Python version de la stratégie de la commission de l'iceberg
Auteur:La bonté, Créé: 2020-07-21 10:21:10, Mis à jour: 2023-10-26 20:08:29
Cet article présente deux stratégies classiques pour la transplantation: la commission Iceberg (achat/vente).https://www.fmz.com/square/s:Iceberg/1
Citant la version JavaScript de l'introduction à la stratégie de trading de commission Iceberg:
La commission Iceberg fait référence au fait que lorsque les investisseurs effectuent des transactions de grande valeur, afin d'éviter un impact excessif sur le marché, la commission de la commande importante est automatiquement divisée en plusieurs commissions, en fonction du dernier prix d'achat / vente 1 actuel et du prix fixé par le commerçant.
Beaucoup de pages de trading d'échange sont livrées avec des outils de mise en service d'iceberg, qui ont des fonctions riches, mais si vous souhaitez personnaliser certaines fonctions ou modifier certaines fonctions en fonction de vos propres besoins, vous avez besoin d'un outil plus flexible. La plateforme FMZ est conçue pour résoudre ce problème correctement. Notre stratégie square n'a pas trop de stratégies de trading Python. Certains traders qui veulent utiliser le langage Python pour écrire des outils et des stratégies de trading doivent se référer à des exemples. Par conséquent, la stratégie de mise en service d'iceberg classique a été portée sur la version Python.
Commission de l'iceberg pour Python - Achat
import random # Import random number library
def CancelPendingOrders(): # The function of CancelPendingOrders is to cancel all pending orders of the current transaction.
while True: # Loop detection, call GetOrders function to detect the current pending order, if orders is an empty array, that is, len(orders) is equal to 0, indicating that all orders have been cancelled, you can exit the function and call return to exit.
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
if len(orders) == 0 :
return
for j in range(len(orders)): # Traverse the current array of pending orders, and call CancelOrder to cancel the orders one by one.
exchange.CancelOrder(orders[j]["Id"])
if j < len(orders) - 1: # Except for the last order, execute Sleep every time and let the program wait for a while to avoid canceling orders too frequently.
Sleep(Interval)
LastBuyPrice = 0 # Set a global variable to record the the latest buying price.
InitAccount = None # Set a global variable to record the initial account asset information.
def dispatch(): # Main functions of iceberg commission logic
global InitAccount, LastBuyPrice # Reference global variables
account = None # Declare a variable to record the account information obtained in real time for comparison calculation.
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker) # Declare a variable to record the latest market quotes.
LogStatus(_D(), "ticker:", ticker) # Output time and latest quotation in the status bar
if LastBuyPrice > 0: # When LastBuyPrice is greater than 0, that is, when the commission has started, the code in the if condition is executed.
if len(_C(exchange.GetOrders)) > 0: # Call the exchange.GetOrders function to get all current pending orders, determine that there are pending orders, and execute the code in the if condition.
if ticker["Last"] > LastBuyPrice and ((ticker["Last"] - LastBuyPrice) / LastBuyPrice) > (2 * (EntrustDepth / 100)): # Detect the degree of deviation, if the condition is triggered, execute the code in the if, and cancel the order.
Log("Too much deviation, the latest transaction price:", ticker["Last"], "Commission price", LastBuyPrice)
CancelPendingOrders()
else :
return True
else : # If there is no pending order, it proves that the order is completely filled.
account = _C(exchange.GetAccount) # Get current account asset information.
Log("The buying order is completed, the cumulative cost:", _N(InitAccount["Balance"] - account["Balance"]), "Average buying price:", _N((InitAccount["Balance"] - account["Balance"]) / (account["Stocks"] - InitAccount["Stocks"]))) # Print transaction information.
LastBuyPrice = 0 # Reset LastBuyPrice to 0
BuyPrice = _N(ticker["Buy"] * (1 - EntrustDepth / 100)) # Calculate the price of pending orders based on current market conditions and parameters.
if BuyPrice > MaxBuyPrice: # Determine whether the maximum price set by the parameter is exceeded
return True
if not account: # If account is null, execute the code in the if statement to retrieve the current asset information and copy it to account
account = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
if (InitAccount["Balance"] - account["Balance"]) >= TotalBuyNet: # Determine whether the total amount of money spent on buying exceeds the parameter setting.
