia que o sistema subjacente recebeu novos dados de rede.EventLoopA função retorna um evento, você só precisa atravessar todas as fontes de dados.websocketligação e objetos criados porexchange.GoVocê pode se referir a um design de biblioteca de classes de código aberto:ligação da biblioteca da classe.
function main() {
var routine_getTicker = exchange.Go("GetTicker")
var routine_getDepth = exchange.Go("GetDepth")
var routine_getTrades = exchange.Go("GetTrades")
// Sleep(2000), if the Sleep statement is used here, the subsequent EventLoop function will miss the previous events, because after waiting for 2 seconds, the concurrent function has received the data, and the EventLoop monitoring mechanism will start later, and these events will be missed
// Unless you start calling EventLoop(-1) on the first line of code, first initialize the listening mechanism of EventLoop, you will not miss these events
// Log("GetDepth:", routine_getDepth.wait()) If the wait function is called in advance to get the result of the concurrent call of the GetDepth function, the event that the GetDepth function receives the request result will not be returned in the EventLoop function
var ts1 = new Date().getTime()
var ret1 = EventLoop(0)
var ts2 = new Date().getTime()
var ret2 = EventLoop(0)
var ts3 = new Date().getTime()
var ret3 = EventLoop(0)
Log("The first concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts1), ret1)
Log("The second concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts2), ret2)
Log("The third concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts3), ret3)
Log("GetTicker:", routine_getTicker.wait())
Log("GetDepth:", routine_getDepth.wait())
Log("GetTrades:", routine_getTrades.wait())
}
import time
def main():
routine_getTicker = exchange.Go("GetTicker")
routine_getDepth = exchange.Go("GetDepth")
routine_getTrades = exchange.Go("GetTrades")
ts1 = time.time()
ret1 = EventLoop(0)
ts2 = time.time()
ret2 = EventLoop(0)
ts3 = time.time()
ret3 = EventLoop(0)
Log("The first concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts1), ret1)
Log("The second concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts2), ret2)
Log("The third concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts3), ret3)
Log("GetTicker:", routine_getTicker.wait())
Log("GetDepth:", routine_getDepth.wait())
Log("GetTrades:", routine_getTrades.wait())
void main() {
auto routine_getTicker = exchange.Go("GetTicker");
auto routine_getDepth = exchange.Go("GetDepth");
auto routine_getTrades = exchange.Go("GetTrades");
auto ts1 = Unix() * 1000;
auto ret1 = EventLoop(0);
auto ts2 = Unix() * 1000;
auto ret2 = EventLoop(0);
auto ts3 = Unix() * 1000;
auto ret3 = EventLoop(0);
Log("The first concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts1), ret1);
Log("The second concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts2), ret2);
Log("The third concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts3), ret3);
Ticker ticker;
Depth depth;
Trades trades;
routine_getTicker.wait(ticker);
routine_getDepth.wait(depth);
routine_getTrades.wait(trades);
Log("GetTicker:", ticker);
Log("GetDepth:", depth);
Log("GetTrades:", trades);
}
Funções integradas
_G(K, V)
_G(K, V), com uma função de um dicionário global que pode ser salvo, suporta tanto backtest e bot.
A estrutura dos dados éKVCada bot tem um banco de dados separado. Ele sempre existirá após a reinicialização ou quando o docker sair.Kdeve ser uma cadeia, que não é sensível a minúsculas e médias.VPode ser qualquerJSONQuando a função_G()é chamado e nenhum parâmetro é passado na operação bot, a função_G()Retorna o valorIDdo bot atual.
function main(){
// Set a global variable num with a value of 1
_G("num", 1)
// Change a global variable num with the value "ok"
_G("num", "ok")
// Delete global variable num
_G("num", null)
// Return the value of the global variable num
Log(_G("num"))
// Delete all global variables
_G(null)
// Return bot ID
var robotId = _G()
}
def main():
_G("num", 1)
_G("num", "ok")
_G("num", None)
Log(_G("num"))
_G(None)
robotId = _G()
void main() {
_G("num", 1);
_G("num", "ok");
_G("num", NULL);
Log(_G("num"));
_G(NULL);
// does not support auto robotId = _G();
}
Nota:
Quando utilizar o_GA função de armazenamento de dados deve ser utilizada de forma razoável de acordo com a memória e o espaço no disco rígido do dispositivo de hardware, e não deve ser abusada.sobrecarga de memória problem.
