Estrategia de seguimiento de tendencias basada en medias móviles adaptativas
Descripción general
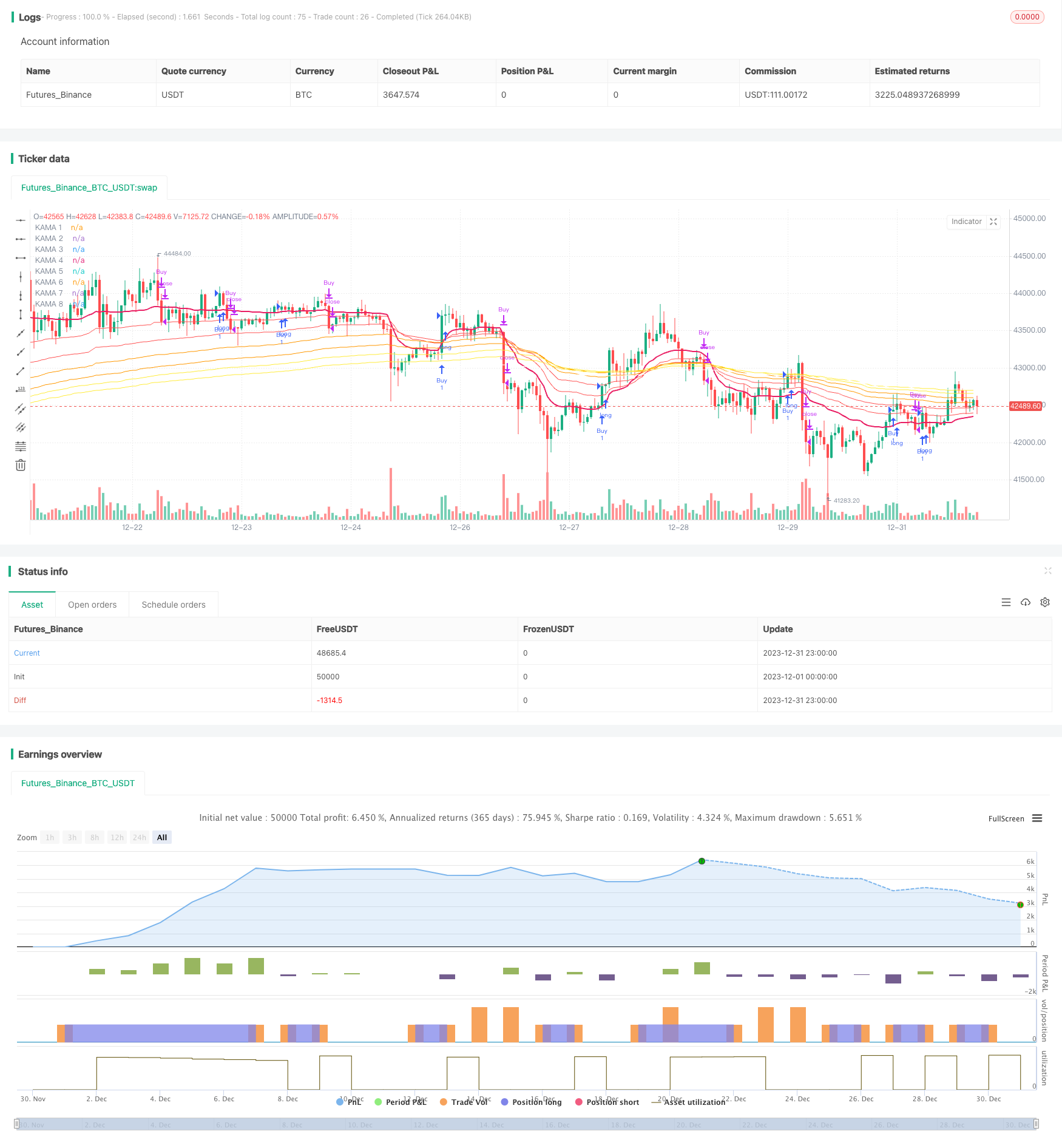
La estrategia utiliza un sistema de seguimiento de tendencias diseñado por Kaufman para adaptarse a las medias móviles (KAMA). El sistema puede seguir rápidamente la tendencia cuando se forma una tendencia y filtrar el ruido en situaciones de volatilidad. Al mismo tiempo, el sistema también integra el sistema de giro de la línea de paralelo (PSAR) y el stop de seguimiento de la tasa de fluctuación real promedio (ATR Trailing Stop) como mecanismo de parada, con una mayor capacidad de control de riesgo.