return False
RandomAvgBuyOnce = (AvgBuyOnce * ((100.0 - FloatPoint) / 100.0)) + (((FloatPoint * 2) / 100.0) * AvgBuyOnce * random.random()) # random number 0~1
UsedMoney = min(account["Balance"], RandomAvgBuyOnce, TotalBuyNet - (InitAccount["Balance"] - account["Balance"]))
BuyAmount = _N(UsedMoney / BuyPrice) # Calculate the buying quantity
if BuyAmount < MinStock: # Determine whether the buying quantity is less than the minimum buying quantity limit on the parameter.
return False
LastBuyPrice = BuyPrice # Record the price of this order and assign it to LastBuyPrice
exchange.Buy(BuyPrice, BuyAmount, "spend:¥", _N(UsedMoney), "Last transaction price", ticker["Last"]) # Place orders
return True
def main():
global LoopInterval, InitAccount # Refer to LoopInterval, InitAccount global variables
CancelPendingOrders() # Cancel all pending orders when starting to run
InitAccount = _C(exchange.GetAccount) # Account assets at the beginning of the initial record
Log(InitAccount) # Print initial account information
if InitAccount["Balance"] < TotalBuyNet: # If the initial assets are insufficient, an error will be thrown and the program will stop
raise Exception("Insufficient account balance")
LoopInterval = max(LoopInterval, 1) # Set LoopInterval to at least 1
while dispatch(): # The main loop, the iceberg commission logic function dispatch is called continuously, and the loop stops when the dispatch function returns false.
Sleep(LoopInterval * 1000) # Pause each cycle to control the polling frequency.
Log("委托全部完成", _C(exchange.GetAccount)) # When the loop execution jumps out, the current account asset information is printed.
Commission de l'iceberg pour Python - Vente
La logique de la stratégie est la même que celle de l'achat, avec seulement une légère différence.
import random
def CancelPendingOrders():
while True:
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
if len(orders) == 0:
return
for j in range(len(orders)):
exchange.CancelOrder(orders[j]["Id"])
if j < len(orders) - 1:
Sleep(Interval)
LastSellPrice = 0
InitAccount = None
def dispatch():
global LastSellPrice, InitAccount
account = None
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
LogStatus(_D(), "ticker:", ticker)
if LastSellPrice > 0:
if len(_C(exchange.GetOrders)) > 0:
if ticker["Last"] < LastSellPrice and ((LastSellPrice - ticker["Last"]) / ticker["Last"]) > (2 * (EntrustDepth / 100)):
Log("Too much deviation, the latest transaction price:", ticker["Last"], "Commission price", LastSellPrice)
CancelPendingOrders()
else :
return True
else :
account = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
Log("The buy order is completed, and the accumulated selling:", _N(InitAccount["Stocks"] - account["Stocks"]), "Average selling price:", _N((account["Balance"] - InitAccount["Balance"]) / (InitAccount["Stocks"] - account["Stocks"])))
LastSellPrice = 0
SellPrice = _N(ticker["Sell"] * (1 + EntrustDepth / 100))
