A Brief Discussion on Several Grid Trading Strategies in the Digital Currency Field
 0
0
 245
245
[TOC]

The digital currency market possesses a unique trading environment that provides an ideal application scenario for grid trading strategies. Compared to traditional financial markets, the digital currency sector operates with 24-hour continuous trading, featuring continuous and frequent price movements that create abundant arbitrage opportunities for grid strategies. Meanwhile, major trading instruments such as spot and perpetual contracts have no expiration time limitations, allowing traders to hold positions for extended periods without worrying about contract expiration risks. Furthermore, the high volatility and relatively high liquidity of digital currency markets provide favorable conditions for implementing grid strategies.
Based on these characteristics, grid trading strategies demonstrate strong applicability and profit potential in digital currency markets. Grid trading strategy is a widely applied approach in digital currency markets that enables traders to profit from market volatility without needing to predict market direction. By placing buy and sell orders across different price ranges, grid trading helps traders capture profits during both price increases and decreases.
Grid trading strategies have many variants, and this article only briefly discusses several formats to help newcomers get started with understanding this classic quantitative trading method. The core concept of grid trading strategy is to place a series of buy and sell orders at different price levels. When prices reach the lower nodes of the grid, purchases are made; when they reach the upper nodes, sales are executed, thereby earning small profits from market fluctuations. The advantage of this strategy lies in the fact that traders do not need to predict market direction, but rather rely on price movements within the grid.
Grid Strategy Principles
Key Elements of Traditional Grid Trading
- Grid Nodes: Predetermined price points where buy or sell orders are placed.
- Grid Spacing: The price distance between adjacent grid nodes, which determines how much the price needs to fluctuate to trigger a trade.
- Grid Size: The total number of grid nodes, controlling the price range covered by the strategy.
How Grid Trading Strategy Works
- When the price rises from a low level and breaks through a set grid node, it triggers a sell order.
- When the price falls from a high level and breaks through a set grid node, it triggers a buy order.
- Through continuous “buy low, sell high” operations across different intervals, profits can be captured from each fluctuation even when prices oscillate back and forth within the range.
Example Illustration
Suppose a grid strategy sets the grid range from \(8,000 to \)9,000 with a grid spacing of \(500. When the price rises from \)8,000 to \(8,500, the strategy will buy at \)8,000 and sell at \(8,500. If the price further rises to \)9,000, it will sell another portion of the position. When the price drops back from \(9,000 to \)8,500, it will buy again. Through such repeated operations, the strategy can continuously accumulate profits from market fluctuations.
Comparison Between Grid Trading Strategy and Rebalancing Strategy
The core of a rebalancing strategy is to always maintain a fixed proportion of assets, such as 50% digital currency and 50% fiat currency. When the coin price rises and the proportion of held coins exceeds 50%, it sells; conversely, it buys to maintain the asset value always near the fixed proportion. Regardless of market changes, the rebalancing strategy will always hold a certain amount of coins.
Similarities and Differences Between Grid Strategy and Rebalancing Strategy
- Similarities: Both profit from volatility through buying low and selling high, and both strategies can achieve appreciation when the market returns to the original price.
- Differences: Grid strategy only operates within preset price ranges, while rebalancing strategy does not depend on specific price ranges. Grid strategy may be unable to continue operating if prices exceed the range, while rebalancing strategy can always conduct buy and sell operations, maintaining capital liquidity.
Contracts: Arithmetic Grid Strategy
Arithmetic grid strategy is a classic quantitative trading strategy commonly used in volatile markets. This strategy captures profits from price fluctuations by placing buy and sell orders at fixed price intervals (arithmetic progression). It is suitable for markets with high volatility but unpredictable direction, such as cryptocurrencies or certain futures contracts.
Core Logic
Core Concepts:
1、Arithmetic Intervals In arithmetic grid strategy, there are fixed price intervals between buy and sell orders, which is the grid in the code. For example, when the price fluctuates by 300 units (such as grid=300 in the code), it triggers a buy or sell order.
2、Grid Initialization The strategy generates initial buy and sell prices based on the current price, namely buyp and sellp. These two prices are set according to the grid interval grid, positioned grid units above and below the current price respectively.
3、Take Profit and Reverse When the price rises to a certain area, the strategy will buy in the long position area while setting sell orders for take profit. If the price continues to rise to the reverse area (upper), the long position will take profit and reverse to short, and vice versa.
4、Position Management Within Grid Each buy or sell action within the grid is triggered when the price reaches the preset buyp or sellp. After each execution, the system automatically adjusts the next set of buy and sell prices to maintain the fixed grid intervals.
5、Adding and Reducing Positions The strategy continuously adjusts positions based on grid prices. When the price touches the buy point, it increases the position (adding); when the price touches the sell point, it gradually reduces the position (reducing). Through multiple trades, it captures profits from each small market fluctuation.
