Estratégia Bipolar de Retorno Mensal
Data de criação:
2023-11-06 16:06:55
última modificação:
2023-11-06 16:06:55
cópia:
0
Cliques:
613
1
focar em
1617
Seguidores
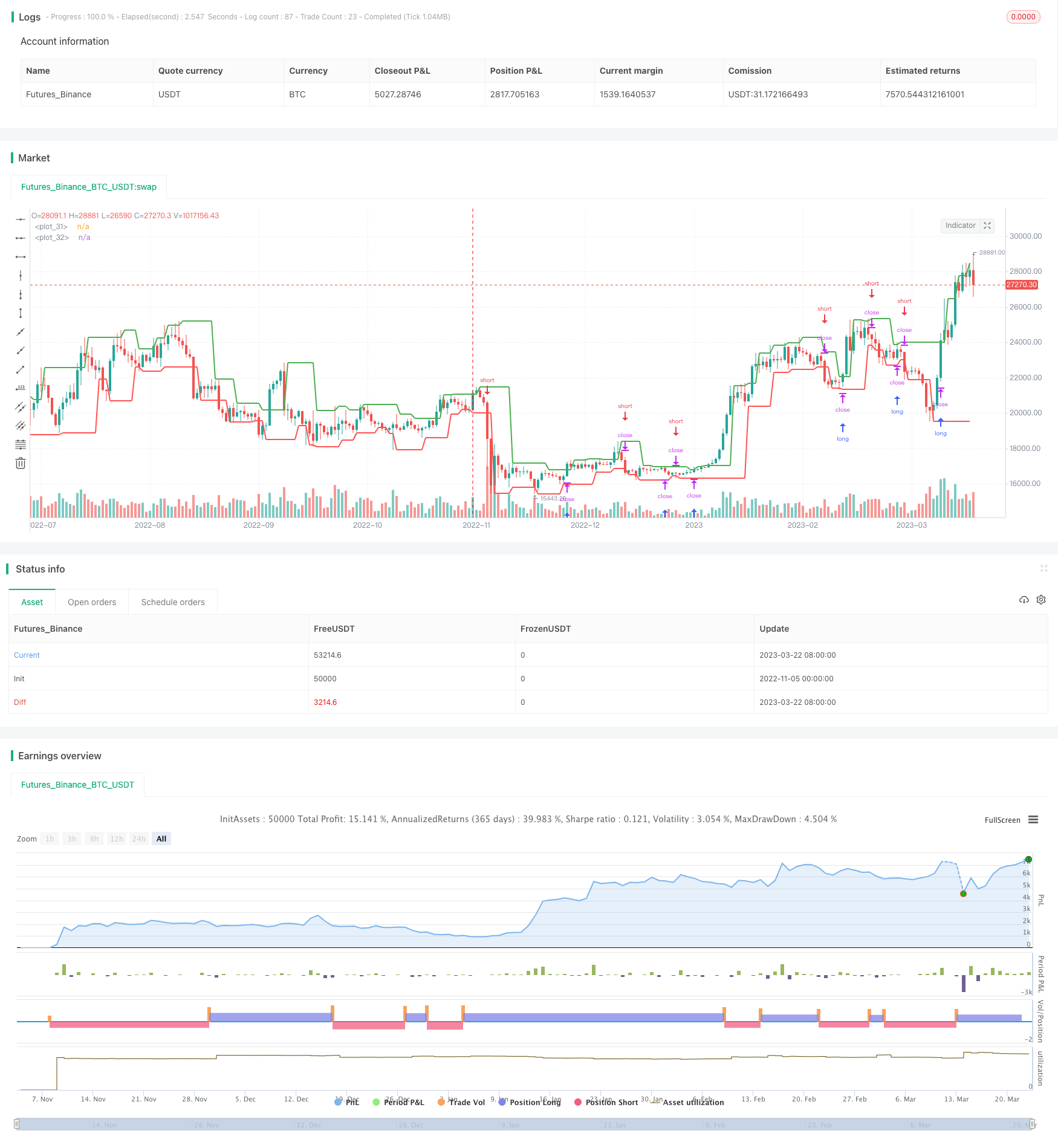
Descrição
A estratégia usa o ponto central da linha K para determinar a reversão de tendência e, assim, sinalizar a negociação de um mercado de ativos em branco. Quando lucrativa, a estratégia bloqueia os ganhos realizados no mês e evita grandes perdas no período de retração.
Princípios da estratégia
- Utilização
pivothigh()epivotlow()A função calcula o eixo central da linha K. O eixo central pode determinar a reversão da tendência. - Quando o preço ultrapassa o ponto do eixo superior, faça uma posição a mais. Quando o preço cai abaixo do ponto do eixo inferior, faça uma posição a menos.
- No início de cada mês, calcula-se a taxa de retorno do mês anterior e é guardada em um array.
- No começo de cada ano, o rendimento do ano anterior é calculado e guardado em uma matriz.
- Grava uma tabela de rendimentos para visualizar o rendimento por mês e ano.
Análise de vantagens
- A utilização de um pivot para determinar a inversão de tendência pode filtrar parte do ruído dos sinais de negociação.
- O bloqueio de receita mensal reduz o impacto de um mês de perdas, o que torna a receita bipolar.
- A tabela de receitas mostra de forma intuitiva os resultados de cada mês, permitindo ver claramente os períodos positivos e negativos da estratégia.
Análise de Riscos
- Quando os pontos de eixo mudam, isso pode causar erros de reversão de abertura de posição. Os parâmetros podem ser apropriadamente otimizados ou as condições de filtragem adicionadas.
