Sistema de negociação de linhas de crocodilo versão Python
Autora:Bem-estar, Criado: 2020-05-07 14:33:19, Atualizado: 2023-11-06 19:40:42
Resumo
As pessoas que fizeram negociação financeira provavelmente terão experiência. Às vezes, as flutuações de preços são regulares, mas mais frequentemente mostra um estado instável de caminhada aleatória. É essa instabilidade que é onde os riscos e oportunidades do mercado estão. A instabilidade também significa imprevisível, então como tornar os retornos mais estáveis em um ambiente de mercado imprevisível também é um problema para todos os comerciantes.
O que é uma linha de crocodilo?
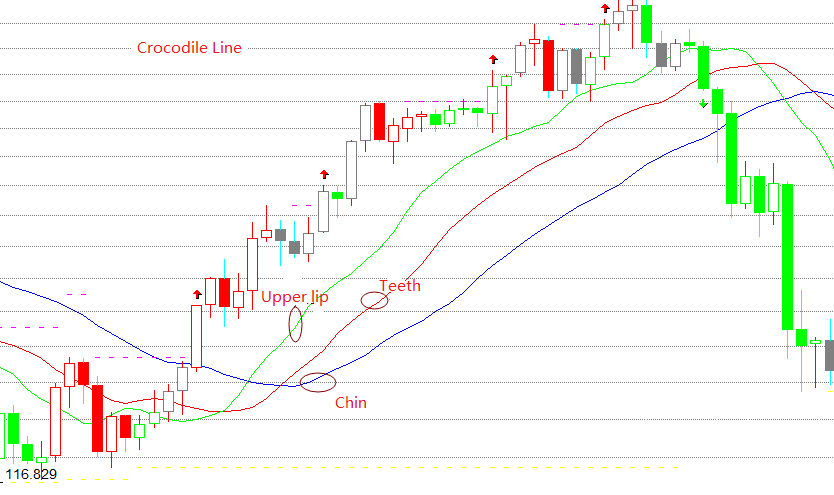
A linha do crocodilo é realmente três médias móveis especiais, que correspondem ao queixo da linha azul, os dentes da linha vermelha e o lábio superior da linha verde. O queixo é uma média móvel de 13 períodos e move 8 bares no futuro. O dente é uma média móvel de 8 períodos e move 5 bares no futuro. O lábio superior é uma média móvel de 5 períodos e move 3 bares no futuro.
Princípio da linha do crocodilo
A linha do crocodilo é um conjunto de métodos de análise técnica resumidos com base na geometria e dinâmica não linear. Quando o queixo, os dentes e o lábio superior do crocodilo estão fechados ou emaranhados, significa que o crocodilo está dormindo.
Quanto mais tempo o crocodilo dorme, mais fome terá quando acordar, então, uma vez acordado, ele abrirá a boca. Se o lábio superior estiver acima dos dentes e os dentes estiverem acima do queixo, isso indica que o mercado entrou em um mercado de touros e os crocodilos vão comer carne bovina. Se o lábio superior estiver abaixo dos dentes e os dentes estiverem abaixo do queixo, isso indica que o mercado entrou em um mercado de ursos e os crocodilos vão comer carne de urso.
Fórmula de cálculo da linha do crocodilo
Limpado superior = REF ((SMA ((VAR1,5,1),3) Dentes = REF(SMA(VAR1,8,1),5) O valor de referência é o valor de referência de cada uma das partes.
Composição da estratégia do crocodilo
Passo 1: Escrever um quadro estratégico
# Strategy main function
def onTick():
pass
# Program entry
def main ():
while True: # Enter infinite loop mode
onTick() # execute strategy main function
Sleep(1000) # sleep for 1 second
FMZ usando o modo de votação, um é a função onTick, e o outro é a função principal, na qual a função onTick é executada em um loop infinito na função principal.