Strategy Code
'''backtest
start: 2024-08-26 00:00:00
end: 2024-09-25 00:00:00
period: 1m
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT","balance":10000000}]
'''
# Trading parameter configuration (set as strategy parameters)
M = 20 # Leverage size
H = 50 # Initial base position shares
n1 = 1 # Single grid trading quantity
grid = 200 # Single grid trading interval
bottom = 35000 # Long entry point
upper = 60000 # Short entry point
def CancelPendingOrders():
orders = _C(exchanges[0].GetOrders)
if len(orders)>0:
for j in range(len(orders)):
exchanges[0].CancelOrder(orders[j].Id, orders[j])
j=j+1
def main():
exchange.SetContractType('swap')
exchange.SetMarginLevel(M)
currency=exchange.GetCurrency()
if _G('buyp') and _G('sellp'):
buyp=_G('buyp')
sellp=_G('sellp')
Log('Load grid prices')
else:
ticker=exchange.GetTicker()
buyp=ticker["Last"]-grid
sellp=ticker["Last"]+grid
_G('buyp',buyp)
_G('sellp',sellp)
Log('Grid data initialization')
while True:
account=exchange.GetAccount()
ticker=exchange.GetTicker()
position=exchange.GetPosition()
orders=exchange.GetOrders()
if len(position)==0:
if ticker["Last"]>upper:
exchange.SetDirection('sell')
exchange.Sell(-1,n1*H)
Log(currency,'Reached short opening area, buy short base position')
else:
exchange.SetDirection('buy')
exchange.Buy(-1,n1*H)
Log(currency,'Reached long opening area, buy long base position')
if len(position)==1:
if position[0]["Type"]==1: #holding short position
if ticker["Last"]<bottom:
Log(currency,'All short positions take profit and reverse')
exchange.SetDirection('closesell')
exchange.Buy(-1,position[0].Amount)
else:
orders=exchange.GetOrders()
if len(orders)==0:
exchange.SetDirection('sell')
exchange.Sell(sellp,n1)
exchange.SetDirection('closesell')
exchange.Buy(buyp,n1)
if len(orders)==1:
if orders[0]["Type"]==1: #take profit executed
Log(currency,'Grid position reduction, current shares:',position[0].Amount)
CancelPendingOrders()
buyp=buyp-grid
sellp=sellp-grid
LogProfit(account["Balance"])
if orders[0]["Type"]==0:
Log(currency,'Grid position increase, current shares:',position[0].Amount)
CancelPendingOrders()
buyp=buyp+grid
sellp=sellp+grid
LogProfit(account["Balance"])
if position[0]["Type"]==0:
if ticker["Last"]>float(upper):
Log(currency,'All long positions take profit and reverse')
exchange.SetDirection('closebuy')
exchange.Sell(-1,position[0].Amount)
else:
orders=exchange.GetOrders()
if len(orders)==0:
exchange.SetDirection('buy')
exchange.Buy(buyp,n1)
exchange.SetDirection('closebuy')
exchange.Sell(sellp,n1)
if len(orders)==1:
if orders[0]["Type"]==0: #take profit executed
Log(currency,'Grid position reduction, current shares:',position[0].Amount)
CancelPendingOrders()
buyp=buyp+grid
sellp=sellp+grid
LogProfit(account["Balance"])
if orders[0]["Type"]==1:
Log(currency,'Grid position increase, current shares:',position[0].Amount)
CancelPendingOrders()
buyp=buyp-grid
sellp=sellp-grid
LogProfit(account["Balance"])
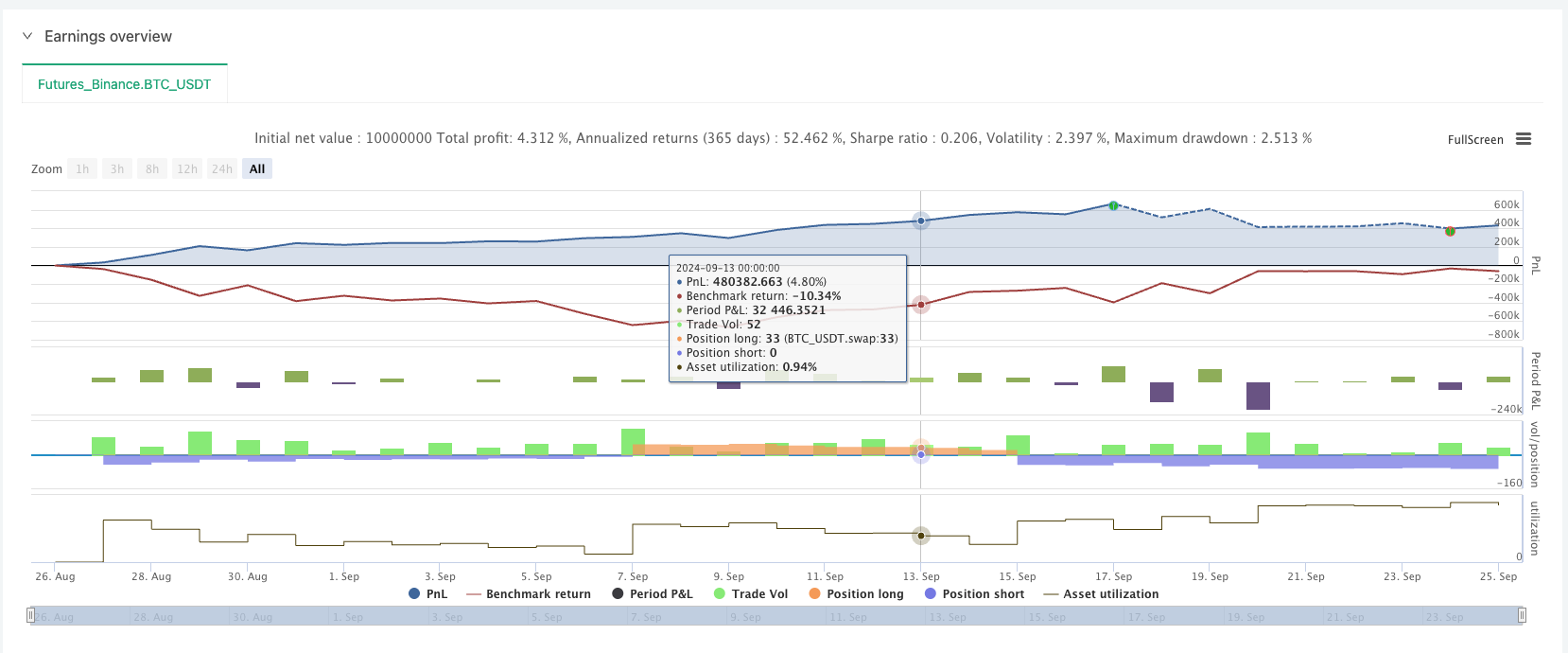
The arithmetic grid strategy has certain applicability in the digital currency field, particularly in markets with high volatility but unpredictable direction. By placing buy and sell orders at fixed price intervals, this strategy can effectively capture market volatility profits while maintaining operational automation and logical simplicity. The high volatility of digital currency markets provides excellent opportunities for this strategy to perform well.