if SellPrice < MinSellPrice:
return True
if not account:
account = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
if (InitAccount["Stocks"] - account["Stocks"]) >= TotalSellStocks:
return False
RandomAvgSellOnce = (AvgSellOnce * ((100.0 - FloatPoint) / 100.0)) + (((FloatPoint * 2) / 100.0) * AvgSellOnce * random.random())
SellAmount = min(TotalSellStocks - (InitAccount["Stocks"] - account["Stocks"]), RandomAvgSellOnce)
if SellAmount < MinStock:
return False
LastSellPrice = SellPrice
exchange.Sell(SellPrice, SellAmount, "Last transaction price", ticker["Last"])
return True
def main():
global InitAccount, LoopInterval
CancelPendingOrders()
InitAccount = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
Log(InitAccount)
if InitAccount["Stocks"] < TotalSellStocks:
raise Exception("Insufficient account currency")
LoopInterval = max(LoopInterval, 1)
while dispatch():
Sleep(LoopInterval)
Log("All commissioned", _C(exchange.GetAccount))
Opération stratégique
Utilisez WexApp pour simuler le test d'échange:
Achat:
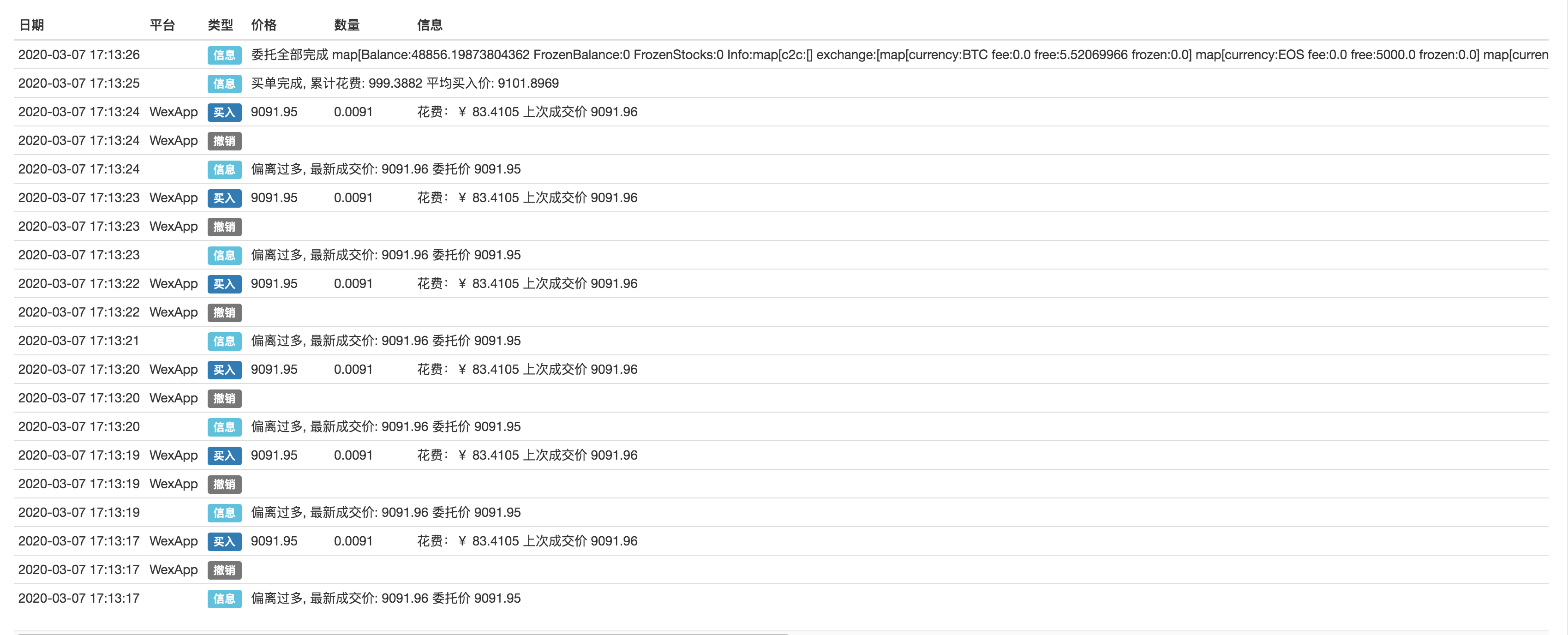
Vente:

La stratégie logique n'est pas compliquée. Lorsque la stratégie est exécutée, elle va dynamiquement placer et annuler des ordres basés sur les paramètres de la stratégie et le prix du marché actuel. Lorsque le montant de la transaction / numéro de pièce atteint ou s'approche du numéro de paramètre, la stratégie s'arrête. Le code de la stratégie est très simple et adapté pour les débutants. Les lecteurs intéressés peuvent le modifier et concevoir une stratégie qui convient à leur style de trading.
- Quantifier l'analyse fondamentale sur le marché des crypto-monnaies: laissez les données parler d'elles-mêmes!
- Les fondements de la recherche quantifiée dans le cercle monétaire - ne croyez plus à tous les professeurs de mathématiques, les données sont objectives!
- Un outil indispensable dans le domaine de la quantification des transactions - l'inventeur du module de recherche de données quantifiées
- Maîtriser tout - Introduction à FMZ Nouvelle version du terminal de négociation (avec le code source TRB Arbitrage)
- Tout savoir sur la nouvelle version du terminal de trading FMZ (source code TRB)
- FMZ Quant: Une analyse des exemples de conception des exigences communes sur le marché des crypto-monnaies (II)
- Comment exploiter les robots de vente sans cerveau avec une stratégie de haute fréquence en 80 lignes de code
- Quantification FMZ: analyse de l'exemple de conception des besoins courants sur le marché des crypto-monnaies (II)
- Comment exploiter les robots sans cerveau pour les vendre avec une stratégie de haute fréquence de 80 lignes de code
- FMZ Quant: Une analyse des exemples de conception des exigences communes sur le marché des crypto-monnaies (I)
- Quantification FMZ: analyse de l'exemple de conception des besoins courants sur le marché des crypto-monnaies (1)