Passo 2: Importação da biblioteca Python
import talib
import numpy as np
A função SMA é usada em nossa estratégia. A SMA é a média aritmética. Já existem funções SMA prontas na biblioteca talib, então importa diretamente a biblioteca talib Python e depois chama-a diretamente. Porque ao chamar essa função, você precisa passar parâmetros de formato numpy, então precisamos usar importar para importar essas duas bibliotecas Python no início da estratégia.
Passo 3: Conversão de dados de matriz de linha K
# Convert the K-line array into an array of highest price, lowest price, and closing price, for conversion to numpy.array
def get_data(bars):
arr = []
for i in bars:
arr.append(i['Close'])
return arr
Aqui criamos uma função get_data, o propósito desta função é processar a matriz K-line comum em dados de formato numpy. O parâmetro de entrada é uma matriz K-line, e o resultado de saída é dados processados em formato numpy.
Passo 4: Obtenção de dados de posição
# Get the number of positions
def get_position ():
# Get position
position = 0 # The number of assigned positions is 0
position_arr = _C (exchange.GetPosition) # Get array of positions
if len (position_arr)> 0: # If the position array length is greater than 0
for i in position_arr:
if i ['ContractType'] == 'rb000': # If the position symbol is equal to the subscription symbol
if i ['Type']% 2 == 0: # If it is long position
position = i ['Amount'] # Assigning a positive number of positions
else:
position = -i ['Amount'] # Assigning a negative number of positions
return position
O status da posição envolve lógica estratégica. Nossas primeiras dez lições sempre usaram posições virtuais, mas em um ambiente de negociação real é melhor usar a função GetPosition para obter informações reais sobre a posição, incluindo: direção da posição, lucro e perda da posição, número de posições, etc.
Passo 5: Obter os dados
exchange.SetContractType('rb000') # Subscribe the futures varieties
bars_arr = exchange.GetRecords() # Get K line array
if len(bars_arr) < 22: # If the number of K lines is less than 22
return
Antes de adquirir dados, você deve primeiro usar a função SetContractType para assinar as variedades de futuros relevantes.
Etapa 6: Calcule os dados
np_arr = np.array (get_data (bars_arr)) # Convert closing price array
sma13 = talib.SMA (np_arr, 130) [-9] # chin
sma8 = talib.SMA (np_arr, 80) [-6] # teeth
sma5 = talib.SMA (np_arr, 50) [-4] # upper lip
current_price = bars_arr [-1] ['Close'] # latest price
Antes de calcular o SMA usando a biblioteca talib, você precisa usar a biblioteca numpy para processar a matriz de linha K comum em dados numpy. Em seguida, obtenha o queixo, os dentes e o lábio superior da linha crocodilo separadamente. Além disso, o parâmetro de preço precisa ser passado ao fazer um pedido, para que possamos usar o preço de fechamento na matriz de linha K.
Passo 7: Faça um pedido
position = get_position ()
if position == 0: # If there is no position
if current_price> sma5: # If the current price is greater than the upper lip
exchange.SetDirection ("buy") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Buy (current_price + 1, 1) # open long position order
if current_price <sma13: # If the current price is less than the chin
exchange.SetDirection ("sell") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Sell (current_price-1, 1) # open short position order
if position> 0: # If you have long positions
if current_price <sma8: # If the current price is less than teeth
exchange.SetDirection ("closebuy") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Sell (current_price-1, 1) # close long position
if position <0: # If you have short position
if current_price> sma8: # If the current price is greater than the tooth
exchange.SetDirection ("closesell") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Buy (current_price + 1, 1) # close short position
Antes de colocar uma ordem, você precisa obter a posição real. A função get_position que definimos anteriormente retornará o número real de posições. Se a posição atual for longa, ela retornará um número positivo. Se a posição atual for curta, ela retornará um número negativo. Se não houver posição, retornará 0. Finalmente, as funções de compra e venda são usadas para colocar ordens de acordo com a lógica de negociação acima, mas antes disso, a direção e o tipo de negociação também precisam ser definidos.