It’s worth noting that the trading costs of arithmetic grid strategy mainly come from frequent buy and sell orders, rather than pending orders or order cancellations. This characteristic requires special attention in digital currency exchanges with high trading fees. To optimize returns, it’s recommended to choose exchanges with lower fees and adjust grid intervals and capital allocation ratios according to specific market conditions.
Overall, the arithmetic grid strategy is very suitable for sideways markets in digital currencies, but may face significant risks in trending markets. Through reasonable parameter settings and optimized fund management, the strategy’s robustness and profitability can be effectively enhanced.
Spot: Dynamic Grid Strategy
Dynamic Grid Strategy differs from traditional fixed grid strategies by dynamically generating and adjusting grid nodes, making the strategy more flexible in market fluctuations. This strategy can generate new grid nodes based on real-time market volatility, thereby improving the strategy’s adaptability and risk control capabilities. The core idea is to generate new nodes only when price fluctuations exceed a certain threshold, and to manage positions reasonably.
Core Features
1、Dynamic Grid Node Generation:
- When market prices break through the previous grid node and the volatility exceeds the preset range (controlled by _GridPointDis), the strategy generates new grid nodes.
- Each grid node records current price and position information, and sets closing conditions (closing price difference controlled by _GridCovDis).
2、Buy and Sell Operations:
- Long Direction (direction = 1): When prices rise and break through grid nodes, sell held assets; during pullbacks, buy again.
- Short Direction (direction = -1): When prices fall and break through grid nodes, buy assets; during rebounds, sell held assets.
3、Closing Operations:
- When prices touch the set closing price difference (set by _GridCovDis), execute buyback (when long) or sell (when short) operations according to the current direction to complete position closing.
4、Grid Quantity Control:
- If the number of grid nodes exceeds the maximum setting (_GridNum), the strategy automatically deletes the earliest grid nodes to prevent excessive positions and reduce risk.
Core Logic
1、Parameter Initialization:
- _GridNum: Maximum number of grid nodes, controlling the maximum number of grid nodes the strategy allows to hold simultaneously.
- _GridPointAmount: Order amount for each grid node.
- _GridPointDis: Price spacing between grid nodes.
- _GridCovDis: Price difference for closing positions; when market price volatility with grid price exceeds this difference, closing operations are executed.
2、UpdateGrid Function:
- Updates grid nodes based on current price (current_price), bid price (bids_price), and ask price (asks_price). Whenever market prices break through a grid node, the strategy generates new grid nodes and executes corresponding trading operations.
- Checks whether closing conditions are triggered and executes closing operations when triggered.
- Controls the maximum number of grid nodes; if exceeded, deletes the earliest grid nodes.
3、Main Loop:
- The main function continuously obtains real-time market price data and calls the UpdateGrid function to update grid nodes and execute trading operations.
- Records current grid status and account information through LogStatus for real-time monitoring of strategy operation.