Principio de estrategia
La longitud del indicador KAMA se ajusta a la dinámica de la volatilidad del mercado durante un período reciente. La ventana EMA se acorta cuando el cambio de precio es mayor que el ruido reciente; la ventana EMA se alarga cuando el cambio de precio es menor que el ruido reciente. Esto permite a KAMA seguir rápidamente las tendencias y filtrar el ruido en situaciones de crisis.
El sistema determina la dirección de la tendencia principalmente en función del KAMA más rápido (KAMA 1) ❚ El KAMA 1 hace más cuando sube y vacío cuando baja. Para filtrar falsas rupturas, se establece un filtro KAMA ❚ La señal de negociación solo se genera cuando el cambio de KAMA 1 supera una diferencia estándar de la oscilación reciente ❚
En cuanto a la detención de pérdidas, el sistema ofrece tres opciones de detención: reversión basada en KAMA, reversión PSAR y detención móvil ATR. El inversor puede elegir individualmente una o más combinaciones.
Análisis de las ventajas
El diseño único del indicador KAMA permite que el sistema capte rápidamente las tendencias emergentes, detenga el comercio en situaciones de agitación, controle eficazmente la frecuencia de comercio y reduzca los puntos de deslizamiento innecesarios y la pérdida de comisiones.
El sistema incluye varios mecanismos de amortización de pérdidas. Los inversores pueden elegir el plan de amortización adecuado de acuerdo con sus preferencias personales de riesgo y controlar con fuerza las pérdidas individuales.
El sistema se basa completamente en indicadores y líneas de stop loss, evitando el error de entrada de transacciones por desplazamiento común.
La configuración de múltiples parámetros y la combinación de condiciones ofrecen un gran espacio para la personalización del sistema. El usuario puede adaptarse a la ubicación y optimizar para diferentes variedades y períodos.
Análisis de riesgos
El sistema no tiene en cuenta el riesgo sistémico y no puede controlar eficazmente las pérdidas en casos extremos.
Los parámetros del sistema pueden necesitar ser ajustados a diferentes ciclos de diferentes variedades, de lo contrario se producen resultados demasiado radicales o demasiado conservadores.
Si se confía únicamente en el indicador KAMA como stop loss, es fácil ser encerrado en situaciones de temblor. Esto requiere un uso combinado con stop loss móvil de PSAR o ATR para resolver.
Dirección de optimización
Añadir indicadores de filtro de tendencia, como el ADX o el indicador de volatilidad oculta, para evitar la generación de señales erróneas en las fases de oscilación y cambio de tendencia.
Optimización de parámetros y retroalimentación para variedades individuales y ciclos fijos para mejorar la estabilidad. Las dimensiones de optimización incluyen combinaciones de parámetros KAMA, parámetros de parada, etc.
Prueba modelos de aprendizaje automático en lugar de optimización de parámetros. Utiliza una gran cantidad de datos históricos para entrenar a las redes neuronales o modelos de árboles de decisión para determinar el tiempo de compra y venta y el cierre de pérdidas.
Intentar trasladar la estrategia a otras variedades, como la moneda digital. Esto puede requerir ajustar los PARAMETROS o agregar otros indicadores auxiliares.
Resumir
Esta estrategia integra la determinación de tendencias de KAMA y varios medios de parada, lo que permite rastrear eficazmente la dirección de la tendencia y controlar el riesgo. La singularidad de los indicadores de KAMA permite a la estrategia determinar rápidamente la dirección de las tendencias emergentes y evitar problemas de falsas rupturas.