_D ((Tempestamp, Fmt)
_D(Timestamp, Fmt), retorna as cadeias de tempo correspondentes da marca de tempo especificada.Timestampé um tipo numérico, em milissegundos.Fmté um tipo de cadeia;Fmtpadrão para:yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss; retorna valor: tipo de cadeia.
Retorna a cadeia de tempo especificada e retorna a hora atual sem passar quaisquer parâmetros; por exemplo:_D()ou_D(1478570053241), cujo formato por defeito éyyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss.
function main(){
var time = _D()
Log(time)
}
def main():
strTime = _D()
Log(strTime)
void main() {
auto strTime = _D();
Log(strTime);
}
Nota:
Quando utilizar_D()emPythonestratégia, precisamos prestar atenção que os parâmetros transmitidos são carimbos de tempo em segundo (os carimbos de tempo de nível de milissegundos noJavaScripteC ++estratégias, e 1 segundo = 1000 milissegundos).
No bot, ao usar a função_D()para analisar uma cadeia de tempo com um selo de tempo legível, você precisa prestar atenção ao fuso horário no sistema operacional do programa docker._D()analisa um carimbo de tempo como uma cadeia de tempo legível com base no tempo do sistema docker.
Por exemplo, analisando um selo de tempo de1574993606000com código:
function main() {
Log(_D(1574993606000))
}
def main():
# Beijing time server runs: 2019-11-29 10:13:26, and the docker on another server in another region runs this code will get the results: 2019-11-29 02:13:26
Log(_D(1574993606))
void main() {
Log(_D(1574993606000));
}
_N ((Num, Precisão)
_N(Num, Precision), um número com vírgula flutuante formatado. Valor do parâmetro:Numé de tipo numérico;Precisioné de tipo inteiro. Valor de retorno: tipo numérico.
Por exemplo:_N(3.1415, 2)eliminará o valor após duas casas decimais de3.1415e voltar3.14.
function main(){
var i = 3.1415
Log(i)
var ii = _N(i, 2)
Log(ii)
}
def main():
i = 3.1415
Log(i)
ii = _N(i, 2)
Log(ii)
void main() {
auto i = 3.1415;
Log(i);
auto ii = _N(i, 2);
Log(ii);
}
Se você precisa mudar N dígitos à esquerda do ponto decimal para 0, você pode escrever:
function main(){
var i = 1300
Log(i)
var ii = _N(i, -3)
// Checking the log shows that it is 1000
Log(ii)
}
def main():
i = 1300
Log(i)
ii = _N(i, -3)
Log(ii)
void main() {
auto i = 1300;
Log(i);
auto ii = _N(i, -3);
Log(ii);
}
- O quê?
_C(function, args…)é uma função de reinicialização, utilizada para a tolerância a falhas das interfaces sobre a obtenção de informações de mercado e aquisição de encomendas inacabadas, etc.
A interface irá chamar a função especificada continuamente até que retorne com sucesso (parâmetrofunctionRetorna o valor nulo ao chamar a função referenciada oufalsePor exemplo,_ C(exchange. GetTicker), o intervalo de reinicialização por defeito é de 3 segundos, que pode chamar a função_CDelay (...)para definir o intervalo de reatendimento, como_CDelay (1000)significa função de mudança_CIntervalo de reatendimento a 1 segundo.
Para as seguintes funções:
exchange.GetTicker()exchange.GetDepth()exchange.GetTrades()exchange.GetRecords()exchange.GetAccount()exchange.GetOrders()exchange.GetOrder()exchange.GetPosition()
Todos eles podem ser chamados para fazer tolerância a falhas por função_C(...). A função_C(function, args...)não se limita à tolerância a falhas das funções acima enumeradas.functioné citado não chamado, e prestar atenção que é_C(exchange.GetTicker), não_C(exchange.GetTicker()).