Strategy Code (requires referencing both Python spot and charting templates)
'''backtest
start: 2024-04-01 00:00:00
end: 2024-09-23 08:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Binance","currency":"ETH_USDT"}]
'''
direction = 1 # Grid direction: 1 for upward, -1 for downward
_GridNum = 10 # Number of grid nodes
_GridPointAmount = 0.1 # Order amount per grid node
_GridPointDis = 100 # Price spacing between grid nodes
_GridCovDis = 150 # Distance between closing price and grid node
_Grid = [] # Grid data list
def UpdateGrid(nowBidsPrice, nowAsksPrice, direction): # up 1, down -1
global _Grid
# Check if new grid node needs to be created
if len(_Grid) == 0 or (direction == 1 and nowBidsPrice - _Grid[-1]['price'] > _GridPointDis) or \
(direction == -1 and _Grid[-1]['price'] - nowAsksPrice > _GridPointDis):
if len(_Grid) == 0:
Log('Strategy start')
if len(_Grid) != 0 and direction == 1 and nowBidsPrice - _Grid[-1]['price'] > _GridPointDis:
Log('Upward breakout, breakout threshold:', nowBidsPrice - _Grid[-1]['price'])
if len(_Grid) != 0 and direction == -1 and _Grid[-1]['price'] - nowAsksPrice > _GridPointDis:
Log('Downward breakout, breakout threshold:', _Grid[-1]['price'] - nowAsksPrice)
# Determine current grid node price based on direction
nowPrice = nowBidsPrice if direction == 1 else nowAsksPrice
_Grid.append({
'price': nowPrice if len(_Grid) == 0 else _Grid[-1]['price'] + _GridPointDis * direction,
'hold': {'price': 0, 'amount': 0},
'coverPrice': (nowPrice - direction * _GridCovDis) if len(_Grid) == 0 else _Grid[-1]['price'] + _GridPointDis * direction - direction * _GridCovDis
})
Log('Grid update quantity:', len(_Grid), 'Latest grid added:', _Grid[-1])
# Order operation: sell on upward breakout, buy on downward breakout
tradeInfo = ext.Sell(_GridPointAmount) if direction == 1 else ext.Buy(_GridPointAmount)
_Grid[-1]['hold']['price'] = tradeInfo['price']
_Grid[-1]['hold']['amount'] = tradeInfo['amount']
Log('Grid operation:', 'Upward sell' if direction == 1 else 'Downward buy')
# Check if position needs to be closed
if len(_Grid) > 0 and (
(direction == 1 and nowAsksPrice < _Grid[-1]['coverPrice']) or
(direction == -1 and nowBidsPrice > _Grid[-1]['coverPrice'])):
coverInfo = ext.Buy(_Grid[-1]['hold']['amount']) if direction == 1 else ext.Sell(_Grid[-1]['hold']['amount'])
Log('Price broke below closing price, buy, remove last added grid' if direction == 1 else 'Price broke above closing price, sell, remove last added grid')
_Grid.pop() # Remove closed grid node
# If grid quantity exceeds set value, close the earliest grid node
elif len(_Grid) > _GridNum:
coverFirstInfo = ext.Buy(_Grid[0]['hold']['amount']) if direction == 1 else ext.Sell(_Grid[0]['hold']['amount'])
Log('Too many grids, buy operation, remove initial grid' if direction == 1 else 'Too many grids, sell operation, remove initial grid')
_Grid.pop(0)
def main():
global _Grid
while True:
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
records = _C(exchange.GetRecords)
ext.PlotRecords(records, "kline")
UpdateGrid(ticker['Buy'], ticker['Sell'], direction)
# Record current grid status
msg = ""
for grid in _Grid:
msg += str(grid) + "\n"
LogStatus(_D(), _C(exchange.GetAccount), "\n", "_Grid.length:", len(_Grid), "_GridNum:", _GridNum, "\n", msg)
Sleep(500)
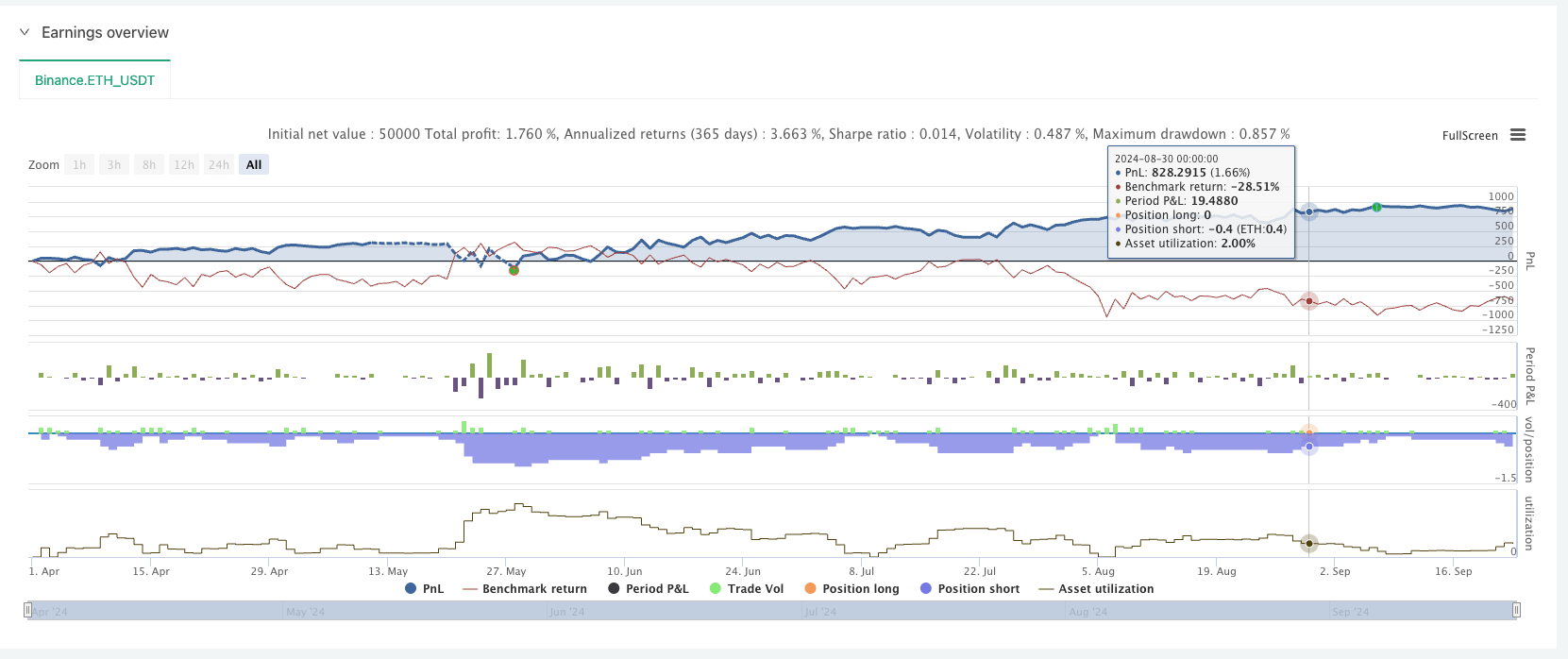
Important Notes:
- To help everyone understand the grid generation process, many comments have been added to the code, which can be deleted in actual application.
