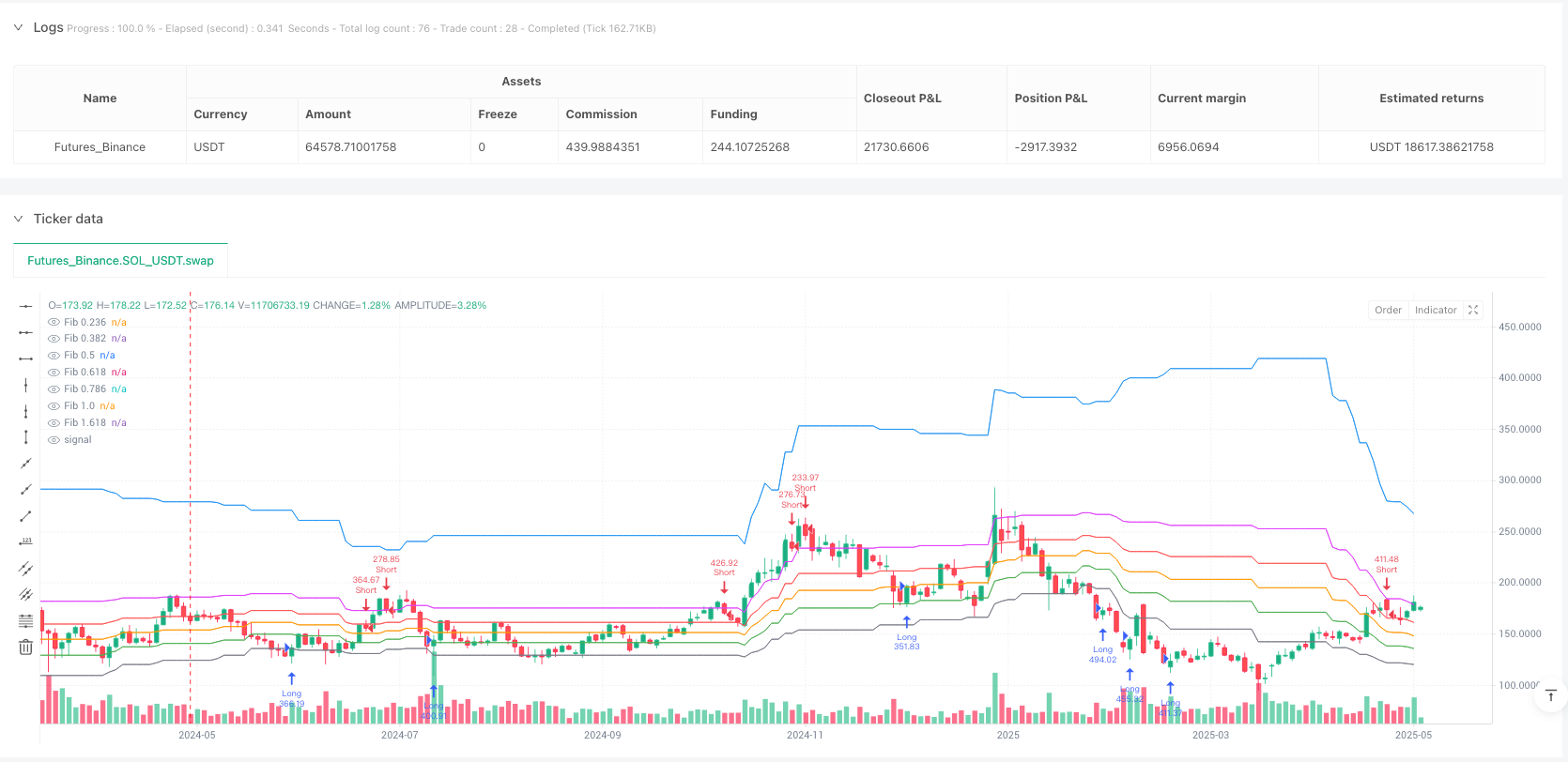
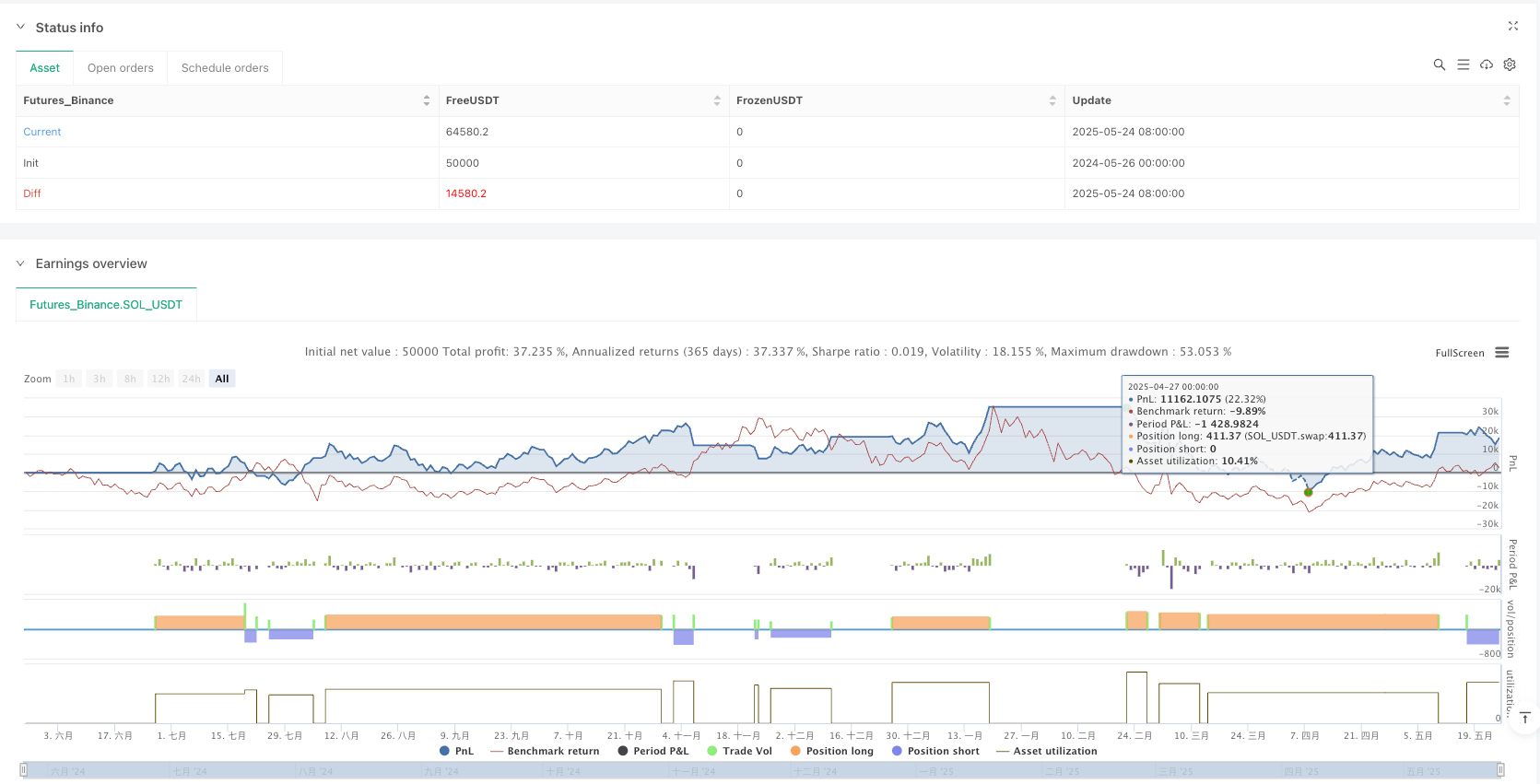
概述
多层次斐波那契趋势跟踪与对冲交易策略系统是一个集成了多种技术分析指标的综合性量化交易策略。该策略以斐波那契回撤理论为核心,结合指数移动平均线(EMA)、平均真实波幅(ATR)、平均趋向指数(ADX)以及方向性移动指标(DMI)等多个技术指标,构建了一个多维度的市场分析框架。策略不仅具备传统的趋势跟踪功能,还集成了反弹交易机制和对冲功能,旨在不同市场条件下都能够捕获盈利机会并有效控制风险。
该策略的独特之处在于其多层次的风险管理体系和灵活的交易模式。通过设置多个止盈目标(TP1和TP2)和基于ATR的动态止损机制,策略能够在保护资本的同时最大化收益潜力。此外,内置的对冲功能为策略增加了额外的风险缓冲,使其在波动性较大的市场环境中也能保持相对稳定的表现。
策略原理
策略的核心逻辑基于斐波那契回撤理论与趋势分析的结合。首先,策略通过计算指定周期内的最高点和最低点来确定斐波那契回撤水平,包括23.6%、38.2%、50%、61.8%、78.6%、100%和161.8%等关键位置。这些水平被用作重要的支撑和阻力位,为交易信号的生成提供关键参考。
在趋势识别方面,策略采用50期指数移动平均线作为主要的趋势判断工具。当价格连续三根K线都位于EMA上方时,被认定为上升趋势;反之则为下降趋势。同时,策略还分析价格结构,通过识别更高的低点和更高的高点来确认多头结构,通过更低的高点和更低的低点来确认空头结构。
ADX和DMI指标的引入增强了趋势强度的判断精确度。ADX值大于20被视为强趋势的标准,而+DI和-DI的相对强弱则用于确定趋势的方向性。成交量分析也是策略的重要组成部分,当成交量超过20期平均值的1.2倍时,被认为是有效的量能确认。
交易信号的生成需要满足多个条件的同时成立:趋势方向明确、价格接近关键斐波那契水平、趋势强度充足、方向性指标确认以及成交量放大。这种多重过滤机制大大提高了信号的可靠性,降低了假信号的概率。
策略优势
该策略具有多项显著优势,首先体现在其综合性的技术分析框架。通过整合斐波那契理论、趋势分析、动量指标和成交量分析,策略能够从多个维度评估市场状况,提供更加全面和准确的交易信号。这种多指标融合的方法有效减少了单一指标可能产生的误导性信号,提高了整体策略的稳定性和可靠性。
策略的风险管理体系是其另一大优势。双重止盈机制允许交易者在达到第一个目标时锁定部分利润,同时保留剩余仓位追求更大收益。基于ATR的动态止损设置能够根据市场波动性自动调整风险控制水平,既能在低波动时收紧止损以保护利润,又能在高波动时放宽止损以避免被正常波动震出。
反弹交易功能为策略增加了额外的盈利机会。当价格在关键支撑或阻力位发生反弹时,策略能够快速识别并参与这种短期逆转行情,从而在趋势交易的基础上增加更多的交易机会。这种灵活性使策略能够适应不同的市场条件,无论是强趋势市场还是区间震荡市场都能找到合适的交易机会。
对冲功能的集成是该策略的一个创新特色。当持有多头仓位时若出现空头信号,策略会开启对冲空头仓位;反之亦然。这种机制能够在市场快速反转时提供额外保护,减少潜在损失并可能转化为新的盈利机会。
时间过滤器的设置防止了过度交易的问题。通过要求连续信号之间至少间隔5根K线,策略避免了在短时间内频繁开仓,降低了交易成本并提高了信号质量。
策略风险
尽管该策略具有多项优势,但仍存在一些需要注意的风险因素。首先是参数依赖性风险。策略涉及多个参数设置,包括斐波那契周期、容忍度、ATR倍数等,这些参数的选择对策略表现有重要影响。不当的参数设置可能导致过度拟合历史数据或在实际市场中表现不佳。因此,需要通过充分的回测和参数优化来找到最适合特定市场和时间框架的参数组合。
市场环境适应性是另一个潜在风险。策略主要基于技术分析,在某些市场条件下可能表现不佳,例如在基本面驱动的强烈单边行情中,技术指标可能会失效。此外,在极低波动性或极高波动性的市场环境中,策略的信号生成频率和准确性都可能受到影响。