function main(){
var ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
// Adjust _C() function's retry interval to 2 seconds
_CDelay(2000)
var depth = _C(exchange.GetDepth)
Log(ticker)
Log(depth)
}
def main():
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
_CDelay(2000)
depth = _C(exchange.GetDepth)
Log(ticker)
Log(depth)
void main() {
auto ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker);
_CDelay(2000);
auto depth = _C(exchange.GetDepth);
Log(ticker);
Log(depth);
}
Para funções com parâmetros, quando utilizadas_C(...)para fazer tolerância a falhas:
function main(){
var records = _C(exchange.GetRecords, PERIOD_D1)
Log(records)
}
def main():
records = _C(exchange.GetRecords, PERIOD_D1)
Log(records)
void main() {
auto records = _C(exchange.GetRecords, PERIOD_D1);
Log(records);
}
Também pode ser utilizado para manipulação de tolerância de falha de funções personalizadas:
var test = function(a, b){
var time = new Date().getTime() / 1000
if(time % b == 3){
Log("Meet the criteria! ", "#FF0000")
return true
}
Log("Retry!", "#FF0000")
return false
}
function main(){
var ret = _C(test, 1, 5)
Log(ret)
}
import time
def test(a, b):
ts = time.time()
if ts % b == 3:
Log("Meet the criteria!", "#FF0000")
return True
Log("Retry!", "#FF0000")
return False
def main():
ret = _C(test, 1, 5)
Log(ret)
// C++ does not support this method for fault tolerance of custom functions.
_Cross ((Arr1, Arr2)
_Cross(Arr1, Arr2)Retorna o número de períodos de cruzamento das matrizesarr1earr2. Um número positivo é o período de ascensão, e um número negativo é o período de desaceleração, e 0 significa o mesmo que o preço atual.
Você pode simular um conjunto de dados para testar a função_Cross(Arr1, Arr2):
// Fast line indicator
var arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,8,8,9]
// Slow line indicator
var arr2 = [2,3,4,5,6,7,7,7,7]
function main(){
Log("_Cross(arr1, arr2) : ", _Cross(arr1, arr2))
Log("_Cross(arr2, arr1) : ", _Cross(arr2, arr1))
}
arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,8,8,9]
arr2 = [2,3,4,5,6,7,7,7,7]
def main():
Log("_Cross(arr1, arr2) : ", _Cross(arr1, arr2))
Log("_Cross(arr2, arr1) : ", _Cross(arr2, arr1))
void main() {
vector<double> arr1 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,8,8,9};
vector<double> arr2 = {2,3,4,5,6,7,7,7,7};
Log("_Cross(arr1, arr2) : ", _Cross(arr1, arr2));
Log("_Cross(arr2, arr1) : ", _Cross(arr2, arr1));
}
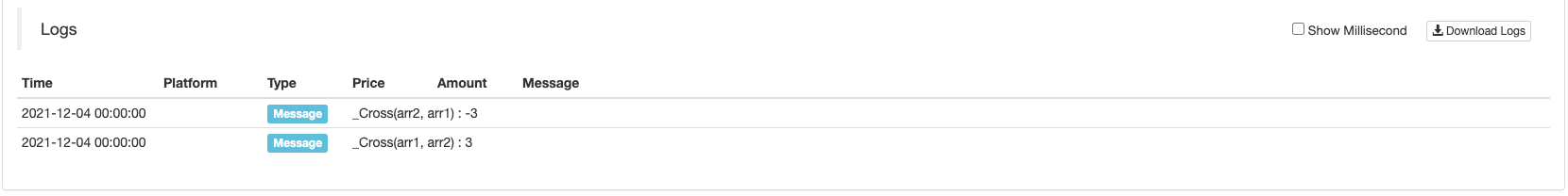
Visualizar os dados simulados para observação
Instruções específicas:Função integrada _Análise cruzada e instruções
JSONParse ((strJson)
JSONParse(strJson), a função é usada para analisar strings JSON. As strings JSON contendo grandes números podem ser analisadas corretamente, e grandes números serão analisados em tipos de strings. O sistema de backtesting não suporta essa função.