- For convenient trading, the spot strategy uses the spot template trading library. You can observe the source code to learn from it.
- When applying to live trading, improvements need to be made according to different exchange characteristics.
Futures: Long-Short Bidirectional Grid Strategy
The long-short bidirectional grid strategy is a more complex but powerful grid variant that can simultaneously trade in both long and short directions, thereby maximizing profit opportunities in sideways markets. The core of this strategy is to dynamically adjust positions based on the degree of price deviation from the initial price, achieving a truly market-neutral strategy.
Core Features
1、Long-Short Mode: Whether prices rise or fall, the strategy can generate profits through corresponding directional operations
2、Dynamic Position Adjustment: Calculate target positions based on the proportion of price deviation from the initial price
3、Bidirectional Grid Orders: Set both buy and sell orders simultaneously to capture price fluctuations in both directions
4、Risk Control: Reduce unidirectional risk through reasonable position management and order control
Strategy Logic
The core logic of the strategy is to determine target positions based on the degree of price deviation from the initial price:
1、When prices rise, the target position is negative (short), the more prices rise, the larger the short position 2、When prices fall, the target position is positive (long), the more prices fall, the larger the long position 3、Gradually adjust actual positions toward target positions through grid order execution
Strategy Code
import time
import math
# Global variable initialization
InitPrice = 800
Funding = 50000
# Strategy parameters (need to be set on strategy page)
pct = 5.0 # Grid spacing percentage
value = 5000 # Investment amount per grid
Interval = 3 # Strategy execution interval (seconds)
# Account asset information
assets = {
'USDT': {
'total_balance': 0,
'margin_balance': 0,
'margin': 0,
'unrealised_profit': 0
}
}
def init():
"""Initialize strategy"""
global symbol, Funding, base_currency
Log('Trading mode: Long-Short Bidirectional')
# Set contract type
exchange.SetContractType('swap')
# Get trading currency
currency = exchange.GetCurrency()
symbol = currency # Keep original format, like "BTC_USDT"
base_currency = symbol.split('_')[0] # Get base currency, like "BTC"
Log('Trading symbol:', symbol)
Log('Base currency:', base_currency)
swapcode = symbol + '.swap'
ticker = exchange.GetTicker(swapcode) # Backtesting system requirement
exchange_info = exchange.GetMarkets()
data = exchange_info.get(swapcode)
# Initialize asset information
assets[base_currency] = {
'amount': 0,
'price': 0,
'hold_price': 0,
'price': 0,
'unrealised_profit': 0,
'leverage': 20,
'liquidation_price': 0,
'AmountPrecision': data['AmountPrecision'],
'PricePrecision': data['PricePrecision'],
'MinQty': data['MinQty']
}
# Cancel all pending orders
cancel_all_orders()
# Get initial funding
account = exchange.GetAccount()
if account:
Funding = account.Balance + account.FrozenBalance
Log('Initial funding:', Funding)
def calculate_grid_orders():
"""Calculate grid orders"""
if InitPrice == 0 or assets[base_currency]['price'] == 0:
return None
current_price = assets[base_currency]['price']
current_amount = assets[base_currency]['amount']
# Long-short mode: calculate target position based on price change
price_change_ratio = (current_price - InitPrice) / InitPrice
target_amount = -price_change_ratio * (value / pct) / current_price
# Calculate buy/sell prices
grid_spacing = current_price * (pct / 100) # Grid spacing
buy_price = current_price - grid_spacing
sell_price = current_price + grid_spacing
# Calculate order amount
order_amount = value / current_price
return {
'buy_price': round(buy_price, assets[base_currency]['PricePrecision']),
'sell_price': round(sell_price, assets[base_currency]['PricePrecision']),
'buy_amount': round(order_amount, assets[base_currency]['AmountPrecision']),