滑点和执行风险也需要考虑。在实际交易中,特别是在波动性较大的市场条件下,可能存在订单执行价格与期望价格之间的差异。这种滑点成本可能会侵蚀策略的理论收益,特别是对于频繁交易的策略。
对冲功能虽然提供了额外保护,但也增加了策略的复杂性。在某些情况下,对冲操作可能会导致多空仓位同时亏损,或者在手续费方面产生额外成本。因此,需要谨慎评估对冲功能的实际效果,并考虑在特定市场条件下是否启用该功能。
策略优化方向
为了进一步提升策略性能,可以从多个方向进行优化。首先是动态参数调整机制的引入。可以根据市场波动性、趋势强度等因素动态调整斐波那契周期、ATR倍数等关键参数。例如,在高波动市场中增加ATR倍数以提供更大的止损空间,在低波动市场中减少ATR倍数以收紧风险控制。
机器学习技术的整合是另一个重要的优化方向。可以使用机器学习算法来识别最佳的入场时机,或者根据历史数据学习参数组合的最优配置。此外,还可以利用自然语言处理技术分析市场情绪和新闻事件对价格的影响,为策略增加基本面分析维度。
多时间框架分析的集成能够提供更全面的市场视角。可以在更长的时间框架上确认大趋势方向,在较短的时间框架上寻找精确的入场点。这种多时间框架的协调分析能够提高信号质量并减少逆势交易的风险。
资金管理优化也是提升策略表现的重要途径。可以根据市场条件、策略信心度等因素动态调整仓位大小。例如,在高信心度信号时增加仓位,在低信心度信号时减少仓位。此外,还可以引入最大回撤控制机制,当策略出现较大亏损时自动减少仓位或暂停交易。
止盈止损逻辑的进一步精细化也值得考虑。可以引入追踪止损机制,根据价格走势动态调整止损位置以锁定更多利润。同时,可以根据市场结构特征设置更加智能的止盈目标,例如在关键阻力位附近提前止盈。
总结
多层次斐波那契趋势跟踪与对冲交易策略系统代表了现代量化交易技术的一个重要发展方向。该策略通过巧妙地整合多种经典技术分析工具,构建了一个既稳健又灵活的交易框架。其多重过滤机制确保了信号质量,多层次风险管理体系提供了有效的资本保护,而对冲功能则为策略增加了额外的安全边际。
策略的成功实施需要充分理解其基本原理和运作机制,并根据具体的交易环境进行适当的参数调整和优化。虽然该策略在理论上具有良好的设计,但实际应用中仍需要考虑市场微观结构、交易成本、滑点等现实因素的影响。
随着人工智能和机器学习技术的不断发展,该策略还有巨大的优化空间。通过引入更先进的数据分析技术和自适应机制,策略的性能有望得到进一步提升。对于量化交易者而言,这类综合性策略提供了一个宝贵的学习和改进平台,有助于深入理解市场动态和风险管理的重要性。
/*backtest
start: 2024-05-26 00:00:00
end: 2025-05-25 00:00:00
period: 2d
basePeriod: 2d
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"SOL_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("Fibonacci Trend v6.4 - TP/SL Labels", overlay=true, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value=100)
// === Parameters ===
fibLen = input.int(50, "Fibonacci Range")
fibTol = input.float(0.01, "Fib Proximity Tolerance (%)", step=0.001)
slMult = input.float(1.5, "SL - ATR", step=0.1)
tp2Mult = input.float(2.0, "TP2 - ATR", step=0.1)
srLookback = input.int(20, "Support/Resistance Lookback Bars")