- A obrigação de fechar posições no início do mês pode fazer com que você perca a oportunidade de lucrar o resto do mês.
- A tabela não pode mostrar indicadores de risco, como a retirada máxima. Pode ser considerado o acréscimo de outros indicadores que medem o risco da estratégia.
direção de otimização
- Pode-se adicionar condições de filtragem nas proximidades do eixo central, evitando a frequência de inverter a transação.
- A possibilidade de bloquear apenas algumas posições, em vez de todas as posições vazias, reduz a possibilidade de perdas.
- Pode-se aumentar a exibição de indicadores de risco, tais como a retirada máxima e a taxa de Sharpe, nos quadros.
Resumo
A estratégia usa o ponto central para determinar a reversão da tendência para negociar e bloquear o lucro no final do mês. Isso permite controlar o risco de retração. No entanto, alguns parâmetros e a lógica da estratégia podem ser ainda mais otimizados, tornando os sinais de negociação mais precisos e o controle de risco mais estável.
Código-fonte da estratégia
/*backtest
start: 2022-11-05 00:00:00
end: 2023-03-23 05:20:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=4
strategy("Monthly Returns in PineScript Strategies", overlay = true, default_qty_type = strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value = 25, calc_on_every_tick = true, commission_type = strategy.commission.percent, commission_value = 0.1)
// Inputs
leftBars = input(2)
rightBars = input(1)
prec = input(2, title = "Return Precision")
// Pivot Points
swh = pivothigh(leftBars, rightBars)
swl = pivotlow(leftBars, rightBars)
hprice = 0.0
hprice := not na(swh) ? swh : hprice[1]
lprice = 0.0
lprice := not na(swl) ? swl : lprice[1]
le = false
le := not na(swh) ? true : (le[1] and high > hprice ? false : le[1])
se = false
se := not na(swl) ? true : (se[1] and low < lprice ? false : se[1])
if (le)
strategy.entry("PivRevLE", strategy.long, comment="PivRevLE", stop=hprice + syminfo.mintick)
if (se)
strategy.entry("PivRevSE", strategy.short, comment="PivRevSE", stop=lprice - syminfo.mintick)
plot(hprice, color = color.green, linewidth = 2)
plot(lprice, color = color.red, linewidth = 2)
///////////////////
// MONTHLY TABLE //
new_month = month(time) != month(time[1])
new_year = year(time) != year(time[1])
eq = strategy.equity
bar_pnl = eq / eq[1] - 1
cur_month_pnl = 0.0
cur_year_pnl = 0.0
// Current Monthly P&L
cur_month_pnl := new_month ? 0.0 :
(1 + cur_month_pnl[1]) * (1 + bar_pnl) - 1
// Current Yearly P&L
cur_year_pnl := new_year ? 0.0 :
(1 + cur_year_pnl[1]) * (1 + bar_pnl) - 1
// Arrays to store Yearly and Monthly P&Ls
var month_pnl = array.new_float(0)
var month_time = array.new_int(0)
var year_pnl = array.new_float(0)
var year_time = array.new_int(0)
if (not na(cur_month_pnl[1]) and (new_month or barstate.islast))
array.push(month_pnl , cur_month_pnl[1])
array.push(month_time, time[1])
if (not na(cur_year_pnl[1]) and (new_year or barstate.islast))
array.push(year_pnl , cur_year_pnl[1])
array.push(year_time, time[1])
// Monthly P&L Table
var monthly_table = table(na)
if (barstate.islast)
monthly_table := table.new(position.bottom_right, columns = 14, rows = array.size(year_pnl) + 1, border_width = 1)
table.cell(monthly_table, 0, 0, "", bgcolor = #cccccc)
table.cell(monthly_table, 1, 0, "Jan", bgcolor = #cccccc)
table.cell(monthly_table, 2, 0, "Feb", bgcolor = #cccccc)
table.cell(monthly_table, 3, 0, "Mar", bgcolor = #cccccc)
table.cell(monthly_table, 4, 0, "Apr", bgcolor = #cccccc)
table.cell(monthly_table, 5, 0, "May", bgcolor = #cccccc)
table.cell(monthly_table, 6, 0, "Jun", bgcolor = #cccccc)
table.cell(monthly_table, 7, 0, "Jul", bgcolor = #cccccc)
table.cell(monthly_table, 8, 0, "Aug", bgcolor = #cccccc)
table.cell(monthly_table, 9, 0, "Sep", bgcolor = #cccccc)
table.cell(monthly_table, 10, 0, "Oct", bgcolor = #cccccc)
table.cell(monthly_table, 11, 0, "Nov", bgcolor = #cccccc)
table.cell(monthly_table, 12, 0, "Dec", bgcolor = #cccccc)
table.cell(monthly_table, 13, 0, "Year", bgcolor = #999999)
for yi = 0 to array.size(year_pnl) - 1
table.cell(monthly_table, 0, yi + 1, tostring(year(array.get(year_time, yi))), bgcolor = #cccccc)
y_color = array.get(year_pnl, yi) > 0 ? color.new(color.green, transp = 50) : color.new(color.red, transp = 50)
table.cell(monthly_table, 13, yi + 1, tostring(round(array.get(year_pnl, yi) * 100, prec)), bgcolor = y_color)
for mi = 0 to array.size(month_time) - 1
m_row = year(array.get(month_time, mi)) - year(array.get(year_time, 0)) + 1
m_col = month(array.get(month_time, mi))
m_color = array.get(month_pnl, mi) > 0 ? color.new(color.green, transp = 70) : color.new(color.red, transp = 70)
table.cell(monthly_table, m_col, m_row, tostring(round(array.get(month_pnl, mi) * 100, prec)), bgcolor = m_color)