'sell_amount': round(order_amount, assets[base_currency]['AmountPrecision']),
'target_amount': target_amount
}
def execute_strategy():
"""Execute trading strategy"""
# Calculate grid orders
grid_info = calculate_grid_orders()
if not grid_info:
return
current_amount = assets[base_currency]['amount']
target_amount = grid_info['target_amount']
amount_diff = target_amount - current_amount
# If position deviation is large, adjust position first
if abs(amount_diff) > assets[base_currency]['MinQty']:
cancel_all_orders()
Sleep(500)
# Determine required operation
if amount_diff > 0:
# Need to increase long position or reduce short position
if current_amount >= 0:
# Currently long or no position, directly open long
Log(f'Current position: {current_amount}, need to open long: {abs(amount_diff):.6f}')
open_position('LONG', assets[base_currency]['price'], abs(amount_diff))
else:
# Currently short, need to close short first then open long
if abs(amount_diff) <= abs(current_amount):
# Only need to close part of short position
Log(f'Current short position: {current_amount}, need to close: {abs(amount_diff):.6f}')
safe_close_position(abs(amount_diff), assets[base_currency]['price'])
else:
# Need to close all short positions, then open long
Log(f'Close all short positions: {abs(current_amount):.6f}')
if safe_close_position(abs(current_amount), assets[base_currency]['price']):
Sleep(1000) # Wait for closure completion
# Update position information
update_account()
remaining_amount = abs(amount_diff) - abs(current_amount)
if remaining_amount > assets[base_currency]['MinQty']:
Log(f'Open long remaining amount: {remaining_amount:.6f}')
open_position('LONG', assets[base_currency]['price'], remaining_amount)
elif amount_diff < 0:
# Need to increase short position or reduce long position
if current_amount <= 0:
# Currently short or no position, directly open short
Log(f'Current position: {current_amount}, need to open short: {abs(amount_diff):.6f}')
open_position('SHORT', assets[base_currency]['price'], abs(amount_diff))
else:
# Currently long, need to close long first then open short
if abs(amount_diff) <= current_amount:
# Only need to close part of long position
Log(f'Current long position: {current_amount}, need to close: {abs(amount_diff):.6f}')
safe_close_position(abs(amount_diff), assets[base_currency]['price'])
else:
# Need to close all long positions, then open short
Log(f'Close all long positions: {current_amount:.6f}')
if safe_close_position(current_amount, assets[base_currency]['price']):
Sleep(1000) # Wait for closure completion
# Update position information
update_account()
remaining_amount = abs(amount_diff) - current_amount
if remaining_amount > assets[base_currency]['MinQty']:
Log(f'Open short remaining amount: {remaining_amount:.6f}')
open_position('SHORT', assets[base_currency]['price'], remaining_amount)
# Check if grid orders need to be re-placed
orders = exchange.GetOrders()
if not orders or len(orders) < 2: # Long-short mode needs 2 orders
cancel_all_orders()
Sleep(500)
# Re-get latest position information
update_account()
current_amount = assets[base_currency]['amount']
# Place buy and sell orders (grid orders)
buy_amount = grid_info['buy_amount']
sell_amount = grid_info['sell_amount']
# Long-short mode: regardless of current position, place bidirectional grid orders
place_grid_orders(current_amount, grid_info, buy_amount, sell_amount)
def place_grid_orders(current_amount, grid_info, buy_amount, sell_amount):
"""Place grid orders - Long-short mode"""
Log(f'Place grid orders - Current position: {current_amount}')
# Long-short mode: regardless of current position, place bidirectional grid orders
Log(f'Long-short mode - Place long order: amount={buy_amount:.6f}, price={grid_info["buy_price"]}')
open_position('LONG', grid_info['buy_price'], buy_amount)
Sleep(200)
Log(f'Long-short mode - Place short order: amount={sell_amount:.6f}, price={grid_info["sell_price"]}')
open_position('SHORT', grid_info['sell_price'], sell_amount)