useBounce = input.bool(true, "Enable Bounce Entry")
// === Indicators ===
ema50 = ta.ema(close, 50)
atr = ta.atr(14)
volAvg = ta.sma(volume, 20)
volHigh = volume > volAvg * 1.2
// === Fibonacci Levels ===
lowWick = ta.lowest(low, fibLen)
highWick = ta.highest(high, fibLen)
rangeWick = highWick - lowWick
fib236 = lowWick + 0.236 * rangeWick
fib382 = lowWick + 0.382 * rangeWick
fib5 = lowWick + 0.5 * rangeWick
fib618 = lowWick + 0.618 * rangeWick
fib786 = lowWick + 0.786 * rangeWick
fib1 = highWick
fib1618 = lowWick + 1.618 * rangeWick
nearSupport = math.abs(low - fib382)/close < fibTol or math.abs(low - fib5)/close < fibTol
nearResist = math.abs(high - fib618)/close < fibTol
// === Trend Structure ===
higherLow = low > low[1] and low[1] > low[2]
higherHigh = high > high[1]
lowerHigh = high < high[1] and high[1] < high[2]
lowerLow = low < low[1]
longStruct = higherLow and higherHigh
shortStruct = lowerHigh and lowerLow
// === ADX / DMI ===
dmiLen = 14
upMove = high - high[1]
downMove = low[1] - low
plusDM = (upMove > downMove and upMove > 0) ? upMove : 0
minusDM = (downMove > upMove and downMove > 0) ? downMove : 0
tr = ta.tr(true)
tr14 = ta.rma(tr, dmiLen)
plusDI = 100 * ta.rma(plusDM, dmiLen) / tr14
minusDI = 100 * ta.rma(minusDM, dmiLen) / tr14
dx = 100 * math.abs(plusDI - minusDI) / (plusDI + minusDI)
adx = ta.rma(dx, dmiLen)
trendStrong = adx > 20
// === EMA Momentum Break ===
emaBreakLong = close > ema50 and close[1] < ema50 and volume > volAvg
emaBreakShort = close < ema50 and close[1] > ema50 and volume > volAvg
// === Time Filter ===
var int lastLongBar = na
var int lastShortBar = na
canLong = na(lastLongBar) or (bar_index - lastLongBar > 5)