/*backtest
start: 2023-12-01 00:00:00
end: 2023-12-31 23:59:59
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © BenHampson
// @version=4
// Credit to:
// - ChuckBanger for much of the KAMA code
// - cheatcountry for the KAMA Filter code
// - millerrh for much of the ATR Stop code
// - racer8 for much of the Position Sizing code
// I have combined aspects of their work and built upon it to form a strategy I like.
// The KAMA, with its filter, is used for entry.
// An ATR trailing stop loss, PSAR, and the KAMA can all optionally be used as exits, or you can use a combination of the three.
strategy(title="KAMA Strategy - Kaufman's Adaptive Moving Average", shorttitle="KAMA Strategy", overlay=true)
src = input(title="Source", type=input.source, defval=close)
// Exits
KAMA1SL = input(title = 'KAMA 1 Stop Loss', type = input.bool, defval = true)
ATRTSL = input(title = 'ATR Trailing Stop Loss', type = input.bool, defval = false)
PSARSL = input(title = 'PSAR Stop Loss', type = input.bool, defval = false)
// KAMA 1 (Fastest)
length1 = input(title="KAMA 1: Length", type=input.integer, defval=14)
fastLength1 = input(title="KAMA 1: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=2)
slowLength1 = input(title="KAMA 1: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=20)
length2 = input(title="KAMA 2: Length 2", type=input.integer, defval=15)
fastLength2 = input(title="KAMA 2: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=3)
slowLength2 = input(title="KAMA 2: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=22)
length3 = input(title="KAMA 3: Length 3", type=input.integer, defval=16)
fastLength3 = input(title="KAMA 3: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=4)
slowLength3 = input(title="KAMA 3: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=24)
length4 = input(title="KAMA 4: Length", type=input.integer, defval=17)
fastLength4 = input(title="KAMA 4: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=5)
slowLength4 = input(title="KAMA 4: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=26)
// KAMA 5 (Medium)
length5 = input(title="KAMA 5: Length", type=input.integer, defval=18)
fastLength5 = input(title="KAMA 5: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=6)
slowLength5 = input(title="KAMA 5: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=28)
length6 = input(title="KAMA 6: Length", type=input.integer, defval=19)
fastLength6 = input(title="KAMA 6: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=7)
slowLength6 = input(title="KAMA 6: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=30)
length7 = input(title="KAMA 7: Length", type=input.integer, defval=20)
fastLength7 = input(title="KAMA 7: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=8)
slowLength7 = input(title="KAMA 7: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=32)
// KAMA 8 (Slowest)
length8 = input(title="KAMA 8: Length", type=input.integer, defval=21)
fastLength8 = input(title="KAMA 8: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=9)
slowLength8 = input(title="KAMA 8: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=34)
// Kaufman's Adaptive Moving Average
getKAMA(src, length1, fastLength1, slowLength1) =>
mom = abs(change(src, length1))
volatility = sum(abs(change(src)), length1)
// Efficiency Ratio
er = volatility != 0 ? mom / volatility : 0
fastAlpha = 2 / (fastLength1 + 1)
slowAlpha = 2 / (slowLength1 + 1)
// KAMA Alpha
sc = pow((er * (fastAlpha - slowAlpha)) + slowAlpha, 2)
kama = 0.0
kama := sc * src + (1 - sc) * nz(kama[1])
kama
kama1 = getKAMA(src, length1, fastLength1, slowLength1)
kama2 = getKAMA(src, length2, fastLength2, slowLength2)
kama3 = getKAMA(src, length3, fastLength3, slowLength3)
kama4 = getKAMA(src, length4, fastLength4, slowLength4)
kama5 = getKAMA(src, length5, fastLength5, slowLength5)
kama6 = getKAMA(src, length6, fastLength6, slowLength6)
kama7 = getKAMA(src, length7, fastLength7, slowLength7)
kama8 = getKAMA(src, length8, fastLength8, slowLength8)
//If the kama1 has increased...