def cancel_all_orders():
"""Cancel all pending orders"""
try:
orders = exchange.GetOrders()
if orders:
for order in orders:
exchange.CancelOrder(order['Id'])
Sleep(100) # Avoid frequent operations
return True
except Exception as e:
Log('Order cancellation error:', str(e))
return False
def get_real_position():
"""Get real position information"""
try:
positions = exchange.GetPosition()
if positions:
for pos in positions:
if pos['ContractType'] == 'swap' and pos['Amount'] > 0:
position_amount = pos['Amount'] * (1 if pos['Type'] == 0 else -1)
return position_amount, pos['Price'], pos['Profit']
return 0, 0, 0
except Exception as e:
Log('Get position error:', str(e))
return 0, 0, 0
def update_account():
"""Update account information"""
try:
account = exchange.GetAccount()
if not account:
Log('Failed to get account information')
return False
# Update USDT asset information
assets['USDT']['total_balance'] = account.Balance + account.FrozenBalance
assets['USDT']['margin_balance'] = account.Balance
# Get real position information
position_amount, hold_price, profit = get_real_position()
assets[base_currency]['amount'] = position_amount
assets[base_currency]['hold_price'] = hold_price
assets[base_currency]['unrealised_profit'] = profit
return True
except Exception as e:
Log('Update account error:', str(e))
return False
def update_price():
"""Update market price"""
global InitPrice
ticker = exchange.GetTicker()
if not ticker:
Log('Failed to get market data')
return False
# Set initial price
if InitPrice == 0:
InitPrice = ticker.Last
Log('Set initial price:', InitPrice)
assets[base_currency]['price'] = ticker.Last
return True
def create_order(side, price, amount, order_type="Open Position"):
"""Create order using CreateOrder function"""
try:
if amount <= 0:
Log(f'Invalid order amount: {amount}')
return False
# Construct futures contract symbol
contract_symbol = f"{symbol}.swap"
# Place order
order_id = exchange.CreateOrder(contract_symbol, side, price, amount)
if order_id:
Log(f'{order_type} {side} order successful: price={price}, amount={amount}, order_id={order_id}')
return order_id
else:
Log(f'{order_type} {side} order failed: price={price}, amount={amount}')
return False
except Exception as e:
Log('Order error:', str(e))
return False
def safe_close_position(close_amount, price=-1):
"""Safe position closing function"""
try:
if close_amount <= 0:
Log(f'Invalid close amount: {close_amount}')
return False
# Get real-time position information
current_position, _, _ = get_real_position()
# Check if there's actually a position
if current_position == 0:
Log('No current position, skip closing operation')
return False
# Check if close amount exceeds position
if abs(close_amount) > abs(current_position):
Log(f'Close amount exceeds position: position{current_position}, close{close_amount}, adjust to position amount')
close_amount = abs(current_position)
# Determine closing operation based on current position direction
if current_position > 0: # Currently long position
side = "closebuy" # Close long position
Log(f'Close long position: amount={close_amount}, price={price}')
else: # Currently short position
side = "closesell" # Close short position
Log(f'Close short position: amount={close_amount}, price={price}')
return create_order(side, price, close_amount, "Close Position")
except Exception as e:
Log('Close position error:', str(e))
return False
def open_position(direction, price, amount):
"""Open position function"""
try:
if amount <= 0:
Log(f'Invalid open position amount: {amount}')
return False
# Determine opening direction
if direction == 'LONG':
side = "buy" # Open long position
Log(f'Open long position: amount={amount}, price={price}')
else: # SHORT
side = "sell" # Open short position
Log(f'Open short position: amount={amount}, price={price}')
return create_order(side, price, amount, "Open Position")
except Exception as e:
Log('Open position error:', str(e))
return False
def update_status():
"""Update status display"""