canShort = na(lastShortBar) or (bar_index - lastShortBar > 5)
priceAboveEMA = close > ema50 and close[1] > ema50 and close[2] > ema50
priceBelowEMA = close < ema50 and close[1] < ema50 and close[2] < ema50
// === Support / Resistance ===
support = ta.lowest(low, srLookback)
resist = ta.highest(high, srLookback)
// === Entry Conditions ===
longTrend = priceAboveEMA and nearSupport and trendStrong and plusDI > minusDI and longStruct and (volHigh or emaBreakLong) and canLong
shortTrend = priceBelowEMA and nearResist and trendStrong and minusDI > plusDI and shortStruct and (volHigh or emaBreakShort) and canShort
bounceLong = useBounce and math.abs(low - support)/close < fibTol and close > open and close > close[1]
bounceShort = useBounce and math.abs(high - resist)/close < fibTol and close < open and close < close[1]
longSignal = longTrend or bounceLong
shortSignal = shortTrend or bounceShort
// === TP/SL Calculations ===
tp1Long = resist
tp2Long = close + atr * tp2Mult
slLong = close - atr * slMult
tp1Short = support
tp2Short = close - atr * tp2Mult
slShort = close + atr * slMult
tp1ColorLong = bounceLong ? color.blue : color.yellow
tp1ColorShort = bounceShort ? color.blue : color.yellow
// === Long Entry ===
if (longSignal and strategy.position_size <= 0)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
strategy.exit("TP1", from_entry="Long", limit=tp1Long, stop=slLong, qty_percent=50)
strategy.exit("TP2", from_entry="Long", limit=tp2Long, stop=slLong)
lastLongBar := bar_index
label.new(bar_index, close, text="ENTRY: " + str.tostring(close, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=color.green, textcolor=color.white)
label.new(bar_index, tp1Long, text="TP1: " + str.tostring(tp1Long, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=tp1ColorLong)