function main() {
let s1 = '{"num": 8754613216564987646512354656874651651358}'
Log("JSON.parse:", JSON.parse(s1)) // JSON.parse: {"num":8.754613216564988e+39}
Log("JSONParse:", JSONParse(s1)) // JSONParse: {"num":"8754613216564987646512354656874651651358"}
let s2 = '{"num": 123}'
Log("JSON.parse:", JSON.parse(s2)) // JSON.parse: {"num":123}
Log("JSONParse:", JSONParse(s2)) // JSONParse: {"num":123}
}
import json
def main():
s1 = '{"num": 8754613216564987646512354656874651651358}'
Log("json.loads:", json.loads(s1)) # json.loads: map[num:8.754613216564987e+39]
Log("JSONParse:", JSONParse(s1)) # JSONParse: map[num:8754613216564987646512354656874651651358]
s2 = '{"num": 123}'
Log("json.loads:", json.loads(s2)) # json.loads: map[num:123]
Log("JSONParse:", JSONParse(s2)) # JSONParse: map[num:123]
void main() {
auto s1 = "{\"num\":8754613216564987646512354656874651651358}";
Log("json::parse:", json::parse(s1));
// Log("JSONParse:", JSONParse(s1)); // The function is not supported
auto s2 = "{\"num\":123}";
Log("json::parse:", json::parse(s2));
// Log("JSONParse:", JSONParse(s2)); // The function is not supported
}
Cor personalizada
Cada cadeia de mensagens pode terminar com um valor RGB como:#ff0000, que representa a cor de primeiro plano a ser exibida.#ff0000112233, as últimas seis traseiras representam a cor de fundo.
function main() {
Log("Red", "#FF0000")
}
def main():
Log("Red", "#FF0000")
void main() {
Log("Red", "#FF0000");
}
Informações de registo
Quando o bot está em execução, as informações do log são gravadas na base de dados do bot, que adota osqlite3Os ficheiros de base de dados localizam-se no dispositivo com o programa docker, e a localização exacta dos ficheiros está no dicionário do programa docker (robotPor exemplo: O arquivo de banco de dados do bot com ID130350Está no catálogo../logs/storage/130350 (..é o dicionário onde o docker dorobotestá localizado), e o nome do arquivo do banco de dados é130350.db3.
Os registos no sistema de backtest podem ser baixados clicando no [Descarregar Registro] botão no canto inferior direito da página do backtest após o final do backtest.
Quando você precisa transferir o bot para um docker em outro servidor, você pode mover os arquivos de banco de dados do bot (arquivos de banco de dados com a extensão
Registo ((...)
Log(message)significa salvar uma mensagem na lista de log. Valor do parâmetro:messagePode ser de qualquer tipo.
Se você adicionar o caractere@Após a cadeia, a mensagem entrará na fila de push e será empurrada para a conta atual do WeChat da plataforma FMZ Quant Trading, e o
Nota:
- Push não é suportado na
Debug Tool . - Push não é suportado no
Backtest System .
function main() {
Log("Hello FMZ Quant!@")
Sleep(1000 * 5)
// Add the string to #ff0000, print the log in red, and push the message
Log("Hello, #ff0000@")
}
def main():
Log("Hello FMZ Quant!@")
Sleep(1000 * 5)
Log("Hello, #ff0000@")
void main() {
Log("Hello FMZ Quant!@");
Sleep(1000 * 5);
Log("Hello, #ff0000@");
}
WebHookempurrar:
Use o programa de serviço DEMO escrito emGolang:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func Handle (w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
defer func() {
fmt.Println("req:", *r)
}()
}
func main () {
fmt.Println("listen http://localhost:9090")
http.HandleFunc("/data", Handle)
http.ListenAndServe(":9090", nil)
}
ConjuntoWebHook: http://XXX.XX.XXX.XX:9090/data?data=Hello_FMZ
Após executar o programa de serviço, execute a estratégia e empurre a informação:
function main() {
Log("msg", "@")
}
def main():
Log("msg", "@")
void main() {
Log("msg", "@");
}
Receba a informação de empurrão e o programa de serviço imprima a informação:
listen http://localhost:9090
req: {GET /data?data=Hello_FMZ HTTP/1.1 1 1 map[User-Agent:[Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_9_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/xx.x.xxxx.xxx Safari/537.36] Accept-Encoding:[gzip]] {} <nil> 0 [] false 1XX.XX.X.XX:9090 map[] map[] <nil> map[] XXX.XX.XXX.XX:4xxx2 /data?data=Hello_FMZ <nil> <nil> <nil> 0xc420056300}
Imprimir obase64imagem codificadaA funçãoLogSuporta a impressão das imagens codificadas embase64, começa com`, e termina com`, por exemplo:
function main() {
Log("`data:image/png;base64,AAAA`")
}
def main():
Log("`data:image/png;base64,AAAA`")
void main() {
Log("`data:image/png;base64,AAAA`");
}
LogSuporta a impressão domatplotlib.pyplotobjetos dePythonDirecto, isto é, enquanto os objetos contêmsavefigmétodo, você pode usarLogpara imprimir directamente, por exemplo:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def main():
plt.plot([3,6,2,4,7,1])
Log(plt)
Alteração automática da língua dos registos impressosA funçãoLogSuporta a comutação de idiomas; quando a função produz texto, ela passa automaticamente para o idioma correspondente de acordo com a configuração de idioma na página da plataforma.
