Estrategia de rendimiento de retorno mensual
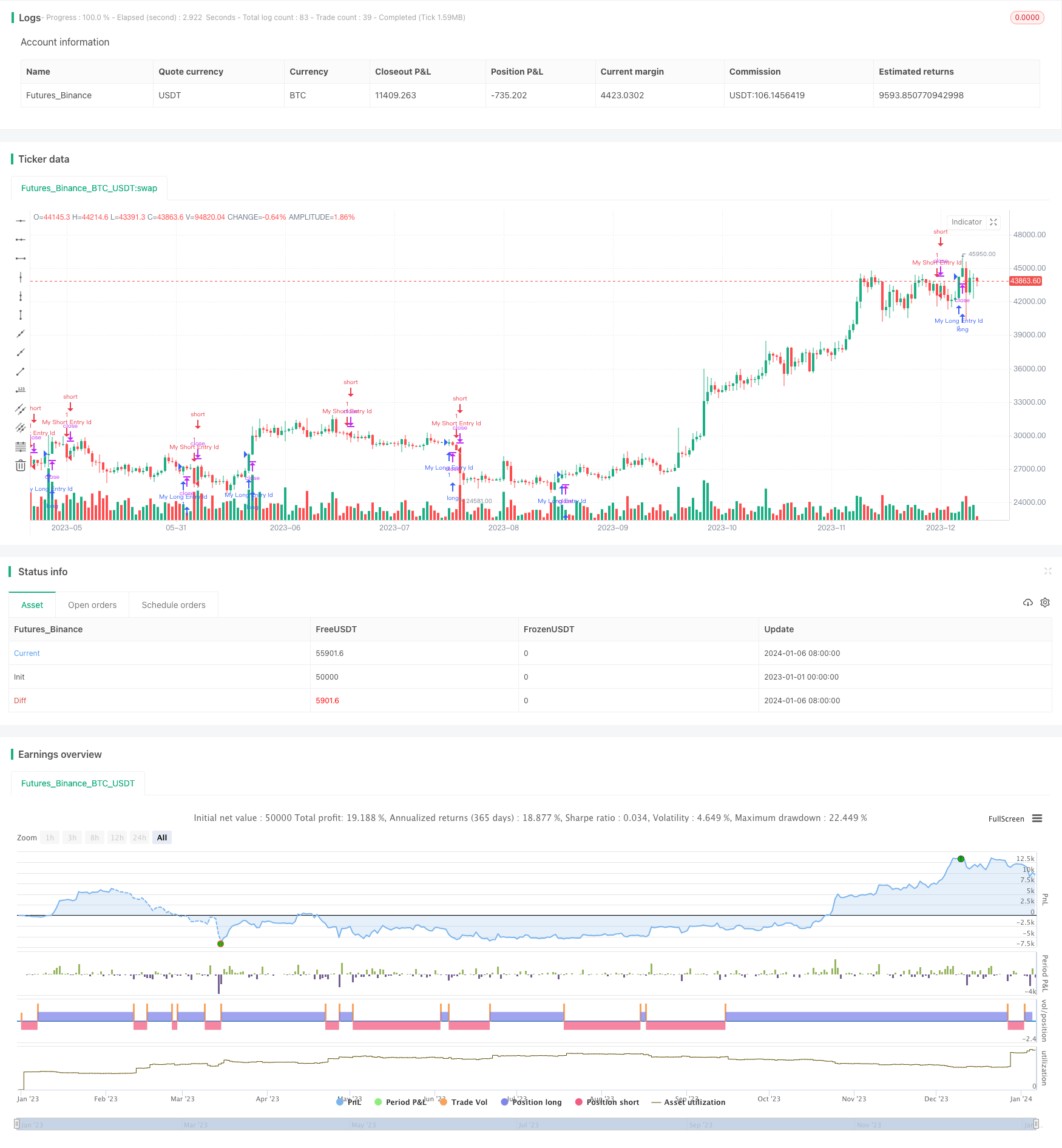
Descripción general
La función principal de esta estrategia es el seguimiento en tiempo real y la visualización de los ingresos y pérdidas de cada mes. Se actualiza en tiempo real en una tabla de los ingresos y pérdidas de cada mes.
El principio
La estrategia permite el seguimiento de la rentabilidad mensual a través de los siguientes pasos:
- Define la variable que registra si el mes ha tenido una transacción cerrada.
- Define el valor de las ganancias y pérdidas concretas registradas en las variables cada mes.
- Define el mes al que corresponde el tiempo de registro de la variable.
- Cuando hay una posición cerrada en el mes, registra los beneficios y pérdidas del mes y el mes en la matriz correspondiente.
- Mostrar el título del mes en la posición especificada en la tabla.
- Arrayos de ganancias y pérdidas a lo largo de los meses, mostrando el valor de ganancias y pérdidas en la columna correspondiente al mes de la tabla.
- También se muestra la información correspondiente al año.
- La suma de las ganancias y pérdidas de cada año.
