Options contracts are sold out.
Author: The Little Dream, Created: 2017-12-18 09:43:21, Updated: 2017-12-18 09:43:52Options contracts are sold out.
-
Selling the option to buy a stock
We all know that the option to sell a hedge contract is a strategy that does not look down, and the difference between it and the buyers' subscription is that the downward trend actually includes two conditions: upward and downward. In other words, buying a subscription will only be profitable when the spot price rises significantly, while selling a hedge will otherwise generate a certain profit when the market does not change, but the benefits of the latter are relatively limited, which is what everyone needs to pay attention to when choosing a strategy.
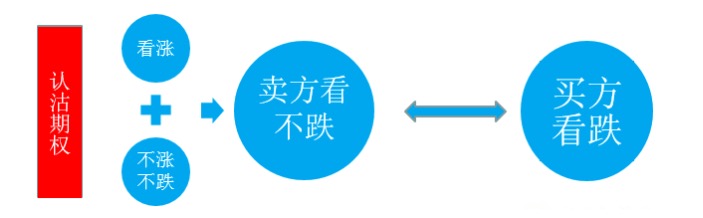
So the question arises, after choosing to sell the bond strategy, how should we choose the contract? Here I will introduce the contract option for the bond obligation stock through two scenario applications.
-
One, stop the decline and stabilize In the course of a continuous decline in the spot price, the underlying options will be significantly overvalued by the market, because during the downturn, investors holding the underlying stock will grab the underlying options to hedge the risk. When the underlying stock starts to stabilize, the panic is calmed and the sale of slightly undervalued underlying contracts is more advantageous. Because after the current price stabilizes, the value of undervalued underlying options tends to be consumed more quickly, while the value of real underlying options will return relatively slowly due to some people's choice of the option, etc. In addition, the underlying securities occupied by undervalued options also have relatively less underlying options.
-
Second, slow addiction When we judge the spot price to be slowly rising, we can open a position and phase out the hedging obligation position, in which case we often choose to sell a slightly real-value hedging contract. In the process of slowly rising prices, we reap the benefits of the intrinsic depreciation that the spot price brings to us, while enjoying the benefits that the passage of time brings to us, both of which add up to a considerable return. In this case, even if the spot price does not rise as expected, the time consuming returns to us will not decrease, which is a relatively stable strategy.
Expand reading: Sell the underwriting options for a low-picking high-picking advance
After hitting the bottom of 2850 at the end of August, the index has been weak in September in the 2850 to 3250 box, with some market participants expecting 2850-3000 to be a strong support area. For this segment, the market does not think that there will be any further significant declines, and investors who are willing to build a stock in the medium and short term can buy the position in advance by selling the options.
For example, according to the market on September 2, the market purchase price of the 50 ETFs in September 2000, the 50 ETFs in September 2050 and the 50 ETFs in September 2100 is 0.1255, 0.1390 and 0.1720 yuan, respectively. If the investor sells one 50 ETF in September 2100, two 50 ETFs in September 2050 and three 50 ETFs in September 2000, it is equivalent to a positioning position of a potential fall in the market price of 2.100, 2.050 and 2.000.
When the 50 ETF is above $2,100 on the expiration date, all contracts will expire worthlessly, and the $8,265 entitlement can be divided equally into a pocket; when the price is between $2,050 and $2,100, the investor actually buys 10,000 shares at $1,928 per share; when the price is between $2,000 and $2,050, he buys 30,000 shares at $1,917, and when the 50 ETF breaks down to $2,000, he ends up throwing a huge amount of space into the investor's pocket when he buys $1,896 per share at a cost of $2,100-0.1720*100+100+100-0.1390) *20000+2,000-0.1255) *30000) /60000.
In fact, Buffett had already successfully applied this strategy as early as April 1993, when he was very optimistic about Coca-Cola and wanted to hold the stock for a long time, but felt that the $40 share price was too high at that time, so he adopted the strategy of selling the Coca-Cola token option for $1.5 million, selling the token option for $35 at the expiration date of December 17, 1993. If the stock price falls below $35 at the expiration date, the token option will be exercised, and Buffett can buy and hold Coca-Cola shares at the price of $35, which is exactly the price at which Buffett wanted to hold the stock, and the original price of the token was calculated, reducing the actual cost of purchase to $3.5 million; if the final price is higher, Buffett will receive $3.5 million.
In summary, we can see that the use of this strategy is based on the premise that the investor has already expected that the wave of the stock market is imminent, and by such a way of arranging, on the one hand, to increase the cash income of the entitlement for himself, and on the other hand, to bury the hole in advance for potential future low-picking opportunities. Of course, the risk of selling the put option will be relatively higher in the open position, and the need to be driven out of the market, so this strategy is also more suitable for investors who prefer the risk, judging more confidently, liquid capital is more abundant.
-
Transcribed from the Department of Light Certificate Derivatives
- Inventor quantification supports the use of mobile watch strategies?
- This quantity and price of the c++ version are the same number.
- The exchange.Go))) method is not working, please check the following version of C++
- Inventor quantified cooperative unit macro futures account
- The js form shows the conversion to C++, how to write it
- Is the robot's Records turned on by default?
- How to use IO
- Okayx's API has an error.
- Bitcoin strategy: find someone to write a strategy or buy a strategy
- Locking in leverage space Boxed leverage in options trading strategies
- Is there a bug in the python policy?
- BotVS simulation disk with instructions for use
- How to catch bugs in robots
- Please allow access to some external URLs in the code
- Does the robot support the WebSocket for the token?
- Thinking about the Uniform Mechanical System
- c++ version GetCommand ((); is this command invalid?
- Can inventors quantify their A-share?
- HitBTC and OKEX have been calling GetTicker for a timeout.
- c++ Account returns all information trueValid or bug