function main() {
Log("[trans]Chinese|abc[/trans]")
}
def main():
Log("[trans]Chinese|abc[/trans]")
void main() {
Log("[trans]Chinese|abc[/trans]");
}
LogProfit ((Profit)
LogProfit(Profit)Regista o valor do lucro, imprime o valor do lucro e desenha uma curva de lucro de acordo com o valor do lucro.Lucroé de tipo numérico.
Se a função termina com o caractere&, só pode realizar o desenho do gráfico de lucros, e não imprimir o registro de lucros, tais como:LogProfit(10, '&').
LogProfitReset (em inglês)
LogProfitReset()limpa todos os registos de lucro; pode tomar um parâmetro de valor inteiro para especificar o número de itens reservados.
function main() {
// Print 30 points on the income chart, then reset, and only retain the last 10 points
for(var i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
LogProfit(i)
Sleep(500)
}
LogProfitReset(10)
}
def main():
for i in range(30):
LogProfit(i)
Sleep(500)
LogProfitReset(10)
void main() {
for(int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
LogProfit(i);
Sleep(500);
}
LogProfitReset(10);
}
LogStatus ((Msg)
LogStatus(Msg), as informações não são salvas na lista de log, apenas as informações de status atual do bot são atualizadas; ele é exibido acima do log e pode ser chamado várias vezes para atualizar o status.MsgPode ser de qualquer tipo.
function main() {
LogStatus('This is a normal status prompt')
LogStatus('This is a status prompt in red font # ff0000')
LogStatus('This is a multi-line status message \n I am the second line')
}
def main():
LogStatus('This is a normal status prompt')
LogStatus('This is a status prompt in red font # ff0000')
LogStatus('This is a multi-line status message \nI am the second line')
void main() {
LogStatus("This is a normal status prompt");
LogStatus("This is a status prompt in red font # ff0000");
LogStatus("This is a multi-line status message \nI am the second line");
}
LogStatus(Msg)Suporte à impressãobase64imagens codificadas, começando por`e terminando com`, tais como:LogStatus("`data:image/png;base64,AAAA`").
LogStatus(Msg)Apoia a importação directa dePythonÉ...matplotlib.pyplotObjeto, desde que o objeto contenha osavefigmétodo, você pode passar na funçãoLogStatus(Msg), tais como:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def main():
plt.plot([3,6,2,4,7,1])
LogStatus(plt)
Exemplo de saída de dados na barra de estado:
function main() {
var table = {type: 'table', title: 'Position Information', cols: ['Column1', 'Column2'], rows: [ ['abc', 'def'], ['ABC', 'support color #ff0000']]}
// After the JSON order is serialized, add the character "`" on both sides, which is regarded as a complex message format (currently supporting tables)
LogStatus('`' + JSON.stringify(table) + '`')
// Table information can also appear in multiple lines
LogStatus('First line message\n`' + JSON.stringify(table) + '`\nThird line message')
// That supports multiple tables displayed at the same time, and that will be displayed in a group with TAB
LogStatus('`' + JSON.stringify([table, table]) + '`')
// You can also construct a button in the table, and the strategy uses "GetCommand" to receive the content of the cmd attribute
var table = {
type: 'table',
title: 'Position operation',
cols: ['Column1', 'Column2', 'Action'],
rows: [
['abc', 'def', {'type':'button', 'cmd': 'coverAll', 'name': 'close position'}]
]
}
LogStatus('`' + JSON.stringify(table) + '`')
// Or create a separate button
LogStatus('`' + JSON.stringify({'type':'button', 'cmd': 'coverAll', 'name': 'close position'}) + '`')
// You can customize the button style (button attribute of bootstrap)
LogStatus('`' + JSON.stringify({'type':'button', 'class': 'btn btn-xs btn-danger', 'cmd': 'coverAll', 'name': 'close position'}) + '`')
}
import json
def main():
table = {"type": "table", "title": "Position Information", "cols": ["Column1", "Column2"], "rows": [["abc", "def"], ["ABC", "support color #ff0000"]]}
LogStatus('`' + json.dumps(table) + '`')
LogStatus('First line message\n`' + json.dumps(table) + '`\nThird line message')
LogStatus('`' + json.dumps([table, table]) + '`')
table = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "Position operation",
"cols" : ["Column1", "Column2", "Action"],
"rows" : [