label.new(bar_index, tp2Long, text="TP2: " + str.tostring(tp2Long, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=color.green)
label.new(bar_index, slLong, text="SL: " + str.tostring(slLong, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=color.red)
// === Short Entry ===
if (shortSignal and strategy.position_size >= 0)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
strategy.exit("TP1", from_entry="Short", limit=tp1Short, stop=slShort, qty_percent=50)
strategy.exit("TP2", from_entry="Short", limit=tp2Short, stop=slShort)
lastShortBar := bar_index
label.new(bar_index, close, text="ENTRY: " + str.tostring(close, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=color.red, textcolor=color.white)
label.new(bar_index, tp1Short, text="TP1: " + str.tostring(tp1Short, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=tp1ColorShort)
label.new(bar_index, tp2Short, text="TP2: " + str.tostring(tp2Short, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_up, color=color.green)
label.new(bar_index, slShort, text="SL: " + str.tostring(slShort, "#.##"), style=label.style_label_down, color=color.red)
// === Hedge Orders ===
if (strategy.position_size > 0 and shortSignal)
strategy.entry("HedgeShort", strategy.short)
if (strategy.position_size < 0 and longSignal)
strategy.entry("HedgeLong", strategy.long)
// === Fibonacci Plotting ===
plot(fib236, "Fib 0.236", color=color.gray)
plot(fib382, "Fib 0.382", color=color.green)
plot(fib5, "Fib 0.5", color=color.orange)
plot(fib618, "Fib 0.618", color=color.red)
plot(fib786, "Fib 0.786", color=color.fuchsia)
plot(fib1, "Fib 1.0", color=color.white)
plot(fib1618, "Fib 1.618", color=color.blue)