kama1delta = kama1[0] - kama1[1]
kama3delta = kama3[0] - kama3[1]
kama8delta = kama8[0] - kama8[1]
// KAMA Plots
plot(kama1, title="KAMA 1", color=#e91e63, display=display.all, linewidth=2)
plot(kama2, title="KAMA 2", color=color.red, display=display.all)
plot(kama3, title="KAMA 3", color=color.red, display=display.all)
plot(kama4, title="KAMA 4", color=color.orange, display=display.all)
plot(kama5, title="KAMA 5", color=color.orange, display=display.all)
plot(kama6, title="KAMA 6", color=color.yellow, display=display.all)
plot(kama7, title="KAMA 7", color=color.yellow, display=display.all)
plot(kama8, title="KAMA 8", color=color.white, display=display.all)
//========================================= KAMA FILTER ===========================================
// Copyright (c) 2019-present, Franklin Moormann (cheatcountry)
// Moving Average Adaptive Filter [CC] script may be freely distributed under the MIT license.
entryFilter = input(title="KAMA Entry Filter", type=input.float, defval=1, minval=0.01)
exitFilter = input(title="KAMA Exit Filter", type=input.float, defval=0.5, minval=0.01)
entryMAAF = entryFilter * stdev(kama1delta, length1)
exitMAAF = exitFilter * stdev(kama1delta, length1)
srcEma = ema(src, length1)
//========================================= TRAILING ATR STOP ====================================
// The following is an adaptation of Trailing ATR Stops by @millerrh
// He based it on scripts by @garethyeo & @SimpleCryptoLife
// Inputs
atrLookback = input(defval=14,title="Trailing ATR Lookback Period",type=input.integer)
multiplier = input(defval=3,title="Trailing ATR Multiplier",type=input.float, step=0.1, minval=0.5, maxval=4)
trailMode = input(title="Trail Mode", defval="Trailing", options=["Running", "Trailing"])
trigInput = input(title="Trigger Trailing Stop On", defval="Wick", options=["Close","Wick"])
// Calculate ATR
atrValue = atr(atrLookback)
atrMultiplied = atrValue * multiplier
// Plot the price minus the ATR
atrLow = low - atrMultiplied
// Calculate the low trailing ATRs every time. The trailing stop loss never goes down.
// Set them to something to start with
trailAtrLow = atrLow
// If the ATR Low has gone up AND it has gone above the trail, the low trailing ATR should also go up. If the ATR Low has gone up or down, but not below the trail, the ATR trail stays where it is
trailAtrLow := na(trailAtrLow[1]) ? trailAtrLow : atrLow >= trailAtrLow[1] ? atrLow : trailAtrLow[1]
// Trigger stop based on candle close or low
trigSupport = trigInput == "Close" ? close : trigInput == "Wick" ? low : na
// Determine if price is below support
supportHit = trigSupport <= trailAtrLow
// If price is below support, reset the trailing ATR
trailAtrLow := supportHit ? atrLow : trailAtrLow
// Plot Lines
plotLow = ATRTSL ? trailAtrLow : na
plot(plotLow, title="ATR Low", color=color.white, transp=50, style=plot.style_linebr, linewidth=1, display=display.all)
//====================================== PSAR STOP ==========================================
start = input(0.02, "PSAR Start")
increment = input(0.02, "PSAR Increment")
maximum = input(0.2, "PSAR Max Value")
psar = sar(start, increment, maximum)
psarPlot = PSARSL ? psar : na
plot(psarPlot, "Parabolic SAR", style=plot.style_cross, color=#3A6CA8, display=display.all)
//========================================= ENTRY & EXITS =====================================================
// Entry
long = kama1delta > 0 and kama1delta > entryMAAF
strategy.entry("Buy", true, when = long)
// Close
longClose = (PSARSL ? crossunder(close, psar) : na) or (KAMA1SL ? kama1delta < 0 and abs(kama1delta) > exitMAAF : na) or (ATRTSL ? supportHit : na)
strategy.close("Buy", when = longClose, comment = "Sell")