["abc", "def", {"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"}]
]
}
LogStatus('`' + json.dumps(table) + '`')
LogStatus('`' + json.dumps({"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"}) + '`')
LogStatus('`' + json.dumps({"type": "button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-danger", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"}) + '`')
void main() {
json table = R"({"type": "table", "title": "Position Information", "cols": ["Column1", "Column2"], "rows": [["abc", "def"], ["ABC", "support color #ff0000"]]})"_json;
LogStatus("`" + table.dump() + "`");
LogStatus("First line message\n`" + table.dump() + "`\nThird line message");
json arr = R"([])"_json;
arr.push_back(table);
arr.push_back(table);
LogStatus("`" + arr.dump() + "`");
table = R"({
"type" : "table",
"title" : "Position operation",
"cols" : ["Column1", "Column2", "Action"],
"rows" : [
["abc", "def", {"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"}]
]
})"_json;
LogStatus("`" + table.dump() + "`");
LogStatus("`" + R"({"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"})"_json.dump() + "`");
LogStatus("`" + R"({"type": "button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-danger", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"})"_json.dump() + "`");
}
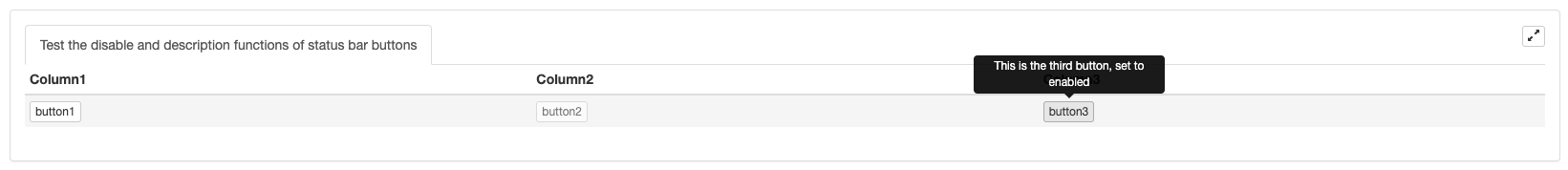
Configure as funções de desativação e descrição dos botões da barra de estado:
function main() {
var table = {
type: "table",
title: "Test the disable and description functions of status bar buttons",
cols: ["Column1", "Column2", "Column3"],
rows: []
}
var button1 = {"type": "button", "name": "button1", "cmd": "button1", "description": "This is the first button"}
var button2 = {"type": "button", "name": "button2", "cmd": "button2", "description": "This is the second button, set to disabled", "disabled": true}
var button3 = {"type": "button", "name": "button3", "cmd": "button3", "description": "This is the third button, set to enabled", "disabled": false}
table.rows.push([button1, button2, button3])
LogStatus("`" + JSON.stringify(table) + "`")
}
import json
def main():
table = {
"type": "table",
"title": "Test the disable and description functions of status bar buttons",
"cols": ["Column1", "Column2", "Column3"],
"rows": []
}
button1 = {"type": "button", "name": "button1", "cmd": "button1", "description": "This is the first button"}
button2 = {"type": "button", "name": "button2", "cmd": "button2", "description": "This is the second button, set to disabled", "disabled": True}
button3 = {"type": "button", "name": "button3", "cmd": "button3", "description": "This is the third button, set to enabled", "disabled": False}
table["rows"].append([button1, button2, button3])
LogStatus("`" + json.dumps(table) + "`")
void main() {
json table = R"({
"type": "table",
"title": "Test the disable and description functions of status bar buttons",
"cols": ["Column1", "Column2", "Column3"],
"rows": []
})"_json;
json button1 = R"({"type": "button", "name": "button1", "cmd": "button1", "description": "This is the first button"})"_json;
json button2 = R"({"type": "button", "name": "button2", "cmd": "button2", "description": "This is the second button, set to disabled", "disabled": true})"_json;
json button3 = R"({"type": "button", "name": "button3", "cmd": "button3", "description": "This is the third button, set to enabled", "disabled": false})"_json;
json arr = R"([])"_json;
arr.push_back(button1);
arr.push_back(button2);
arr.push_back(button3);
table["rows"].push_back(arr);
LogStatus("`" + table.dump() + "`");
}
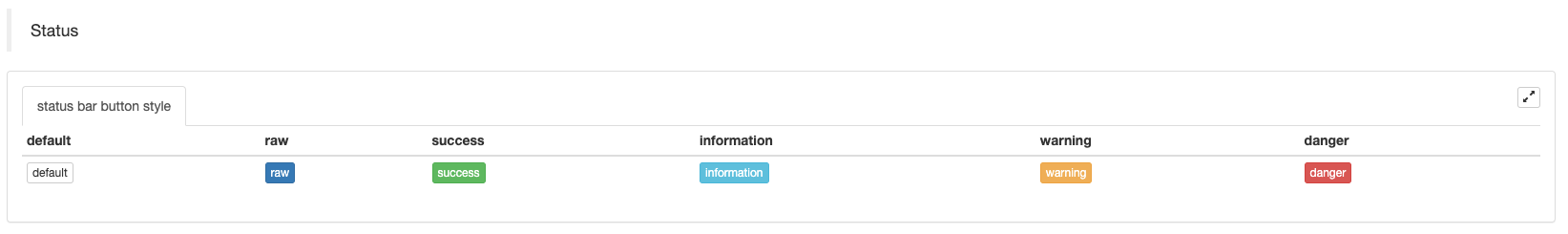
Configure o estilo dos botões da barra de status:
function main() {
var table = {
type: "table",
title: "status bar button style",
cols: ["default", "raw", "success", "information", "warning", "danger"],
rows: [
[
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-default", "name": "default"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-primary", "name": "raw"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-success", "name": "success"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-info", "name": "information"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-warning", "name": "warning"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-danger", "name": "danger"}