Estratégia completa
'' 'backtest
start: 2019-01-01 00:00:00
end: 2020-01-01 00:00:00
period: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid": "Futures_CTP", "currency": "FUTURES"}]
'' '
import talib
import numpy as np
# Convert the K-line array into an array of highest price, lowest price, and closing price, used to convert to numpy.array type data
def get_data (bars):
arr = []
for i in bars:
arr.append (i ['Close'])
return arr
# Get the number of positions
def get_position ():
# Get position
position = 0 # The number of assigned positions is 0
position_arr = _C (exchange.GetPosition) # Get array of positions
if len (position_arr)> 0: # If the position array length is greater than 0
for i in position_arr:
if i ['ContractType'] == 'rb000': # If the position symbol is equal to the subscription symbol
if i ['Type']% 2 == 0: # If it is long
position = i ['Amount'] # Assign a positive number of positions
else:
position = -i ['Amount'] # Assign a negative number of positions
return position
# Strategy main function
def onTick ():
# retrieve data
exchange.SetContractType ('rb000') # Subscribe to futures varieties
bars_arr = exchange.GetRecords () # Get K line array
if len (bars_arr) <22: # If the number of K lines is less than 22
return
# Calculation
np_arr = np.array (get_data (bars_arr)) # Convert closing price array
sma13 = talib.SMA (np_arr, 130) [-9] # chin
sma8 = talib.SMA (np_arr, 80) [-6] # teeth
sma5 = talib.SMA (np_arr, 50) [-4] # upper lip
current_price = bars_arr [-1] ['Close'] # latest price
position = get_position ()
if position == 0: # If there is no position
if current_price> sma5: # If the current price is greater than the upper lip
exchange.SetDirection ("buy") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Buy (current_price + 1, 1) # open long position order
if current_price <sma13: # If the current price is less than the chin
exchange.SetDirection ("sell") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Sell (current_price-1, 1) # open short position order
if position> 0: # If you have long positions
if current_price <sma8: # If the current price is less than teeth
exchange.SetDirection ("closebuy") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Sell (current_price-1, 1) # close long position
if position <0: # If you have short positions
if current_price> sma8: # If the current price is greater than the tooth
exchange.SetDirection ("closesell") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Buy (current_price + 1, 1) # close short position
# Program main function
def main ():
while True: # loop
onTick () # execution strategy main function
Sleep (1000) # sleep for 1 second
Clique diretamente no link abaixo para copiar a estratégia completa sem configuração:https://www.fmz.com/strategy/199025
Fim
O maior papel da regra de negociação do crocodilo é nos ajudar a manter a mesma direção do mercado ao negociar, independentemente de como o preço atual do mercado muda, e continuar a lucrar até que o mercado de consolidação apareça.
- Quantificar a análise fundamental no mercado de criptomoedas: deixe os dados falarem por si mesmos!
- A pesquisa quantitativa básica do círculo monetário - deixe de acreditar em todos os professores de matemática loucos, os dados são objetivos!
- Uma ferramenta indispensável no campo da transação quantitativa - inventor do módulo de exploração de dados quantitativos
- Dominar tudo - Introdução ao FMZ Nova versão do Terminal de Negociação (com TRB Arbitrage Source Code)
- Conheça tudo sobre a nova versão do terminal de negociação da FMZ
- FMZ Quant: Análise de Exemplos de Design de Requisitos Comuns no Mercado de Criptomoedas (II)
- Como explorar robôs de venda sem cérebro com uma estratégia de alta frequência em 80 linhas de código
- Quantificação FMZ: Análise de casos de design de necessidades comuns do mercado de criptomoedas (II)
- Como usar estratégias de 80 linhas de código de alta frequência para explorar robôs sem cérebro para venda
- FMZ Quant: Análise de Exemplos de Design de Requisitos Comuns no Mercado de Criptomoedas (I)
- Quantificação FMZ: Análise de casos de design de necessidades comuns do mercado de criptomoedas (I)