try:
if Funding > 0:
current_balance = assets['USDT']['total_balance']
profit = current_balance - Funding
profit_rate = (profit / Funding) * 100
status_info = f"""
Strategy Status - {symbol}
Trading Mode: Long-Short Bidirectional
Current Price: {assets[base_currency]['price']}
Initial Price: {InitPrice}
Position Amount: {assets[base_currency]['amount']}
Position Price: {assets[base_currency]['hold_price']}
Account Balance: {current_balance:.4f} USDT
Total Profit: {profit:.4f} USDT ({profit_rate:.2f}%)
Unrealized P&L: {assets[base_currency]['unrealised_profit']:.4f} USDT
"""
LogStatus(status_info)
except Exception as e:
Log('Status update error:', str(e))
def main():
"""Main function"""
# Set error filter
SetErrorFilter("502:|503:|tcp|character|unexpected|network|timeout|WSARecv|Connect|GetAddr|no such|reset|http|received|EOF|reused|Unknown")
# Initialize
init()
Log('Strategy started successfully')
while True:
try:
# Update account information
if not update_account():
Log('Failed to update account information, waiting for retry')
Sleep(5000)
continue
# Update price information
if not update_price():
Log('Failed to update price information, waiting for retry')
Sleep(5000)
continue
# Execute strategy
execute_strategy()
# Update status
update_status()
# Sleep
Sleep(Interval * 1000)
except Exception as e:
Log('Main loop error:', str(e))
Sleep(5000) # Wait 5 seconds when exception occurs before continuing
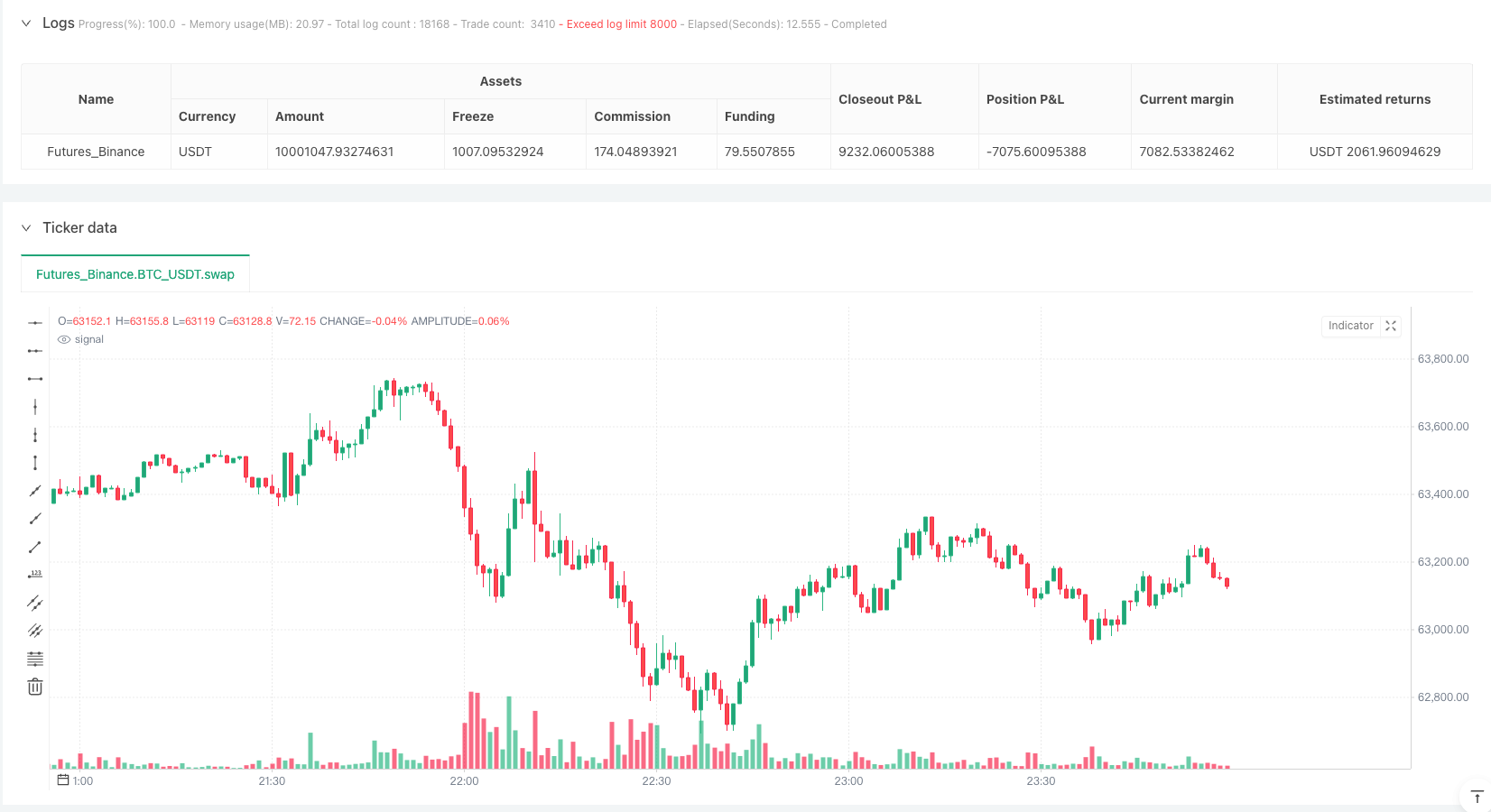
The advantage of the long-short bidirectional grid strategy lies in its ability to adapt to various market conditions, whether rising, falling, or sideways, it can generate profits through corresponding operations. However, attention must also be paid to risk control, especially fund management in extreme market conditions.
Summary
The flexibility and automation characteristics of grid strategies make them commonly used tools in quantitative trading. Different grid variants can adapt to various market environments. Each strategy has its specific applicable scenarios and advantages. Investors can choose suitable grid strategies based on specific market volatility characteristics and personal risk preferences, and further optimize strategy effectiveness by combining dynamic position management, take-profit and stop-loss tools.
It should be noted that the three types discussed in this article are all derived from the strategy square of the FMZ platform, with some summarization. As a classic type in quantitative strategies, grid strategies still have many areas worth exploring in depth, such as how to avoid liquidation and reduce risk, as well as better improve capital utilization efficiency to enhance returns. For interested friends, you can click on the strategy square, where there are live trading-level grid strategies available for reference and learning.
- From Manual Analysis to Automation: Building Aster Smart Money Tracking Tool on Inventor Platform
- 从手工分析到自动化:发明者平台搭建Aster聪明钱追踪工具
- Demystifying Crypto Influencers: A Professional Analysis System for Replicating Founder Workflows
- 祛魅加密货币大V:发明者工作流复现专业分析系统
- A New Paradigm in Quantitative Trading: A Guide to Workflow Development on the FMZ Platform
- 量化交易新范式:发明者平台工作流开发指南
- Python Multi-Currency Quantitative Strategy Framework: Design Concepts and Implementation Details
- Python多币种量化策略框架:设计思路与实现详解
- FMZ Platform Gold Rush: Practical Analysis of a Highly Flexible Python Trend Trading Framework
- 发明者平台淘金记:高灵活性Python趋势交易框架实战解析
- 浅谈数字货币领域几种网格策略
- Data Stream Acceleration Guide Implementing Protobuf in FMZ Platform
- From Fixed Weights to Neural Networks Machine Learning for a Pine Strategy
- 从固定权重到神经网络:一个Pine策略的机器学习改造实践
- 数据流提速攻略:FMZ平台Protobuf技术实践
- A Brief Discussion on Digital Currency Market Making Strategies (2): Order Book Strategies
- 浅谈数字货币做市策略(2):盘口策略
- 机器学习之 预测价格走势(1)
- An Overview of Market Making Strategies in Crypto: Architecture Design and FMZ Implementation of the Self-Matching Trading Strategy
- 浅谈数字货币做市策略:对敲策略的架构设计与FMZ平台实现