]
]
}
LogStatus("`" + JSON.stringify(table) + "`")
}
import json
def main():
table = {
"type": "table",
"title": "status bar button style",
"cols": ["default", "raw", "success", "information", "warning", "danger"],
"rows": [
[
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-default", "name": "default"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-primary", "name": "raw"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-success", "name": "success"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-info", "name": "information"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-warning", "name": "warning"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-danger", "name": "danger"}
]
]
}
LogStatus("`" + json.dumps(table) + "`")
void main() {
json table = R"({
"type": "table",
"title": "status bar button style",
"cols": ["default", "raw", "success", "information", "warning", "danger"],
"rows": [
[
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-default", "name": "default"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-primary", "name": "raw"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-success", "name": "success"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-info", "name": "information"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-warning", "name": "warning"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-danger", "name": "danger"}
]
]
})"_json;
LogStatus("`" + table.dump() + "`");
}
Combinar a funçãoGetCommand()Para construir a função interactiva dos botões da barra de estado:
function test1() {
Log("Call a custom function")
}
function main() {
while (true) {
var table = {
type: 'table',
title: 'operation',
cols: ['Column1', 'Column2', 'Action'],
rows: [
['a', '1', {
'type': 'button',
'cmd': "CoverAll",
'name': 'close position'
}],
['b', '1', {
'type': 'button',
'cmd': 10,
'name': 'Send value'
}],
['c', '1', {
'type': 'button',
'cmd': _D(),
'name': 'Call a function'
}],
['d', '1', {
'type': 'button',
'cmd': 'test1',
'name': 'Call a custom function'
}]
]
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", '`' + JSON.stringify(table) + '`')
var str_cmd = GetCommand()
if (str_cmd) {
Log("Received interactive data str_cmd:", "Types of:", typeof(str_cmd), "Value:", str_cmd)
if(str_cmd == "test1") {
test1()
}
}
Sleep(500)
}
}
import json
def test1():
Log("Call a custom function")
def main():
while True:
table = {
"type": "table",
"title": "Operation",
"cols": ["Column1", "Column2", "Action"],
"rows": [
["a", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": "CoverAll",
"name": "close position"
}],
["b", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": 10,
"name": "Send value"
}],
["c", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": _D(),
"name": "Call a function"
}],
["d", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": "test1",
"name": "Call a custom function"
}]
]
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + json.dumps(table) + "`")
str_cmd = GetCommand()
if str_cmd:
Log("Received interactive data str_cmd", "Types:", type(str_cmd), "Value:", str_cmd)
if str_cmd == "test1":
test1()
Sleep(500)
void test1() {
Log("Call a custom function");
}
void main() {
while(true) {
json table = R"({
"type": "table",
"title": "Operation",
"cols": ["Column1", "Column2", "Action"],
"rows": [
["a", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": "CoverAll",
"name": "close position"
}],
["b", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": 10,
"name": "Send value"
}],
["c", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": "",
"name": "Call a function"
}],
["d", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": "test1",
"name": "Call a custom function"
}]
]
})"_json;
table["rows"][2][2]["cmd"] = _D();
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + table.dump() + "`");
auto str_cmd = GetCommand();
if(str_cmd != "") {
Log("Received interactive data str_cmd", "Type:", typeid(str_cmd).name(), "Value:", str_cmd);
if(str_cmd == "test1") {
test1();
}
}
Sleep(500);
}
}
Ao construir um botão de barra de estado para interação, os dados de entrada também são suportados, e o comando interativo é finalmente capturado peloGetCommand()função.