- El uso de colores para distinguir ganancias y pérdidas.
Estos son los pasos básicos y el funcionamiento de la estrategia.
Análisis de las ventajas
Esta estrategia de seguimiento de ganancias y pérdidas por mes tiene las siguientes ventajas:
- Las actualizaciones en tiempo real permiten ver las ganancias y pérdidas mensuales más recientes en cualquier momento.
- A primera vista, el uso de la tabla para mostrar de forma intuitiva las ganancias y pérdidas mensuales.
- La granularidad permite ver claramente los detalles de cada mes.
- En comparación, el uso de colores permite una comparación más intuitiva de las ganancias y pérdidas mensuales.
- La cuenta presidencial, que también muestra los resultados de la cuenta presidencial anual.
- Dispone de una pantalla personalizada que permite ajustar la ubicación, el tamaño, etc.
Análisis de riesgos
La estrategia también tiene sus riesgos:
- La lógica de cálculo es más compleja, y los errores pueden causar inexactitudes en los datos.
- La visualización de las tablas se actualiza con demasiada frecuencia y puede afectar su rendimiento.
- La eficiencia de almacenamiento de datos en serie es baja.
- La hora y el mes pueden estar mal calculados.
El riesgo puede reducirse de la siguiente manera:
- El código es revisado rigurosamente para asegurar que la lógica de cálculo es correcta.
- Optimice la frecuencia de actualización de las hojas de cálculo para evitar que se actualicen en exceso.
- El uso de estructuras de datos más eficientes para almacenar datos.
- Tratamiento de excepciones para la conversión de horas y meses.
Optimización de la estrategia
La estrategia puede ser optimizada en los siguientes aspectos:
- El uso de estructuras de datos más eficientes, como diccionarios para almacenar datos mensuales.
- Cálculo de la rentabilidad añadida.
- Aumentar las fluctuaciones y otros indicadores.
- Visualizar el movimiento de la curva de ganancias.
- Apoya el inicio y el final de períodos estadísticos personalizados.
- Soporta la exportación de datos a archivos CSV.
Estas optimizaciones pueden hacer que las estrategias sean más completas y fuertes, y que la experiencia de uso sea mejor.
Resumir
La estrategia utiliza una forma de array y tabla, que permite el seguimiento en tiempo real y la presentación de los resultados de cada mes. Es simple, eficiente y fácil de usar. También tiene ciertas ventajas, pero también hay algunos riesgos que deben evitarse.
/*backtest
start: 2023-01-01 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-07 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © MAURYA_ALGO_TRADER
//@version=5
strategy("Monthly Performance", overlay=true)
period = input(20, "Length")
longCondition = close > high[20] //ta.crossover(ta.sma(close, 14), ta.sma(close, 28))
if (longCondition)
strategy.entry("My Long Entry Id", strategy.long)
shortCondition = close < low[20] //ta.crossunder(ta.sma(close, 14), ta.sma(close, 28))
if (shortCondition)
strategy.entry("My Short Entry Id", strategy.short)
// Copy below code to end of the desired strategy script
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// monthly pnl performance by Dr. Maurya @MAURYA_ALGO_TRADER //
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
show_performance = input.bool(true, 'Show Monthly Monthly Performance ?', group='Monthly Performance')
dash_loc_mp = input("Bottom Right","Location" ,options=["Top Right","Bottom Right","Top Left","Bottom Left", "Middle Right","Bottom Center"] ,group='Monthly Performance', inline = "performance")
text_size_mp = input('Small',"Size" ,options=["Tiny","Small","Normal","Large"] ,group='Monthly Performance', inline = "performance")
var table_position_mp = dash_loc_mp == 'Top Left' ? position.top_left :
dash_loc_mp == 'Bottom Left' ? position.bottom_left :
dash_loc_mp == 'Middle Right' ? position.middle_right :
dash_loc_mp == 'Bottom Center' ? position.bottom_center :
dash_loc_mp == 'Top Right' ? position.top_right : position.bottom_right
var table_text_size_mp = text_size_mp == 'Tiny' ? size.tiny :
text_size_mp == 'Small' ? size.small :
text_size_mp == 'Normal' ? size.normal : size.large
/////////////////
text_c = color.white
/////////////////////////////////////////////
// var bool new_month = na
new_month = ta.change(month) //> 0 ? true : false
newest_month = new_month and strategy.closedtrades >= 1
strategy.initial_capital = 50000
// profit
only_profit = strategy.netprofit
initial_balance = strategy.initial_capital
// month number
var int month_number = na
month_number := (ta.valuewhen(newest_month, month(time), 0)) //and month(time) > 1 ? (ta.valuewhen(newest_month, month(time), 0) - 1) : 12 //1 to 12
//month_year
var int month_time = na
month_time := ta.valuewhen(newest_month, time, 0) - 2419200000
var int m_counter = 0
if newest_month
m_counter += 1
// current month values
var bool new_year = na
new_year := ta.change(year)
curr_m_pnl = only_profit - nz(ta.valuewhen(newest_month, only_profit, 0), 0)
curr_m_number = newest_month ? ta.valuewhen(newest_month, month(time), 0) : month(time)
curr_y_pnl = (only_profit - nz(ta.valuewhen(new_year, only_profit, 0),0))