Para acrescentar uminputitem para a estrutura de dados de um controle de botão na barra de status, por exemplo, adicionar"input": {"name": "Number of opening orders", "type": "number", "defValue": 1}para{"type": "button", "cmd": "open", "name": "open position"}, você pode fazer o botão aparecer uma caixa de diálogo com um controle de caixa de entrada quando clicado (O valor padrão na caixa de entrada é 1, que é definido pelos dados 111na caixa de entrada e clicando em GetCommandA função irá capturar a mensagem:open:111.
function main() {
var tbl = {
type: "table",
title: "operation",
cols: ["column 1", "column2"],
rows: [
["Open position operation", {"type": "button", "cmd": "open", "name": "open position", "input": {"name": "number of opening positions", "type": "number", "defValue": 1}}],
["Close position operation", {"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close all positions"}]
]
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
while (true) {
var cmd = GetCommand()
if (cmd) {
Log("cmd:", cmd)
}
Sleep(1000)
}
}
import json
def main():
tbl = {
"type": "table",
"title": "operation",
"cols": ["column 1", "column 2"],
"rows": [
["Open position operation", {"type": "button", "cmd": "open", "name": "open position", "input": {"name": "number of opening positions", "type": "number", "defValue": 1}}],
["Close position operation", {"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close all positions"}]
]
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + json.dumps(tbl) + "`")
while True:
cmd = GetCommand()
if cmd:
Log("cmd:", cmd)
Sleep(1000)
void main() {
json tbl = R"({
"type": "table",
"title": "operation",
"cols": ["column 1", "column 2"],
"rows": [
["Open position operation", {"type": "button", "cmd": "open", "name": "open position", "input": {"name": "number of opening positions", "type": "number", "defValue": 1}}],
["Close position operation", {"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close all positions"}]
]
})"_json;
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + tbl.dump() + "`");
while(true) {
auto cmd = GetCommand();
if(cmd != "") {
Log("cmd:", cmd);
}
Sleep(1000);
}
}
Combinar as células da tabela desenhada peloLogStatus(Msg)Função:
-
Fusão horizontal
function main() { var table = { type: 'table', title: 'position operation', cols: ['Column1', 'Column2', 'Action'], rows: [ ['abc', 'def', {'type':'button', 'cmd': 'coverAll', 'name': 'close position'}] ] } var ticker = exchange.GetTicker() // Add a row of data, merge the first and second cells, and output the ticker variable in the merged cell table.rows.push([{body : JSON.stringify(ticker), colspan : 2}, "abc"]) LogStatus('`' + JSON.stringify(table) + '`') }import json def main(): table = { "type" : "table", "title" : "position operation", "cols" : ["Column1", "Column2", "Action"], "rows" : [ ["abc", "def", {"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"}] ] } ticker = exchange.GetTicker() table["rows"].append([{"body": json.dumps(ticker), "colspan": 2}, "abc"]) LogStatus("`" + json.dumps(table) + "`")void main() { json table = R"({ "type" : "table", "title" : "position operation", "cols" : ["Column1", "Column2", "Action"], "rows" : [