var float [] net_profit_array = array.new_float()
var int [] month_array = array.new_int()
var int [] month_time_array = array.new_int()
if newest_month
array.push(net_profit_array, only_profit)
array.push(month_array, month_number)
array.push(month_time_array, month_time)
var float [] y_pnl_array = array.new_float()
var int [] y_number_array = array.new_int()
var int [] y_time_array = array.new_int()
newest_year = ta.change(year) and strategy.closedtrades >= 1
get_yearly_pnl = nz(ta.valuewhen(newest_year, strategy.netprofit, 0) - nz(ta.valuewhen(newest_year, strategy.netprofit, 1), 0), 0)
get_m_year = ta.valuewhen(newest_year, year(time), 1)
get_y_time = ta.valuewhen(newest_year, time, 0)
if newest_year
array.push(y_pnl_array, get_yearly_pnl)
array.push(y_number_array, get_m_year)
array.push(y_time_array, get_y_time)
var float monthly_profit = na
var int column_month_number = na
var int row_month_time = na
var testTable = table.new(position = table_position_mp, columns = 14, rows = 40, bgcolor = color.rgb(7, 226, 242, 38), border_color = color.white, border_width = 1)
if barstate.islastconfirmedhistory and show_performance
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 0, row = 0, text = "YEAR", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 1, row = 0, text = "JAN", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 2, row = 0, text = "FEB", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 3, row = 0, text = "MAR", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 4, row = 0, text = "APR", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 5, row = 0, text = "MAY", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 6, row = 0, text = "JUN", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 7, row = 0, text = "JUL", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 8, row = 0, text = "AUG", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 9, row = 0, text = "SEP", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 10, row = 0, text = "OCT", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 11, row = 0, text = "NOV", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 12, row = 0, text = "DEC", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 13, row = 0, text = "YEAR P/L", text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
for i = 0 to (array.size(y_number_array) == 0 ? na : array.size(y_number_array) - 1)
row_y = year(array.get(y_time_array, i)) - year(array.get(y_time_array, 0)) + 1
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 13, row = row_y, text = str.tostring(array.get(y_pnl_array , i), "##.##") + '\n' + '(' + str.tostring(array.get(y_pnl_array , i)*100/initial_balance, "##.##") + ' %)', bgcolor = array.get(y_pnl_array , i) > 0 ? color.green : array.get(y_pnl_array , i) < 0 ? color.red : color.gray, text_color = color.rgb(0, 0, 0), text_size=table_text_size_mp)
curr_row_y = array.size(month_time_array) == 0 ? 1 : (year(array.get(month_time_array, array.size(month_time_array) - 1))) - (year(array.get(month_time_array, 0))) + 1
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 13, row = curr_row_y, text = str.tostring(curr_y_pnl, "##.##") + '\n' + '(' + str.tostring(curr_y_pnl*100/initial_balance, "##.##") + ' %)', bgcolor = curr_y_pnl > 0 ? color.green : curr_y_pnl < 0 ? color.red : color.gray, text_color = color.rgb(0, 0, 0), text_size=table_text_size_mp)
for i = 0 to (array.size(net_profit_array) == 0 ? na : array.size(net_profit_array) - 1)
monthly_profit := i > 0 ? ( array.get(net_profit_array, i) - array.get(net_profit_array, i - 1) ) : array.get(net_profit_array, i)
column_month_number := month(array.get(month_time_array, i))
row_month_time :=((year(array.get(month_time_array, i))) - year(array.get(month_time_array, 0)) ) + 1
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = column_month_number, row = row_month_time, text = str.tostring(monthly_profit, "##.##") + '\n' + '(' + str.tostring(monthly_profit*100/initial_balance, "##.##") + ' %)', bgcolor = monthly_profit > 0 ? color.green : monthly_profit < 0 ? color.red : color.gray, text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 0, row =row_month_time, text = str.tostring(year(array.get(month_time_array, i)), "##.##"), text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
curr_row_m = array.size(month_time_array) == 0 ? 1 : (year(array.get(month_time_array, array.size(month_time_array) - 1))) - (year(array.get(month_time_array, 0))) + 1
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = curr_m_number, row = curr_row_m, text = str.tostring(curr_m_pnl, "##.##") + '\n' + '(' + str.tostring(curr_m_pnl*100/initial_balance, "##.##") + ' %)', bgcolor = curr_m_pnl > 0 ? color.green : curr_m_pnl < 0 ? color.red : color.gray, text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
table.cell(table_id = testTable, column = 0, row =curr_row_m, text = str.tostring(year(time), "##.##"), text_color = text_c, text_size=table_text_size_mp)
//============================================================================================================================================================================